2
2-3
判断:从返回值的角度看,利用指针比引用形参更为方便。错误
2-11
void dis_1(const int x){
array <int,x> myarr{1,2,3,4,5};
cout << myarr[1] << endl;
}
void dis_2(){
const int x = 5;
array <int,x> myarr{1,2,3,4,5};
cout << myarr[1] << endl;
}
int main()
{
dis_1(5);
dis_2();
}
dis_1()运行出错,dis_2()能够正常运行//?为啥?明天看ppt时注意
3
3-6
有一个关于C++类访问控制的笑话:“你是人,我也是人,所以我能访问你的大脑”,这反映的是
同一个类的不同对象可以互相访问对方的private成员
3-9
下面关于构造函数和成员常量描述正确的是
构造函数也能对成员常量初始化
3-11
下面代码运行结果为?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A{
A(){
cout<<"hello world"<<endl;
}
};
int main(){
A a;
}
因为调用了private成员函数而编译错误
4
4-4
一个类中最多能够包含几个构造函数?
任意多个
4-13
获取类A中静态成员value的正确语法是:
Example class:
class A
{
public:
static int value;
}A::value
4-19
this指针的作用是
A.当局部变量的命名与类中成员命名相同时,可以通过this指针获取类中成员
B.返回调用对象的引用
C.可以用于链式函数的调用
5
5-4(判断)
对于使用 new[] 方式(形如T* p = new T[n])为类类型动态分配的空间,使用 delete 仍可以释放先前 new[] 分配的数组空间,建议使用使用 delete[] 方式(形如delete[] p)释放是为了确保分配的数组中所有对象的析构函数都被调用以进行必要的资源释放。
错误//那为了什么?
5-5
下列选项正确的是?
class Test {
public:
int x;
Test() {this->x = 0;}
Test(int x = 1) {this->x = x;}
};
int main() {
Test* t = new Test();
cout << t->x << endl;
return 0;
}
编译错误//奇怪的代码,具体还要看看ppt
Test* t = new Test(); [Error] call of overloaded 'Test()' is ambiguous
5-9
Test* t = new Test();
cout << t << endl; // 输出0xe12590
delete t;
cout << t << endl; // 输出?
该段代码的输出是:
0xe12590//地址仍然存在且就是那个
5-12
class Test
{
public:
Test() {
cout << "Constructor called" << endl;
} = delete;
};
int main() {
Test t;
return 0;
}
代码的运行输出是:
错误,因为错误地使用了delete说明符//那怎样正确使用?
5-16
以下代码中,A 的构造函数和析构函数分别执行了几次
A*pa=new A[10];
delete[] pa;
10,10
5-19
以下代码关于=delete的使用正确与否?
class C {
public:
C();
};
C::C() = delete;
错误
6
6-2
使用初始化列表除了可以在某些情况下提升程序性能外,还可以完成一些使用常规的构造函数无法完成的功能。请选择下列说法中正确的选项
A.可以初始化const成员
C.可以初始化reference(引用)成员
D.可以省去对类类型成员的默认构造函数调用
//这些概念,明天好好背
6-7
下面哪种情况会导致内存泄漏?
申请了内存空间但没有释放
//还有哪些情况来着
6-9
请问以下代码输出的是什么?
class Test {
public:
int first;
int second;
Test(int value): second(value), first(second) {}
};
int main() {
Test t(1);
cout << t.first << endl;
return 0;
}
无法预期的值//因为没有初始化?不会自动赋为0吗?
6-10
下面代码的输出是
class Test1 {
public:
int a;
Test1(int a)
{
this->a = a;
cout << "Construct Test1" << endl;
}
Test1(const Test1& t1) // 拷贝构造函数
{
cout << "Copy constructor for Test1" << endl;
this->a = t1.a;
}
Test1& operator = (const Test1& t1) // 赋值运算符
{
cout << "assignment for Test1" << endl;
this->a = t1.a;
return *this;
}
};
class Test2 {
public:
Test1 test1;
Test2(Test1 &t1)
{
test1 = t1;
}
};
int main() {
Test1 t1(1);
Test2 t2(t1);
return 0;
}
编译错误,因为t2无法实现对其成员的初始化
Test2(Test1 &t1) [Error] no matching function for call to 'Test1::Test1()'
6-11
将上一题中Test2的定义改为如下所示的代码,程序输出是
class Test2 {
public:
Test1 test1;
Test2(Test1 &t1) : test1(t1) {}
};
Construct Test1
Copy constructor for Test1
//有对应关系的
6-16
拷贝构造函数应该是
带有一个参数的构造函数
6-17
下面哪种情况需要使用深拷贝?
类中有指针成员变量
6-18
下面哪种写法是正确地实现深拷贝的赋值运算符?
A.
class A {
public:
A& operator=(const A& a) {
if (this != &a) {
delete[] x;
delete[] y;
x = new char[strlen(a.x)+1];
strcpy(x, a.x);
y = new char[strlen(a.y)+1];
strcpy(y, a.y);
}
return *this;
}
private:
char* x;
char* y;
};
B.
class A {
public:
A& operator=(const A& a) {
if (this != &a) {
delete[] data;
size = a.size;
data = new double[size];
for (int i=0;i<size;i++) {
data[i] = a.data[i];
}
}
return *this;
}
private:
int size;
double* data;
};C.
class A {
public:
A& operator=(const A& a) {
if (this != &a) {
delete x;
delete y;
x = new int(*a.x);
y = new int(*a.y);
}
return *this;
}
private:
int* x;
int* y;
};//明天结合ppt好好看一下
6-20
下面哪种写法可以利用复制省略提高性能?
std::string s = std::string("hello");
7
7-6
在同一个程序中,一个函数可以有const和non-const两个版本吗?
可以,使用函数重载
//函数重载&&函数覆盖,啥区别
7-9
下列描述是否正确: 如果对象是通过引用传递给函数的,则必须返回该对象。
否
7-11
定义常对象的形式为
A.class const object(parameter);
D.const class object(parameter);
7-13
下面程序中哪一行会报错?
class date{
private:
int y,m,d;
public:
date(): y(0), m(0), d(0) {}
int year() const;
int month() const;
int day() const {
return d;
}
int day(){
return d++;
}
int addyear(int i){
return y+i;
}
};
int date::month(){ //lineA
return m;
}
int main() {
const date d;
int test;
test = d.year(); //lineB
test = d.addyear(10); //lineC
date d2;
test = d2.year();
test = d2.day(); //lineD
return 0;
}
lineABC会报错
//报啥错?没看出啥问题
7-14
下列哪个说法是正确的?
void swap1(int *p1, int* p2){
int tmp;
tmp= *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = tmp;
}
void swap2(int *p1, int* p2){
int t;
int *tmp = &t;
*tmp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = *tmp;
}
void swap3(int *p1, int* p2){
int tmp = p1;
p1 = p2;
p2 = tmp;
}
swap1() 和swap2() 函数都能够实现两数交换的效果
7-20
从自身可修改性、对数据的访问权限等角度考虑a的特性,const int& a = b 相当于 const int* const a = &b
正确
//明天好好背背语法吧
8
8-6
下列哪个陈述是错误的?
无论运算符是作为成员函数实现的还是作为非成员函数实现的,该运算符在表达式中的使用都是相同的。//有什么区别吗?
8-9
对于作为非静态成员函数重载的运算符:
二元运算符可以有两个参数,一元运算符可以有一个参数。
8-12
关于对输出运算符<<进行重载使cout << obj1能输出类obj1中的成员变量,以下哪个用法正确?
class obj1{
private:
....
public:
.....
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const obj1& a);
};//好像有些必修用友元函数?
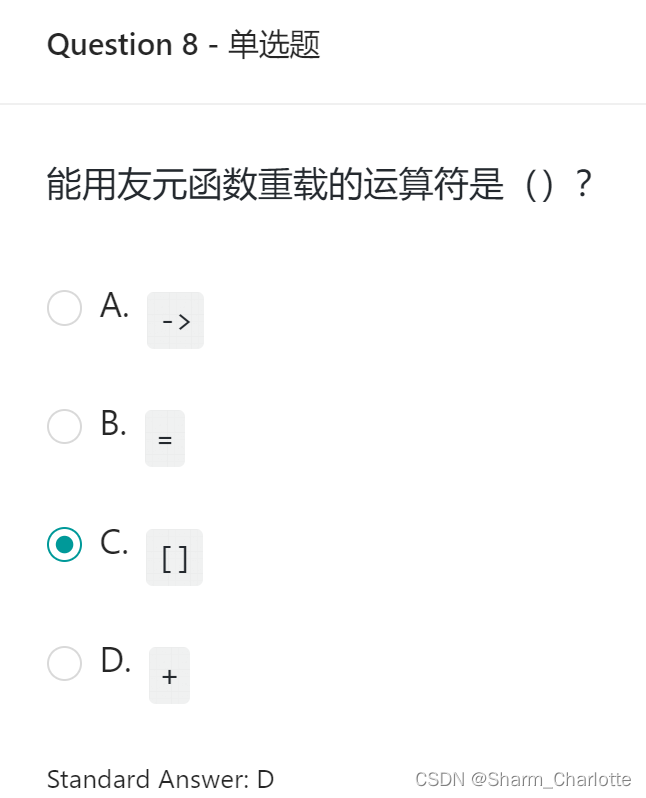
9
11

12
13
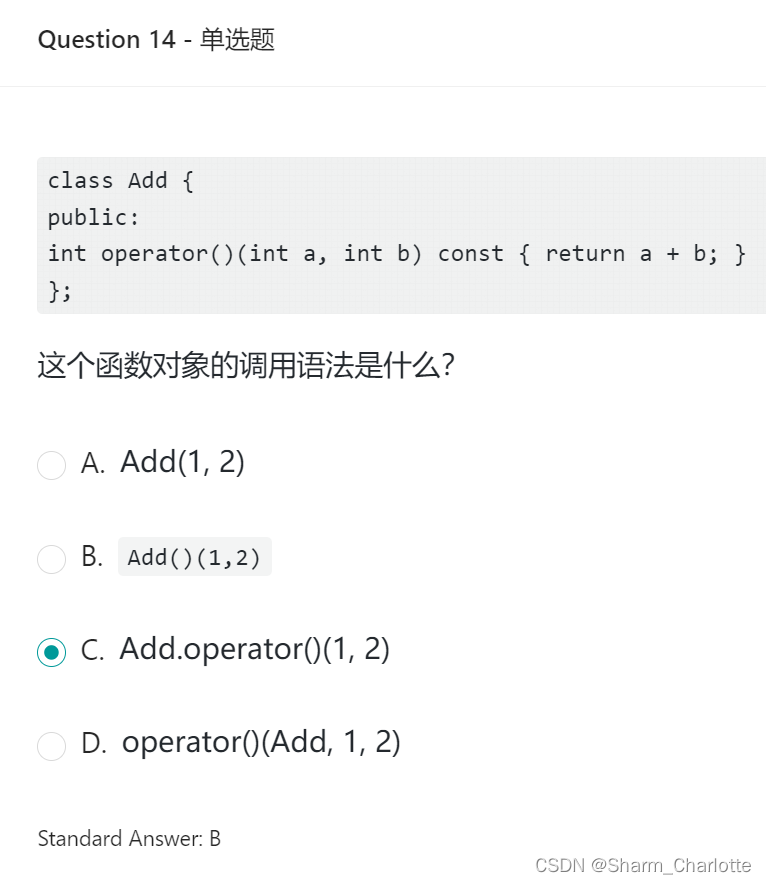
14
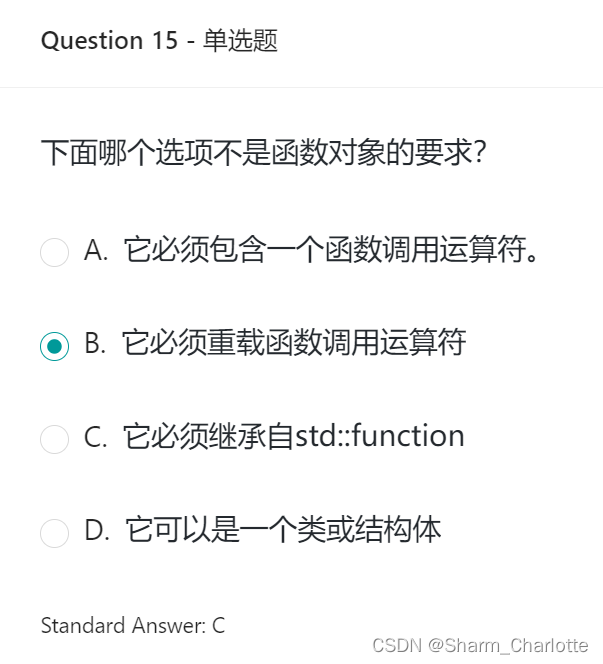
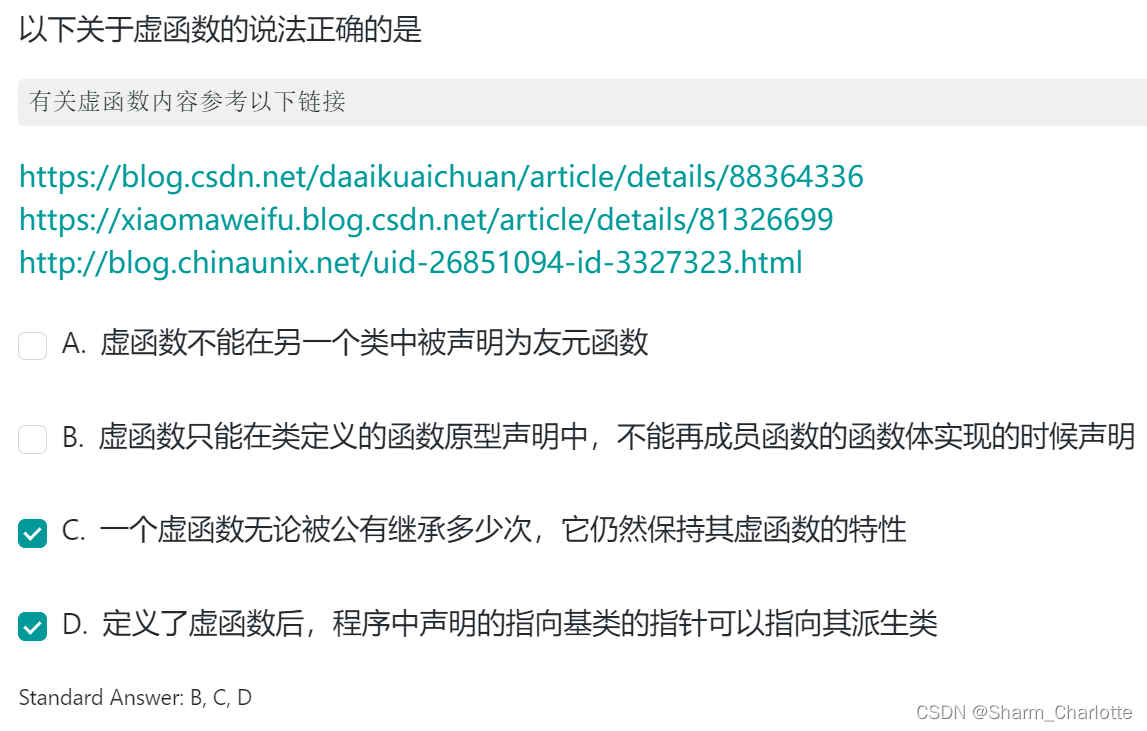
15