引言
在实际实现3D目标检测时,在不依靠深度学习的训练模型时,仅采用传统方法实现目标检测。而在聚类领域里面,多采用欧几里得、区域生长、Ransac等方法实现聚类。其实还有一种方法可实现聚类,也就是CloudCompare软件内的标签连通域聚类方法。这种方法的好处是耗时较短,也同样能够实现较高精度的距离聚类。
本文根据其特性做出相对应的修改,使其能够脱离CC软件插件,用C++程序以及PCL点云库实现。
标签连通域聚类原理
标签连通域算法起源来自于图像聚类,其聚类思路简单易懂。
- 一般来说都是从图片的左上角第一个像素点开始进行搜索,首先通过搜索其相邻的像素点的灰度值(或其他判定值)来进行判定。
- 得到搜索点的判定值之后,与设定阈值 T h d i s \ Th_{dis} Thdis进行比较,若满足条件,则可以视作是同一类别,则对搜索点打上类别标签,若不满足则跳过。进一步将该搜索点作为新一轮的起始点,进行递归搜索,反复打上标签,直至完全搜索不到新的像素点。
- 继续选取未打上标签点进行新一轮的标签搜索,标记上不同于之前的标签值,按照上述步骤继续标记,最终完成标签连通域聚类。
阐述完图像的标签连通域算法的基本流程后,我们需要进一步了解在空间点云上是如何实现标签连通域算法的。
CloudCompare上的连通域算法思路:
- 首先将输入的点云 P i n p u t \ P_{input} Pinput做八叉树处理。
- 进一步将八叉树内部所有分块的中心点提取出来,重新组成新的点云数据 P o c t r e e \ P_{octree} Poctree。
- 针对 P o c t r e e \ P_{octree} Poctree实现 K n n \ Knn Knn搜索,即对起始点找到 K \ K K个搜索点 p k \ p_{k} pk。并获取到每个搜索点 p k \ p_{k} pk与起始点 p 0 \ p_{0} p0的距离值 D k \ D_{k} Dk。
- 设定距离阈值 D t h \ D_{th} Dth来进行判定,当得到 D k < D t h \ D_{k}<D_{th} Dk<Dth时,即可认定该搜索点与起始点的标签一致,若 D k > D t h \ D_{k}>D_{th} Dk>Dth,则认为该 p k \ p_{k} pk不同于起始点标签,跳过即可。
- 进一步通过递归迭代对未实现标记的点云重复3、4步骤,即可实现八叉树结构的标签连通域聚类。即可将点云数据 P o c t r e e \ P_{octree} Poctree聚类成带 m \ m m个标签的点云 P l a b l e \ P_{lable} Plable。
- 进一步提取 P l a b l e \ P_{lable} Plable的每个点定义为新的起始点,搜索的方法采用八叉树的体素搜索方式,即只对 P i n p u t \ P_{input} Pinput搜索八叉树内部的其余点,并对这些搜索后的点打上中心点的相同标签。最终完成对整个 P i n p u t \ P_{input} Pinput的聚类任务。
其实整体看下来,距离判定处理的方式与欧几里得聚类方法相同,不同的是一个采用 K n n \ Knn Knn搜索,一个为半径搜索。那么相信在讲解该算法的运行流程之后,大家会理解基于八叉树的标签连通域聚类原理。然后只需要一步步实现其代码即可。
Octree + LCC 代码实现
首先头文件。
#pragma once
#ifndef OCTREE_CONNECTION
#define OCTREE_CONNECTION
#define PCL_NO_PRECOMPILE
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/conversions.h>
#include <pcl/common/centroid.h>
#include <pcl/filters/filter.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/filters/extract_indices.h>
#include <pcl/filters/plane_clipper3D.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/extract_clusters.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/conditional_euclidean_clustering.h>
#include <pcl/features/moment_of_inertia_estimation.h>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <vector>
#include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> //文件输入输出
using namespace pcl;
using namespace std;
/*
*@brief 输入需要聚类的点云,参数;输出聚类完成带标签的点云
*/
class OTC
{
private:
typedef pcl::PointXYZ VPoint; ///< 定义点云类型
typedef std::vector<VPoint,Eigen::aligned_allocator<VPoint>> AlignedPointTVector;
/*
* @brief 计算点云至原点的距离
* @param points 输入三维点
* @return double 返回距离长度
*/
double get_points2dis(VPoint points);
float octree_leaf_size = 0.3f; ///< 八叉树深度参数
int max_points_size = 20000; ///< 聚类最大点云数
int min_points_size = 2; ///< 聚类最小点云数
int sourch_k_num = 10; ///< 聚类K近邻搜索数
double dis_th = 0.1; ///< 聚类放大比例系数
public:
/*
* @brief 八叉树结构去噪算法
* @param cloud 输入需要去噪点云
* @param filter_cloud 输出去噪后的点云
* @return bool 返回是否成功去噪
*/
bool octree_denoise( const pcl::PointCloud<VPoint>::Ptr cloud,
pcl::PointCloud<VPoint> & filter_cloud);
/*
* @brief 设定八叉树最小深度值
* @param size 输入定义深度值
*/
void set_octree_leafsize(const float size){
octree_leaf_size = size;
};
/*
* @brief 设定聚类最小值
* @param min_size 输入定义聚类最小值
*/
void set_min_points_size(const int min_size){
min_points_size = min_size;
};
/*
* @brief 设定聚类比例系数
* @param distance_th 输入定义聚类比例系数
*/
void set_distance_th(const double distance_th){
dis_th = distance_th;
};
/*
* @brief 欧几里得聚类算法(采用KNN搜索)
* @param cloud 输入需要聚类的点云
* @param tree 输入搜索方式,默认为KDtree结构
* @param tolerance 输入八叉树搜索间隔
* @param clusters 输出聚类后的类别集合
* @param min_pts_per_cluster 输入聚类点云的最小值
* @param max_pts_per_cluster 输入聚类点云的最大值
*/
void euclidean_clusters(const PointCloud<VPoint> cloud,
const typename search::Search<VPoint>::Ptr &tree,
double tolerance, std::vector<PointIndices> &clusters,
unsigned int min_pts_per_cluster,
unsigned int max_pts_per_cluster);
/*
* @brief 八叉树连通域聚类算法
* @param input_cloud 输入需要聚类的点云
* @param octree_connect_cloud 输出聚类后的点云集合
*/
void octree_connection(const PointCloud<VPoint>::Ptr input_cloud,
std::vector<pcl::PointCloud<VPoint>>& octree_connect_cloud);
OTC(){};
~OTC(){};
};
#endif
后续对应的cpp文件,参考欧几里得的聚类源代码实现。
void OTC::euclidean_clusters(const PointCloud<VPoint> cloud,
const typename search::Search<VPoint>::Ptr & tree,
double tolerance,
std::vector<PointIndices> & clusters,
unsigned int min_pts_per_cluster,
unsigned int max_pts_per_cluster){
if (tree->getInputCloud ()->points.size () != cloud.points.size ()){
PCL_ERROR ("[pcl::extracteuclidean_clusters] Tree built for a different point cloud dataset (%lu) than the input cloud (%lu)!\n", tree->getInputCloud ()->points.size (), cloud.points.size ());
return;
}
int nn_start_idx = tree->getSortedResults () ? 1 : 0;
std::vector<bool> processed (cloud.points.size (), false);
std::vector<int> nn_indices;
std::vector<float> nn_distances;
//遍历点云中的每一个点
for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int> (cloud.points.size ()); ++i) {
if (processed[i]) ///< 如果该点已经处理则跳过
continue;
std::vector<int> seed_queue; ///< 定义一个种子队列
int sq_idx = 0;
seed_queue.push_back(i); ///< 加入一个种子
processed[i] = true;
while (sq_idx < static_cast<int> (seed_queue.size())) {
/*采用KNN搜索方式进行相邻点判定*/
if (!tree->nearestKSearch(seed_queue[sq_idx], sourch_k_num, nn_indices, nn_distances)) {
sq_idx++;
continue; ///< 没找到近邻点就继续
}
double dis = get_points2dis(cloud.points[seed_queue[sq_idx]]);
for (size_t j = nn_start_idx; j < nn_indices.size (); ++j){
if (nn_indices[j] == -1 || processed[nn_indices[j]])
continue; ///< 种子点的近邻点中如果已经处理就跳出此次循环继续
if(nn_distances[j]>max(dis_th * tolerance * dis ,tolerance))
continue;
seed_queue.push_back (nn_indices[j]); ///< 将此种子点的临近点作为新的种子点。入队操作
processed[nn_indices[j]] = true; ///< 该点已经处理,打标签
}
sq_idx++;
}
/*最大点数和最小点数的类过滤*/
if (seed_queue.size () >= min_pts_per_cluster && seed_queue.size () <= max_pts_per_cluster){
pcl::PointIndices r;
r.indices.resize (seed_queue.size ());
for (size_t j = 0; j < seed_queue.size (); ++j)
r.indices[j] = seed_queue[j];
std::sort (r.indices.begin (), r.indices.end ());
r.indices.erase (std::unique (r.indices.begin (), r.indices.end ()), r.indices.end ());
r.header = cloud.header;
clusters.push_back (r);
}
}
}
进一步分析连通域聚类算法,通过八叉树建立点云数据,采用距离聚类,并最后恢复点云标签,从而完成整个连通域聚类算法。
void OTC::octree_connection(const pcl::PointCloud<VPoint>::Ptr input_cloud,
std::vector<pcl::PointCloud<VPoint>>& octree_connect_cloud){
AlignedPointTVector voxel_center_list_arg;
voxel_center_list_arg.clear();
octree_connect_cloud.clear();
pcl::octree::OctreePointCloudSearch<VPoint> octree(octree_leaf_size);
octree.setInputCloud(input_cloud);
octree.addPointsFromInputCloud();
octree.getOccupiedVoxelCenters(voxel_center_list_arg);
// 等同于 occupiedVoxelCenters
pcl::PointCloud<VPoint> v_cloud,euc_cloud;
v_cloud.resize(voxel_center_list_arg.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < voxel_center_list_arg.size(); i++){
v_cloud[i].x = voxel_center_list_arg[i].x;
v_cloud[i].y = voxel_center_list_arg[i].y;
v_cloud[i].z = voxel_center_list_arg[i].z;
}
//欧几里得聚类
float dis_th = pow(pow((octree_leaf_size * 2 ),2) + pow((octree_leaf_size * 2 ),2),0.5)+0.001; ///< 计算聚类深度阈值
pcl::search::KdTree<VPoint>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<VPoint>);
std::vector<pcl::PointIndices>ece_inlier;
tree->setInputCloud(v_cloud.makeShared());
euclidean_clusters(v_cloud,tree,dis_th, ece_inlier,1,max_points_size); ///< 聚类
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("cloud viewer");
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0);
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "cloud viewer");
int num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < ece_inlier.size();i++){
/*聚类完成后,需要重新找到八叉树内部所有点(体素搜索)*/
std::vector<int> ece_inlier_ext = ece_inlier[i].indices; ///< 输入所聚类到的体素中心点
pcl::PointCloud<VPoint> voxel_cloud,cloud_copy;
pcl::copyPointCloud(v_cloud, ece_inlier_ext, cloud_copy); ///< 按照索引提取点云数据
for (int j =0 ; j<cloud_copy.points.size();j++){
std::vector<int> pointIdxVec; ///< 保存体素近邻搜索的结果向量
if (octree.voxelSearch(cloud_copy.points[j], pointIdxVec)){
for (size_t k = 0; k < pointIdxVec.size(); ++k){
voxel_cloud.push_back(input_cloud->points[pointIdxVec[k]]);
}
}
}
if(voxel_cloud.points.size()>min_points_size){
uint8_t R = rand() % (256) + 0;
uint8_t G = rand() % (256) + 0;
uint8_t B = rand() % (256) + 0;
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<VPoint> ramdonColor(input_cloud, R, G, B);
viewer.addPointCloud(voxel_cloud.makeShared(), ramdonColor, std::to_string(num));
num++;
octree_connect_cloud.push_back(voxel_cloud);
}
}
while(!viewer.wasStopped())//要想让自己所创窗口一直显示
{
viewer.spinOnce();
};
}
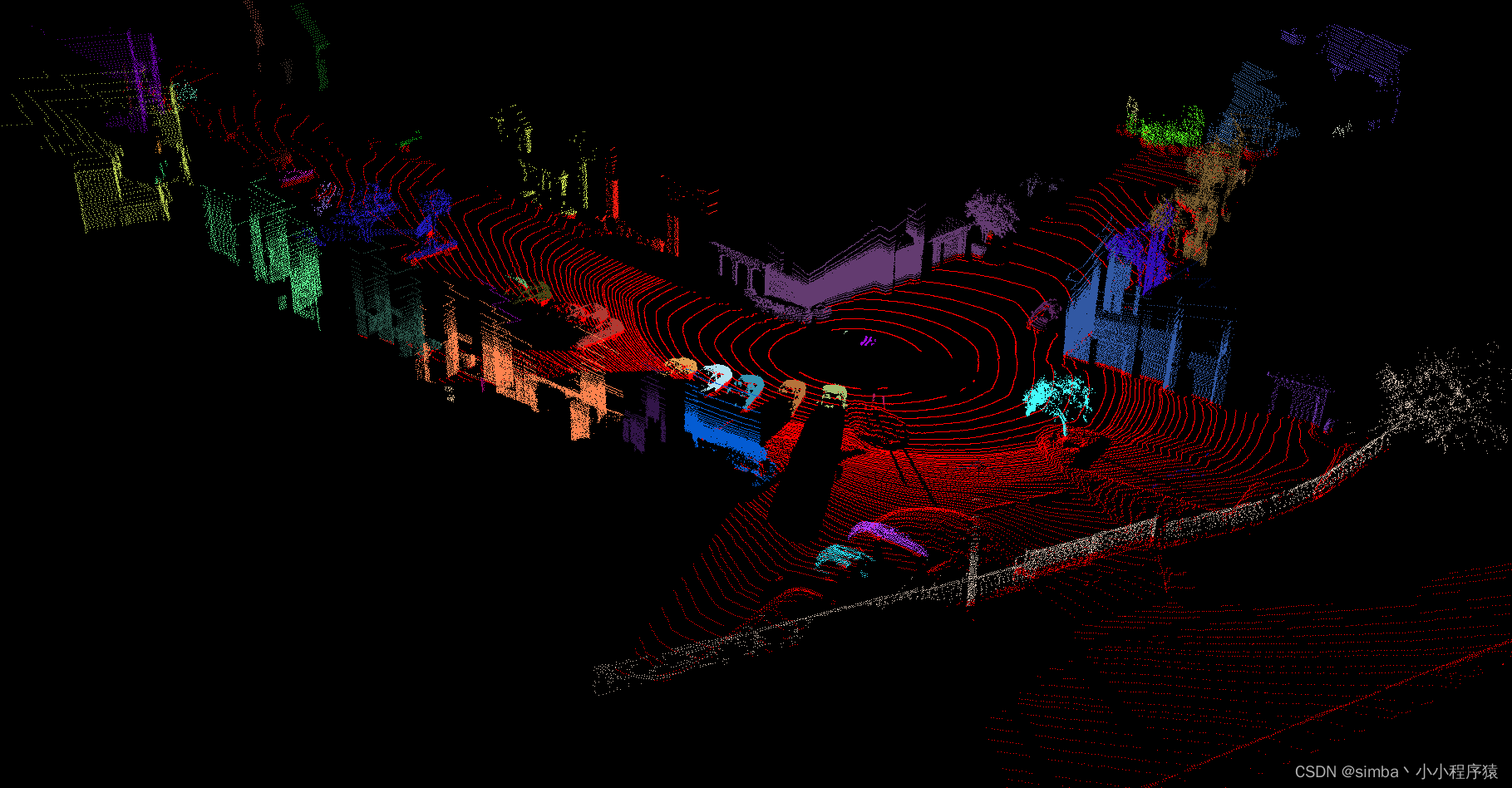
Octree + LCC 测试结果
测试结合地面分割算法实现,在地面分割的基础上完成连通域聚类可以有效防止错误聚类的情况发生。地面分割算法可以参考上一篇博客 [自动驾驶-目标检测] C++ PCL 地面点云分割。
Octree + LCC 的优缺点
优点:
- 具有很强的鲁棒性及聚类效率,不用针对整个点云数据即可实现聚类,可以适应绝大多数点云聚类场景。
- 算法扩展性较强。距离判定的方式也可以采用其他判定方式实现,比如对八叉树分块中的局部点云特征值(反光强度分布、曲率)等等进行判别,因此可以根据实际场景进一步设计该算法。
缺点:
- 比较依赖人工参数设定,不同的激光雷达传感器所设定的参数不一样,尤其是在点云密度分布一样的传感器其效果差别更大。
- 无法适应于具有遮挡、重合、内部嵌套等等点云场景,这一点是现阶段传统点云聚类方法的通病。
改进思路
- 在进行远距离的距离判定时,可以采用距离系数来进行判定,而不采用具体的值来完成,这样可以避免同一物体在远距离聚类时被划分为多个聚类点云。比如将距离阈值 D t h \ D_{th} Dth转成 d t h \ d_{th} dth,利用 D k / D p < d t h \ D_{k} / D_{p}< d_{th} Dk/Dp<dth来进行判定。其中 D p \ D_{p} Dp表示起始点到坐标系远点的距离。
- 在实践过程中,可以配合Kdtree的数据结构实现距离搜索,提高搜索效率也是可以的。
参考文献
[1] opencv connectedComponents函数
[2] Vo A V , Truong-Hong L , Laefer D F , et al. Octree-based region growing for point cloud segmentation[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2015, 104:88-100.
[3] Leon_Chan0 OpenCV学习(二十一) :计算图像连通分量
…