连续问题的一个总结
连续问题是判断在某个期间,某些动作(状态)是否连续出现。在帖子连续性问题 中, 已经提到了用户连续登录、最大假期等。这些问题的解法是使用大小等差数列相减的办法。其实还有一种算法可以解决此问题,它就是合并集办法。合并集往往使用在计算二维数组的连通性问题,例如,leetcode 的 friend-circle 和 island-size 两个问题。并查集能解决二维数组的问题,那么一维数组的问题一定也能完美解决,在之前文章中提到的连续性问题就是一维数组上的连通性问题。
啥叫并查集合
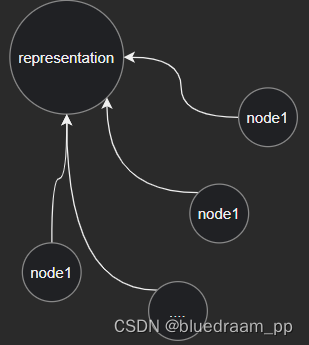
并查集是将多个集合做并集的方法,它里面保存了一个 key-value 关系,key 表示集合中的某个节点,value 代表节点。如下图所示,集合中的元素,除了代表节点之外,其中节点都指向了代表节点。
这种结构,可以使用对象引用的方式来表示,如下的 Node 类的设计。
public class Node<V>{
public V value ;
public Node rep ;
public boolean equals(Node n){
// 判断两个 Node 是否相等
}
}
也可以使用 Map 的方式保存这种关系。最好是使用数组下标的方式了表示,例如,parents[children_index] = parent_index 这样的方式。
还有一个合并两个 Node 所在集合的操作,他是实现并集操作的关键。下面是一个使用 Map 结构实现的一种方式:
public static class Node<V>{
public V value ;
public Node(V v){
value = v ;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return this.value.equals(obj) ;
}
}
public static class UnionSet<V>{
// 设置 V 和 Node 的对应关系。
private Map<V,Node<V>> nodes = new HashMap<>();
// 保存 Node 和 Node 直接的父子关系
private Map<Node<V> , Node<V>> parents = new HashMap<>();
// 保存每个大集合的元素大小
private Map<Node<V> , Integer> sizeMap = new HashMap<>();
public UnionSet(List<V> values){
for (V value : values) {
Node node = new Node(value);
nodes.put(value , node);
parents.put(node , node);
sizeMap.put(node , 1);
}
}
public Node<V> getFather(V v){
Stack<Node<V>> stack = new Stack<>();
Node<V> curr = nodes.get(v);
while(!parents.get(curr).equals(curr)){
curr = nodes.get(v);
}
// 这里是做了优化,举个例子,本来是 A -> B -> C -> D
// 这样的结果,下面的优化后,就变成了 A -> D , B -> D , C -> D 这样的结构
// 这样优化后,再去查询的时候,就能做到一步到位了。gi
Node<V> head = stack.pop();
while(!stack.empty()){
parents.put(stack.pop() , head);
}
return curr ;
}
public boolean isSameSet(V a , V b){
return getFather(a).equals(getFather(b));
}
public void union(V a , V b){
Node<V> A = nodes.get(a);
Node<V> B = nodes.get(b);
if(!A.equals(B)){
int aSize = sizeMap.get(A);
int bSize = sizeMap.get(B);
Node<V> big = (aSize > bSize ? A : B);
Node<V> small = (aSize <= bSize ? A : B);
parents.put(small , big);
sizeMap.put(big , aSize + bSize);
}
}
}
采用并查集的方式,可以计算一段阶段中,有多少个连续的集合以及集合的大小,但是集合具体的元素不能方便的取出了 ,其实在 UnionSet 类中加入一个 Map ,其中 key 是代表节点,value 是一个 List 里面保存了集合中的其他节点。这样就能方便的取出集合中的元素了。
下面是实现的代码:
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import util.RandomUtil;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class ConsistanceLogin {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 找出每周连续登录超过 n (n < 8) 的用户
* */
List<String> row = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 1000 ; i++){
int userId = RandomUtil.randIntRange(2 , 20 ,99);
for (int j = 0; j < 30; j++) {
row.add(String.format("%s %s %s",userId , j , RandomUtil.randIntRange(2 , 20 ,99) >= 30 ? "1" : "0"));
}
}
List<String> rs = getMaxLoginUser(row);
for(String userId ; rs){
System.out.println(userId);
}
}
public static List<String> getMaxLoginUser(List<String> rows , int days){
List<String> rs = new ArrayList<>();
List<LoginInfo> loginInfos = new ArrayList<>();
for (String row : rows) {
String[] split = row.split("\\s+");
String userId = split[0];
String date = split[1];
String isLogin = split[2];
loginInfos.add(new LoginInfo(userId , date , isLogin));
}
List<LoginInfo> ordered = loginInfos.stream().sorted(new Comparator<LoginInfo>() {
@Override
public int compare(LoginInfo o1, LoginInfo o2) {
if(Integer.parseInt(o1.userId) == Integer.parseInt(o2.userId)){
return Integer.parseInt(o1.date) - Integer.parseInt(o2.date);
}else{
return Integer.parseInt(o1.userId) - Integer.parseInt(o2.userId) ;
}
}
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
Map<String , List<Integer>> userLoginInfo = new HashMap<>();
for (LoginInfo loginInfo : ordered) {
userLoginInfo.computeIfPresent(loginInfo.userId , (key , value)->{
value.add(Integer.parseInt(loginInfo.isLogin));
return value ;
});
userLoginInfo.computeIfAbsent(loginInfo.userId , (key) -> {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(Integer.parseInt(loginInfo.isLogin));
return list;
});
}
UnionSet us = new UnionSet();
userLoginInfo.forEach((key , value)->{
us.parents = new int[value.size()];
us.setElement = new int[value.size()][value.size()];
us.setIndex = new int[value.size()];
us.sizeSet = new int[value.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < value.size() ; i++) {
if(value.get(i).equals(1)){
us.parents[i] = i ;
us.sizeSet[i] = 1 ;
us.setIndex[i] = 1 ;
us.setElement[i] = new int[]{i};
}
}
for(int i = 1 ; i < value.size() ; i++){
if(value.get(i-1).equals(value.get(i)) && value.get(i).equals(1)){
us.union(i -1 , i);
}
}
int maxNode = 0 ;
for(int i : us.sizeSet){
maxNode = Math.max(i , maxNode);
}
if(maxNode > days){
rs.add(key);
}
});
return rs ;
}
public static class LoginInfo{
public String userId ;
public String date ;
public String isLogin ;
public LoginInfo(String s , String d , String i){
userId = s ;
date = d ;
isLogin = i ;
}
}
public static class UnionSet{
public int[] parents ;
public int[] sizeSet ;
public int[] help ;
public int[][] setElement ;
public int[] setIndex;
public void union(int i , int j){
int iFather = getFather(i);
int jFather = getFather(i);
if(iFather != jFather){
int big = (iFather > jFather ? iFather : jFather);
int small = (iFather <= jFather ? iFather : jFather);
parents[small] = small ;
for(int a = 0 ; a < setElement[small].length ; a++){
setElement[big][setIndex[big]++] = setElement[small][a] ;
}
setElement[small] = null ;
sizeSet[big] += sizeSet[small];
sizeSet[small] = 0 ;
}
}
public int getFather(int i){
int idx = 0 ;
int cur = 0 ;
while(cur != parents[cur]){
help[idx++] = cur ;
cur = parents[cur];
}
idx--;
while(idx>=0){
parents[help[idx]] = cur ;
idx--;
}
return cur ;
}
}
}