980. Unique Paths III
You are given an m x n integer array grid where grid[i][j] could be:
- 1 representing the starting square. There is exactly one starting square.
- 2 representing the ending square. There is exactly one ending square.
- 0 representing empty squares we can walk over.
- -1 representing obstacles that we cannot walk over.
Return the number of 4-directional walks from the starting square to the ending square, that walk over every non-obstacle square exactly once.
Example 1:
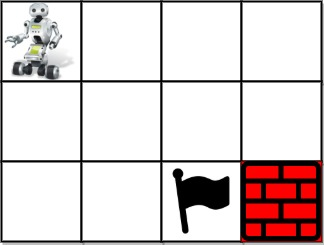
Input: grid = [[1,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0],[0,0,2,-1]]
Output: 2
Explanation: We have the following two paths:
1. (0,0),(0,1),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(1,2),(1,1),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(2,2)
2. (0,0),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(1,1),(0,1),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(1,2),(2,2)
Example 2:
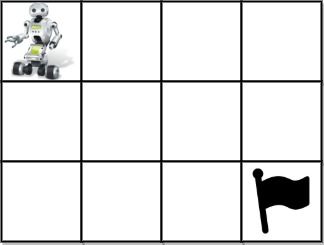
Input: grid = [[1,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,2]]
Output: 4
Explanation: We have the following four paths:
1. (0,0),(0,1),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(1,2),(1,1),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(2,2),(2,3)
2. (0,0),(0,1),(1,1),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(2,2),(1,2),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(2,3)
3. (0,0),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(2,2),(1,2),(1,1),(0,1),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(2,3)
4. (0,0),(1,0),(2,0),(2,1),(1,1),(0,1),(0,2),(0,3),(1,3),(1,2),(2,2),(2,3)
Example 3:
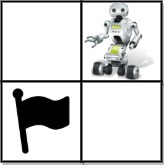
Input: grid = [[0,1],[2,0]]
Output: 0
Explanation: There is no path that walks over every empty square exactly once.
Note that the starting and ending square can be anywhere in the grid.
问题理解
我们有一个 m x n 的二维数组 grid,其中每个单元格的值代表不同的含义:
- 1:起点,只有一个。
- 2:终点,只有一个。
- 0:可以行走的空单元格。
- -1:障碍物,不能行走。
要求从起点出发,经过所有非障碍物的单元格(即所有值为 0 的单元格)恰好一次,最终到达终点。需要计算所有满足条件的路径数量。
初步思考
- 确定起点和终点:首先需要找到
grid中值为 1 和 2 的单元格,分别作为起点和终点。 - 计算需要覆盖的空单元格数量:统计
grid中值为 0 的单元格数量,记为empty。 - 深度优先搜索(DFS):从起点开始,使用 DFS 遍历所有可能的路径,确保每条路径覆盖所有
empty个空单元格,并最终到达终点。 - 回溯:在 DFS 过程中,使用回溯来撤销选择,以便探索所有可能的路径。
具体步骤
- 初始化:
- 找到起点
(start_x, start_y)和终点(end_x, end_y)。 - 计算
empty的数量。 - 初始化一个变量
result用于记录满足条件的路径数量。
- 找到起点
- DFS 函数:
- 参数:当前坐标
(x, y),已覆盖的空单元格数量count。 - 终止条件:
- 如果当前坐标是终点且
count == empty,则result加一。
- 如果当前坐标是终点且
- 递归条件:
- 遍历四个方向(上、下、左、右)。
- 如果下一个单元格是空单元格且未被访问过,则标记为已访问,递归调用 DFS,然后回溯。
- 参数:当前坐标
- 实现细节:
- 使用一个二维数组
visited来记录哪些单元格已经被访问过。 - 在 DFS 开始时,标记起点为已访问。
- 在递归调用前,检查下一个单元格是否在边界内,且不是障碍物,且未被访问过。
- 使用一个二维数组
C++ 实现
class Solution {
public:
int uniquePathsIII(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size();
int n = grid[0].size();
int start_x = -1, start_y = -1, end_x = -1, end_y = -1;
int empty = 0;
int result = 0;
// 找到起点、终点,并计算空单元格数量
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
start_x = i;
start_y = j;
} else if (grid[i][j] == 2) {
end_x = i;
end_y = j;
} else if (grid[i][j] == 0) {
empty++;
}
}
}
// 初始化访问数组
vector<vector<bool>> visited(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
// DFS 函数
function<void(int, int, int)> dfs = [&](int x, int y, int count) {
// 如果到达终点且覆盖了所有空单元格
if (x == end_x && y == end_y) {
if (count == empty) {
result++;
}
return;
}
// 标记当前单元格为已访问
visited[x][y] = true;
// 遍历四个方向
int directions[4][2] = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
for (auto& dir : directions) {
int nx = x + dir[0];
int ny = y + dir[1];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < m && ny >= 0 && ny < n && !visited[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] != -1) {
dfs(nx, ny, count + (grid[nx][ny] == 0 ? 1 : 0));
}
}
// 回溯
visited[x][y] = false;
};
// 从起点开始 DFS
dfs(start_x, start_y, 0);
return result;
}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:最坏情况下,每个空单元格都有多个选择,时间复杂度为
O
(
4
m
∗
n
)
O(4^{m*n})
O(4m∗n),其中
m和n分别是网格的行数和列数。 - 空间复杂度:主要是递归栈和访问数组的空间,为 O ( m ∗ n ) O(m*n) O(m∗n)。
总结
通过深度优先搜索和回溯的方法,我们可以有效地解决这个问题。关键在于正确地标记已访问的单元格,并在递归过程中确保覆盖所有必要的空单元格。