一、安装postgres_postgis_pgrouting
version: '3'
services:
postgres:
image: starefossen/pgrouting
container_name: postgres_postgis_pgrouting
restart: always
privileged: true
volumes:
- ./pgdata:/var/lib/postgresql
environment:
TZ: Asia/Shanghai
POSTGRES_USER: postgres #在此填写postgres的用户名
POSTGRES_DB: postgres #在此填写postgres的数据库名,默认是postgres
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: postgres #在此填写posgres的数据库密码
ports:
- "5432:5432"
logging:
options:
max-size: 10mb
二、创建扩展:
pgrouting要依赖postgis。
新建数据库后,运行:
CREATE EXTENSION PostGIS
CREATE EXTENSION pgRouting
三、样例数据:
pgrouting官网提供了一个很简单的样例数据,讲拓扑路网数据如何构建:
https://docs.pgrouting.org/3.0/en/sampledata.html
创建表
# edge_table
# 新建数据表edge_table,这张表存储所有道路线信息,查询大部分都是基于这张表:
CREATE TABLE edge_table (
id BIGSERIAL,
dir character varying,
source BIGINT,
target BIGINT,
cost FLOAT,
reverse_cost FLOAT,
capacity BIGINT,
reverse_capacity BIGINT,
category_id INTEGER,
reverse_category_id INTEGER,
x1 FLOAT,
y1 FLOAT,
x2 FLOAT,
y2 FLOAT,
the_geom geometry
);
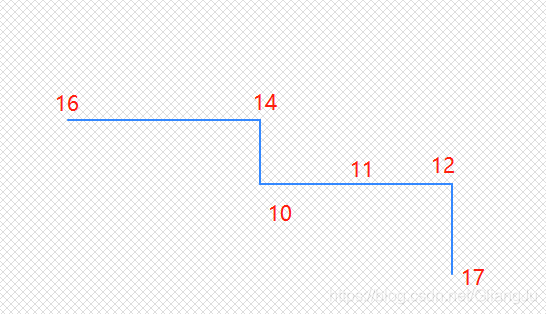
插入数据,都是两点线段(添加原数据17-18段路网不通):
INSERT INTO edge_table (
category_id, reverse_category_id,
cost, reverse_cost,
capacity, reverse_capacity,
x1, y1,
x2, y2) VALUES
(3, 1, 1, 1, 80, 130, 2, 0, 2, 1),
(3, 2, -1, 1, -1, 100, 2, 1, 3, 1),
(2, 1, -1, 1, -1, 130, 3, 1, 4, 1),
(2, 4, 1, 1, 100, 50, 2, 1, 2, 2),
(1, 4, 1, -1, 130, -1, 3, 1, 3, 2),
(4, 2, 1, 1, 50, 100, 0, 2, 1, 2),
(4, 1, 1, 1, 50, 130, 1, 2, 2, 2),
(2, 1, 1, 1, 100, 130, 2, 2, 3, 2),
(1, 3, 1, 1, 130, 80, 3, 2, 4, 2),
(1, 4, 1, 1, 130, 50, 2, 2, 2, 3),
(1, 2, 1, -1, 130, -1, 3, 2, 3, 3),
(2, 3, 1, -1, 100, -1, 2, 3, 3, 3),
(2, 4, 1, -1, 100, -1, 3, 3, 3.5, 3),
(2, 4, 1, -1, 100, -1, 3.5, 3, 4, 3),
(3, 1, 1, 1, 80, 130, 2, 3, 1.999999999999,3.5),
(3, 1, 1, 1, 80, 130, 1.999999999999,3.5, 2, 4),
(3, 4, 1, 1, 80, 50, 4, 2, 4, 3),
(3, 3, 1, 1, 80, 80, 4, 1, 4, 2),
(1, 2, 1, 1, 130, 100, 0.5, 3.5, 1.999999999999,3.5),
(4, 1, 1, 1, 50, 130, 3.5, 2.3, 3.5, 3),
(4, 1, 1, 1, 50, 130, 3.5, 3, 3.5,4);
更新数据,根据x1、y1、x2、y2构建两点间线段,并指定线段的通达性:
UPDATE edge_table SET the_geom = st_makeline(st_point(x1,y1),st_point(x2,y2)),
dir = CASE WHEN (cost>0 AND reverse_cost>0) THEN 'B' -- both ways,双向通行
WHEN (cost>0 AND reverse_cost<0) THEN 'FT' -- direction of the LINESSTRING,沿路通行
WHEN (cost<0 AND reverse_cost>0) THEN 'TF' -- reverse direction of the LINESTRING,反向通行
ELSE '' END; -- unknown,未知
构建拓扑,这个比较关键,必须得构建拓扑之后,才能进行路径规划,0.001是拓扑容差(填充source和target列):
SELECT pgr_createTopology('edge_table',0.001);
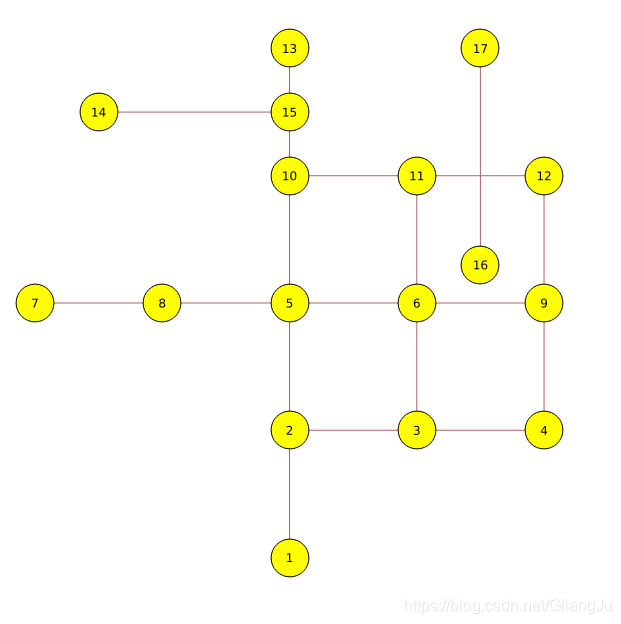
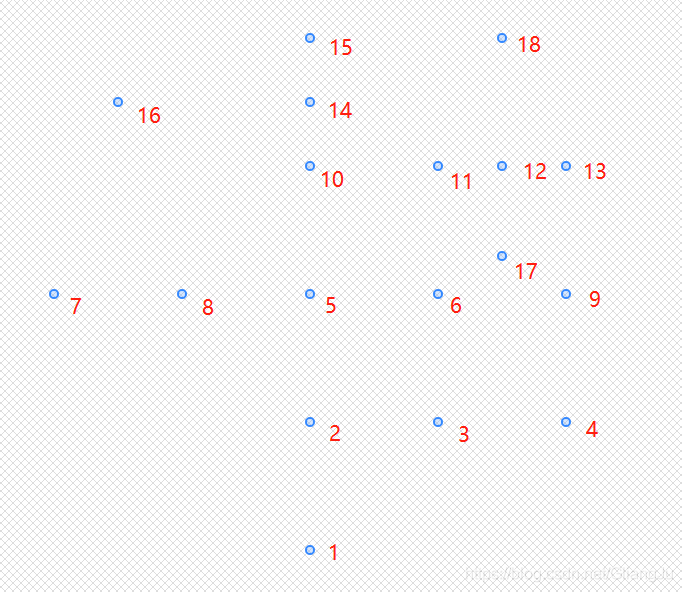
原始节点和路网
修改后的节点点和路网
四、数据查询
pgr_dijkstra算法:
# 查看节点16到节点17经过节点
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edge_table',
16, 17,directed := FALSE) as dijkstra LEFT JOIN edge_table_vertices_pgr as etvg ON (dijkstra.node = etvg.id) ORDER BY seq;
结果:
# 查看节点16到节点17路径
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edge_table',
16, 17,directed := FALSE) as dijkstra LEFT JOIN edge_table as et ON (dijkstra.edge = et.id) ORDER BY seq;
结果:
获取节点几何对象:
# 例如,要取edge_table_vertices_pgr编号为17的节点。
SELECT st_astext(the_geom) FROM edge_table_vertices_pgr WHERE id=17
# 取edge编号为17的边。
SELECT st_astext(the_geom) FROM edge_table WHERE id=17
捕获最近节点:
# pgr_dijkstra函数入参,需要输入节点编号,并不支持坐标入参。
# 大多数情况下,路径规划的起终点都不在节点上。
# 这时候需要做的是,先获取节点的编号。
# 根据坐标x,y从edge_table_vertices_pgr中获取一个在点(x,y)半径0.1内的点,并返回该点的节点id属性。
# 用获取的节点,就可以使用pgr_dijkstra了。
SELECT id FROM edge_table_vertices_pgr WHERE st_dwithin(the_geom, st_makePoint(x,y),0.1)=true limit 1
# 还可以直接传入点坐标使用pgr_dijkstra
SELECT * FROM
(SELECT id FROM edge_table_vertices_pgr WHERE st_dwithin(the_geom, st_makePoint(3.5,4),0.1)=true limit 1) t1,
(SELECT id FROM edge_table_vertices_pgr WHERE st_dwithin(the_geom, st_makePoint(3.5,2.3),0.1)=true limit 1) t2,
pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edge_table',
t1.id,t2.id,directed := FALSE) as dijkstra LEFT JOIN edge_table as et ON (dijkstra.edge = et.id) ORDER BY seq;
# 传入三个坐标
(SELECT * FROM
(SELECT id FROM new_edge_table_vertices_pgr WHERE st_dwithin(the_geom, st_makePoint(0.5,3.5),0.1)=true limit 1) t1,
(SELECT id FROM new_edge_table_vertices_pgr WHERE st_dwithin(the_geom, st_makePoint(2,3),0.1)=true limit 1) t2,
pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM new_edge_table',
t1.id,t2.id,directed := FALSE) as dijkstra LEFT JOIN new_edge_table as et ON (dijkstra.edge = et.id) where edge != '-1' ORDER BY seq)
UNION ALL
(SELECT * FROM
(SELECT id FROM new_edge_table_vertices_pgr WHERE st_dwithin(the_geom, st_makePoint(2,3),0.1)=true limit 1) t2,
(SELECT id FROM new_edge_table_vertices_pgr WHERE st_dwithin(the_geom, st_makePoint(3.5,2.3),0.1)=true limit 1) t3,
pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM new_edge_table',
t2.id,t3.id,directed := FALSE) as dijkstra LEFT JOIN new_edge_table as et ON (dijkstra.edge = et.id) where edge != '-1' ORDER BY seq)