文章目录
一、理解回车换行
在我们熟悉的C语言中,换行就可以跳转的下一行开头 ,但其实这一操作有两个步骤,\r (回车)和 \n(换行)
\r 回车就是回到这一行开头
\n 换行就是另起一行
二、认识行缓冲
在内存中预留了一块空间,用来缓冲输入或输出的数据,这个保留的空间被称为缓冲区。下面我们通过几个代码例子来理解行缓冲概念
1、代码一、二(回车换行理解)
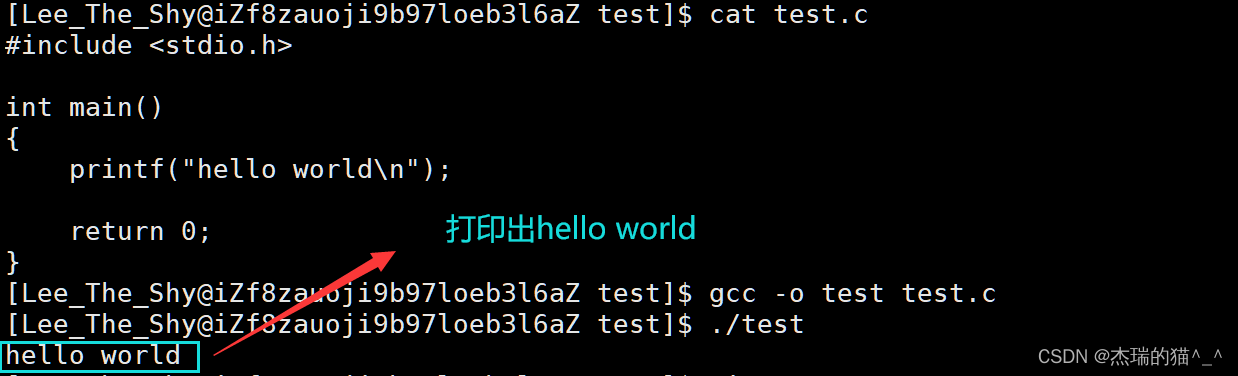
代码一:
1#include <stdio.h>
2 int main()
3 {
4 printf("hello world\n");
5 return 0;
6 }
 代码二:
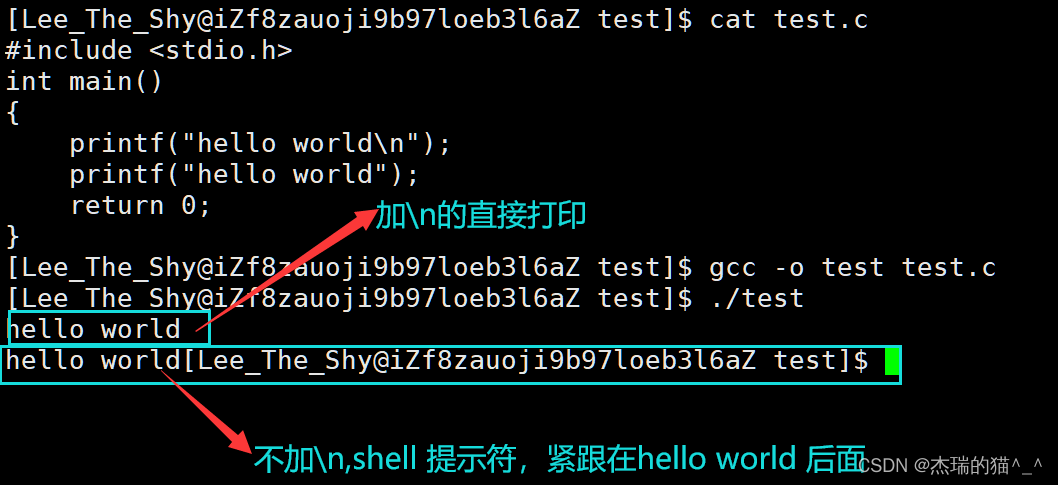
代码二:
1#include <stdio.h>
2 int main()
3 {
4 printf("hello world\r");
5 return 0;
6 }

不难发现 \n 可以打印出来,而 \r,不能打印出来,因为显示器模式是行刷新缓冲区是按行缓冲的,没有\n,就不能立即刷新。 \r 回到行首后,会进行覆盖写,shell 提示符会覆盖掉之前写的 “hello world”,如果我们在 “hello world” 不加 \r,则不会进行覆盖写,shell 提示符会顺着 “hello world” 往后写
如下:
2、代码三、四(sleep函数和ffush函数理解)
行缓冲是缓冲区刷新策略的一种,在行缓冲模式下,当输入和输出中遇到 ‘\n’ 换行时,就会刷新缓冲区,下面我们认识头文件<unistd.h>的三个函数
s l e e p sleep sleep : Linux 下的休眠函数,单位是秒
u s l e e p usleep usleep:和sleep 一样,单位ms(即10-6 m)
f f l u s h fflush fflush :刷新缓冲区
代码 3:
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <unistd.h>
3 int main()
4 {
5 printf("hello world");
6 sleep(3);
7 return 0;
8 }
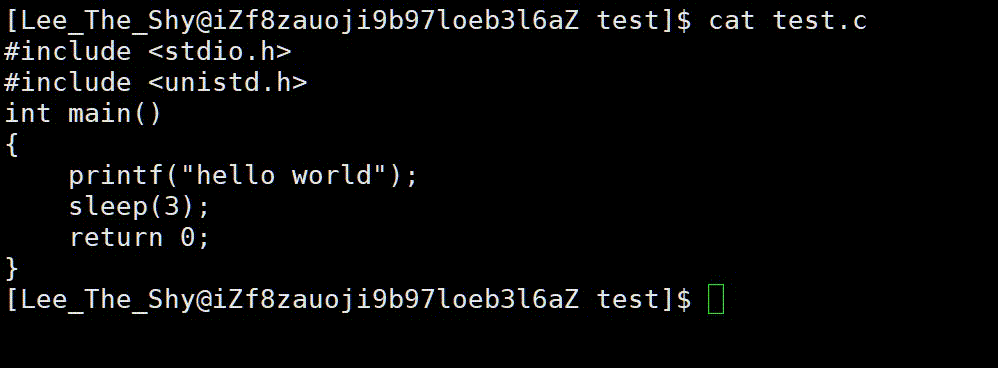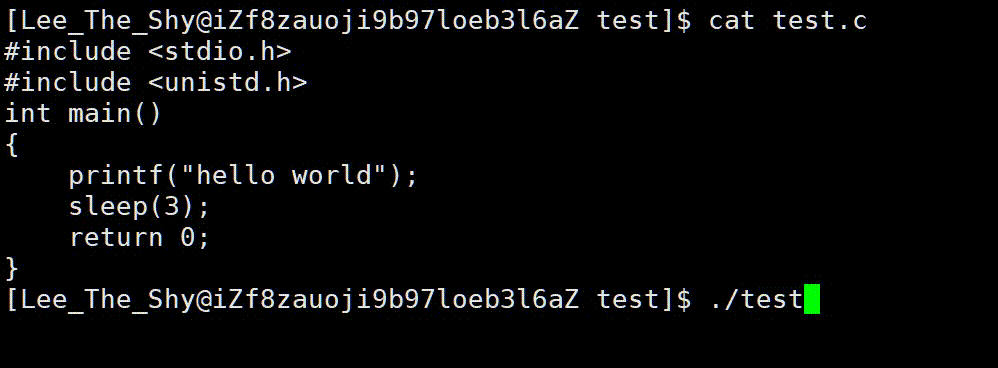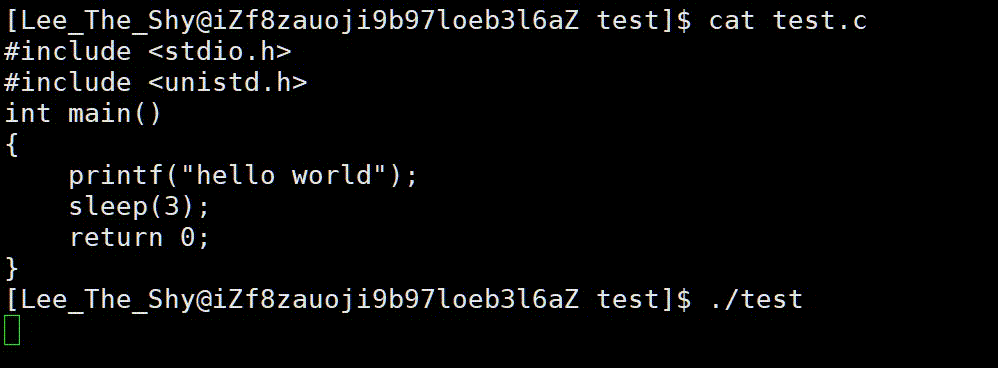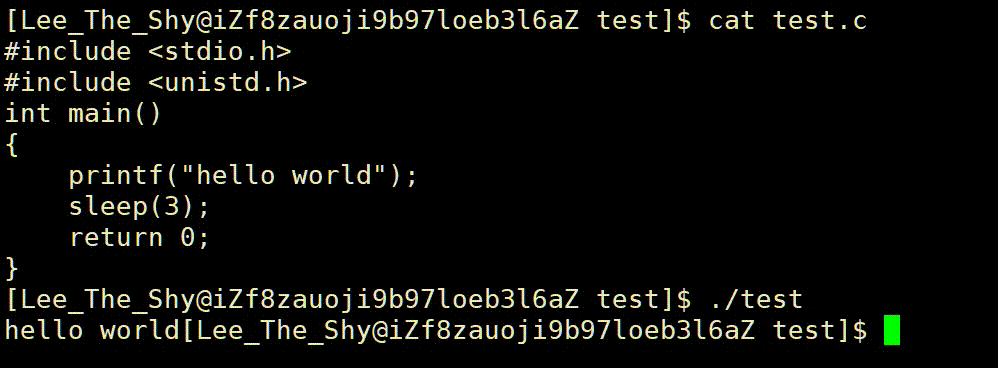
我们知道函数代码语句是从上到下依次进行的,而我们看到的却是先休眠三秒,然后再打印出"hello world",原因是因为数据保存在缓冲区中,没有主动刷新。当程序退出后,保存在缓冲区中的数据被自动刷新出来了,如果我们想提前刷新,便可以调用 f f l u s h fflush fflush函数来刷新缓冲区
代码四:
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <unistd.h>
3 int main()
4 {
5 printf("hello world");
6 fflush(stdout);
7 printf("\n");
8 sleep(3);
9 return 0;
10}

这次 “hello world” 被直接打印出来,我们加 \n避免 s h e l l shell shell 提示符出现在 “hello world” 后面
三、简单倒计时
1、效果展示
 有了以上的准备工作,能够让我们理解倒计时和进度条工作原理,下面我们先给代码和效果,在讲其中细节
有了以上的准备工作,能够让我们理解倒计时和进度条工作原理,下面我们先给代码和效果,在讲其中细节
2、倒计时代码
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <unistd.h>
3 int main()
4 {
5 int cnt=10;
6 while(cnt>=0)
7 {
8 printf("%-2d\r",cnt);
9 fflush(stdout);
10 sleep(1);
11 cnt--;
12 }
13 printf("\n");
14 return 0;
15 }
3、实现过程分析
1、定义倒计时变量 cnt,让其逐渐递降
2、核心就是用 \r 回到缓冲区行首进行覆盖写,然后fflush不断刷新出出来
3、格式调整,打印 cnt==10 时,在缓冲区打印的其实是字符1和字符0,如果我们不用 2d% 来调整格式,而用 d% 的话,那么覆盖写只会覆盖第一位字符 1 1 1 的位置,而第二位的字符 0 0 0, 还留在缓冲区原来的位置,于是倒计时便会变为下面这样
10->90->80->70->60->50->40->30->20->10->00 ,-2d% 加个负号保证其向左对齐
4、倒计时完加个 \n符,shell 提示符就不会出现在倒计时后面
四、进度条
1、效果展示
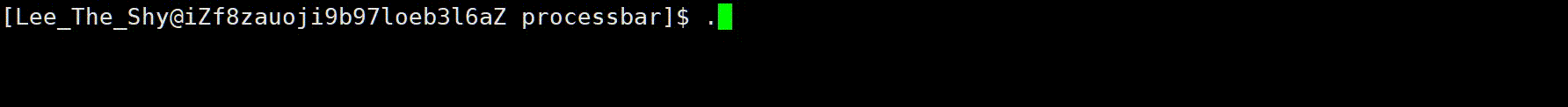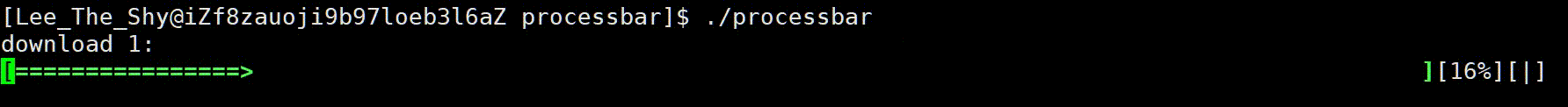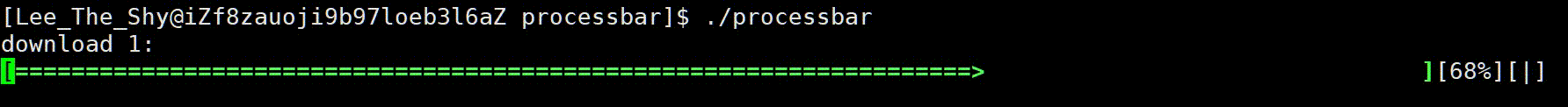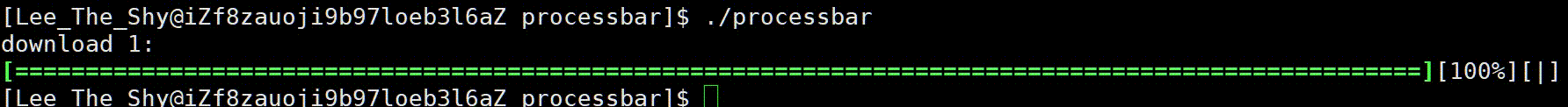
2、进度条代码
makefile
1 processbar:processBar.c main.c
2 gcc -o $@ $^
3 .PHONY:clean
4 clean:
5 rm -f processbar
头文件processBar.h
1 #pragma once
2 #include<stdio.h>
3
4 #define SIZE 102
5 #define BODY '='
6 #define TAIL '>'
7
8 extern void processbar(int rate);
9 extern void initbar();
.c 文件processBar.c
1 #include "processBar.h"
2 #include <string.h>
3 #include <unistd.h>
4
5 #define LIGHT_GREEN "\033[1;32m" //亮绿色
6 #define NONE "\033[m" //截断
7
8 const char *lable="|/-\\";
9 char bar[SIZE];
10
11 void processbar(int rate)
12 {
13 if(rate<0 || rate > 100)
14 return;
15 //没有\n,就没有立即刷新,因为显示器模式是行刷新
16 printf(LIGHT_GREEN"[%-100s]"NONE"[%d%%][%c]\r",bar,rate,lable[rate%4]);
17 fflush(stdout);
18 bar[rate++]=BODY;
19 if(rate<100)
20 bar[rate]=TAIL;
21 }
22
23 void initbar()
24 {
25 memset(bar,'\0',sizeof(bar));
26 }
.c文件main.c
1 #include "processBar.h"
2 #include <unistd.h>
3
4 typedef void(*callback_t)(int);
5 void downLoad(callback_t cb)
6 {
7 initbar();
8 int total=1000; // 1000MB
9 int curr=0; //0MB
10 while(curr<=total)
11 {
12 // 进行某种下载任务
13 usleep(50000); //模拟下载花费时间
14 int rate=curr*100/total;//更新进度
15
16 cb(rate); //回调展示进度
17 //processbar(curr*100/total);
18
19 curr+=10; // 循环下载了一部分,更新进度
20 }
21 printf("\n");
22 }
23
24
25 int main()
26 {
27 printf("download 1:\n");
28 downLoad(processbar);
29 printf("download 2:\n");
30 downLoad(processbar);
31 printf("download 3:\n");
32 downLoad(processbar);
33 printf("download 4:\n");
34 downLoad(processbar);
35 return 0;
36 }
3、实现过程分析
进度条实现样式
进度条样式 :
主体样式为两个中括号包裹,中间 => 推进的方式呈现,比如:[======>]
主体右侧中括号位置保持不变,中间元素不断推进,比如:[=> ]
因此我们把中间主体 = 宏定义为 BODY ,把尾侧 > 宏定义为 TAIL
进度条百分比:
显示当前加载进度,用 [rate%] 显示,rate 随着进度条的不断推进而变化,而打印 %(转义字符)则需要两个 %%
进度条旋转字符:
显示加载样式,可以利用一个旋转的字符,例如 [] 的样式,顺时针不断旋转,依次为 “| / - \”,注意 \ 也是转义字符,因此需要两个 \ \,对此我们定义一个lable指针指向常量字符串const char *lable=" | / - \ "
进度条颜色: c语言颜色参考
我们可以根据自己的喜好给进度条上色,在此我们找到颜色参照表
把亮绿色宏定义为 #define LIGHT_GREEN “\033[1;32m”
结束的地方宏定义为 #define NONE “\033[m”
进度条实现方法
预留进度条大小为 100 个 = ,外加 1 个 > ,加上保存 \0 的位置,建一个存储为102 (宏定义为SIZE)个单位的bar数组。processbar()函数,将某比率的进度条打印出来,\r 回到行首后,fflush 刷新缓冲区,同时bar数组尾插上 =,再插入 >,注意当rate为100时,进度条加载完毕,因此不需要再插入 >
将其模拟为执行某个下载任务,把实现方法 processbar()函数 作为参数传递给 downLoad()模拟下载函数 ,对此我们定义一个processbar()类型的函数指针,重命名为 callback_t。我们定义下载包大小为
t
o
t
a
l
total
total ,当前进度为
c
u
r
r
curr
curr ,因此进度比例为 rate=curr*100/total。用usleep函数模拟下载时间,然后循环起来回调processbar()函数,便实现了进度条,最后考虑到第二次下载,bar数组满了,我们再每次调用downLoad()函数时,清空bar数组