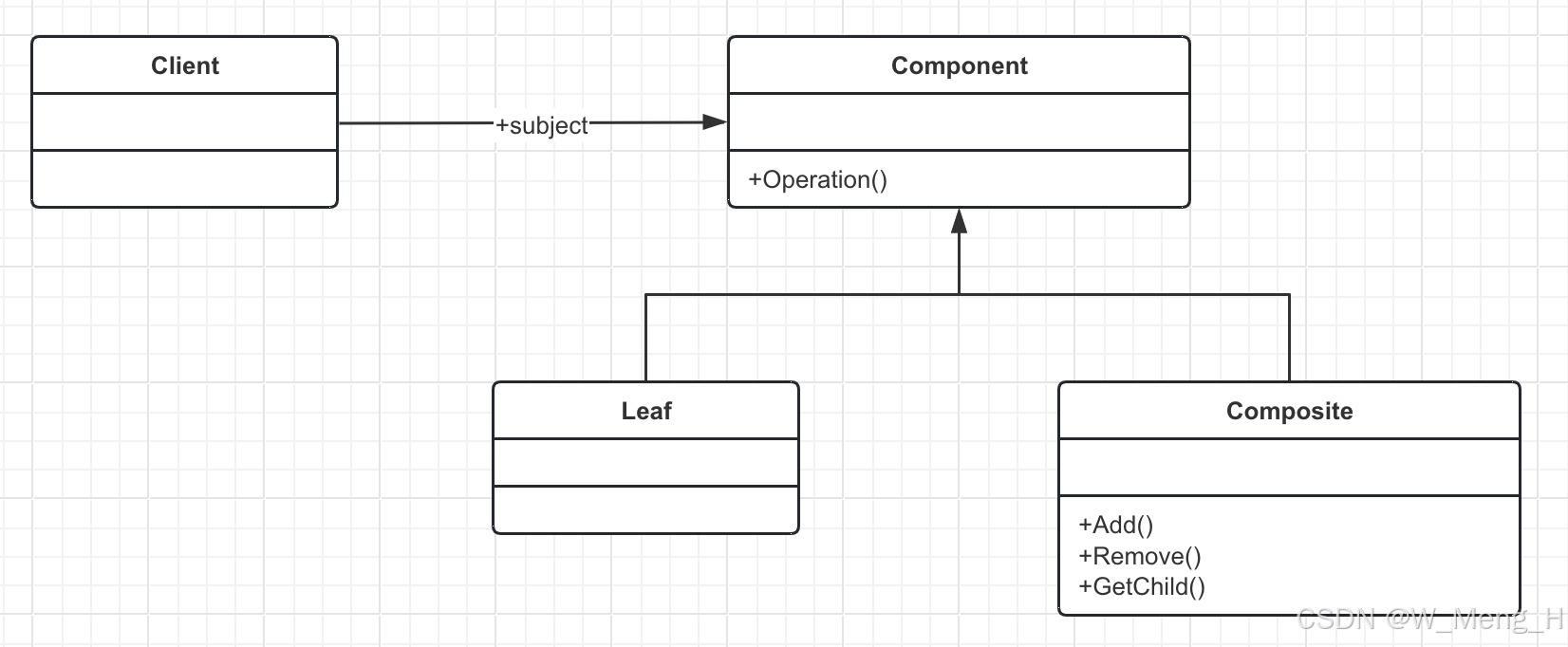
组合模式UML类图:
Component抽象组件角色:所有树形结构的叶子结点和非叶子节点都需要继承该抽象角色
Leaf叶子构件角色:叶子节点
Composite树枝构件角色:非叶子节
一、抽象组件角色
public abstract class Component {
protected String name;
public Component(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public abstract void add(Component component);
public abstract void remove(Component component);
public abstract void display(int depth);
}
二、叶子组件角色
public class Leaf extends Component {
public Leaf(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void add(Component component) {
System.out.println(name + " 不能添加子组件");
}
@Override
public void remove(Component component) {
System.out.println(name + " 不能移除子组件");
}
@Override
public void display(int depth) {
System.out.println(" ".repeat(depth * 2) + name);
}
}三、容器组件角色
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Composite extends Component {
private List<Component> children = new ArrayList<>();
public Composite(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void add(Component component) {
children.add(component);
}
@Override
public void remove(Component component) {
children.remove(component);
}
@Override
public void display(int depth) {
System.out.println(" ".repeat(depth * 2) + name + ":");
for (Component component : children) {
component.display(depth + 1);
}
}
}四、测试
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Composite root = new Composite("Root");
Composite node1 = new Composite("Node1");
Composite node2 = new Composite("Node2");
Leaf leaf1 = new Leaf("Leaf1");
Leaf leaf2 = new Leaf("Leaf2");
root.add(node1);
root.add(node2);
node1.add(leaf1);
node2.add(leaf2);
root.display(1);
}
}通过组合模式,我们可以将对象组织成树状结构,并且可以对叶子节点和容器节点使用相同的接口。这使得我们可以更容易地管理复杂的层次结构,并且可以递归地处理这些结构。组合模式是处理树状结构问题的强大工具。