1.认识String类
2.常用的方法
2.1.字符串的构造
代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1="hello world";
System.out.println(s1);
String s2=new String("hello world");
System.out.println(s2);
char arr[]={'h','e','l','l','o'};
String s3=new String(arr);
System.out.println(s3);
}1.使用常量串构造2.直接newString对象3.使用字符数组进行构造

2.2String对象的比较
在字符串比较中:
1.地址比较
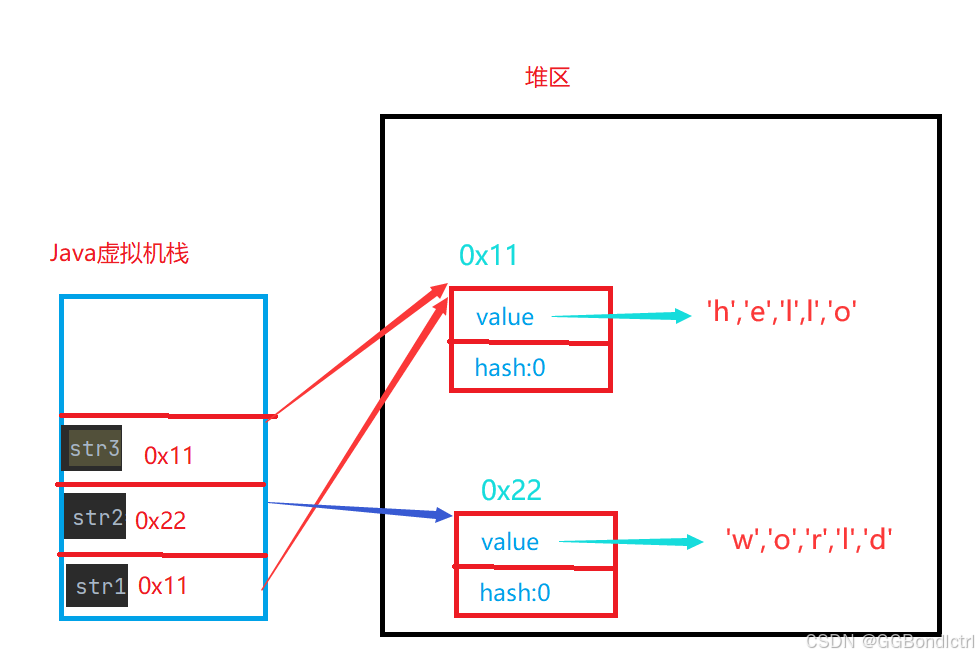
String s4 = new String("hello");
String s5 = new String("world");
String s6 = s4;
System.out.println(s4 == s5); //false
System.out.println(s5 == s6); //false
System.out.println(s6 == s4); //trues4与s5对象的地址值是不一样的,所以是false,在将s6的地址传给s4,再次比较此时,输出的就是true。
2.内容比较
在String重写了Object类的equals方法后,就大大简化了我们的比较过程
比较代码如下:
String s4 = new String("hello");
String s5 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s4==s5); //false
System.out.println(s4.equals(s5)); //true如图,在地址不同时,虽然内容一样但是==表示的是地址的比较,而equals是进行内容比较
通常比较方式是:
对象1.equals(对象2)
3.intcompareTo(Strings)比较
1. 先按照字典次序大小比较,如果出现不等的字符,直接返回这两个字符的大小差值2. 如果前 k 个字符相等 (k 为两个字符长度最小值 ) ,返回值两个字符串长度差值
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("ac");
String s3 = new String("abc");
String s4 = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); //不同输出字符差值-1
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3)); //相同输出0
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s4)); //前面字符一样输出后面字符数量的差值-3a与b的ASCII码值相差为1;所以如注解,输出-1;如果两内容一样,则输出0;如果前面字符一样,则在后面输出相差的字符数量。
4. intcompareToIgnoreCase(Stringstr)比较
与compareTo方式相同,但是忽略大小写比较。
例如:
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s5=new String("ABc");
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s5)); //忽略大小写,相同输出0忽略了AB大写,所以s1与s5对象指向的地址对应的内容一样,输出为0。
2.3.字符串的查找
以下是一些相关功能代码
1.char charAt(int index)
返回index位置上字符,如果index为负数或者越界,抛出
IndexOutOfBoundsException 异常。2.int indexOf( ch)返回 ch 第一次出现的位置,没有返回 -13. int indexOf( ch, int fromIndex)从 fromIndex 位置开始找 ch 第一次出现的位置,没有返回 -14.int indexOf(String str)返回 str 第一次出现的位置,没有返回 -15. int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex)从 fromIndex 位置开始找 str 第一次出现的位置,没有返回 -16.int lastIndexOf( ch)从后往前找,返回 ch 第一次出现的位置,没有返回 -17. int lastIndexOf(ch, int fromIndex)从 fromIndex 位置开始找,从后往前找 ch 第一次出现的位置,没有返回-18.int lastIndexOf(String str)从后往前找,返回 str 第一次出现的位置,没有返回 -19. int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex)从 fromIndex 位置开始找,从后往前找 str 第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
代码如下:
String s = "aaabbbcccaaabbbccc";
System.out.println(s.charAt(3)); //'b'
System.out.println(s.indexOf('c')); //6
System.out.println(s.indexOf('c', 10)); //15
System.out.println(s.indexOf("bbb")); //3
System.out.println(s.indexOf("bbb", 10)); //12
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c'));//17
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c', 10)); //8
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bbb"));//12
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bbb",10));//52.4.转化
1.数值和字符串转化
String s1 = String.valueOf(1234);
String s2 = String.valueOf(12.34);
String s3 = String.valueOf(true);
String s4 = String.valueOf(new Student("Hanmeimei", 18));
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s4);
}
}
class Student{
public String name;
public int age;
public Student(String name,int age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
这里对像转化成字符串要进行toString方法的重写,才能打印。
主要运用String的valueOf()方法;
int data1=Integer.parseInt("1234");
double data2=Double.parseDouble("12.34");
System.out.println(data1);
System.out.println(data2);这里要注意:不同类型数字的不同写法
2.大小写转换
String s1="hello";
String s2="HELLO";
//小写转大写
System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase());
//大写转小写
System.out.println(s2.toLowerCase());}两个方法 toUpperCase();toLowerCase()
3.字符串转数组
代码如下:
String s = "hello";
//字符串转数组
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {
System.out.print(ch[i]);
}方法 toCharArray(),注意要用char类型的数组接收
4.格式化
Strings=String.format("%d-%d-%d",2019,9,14);
System.out.println(s);
}方法 format()的使用
2.5字符串替换
String str="helloworld";
System.out.println(str.replaceAll("l","_"));
System.out.println(str.replaceFirst("l","_"));运行结果:
he__owor_d
he_loworld
注意事项: 由于字符串是不可变对象, 替换不修改当前字符串, 而是产生一个新的字符串.
2.6字符串的拆分
String[] split(String regex) String[] split(String regex, int limit)将字符串全部拆分 将字符串以指定的格式,拆分为 limit 组
String str1 = "hello world" ;
String[] result = str1.split(" ") ; // 按照空格拆分
for(String s1: result)
{
System.out.println(s1);
}输出:
hello
world
String str = "hello world hello bit" ;
String[] result = str.split(" ",3) ; //拆分为两组
for(String s: result) {
System.out.println(s);
}输出:
hello
world
hello you
注意:拆分是特别常用的操作. 一定要重点掌握. 另外有些特殊字符作为分割符可能无法正确切分, 需要加上转义.
String s2=new String("name=zhangsan&age=15");
String[] arr=s2.split("=|&");
for(String s: arr){
System.out.println(s);
}name
zhangsan
age
15
2.7.字符串截取
String substring(int beginIndex)从指定索引截取到结尾String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)截取部分内容
代码实例:
String str = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(str.substring(5));
System.out.println(str.substring(0, 5));helloworld
注意:在java中一般是左开右闭,所以(0,5)指的是重0下标到4下标。
2.8字符串空白去除
String trim()去掉字符串中的左右空格 , 保留中间空格
String st=" hello world ";
System.out.println(st);
String st1=st.trim();
System.out.println(st1);代码输出:
hello world
hello world
2.9字符串的不可变性
1. String 类被 final 修饰,表明该类不能被继承2. value 被修饰被 final 修饰,表明 value 自身的值不能改变,即不能引用其它字符数组,但是其引用空间中的内容可以改。3.所有涉及到可能修改字符串内容的操作都是创建一个新对象,改变的是新对象

final 修饰类表明该类不想被继承, final 修饰引用类型表明该引用变量不能引用其他对象,但是其引用对象中的内容是可以修改的 。
3.总结
String类的方法小编在这里列举了很多,如果还有,希望各位uu在评论区提出宝贵意见。
制作不易,麻烦给小编一个小小的赞吧。