C++---实用编程技巧记录
注:为了写出高质量的代码,一些简单的逻辑尽量用库函数去实现,减少代码量;
1. 求最小值/最大值
- 普通vector 求最小值
std::vector<double> x={0,2,3,7,4,1};
auto min_inter = std::min_element(x.begin(), x.end());
double min= *min_inter; // 值
int index = std::distance(x.begin(),min_inter); //索引
- map或者vector 根据需要根据某一维度数值获得最大最小值
// 使用lambda表达式
std::vector<cv::Point2f> pts;
auto compare_x = [](const cv::Point2f &p0, const cv::Point2f &p1) -> bool {
return (p0.x < p1.x);
};
auto min_inter = std::min_element(pts.begin(), pts.end(),compare_x);
cv::Point2f min= *min_inter; // 值
int index = std::distance(pts.begin(),min_inter); //索引
以上当然可以直接进行排序,使用 sort函数
2. 排序
std::vector<cv::Point2f> pts;
// 升序
auto sort_x = [](const cv::Point2f &p0, const cv::Point2f &p1) -> bool {
return (p0.x < p1.x);
};
std::sort(pts.begin(), pts.end(), sort_x);
lambda表达式 简写版:
std::sort(pts.begin(), pts.end(), [](const cv::Point2f &p0, const cv::Point2f &p1) {return p0.x < p1.x;});
3. 均值
double mean_ms = std::accumulate(std::begin(all_times),
std::end(all_times), 0.0) /
all_times.size();
4 lambda 与多线程
4.1 多线程(类函数)
买东西 :
class MyClassTest() {
bool Buy(std::string type, int money) {
// do something
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
std::cout << "now is buy : " << type << std::endl;
}
return true;
}
bool RunMultiBuy() {
auto buy_thread_0 =
std::make_shared<std::thread>(&MyClassTest::Buy, this, "book", 20);
buy_thread_0->join();
auto buy_thread_1 =
std::make_shared<std::thread>(&MyClassTest::Buy, this, "pen", 10);
buy_thread_1->join();
}
}
4.2 多线程(使用lambda)
买东西 :
class MyClassTest() {
bool RunMultiBuy() {
// lambda 已获取 this
auto buy = [this](std::string type, int money) {
// do something
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
std::cout << "now is buy : " << type << std::endl;
}
return true;
};
auto buy_thread_0 = std::make_shared<std::thread>(buy, "book", 20);
buy_thread_0->join();
auto buy_thread_1 = std::make_shared<std::thread>(buy, "pen", 10);
buy_thread_1->join();
}
}
5. 查找
map 根据value 查找 key
const std::map<std::string, int> str_id_map = {
{"jack", 23424}, {"tom", 12533}, {"hopo", 5496}};
int id = 12533;
std::string name = "";
const auto& str_map = str_id_map;
auto iter =
std::find_if(str_map.begin(), str_map.end(),
[id](const auto& item) { return item.second == id; });
if (iter != str_map.end()) {
name = iter->first;
}
6. 对数组根据某个值进行分段
- 包含对数据的打印
- 对分段使用库函数处理
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
template <typename T>
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &out, const std::vector<T> &ve) {
out << "[";
std::string delimiter = "\0";
for (auto &item : ve) {
out << delimiter << item;
delimiter = ",";
}
out << "]\n";
return out;
}
int main() {
std::vector<int> points{1, 2, 3, 6};
int cut_x = 6;
auto iter =
std::find_if(points.begin(), points.end(),
[&cut_x](const auto &val) { return val >= cut_x; });
std::vector<int> points_1, points_2;
if (iter == points.begin()) {
points_2 = points;
} else if (iter == points.end() || std::next(iter) == points.end()) {
points_1 = points;
} else {
if (cut_x == (*iter)) {
points_1.insert(points_1.end(), points.begin(), iter + 1);
points_2.insert(points_2.end(), iter, points.end());
}
std::cout << *iter << std::endl;
}
std::cout << points_1;
std::cout << points_2;
}
7. 查找
优雅的实现查找,在很多场景可以复用其中查找功能
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
#define DEFINE_SMART_PTR(...) \
DEFINE_PTR(__VA_ARGS__) \
DEFINE_UNIQUE_PTR(__VA_ARGS__)
#define DEFINE_PTR(...) \
using Ptr = std::shared_ptr<__VA_ARGS__>; \
using ConstPtr = std::shared_ptr<const __VA_ARGS__>;
#define DEFINE_CONTAINER(...) \
using CVector = std::vector<__VA_ARGS__::ConstPtr>; \
using Vector = std::vector<__VA_ARGS__::Ptr>; \
using CTable = std::unordered_map<uint64_t, __VA_ARGS__::ConstPtr>; \
using Table = std::unordered_map<uint64_t, __VA_ARGS__::Ptr>;
#define DEFINE_UNIQUE_PTR(...) \
using UniquePtr = std::unique_ptr<__VA_ARGS__>; \
using ConstUniquePtr = std::unique_ptr<const __VA_ARGS__>;
template <typename T>
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &out, const std::vector<T> &ve) {
out << "[";
std::string delimiter = "\0";
for (auto &item : ve) {
out << delimiter << item;
delimiter = ",";
}
out << "]\n";
return out;
}
class LaneLine {
public:
DEFINE_SMART_PTR(LaneLine)
LaneLine() = default;
id_t GetId() const { return id_; }
void SetId(id_t id) { id_ = id; }
std::vector<int> GetPts() const { return pts_; }
void SetPts(std::vector<int> pts) { pts_ = pts; }
private:
std::vector<int> pts_;
id_t id_;
};
int main() {
auto new_line = std::make_shared<LaneLine>();
std::vector<int> vec{1, 2, 3};
new_line->SetId(1);
new_line->SetPts(vec);
auto new_line2 = std::make_shared<LaneLine>();
std::vector<int> vec2{7, 8, 9};
new_line2->SetId(2);
new_line2->SetPts(vec2);
std::vector<LaneLine::Ptr> lines{new_line, new_line2};
auto findLine = [](const std::vector<LaneLine::Ptr> &lines, id_t id,
id_t *index) -> bool {
auto iter = std::find_if(
lines.begin(), lines.end(),
[id](const auto &line) { return line->GetId() == id; });
if (iter == lines.end()) return false;
*index = std::distance(lines.begin(), iter);
return true;
};
std::vector<id_t> line_ids = std::vector<id_t>({1, 2, 3});
for (const auto &id : line_ids) {
id_t index = 0;
if (findLine(lines, id, &index) == true) {
const auto &line = lines.at(index);
std::cout << "fine line id: " << line->GetId()
<< ", values: " << line->GetPts();
}
}
}
5 坐标转换与transform
将朝x轴方向的点集,转为朝z轴方向 (将朝前改为朝天上),有如下特点
- 定义Point3D_t数据结构,并重载基本运算符,便于简单运算
- 重载矩阵相乘,便于坐标转换
- 分别使用旋转向量+旋转角度,欧拉角表示旋转矩阵
- 使用三种方式利用
std::transform库函数进行转换
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
#include <sophus/se3.hpp>
#include <sophus/so3.hpp>
// #include <Sophus/se3.h>
// #include <Sophus/so3.h>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
template <typename T>
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &out, const std::vector<T> &ve) {
out << "[";
std::string delimiter = "\0";
for (auto &item : ve) {
out << delimiter << item;
delimiter = ",";
}
out << "]\n";
return out;
}
typedef float float32_t;
typedef double float64_t;
typedef long double float128_t;
template <typename T>
bool FloatEqual(const T x, const T y) {
const T max_val = std::max({1.0, std::fabs(x), std::fabs(y)});
return std::fabs(x - y) <= std::numeric_limits<T>::epsilon() * max_val;
}
// typedef Sophus::SE3d SE3;
// typedef Sophus::SO3d SO3;
struct Point3D_t {
float64_t x = 0.0;
float64_t y = 0.0;
float64_t z = 0.0;
float32_t weight = 1.0;
Point3D_t() = default;
Point3D_t(float64_t _x, float64_t _y) : x(_x), y(_y) {}
Point3D_t(float64_t _x, float64_t _y, float64_t _z, float32_t _weight = 1.0)
: x(_x), y(_y), z(_z), weight(_weight) {}
Point3D_t operator-() const {
Point3D_t p;
p.x = -this->x;
p.y = -this->y;
p.z = -this->z;
return p;
}
Point3D_t operator+(const Point3D_t &b) const {
Point3D_t c;
c.x = this->x + b.x;
c.y = this->y + b.y;
c.z = this->z + b.z;
return c;
}
Point3D_t operator-(const Point3D_t &b) const {
Point3D_t c;
c.x = this->x - b.x;
c.y = this->y - b.y;
c.z = this->z - b.z;
return c;
}
template <typename N,
std::enable_if_t<std::is_arithmetic<N>::value, int> = 0>
Point3D_t operator*(const N scalar) const {
Point3D_t q;
q.x = this->x * scalar;
q.y = this->y * scalar;
q.z = this->z * scalar;
return q;
}
template <typename N,
std::enable_if_t<std::is_arithmetic<N>::value, int> = 0>
Point3D_t operator/(const N scalar) {
Point3D_t c;
c.x = this->x / scalar;
c.y = this->y / scalar;
c.z = this->z / scalar;
return c;
}
bool operator==(const Point3D_t &b) const {
return FloatEqual(this->x, b.x) && FloatEqual(this->y, b.y) &&
FloatEqual(this->z, b.z);
}
bool operator!=(const Point3D_t &b) const {
return !FloatEqual(this->x, b.x) || !FloatEqual(this->y, b.y) ||
!FloatEqual(this->z, b.z);
}
friend std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &out, const Point3D_t &point) {
out << "(" << point.x << ", " << point.y << ", " << point.z << ")";
return out;
}
};
template <typename D>
Point3D_t operator+(const Point3D_t &a, const Eigen::Matrix<D, 3, 1> &b) {
Point3D_t c;
c.x = a.x + b(0, 0);
c.y = a.y + b(1, 0);
c.z = a.z + b(2, 0);
return c;
}
template <typename D>
Point3D_t operator*(const Eigen::Matrix<D, 3, 3> &R, const Point3D_t &q) {
Point3D_t r(0, 0, 0);
r.x = R(0, 0) * q.x + R(0, 1) * q.y + R(0, 2) * q.z;
r.y = R(1, 0) * q.x + R(1, 1) * q.y + R(1, 2) * q.z;
r.z = R(2, 0) * q.x + R(2, 1) * q.y + R(2, 2) * q.z;
return r;
}
template <typename D>
Point3D_t operator*(const Eigen::Matrix<D, 4, 4> &T, const Point3D_t &q) {
Point3D_t r(0, 0, 0);
r.x = T(0, 0) * q.x + T(0, 1) * q.y + T(0, 2) * q.z + T(0, 3);
r.y = T(1, 0) * q.x + T(1, 1) * q.y + T(1, 2) * q.z + T(1, 3);
r.z = T(2, 0) * q.x + T(2, 1) * q.y + T(2, 2) * q.z + T(2, 3);
return r;
}
inline Point3D_t operator*(const Sophus::SE3d &T, const Point3D_t &p) {
return T.so3().matrix() * p + Point3D_t(T.translation().x(),
T.translation().y(),
T.translation().z());
}
inline Point3D_t operator*(const Sophus::SO3d &R, const Point3D_t &p) {
return R.matrix() * p;
}
Eigen::Matrix3d ypr2R(const Eigen::Vector3d &ypr) {
double y = ypr(0);
double p = ypr(1);
double r = ypr(2);
Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 3> Rz;
Rz << cos(y), -sin(y), 0, sin(y), cos(y), 0, 0, 0, 1;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 3> Ry;
Ry << cos(p), 0., sin(p), 0., 1., 0., -sin(p), 0., cos(p);
Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 3> Rx;
Rx << 1., 0., 0., 0., cos(r), -sin(r), 0., sin(r), cos(r);
return Rz * Ry * Rx;
}
int main() {
// 前左上坐标系(x轴朝前)
const std::vector<Point3D_t> pts{Point3D_t(1, 1, 0), Point3D_t(5, 1, 0)};
// 将朝x轴方向的 点集,转为朝z轴
// 定义旋转矩阵: 旋转角度+旋转向量,即绕(0,1,0)方向转90度
Eigen::Matrix3d to_up =
Eigen::AngleAxisd(-90.0 * M_PI / 180.0, Eigen::Vector3d(0, 1, 0))
.toRotationMatrix();
// 定义旋转矩阵: 欧拉角转为旋转矩阵
// (将前左上的坐标系,变为下右前坐标系,这样原先在x轴朝向的点 会变为
// z轴朝向)
Eigen::Vector3d ypr;
ypr << 0.0, -90.0 * M_PI / 180.0, 0.0; // ypr(zyx)
Eigen::Matrix3d to_up2 = ypr2R(ypr);
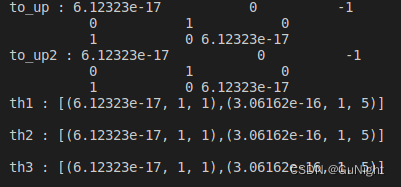
std::cout << "to_up : " << to_up << std::endl;
std::cout << "to_up2 : " << to_up2 << std::endl;
{
// 第1种转换
// 改变输入数据值,构建lambda函数
std::vector<Point3D_t> input_pts = pts;
auto Transform = [&](std::vector<Point3D_t> *geometry) {
std::transform(geometry->begin(), geometry->end(),
geometry->begin(),
[&](const Point3D_t &pt) { return to_up * pt; });
};
Transform(&input_pts);
std::cout << "th1 : " << input_pts << std::endl;
}
{
// 第2种转换
// 改变输入数据值
std::vector<Point3D_t> input_pts = pts;
std::transform(input_pts.begin(), input_pts.end(), input_pts.begin(),
[&](const Point3D_t &pt) { return to_up * pt; });
std::cout << "th2 : " << input_pts << std::endl;
}
{
// 第3种转换
// 不改变输入数据值
std::vector<Point3D_t> pts_out;
std::transform(pts.begin(), pts.end(), std::back_inserter(pts_out),
[&](const Point3D_t &pt) { return to_up2 * pt; });
std::cout << "th3 : " << pts_out << std::endl;
}
}