1、归并排序原理
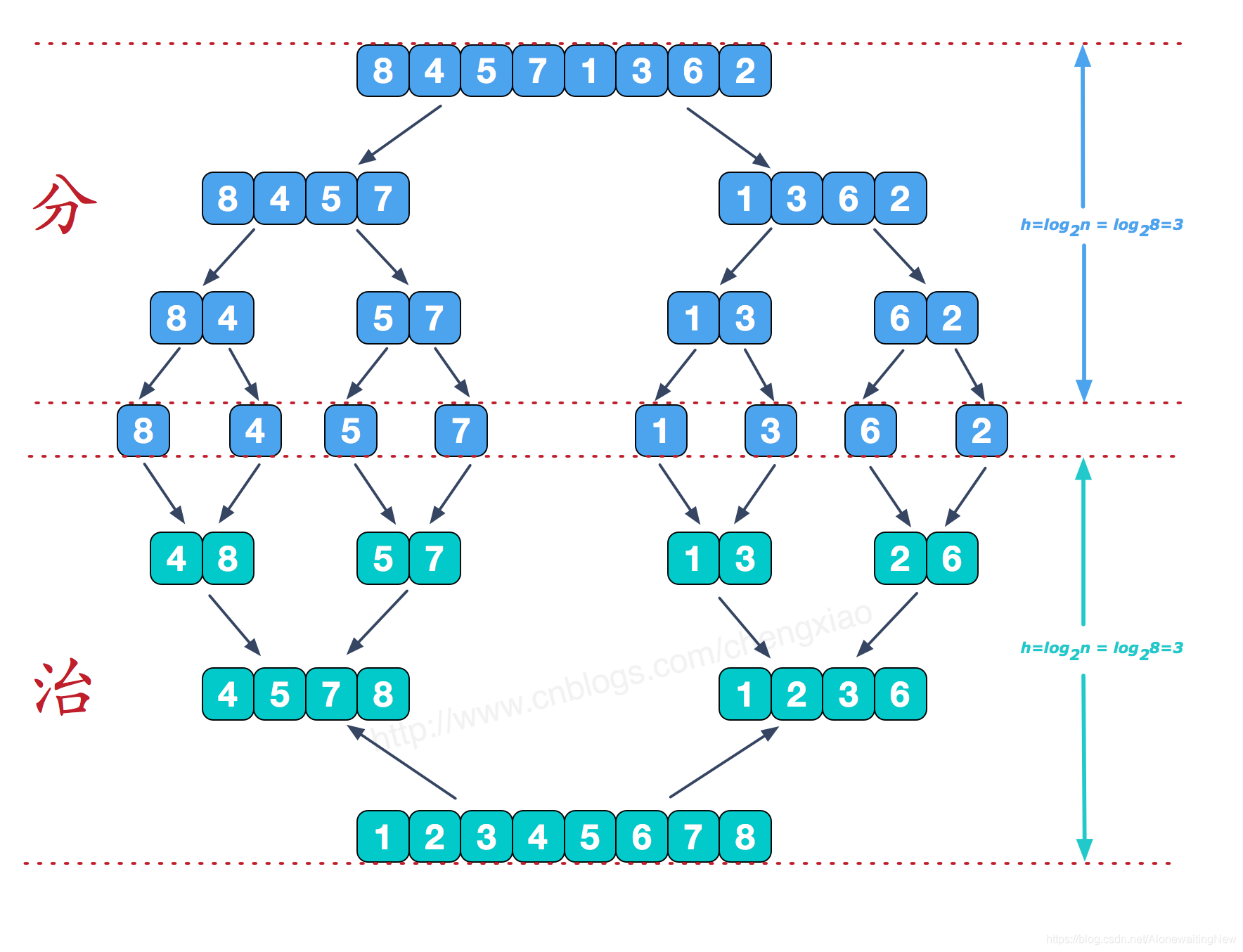
归并排序的目的就是分而治之,把一个大的问题,分解成若干个小问题,然后再把问题合并起来。具体的原理如下图所示
那就是说,整个过程需要两步,
一:分,
二:合。
对于普通的数组我们可以递归的分,然后合并。如下所示:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void mergeTwoVector(vector<int> &v1, vector<int> &v2, vector<int> &out){
out.clear();
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < v1.size() && j < v2.size()) {
if(v1[i] <= v2[j]){
out.push_back(v1[i++]);
} else {
out.push_back(v2[j++]);
}
}
while (i < v1.size()) {
/* code */
out.push_back(v1[i++]);
}
while (j < v2.size()) {
out.push_back(v2[j++]);
}
}
void mergeSort(vector<int>& vec) {
//分
if(vec.size() < 2) {
return;
}
vector<int> subVectorL;
vector<int> subVectorR;
int mid = vec.size() / 2;
subVectorL.assign(vec.begin(), vec.begin() + mid);
subVectorR.assign(vec.begin() + mid, vec.end());
//左
mergeSort(subVectorL);
//右
mergeSort(subVectorR);
//合二为一
mergeTwoVector(subVectorL,subVectorR,vec);
}
int main() {
vector<int> input{2,1,3432,12,3,35,6,57,23,465};
for(auto k : input){
cout << k << ",";
}
cout << endl;
mergeSort(input);
cout << "after sort" << endl;
for(auto k : input) {
cout << k << ",";
}
cout << endl;
}
2、链表的归并排序
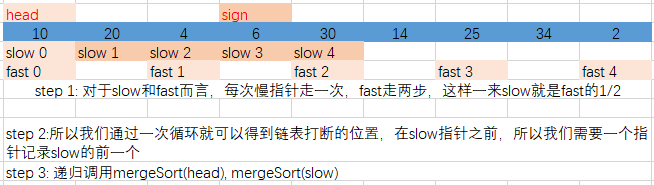
对于链表的归并排序不像数组,我们可以直接定位到一个数组的中间。所以解决链表定位到中间位置也就解决了这个问题
如上图所示,记录了一次循环后把链表分成了两部分,两部分的头节点分别是head和slow。然后递归调用即可,代码如下
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//单链表结构
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
//单链表的归并排序
struct ListNode* mergeSort(struct ListNode* left, struct ListNode* right) {
struct ListNode* res = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
res->val = 0;
res->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* head = res;
//归并中的 "合"
while (left && right) {
if (left->val < right->val) {
//左边小
head->next = left;
head = head->next;
left = left->next;
} else {
//右边小
head->next = right;
head = head->next;
right = right->next;
}
}
//剩下的左边
while (left) {
head->next = left;
head = head->next;
left = left->next;
}
//剩下的右边
while (right) {
head->next = right;
head = head->next;
right = right->next;
}
return res->next;
}
struct ListNode* sortList(struct ListNode* head) {
if (!head->next) return head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
struct ListNode* fast = head;
struct ListNode* sign = NULL;
//快慢指针找到单链表的中间节点
while (fast && fast->next) {
sign = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
sign->next = NULL;
//进行递归处理,归并中的 "合"
struct ListNode* left = sortList(head);
struct ListNode* right = sortList(slow);
return mergeSort(left, right);
}
int main() {
//构造单链表
struct ListNode* head = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
head->val = 56;
head->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cur->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
cur->next->val = i + 24;
cur->next->next = NULL;
cur = cur->next;
}
//归并排序前
printf("sort before: ");
struct ListNode* a = head;
while (a->next) {
printf("%d ", a->val);
a = a->next;
}
printf("%d ", a->val);
printf("\n");
//归并排序后
head = sortList(head);
printf("sort after: ");
cur = head;
while (cur->next) {
printf("%d ", cur->val);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("%d ", cur->val);
printf("\n");
}