前言
在上期:【Apache POI】Excel操作(五):Excel数据的读取 的博客中,如果有细心的小伙伴的话,恐怕会发现Excel还有一种数据类型我们并没有使用到,那就是:
HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA
那这个是啥呢?
好了,不卖关子了,这个就是Excel的计算公式啦!
具体如何使用,请接着往下看!!!
Excel准备
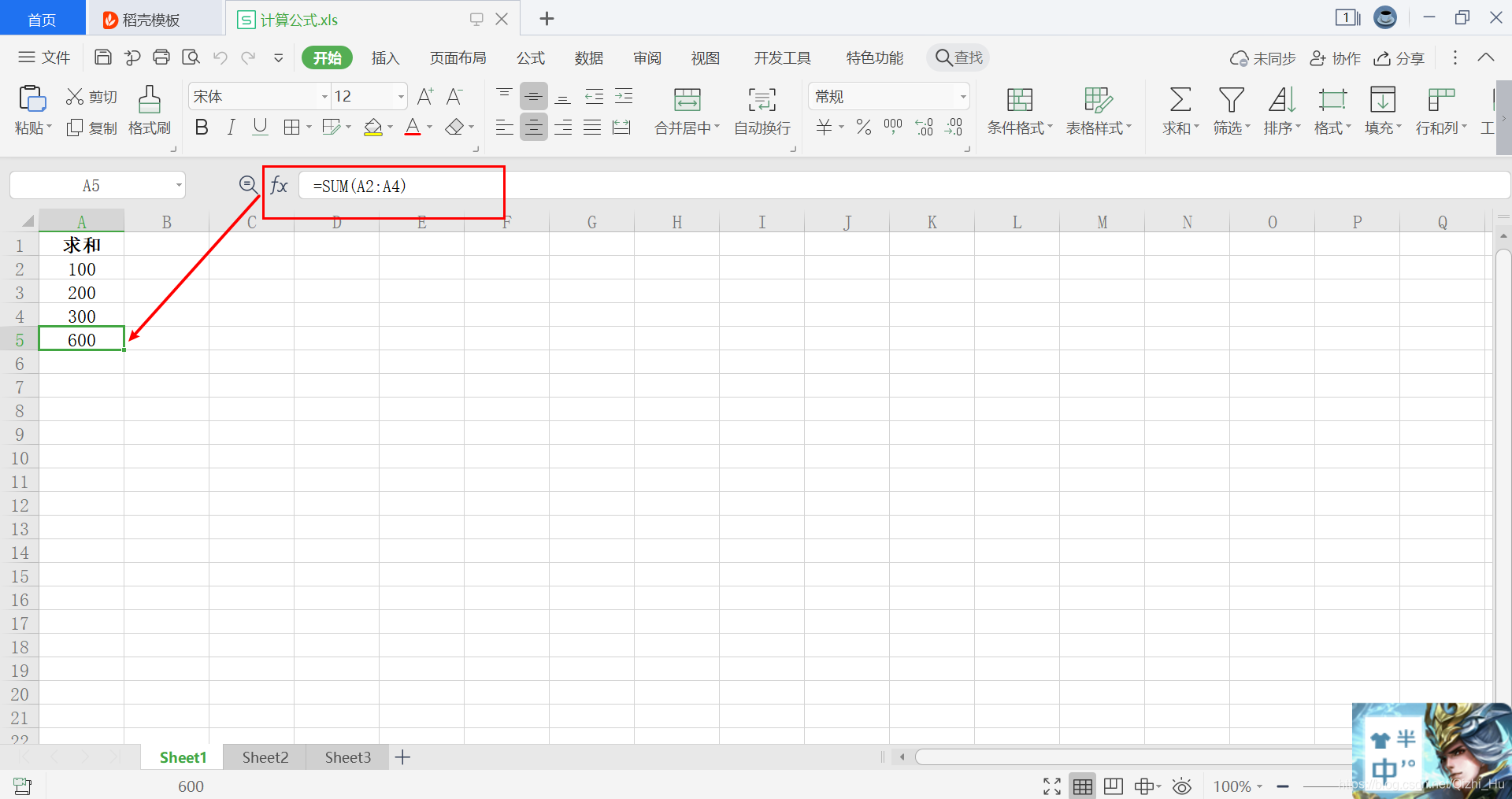
首先,我们先准备一张名为计算公式.xls用以读取Excel计算公式的excel表格。如下图所示,Excel第五行第一列为一个简单的求和公式:=SUM(A2:A4),即第五行第一列的值为第二行第一列 至 第四行第一列之和。
那我们这篇博客就准备把第五行第一列的计算公式以及值通过Java程序给它读取出来。
计算公式读取
话不多说,直接上代码
这是excel文件的路径:
/**
* 路径
*/
String PATH = "D:\\IdeaProjects\\my_study_demo\\src\\main\\java\\excel\\read";
这是excel文件的名称:
/**
* 文件名
*/
String FILENAME = "计算公式.xls";
主菜:
/**
* 读取计算公式
*/
@Test
public void readExcelTest() throws Exception {
/**
* 读取Excel工作簿
*/
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(PATH + File.separator + FILENAME);
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(in);
// 拿到计算公式
FormulaEvaluator formulaEvaluator = new HSSFFormulaEvaluator((HSSFWorkbook) workbook);
if (workbook != null) {
// 获取第一个工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
if (sheet != null) {
// 获取第五行
Row row = sheet.getRow(4);
if (row != null) {
// 获取第一列
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
// 拿到数据类型
int type = cell.getCellType();
switch (type) {
case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA:
String formula = cell.getCellFormula();
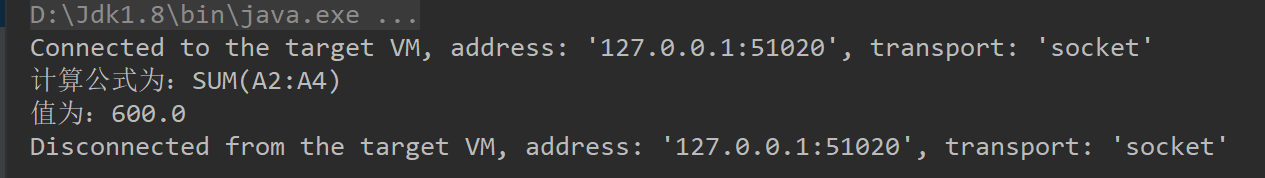
System.out.println("计算公式为:" + formula);
// 进行计算并拿到值
CellValue value = formulaEvaluator.evaluate(cell);
// 将值转化成字符串
String format = value.formatAsString();
System.out.println("值为:" + format);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
运行得:
直接读取
这个时候可能有小伙伴就会发出灵魂三问了:不就读值吗?整的这么麻烦干什么?我按照博主上期的博客直接读值不就行了吗?
那我们就来试试直接读值吧:
/**
* 试图直接读取计算公式的值
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void readTest() throws Exception {
/**
* 读取Excel工作簿
*/
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(PATH + File.separator + FILENAME);
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(in);
if (workbook != null) {
// 获取第一个工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
if (sheet != null) {
// 获取第五行
Row row = sheet.getRow(4);
if (row != null) {
// 获取第一列
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
if (cell != null) {
// 读值
double value = cell.getNumericCellValue();
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
}
}
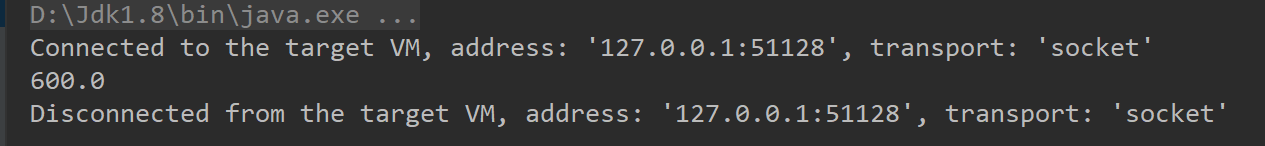
运行:
结果发现,也很顺利的把值给读取出来了!
屠龙秘技
那既然按照上文所说直接读值也能读取值,那我们还费那么大周折干嘛呢???俗话说得好:存在即合理。 既然存在,那么就是有它的道理所在的。如我们试着在读取之前直接通过程序将第二行第一列的值从100改为200:
// 拿到第二行第一列,把值从100改为200
Row row2 = sheet.getRow(1);
Cell cell21 = row2.getCell(0);
cell21.setCellValue(200);
再直接读取
/**
* 试图直接读取计算公式的值
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void readTest() throws Exception {
/**
* 读取Excel工作簿
*/
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(PATH + File.separator + FILENAME);
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(in);
if (workbook != null) {
// 获取第一个工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// 拿到第二行第一列,把值从100改为200
Row row2 = sheet.getRow(1);
Cell cell21 = row2.getCell(0);
cell21.setCellValue(200);
if (sheet != null) {
// 获取第五行
Row row = sheet.getRow(4);
if (row != null) {
// 获取第一列
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
if (cell != null) {
// 读值
double value = cell.getNumericCellValue();
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
}
}
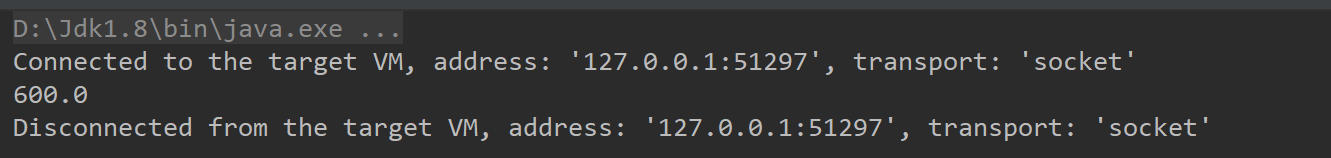
运行得:
我们会发现这个时候结果没变,还是600,但是理论上这个值应该是700!
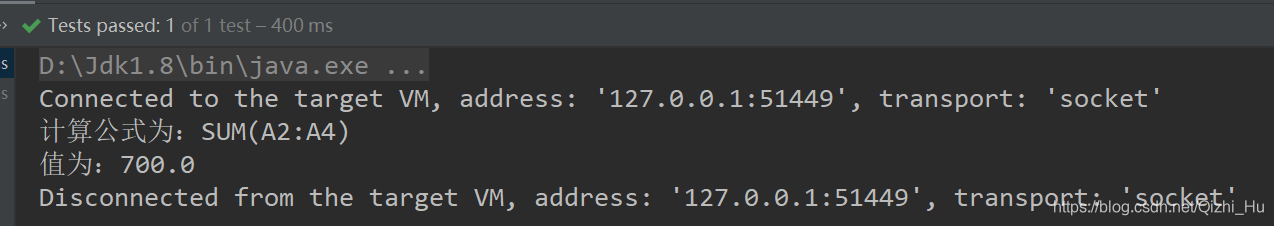
再通过计算公式读取
/**
* 读取计算公式
*/
@Test
public void readExcelTest() throws Exception {
/**
* 读取Excel工作簿
*/
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(PATH + File.separator + FILENAME);
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(in);
// 拿到计算公式
FormulaEvaluator formulaEvaluator = new HSSFFormulaEvaluator((HSSFWorkbook) workbook);
if (workbook != null) {
// 获取第一个工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
if (sheet != null) {
// 拿到第二行第一列,把值从100改为200
Row row2 = sheet.getRow(1);
Cell cell21 = row2.getCell(0);
cell21.setCellValue(200);
// 获取第五行
Row row = sheet.getRow(4);
if (row != null) {
// 获取第一列
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
// 拿到数据类型
int type = cell.getCellType();
switch (type) {
case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA:
String formula = cell.getCellFormula();
System.out.println("计算公式为:" + formula);
// 进行计算并拿到值
CellValue value = formulaEvaluator.evaluate(cell);
// 将值转化成字符串
String format = value.formatAsString();
System.out.println("值为:" + format);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
运行程序得:
完美!!!
完整代码
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFDateUtil;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFFormulaEvaluator;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.joda.time.DateTime;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @ClassName ExcelReadTest
* @Description excel读取操作 - 计算公式
* @Author 古阙月
* @Date 2020/11/12 21:58
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class ExcelReadTest2 {
/**
* 路径
*/
String PATH = "D:\\IdeaProjects\\my_study_demo\\src\\main\\java\\excel\\read";
/**
* 文件名
*/
String FILENAME = "计算公式.xls";
/**
* 试图直接读取计算公式的值
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void readTest() throws Exception {
/**
* 读取Excel工作簿
*/
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(PATH + File.separator + FILENAME);
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(in);
if (workbook != null) {
// 获取第一个工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// 拿到第二行第一列,把值从100改为200
Row row2 = sheet.getRow(1);
Cell cell21 = row2.getCell(0);
cell21.setCellValue(200);
if (sheet != null) {
// 获取第五行
Row row = sheet.getRow(4);
if (row != null) {
// 获取第一列
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
if (cell != null) {
// 读值
double value = cell.getNumericCellValue();
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 读取计算公式
*/
@Test
public void readExcelTest() throws Exception {
/**
* 读取Excel工作簿
*/
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(PATH + File.separator + FILENAME);
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(in);
// 拿到计算公式
FormulaEvaluator formulaEvaluator = new HSSFFormulaEvaluator((HSSFWorkbook) workbook);
if (workbook != null) {
// 获取第一个工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
if (sheet != null) {
// 拿到第二行第一列,把值从100改为200
Row row2 = sheet.getRow(1);
Cell cell21 = row2.getCell(0);
cell21.setCellValue(200);
// 获取第五行
Row row = sheet.getRow(4);
if (row != null) {
// 获取第一列
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
// 拿到数据类型
int type = cell.getCellType();
switch (type) {
case HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA:
String formula = cell.getCellFormula();
System.out.println("计算公式为:" + formula);
// 进行计算并拿到值
CellValue value = formulaEvaluator.evaluate(cell);
// 将值转化成字符串
String format = value.formatAsString();
System.out.println("值为:" + format);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
}
往期回顾
以下是往期Excel操作的回顾:
【Apache POI】Excel操作(一):Excel本地写入基本操作的实现
【Apache POI】Excel操作(二):Excel本地写入基本操作的实现(进阶版)
【Apache POI】Excel操作(三):Excel在浏览器端即Web端写入操作的实现
【Apache POI】Excel操作(四):Excel大数据量的写入
【Apache POI】Excel操作(五):Excel数据的读取
参考资料:【狂神说Java】POI及EasyExcel一小时搞定通俗易懂