JUC 即 java.util.concurrent 包,提供了大量的工具类来简化并发编程。
Semaphore 信号量,通过设置信号量资源的数量对并发线程进行协调。
Semaphore 设置的资源数是指能够被抢占的互斥资源数量。从而限制了同时执行的线程数量。因此,Semaphore 能够用于限流和线程协调。
1. 当资源数设置为1时,类似于一把锁。
public class SemaphoreTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(1);
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("t1 semaphore requiring");
semaphore.acquire();
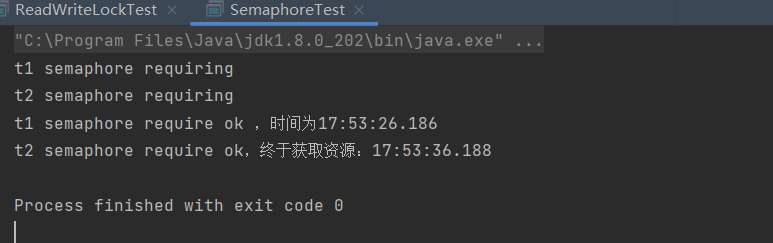
System.out.println("t1 semaphore require ok ,时间为" + LocalTime.now());
Thread.sleep(10000);
semaphore.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("t2 semaphore requiring");
semaphore.acquire();
System.out.println("t2 semaphore require ok,终于获取资源:" + LocalTime.now());
Thread.sleep(1000);
semaphore.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
运行结果:
2. 当资源数设置为多个时,起到限流作用。
public class SemaphoreTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(10, true);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
semaphore.acquire(1);
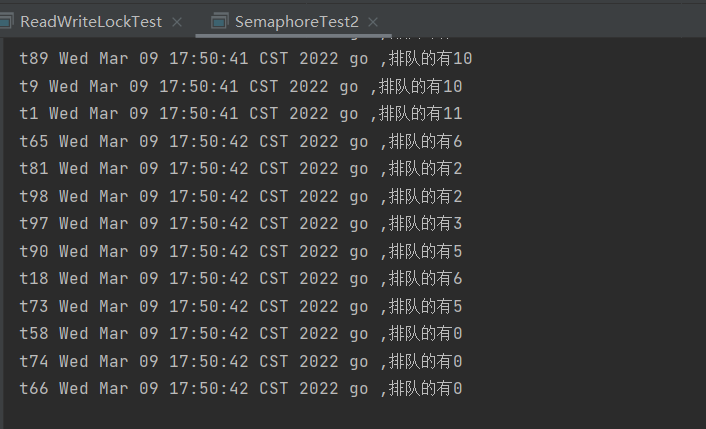
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + new Date() + " go ,排队的有" + semaphore.getQueueLength());
Thread.sleep(1000);
semaphore.release(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "t" + i).start();
}
}
}
运行结果:
3. 用Semaphore 写一段程序实现死锁
public class DeadLockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Semaphore semaphore1 = new Semaphore(1);
Semaphore semaphore2 = new Semaphore(1);
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
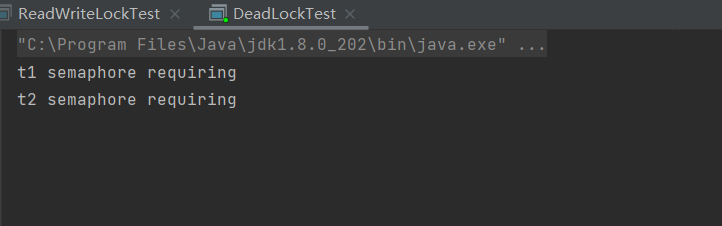
System.out.println("t1 semaphore requiring");
semaphore1.acquire();
Thread.sleep(1000);
semaphore2.acquire();
semaphore2.release();
semaphore1.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("t2 semaphore requiring");
semaphore2.acquire();
Thread.sleep(1000);
semaphore1.acquire();
semaphore1.release();
semaphore2.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
运行结果:
总结
Semaphore 在本科计算机操作系统里就曾提及,通过信号灯的占有与请求,保证了线程的同步与限流。同时,Semaphore 可以很好的演示死锁情况。
多线程系列在github上有一个开源项目,主要是本系列博客的实验代码。
https://github.com/forestnlp/concurrentlab
如果您对软件开发、机器学习、深度学习有兴趣请关注本博客,将持续推出Java、软件架构、深度学习相关专栏。
您的支持是对我最大的鼓励。