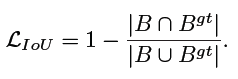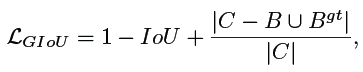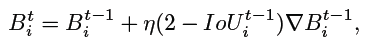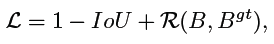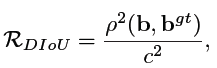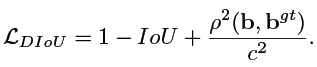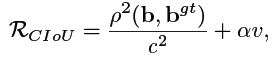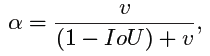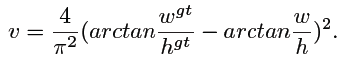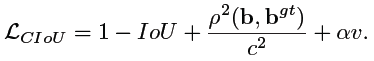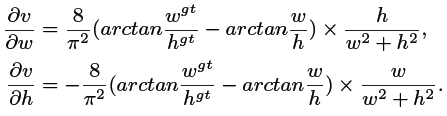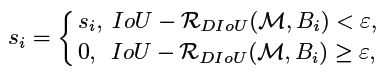AAAI-2020
文章目录
1 Background and Motivation
IoU-loss not provide any moving gradient for non-overlapping cases.
GIoU-Loss 相较于 IoU-Loss 有提升,但仍 suffer from the problems of slow convergence and inaccurate regression
仔细分析下,不相交时
L
G
I
o
U
=
2
−
I
o
U
+
U
C
=
2
+
U
C
L_{GIoU} = 2 - IoU + \frac{U}{C} = 2 + \frac{U}{C}
LGIoU=2−IoU+CU=2+CU
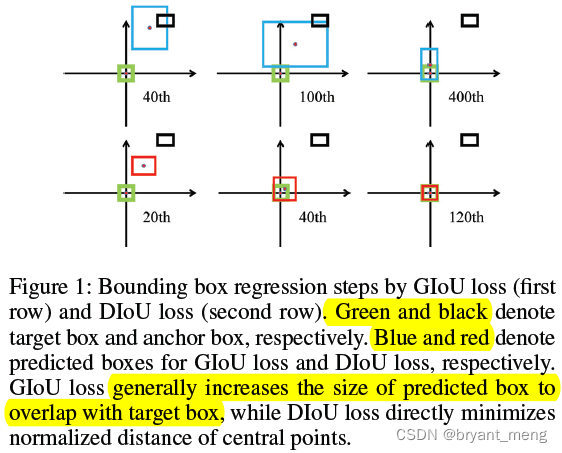
降低 L G I o U L_{GIoU} LGIoU 的方式有两种,缩小 U U U 也即 predict 靠近 GT,或者增大 C C C 也即扩大闭包(图1第一行所示,这种方式是我们不想看到的)
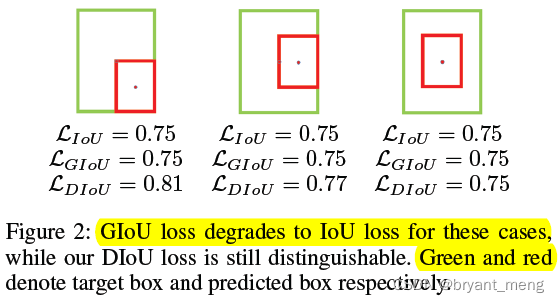
且 GT 与 prediction 属于包含关系时,GIoU-Loss 退化成了 IoU-Loss
本文 incorporating the normalized distance,提出 Distance-IoU(D-IoU),比 GIoU-Loss 收敛更快
基于 overlap area, central point distance and aspect ratio, 提出 Complete IoU(CIoU),leading to faster convergence and better performance
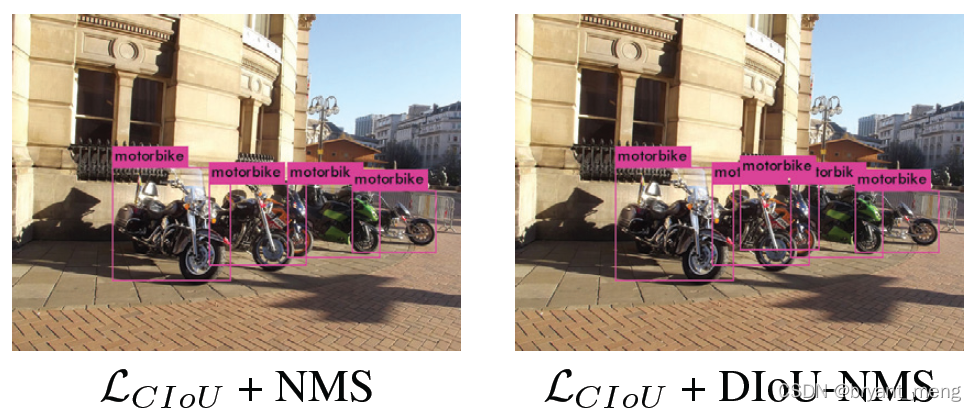
此外,D-IoU 也能 adopted into non-maximum suppression (NMS) to
act as the criterion(DIoU-NMS)
which not only the overlap area but also the distance between central points of two bounding boxes are considered when suppressing redundant boxes, making it more robust for the cases with occlusions.
2 Related Work
- Object Detection
- Loss Function for Bounding Box Regression
- Non-Maximum Suppression
3 Advantages / Contributions
- DIoU Loss
- CIoU Loss
- DIoU NMS
4 Method
4.1 Analysis to IoU and GIoU Losses
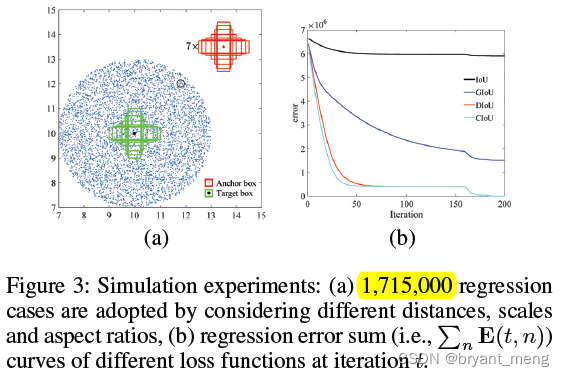
target box (7种不同 aspect ratio 绿色的框框)的中心点在 (10,10)
anchor box (7种不同 aspect ratio 红色的框框)散布在其周围,uniformly scattered at 5,000 points,半径为 3
x7 是表示有 7 个 scale,分别为 0.5, 0.67, 0.75, 1, 1.33, 1.5 and 2,图示仅展现了某一种 scale,即面积为 1 的 7 种 sacle
共 7x7x7x5000 个 regression cases(每个空间位置同一 scale 7种 aspect ratio anchor 和 7 种 aspect ratio target 一共 7x7 种 regression case,5000 个位置,7 种 scale 就是 7x7x7x5000 种 regression cases 了)
迭代方式
明显看出 DIoU-Loss 和 CIoU-Loss 收敛的比较快
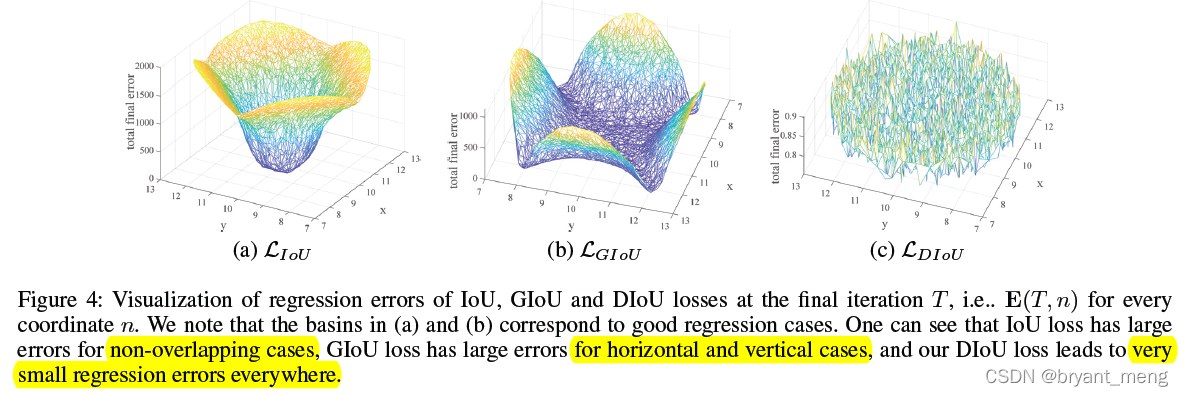
图4(a)可以看出,仅与 target bbox 有 overlap 的 anchor box,loss 才下降了
图4(b)可以看出,GIoU loss is with slow convergence especially for the boxes at horizontal and vertical orientations. 水平竖直方向如果 predict 和 target 有 overlap 且尺寸接近时,U 和 C 很接近,此时 LGIoU 就和 LIoU 相仿了
4.2 The Proposed Method
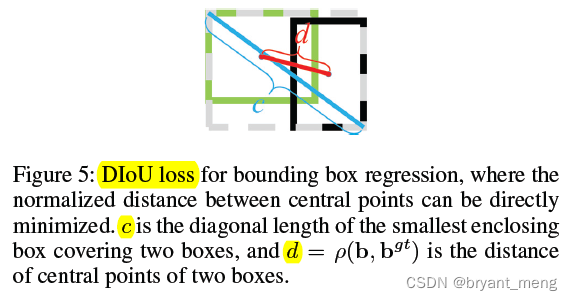
1)Distance-IoU Loss(DIoU)
相比于 IoU-Loss 和 GIoU-Loss
一样:
- 一样 invariant to the scale
- 和 GIoU-Loss 一样,non-overlapping 的时候也可以 provide moving directions for bounding boxes
- 和 GIoU-Loss 一样取值范围 [0,2)
区别:
- can directly minimize the distance of two boxes, and thus converges much faster than GIoU loss.
- 包含情况下 DIoU loss 比 GIoU loss 收敛更快
2)Complete IoU Loss(CIoU)
α
\alpha
α is a positive trade-off parameter
v
v
v measures the consistency of aspect ratio
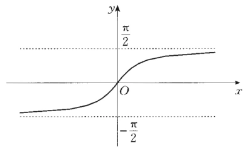
在 DIoU 的基础上引入了 aspect ratio 的监督,看到 v v v 第一反应是 4 π 2 \frac{4}{\pi^2} π24 背后的原理是什么,看这个图就秒懂了
原来是 ( 2 π ) 2 (\frac{2}{\pi})^2 (π2)2,对 arctan 宽高比做一个归一化,那问题又来了,为啥要 arctan 一下,应该是压缩数据范围吧(防止比值过大过小)
看看梯度
ps:这个正负号感觉。。。我算出来怎么正负号正好反了
w w w 和 h h h 范围都是 [0,1],过小很容易梯度爆炸,作者处理时把 1 w 2 + h 2 \frac{1}{w^2+h^2} w2+h21 置为了1
但看看下面的例子,距离我保持了,aspect ratio 我也保持了,好像 DIoU 和 CIoU 都 GG 了,哈哈
来自损失函数之DIoU Loss和CIoU Loss
3)Non-Maximum Suppression using DIoU
-
s i s_i si is the classification score
-
ε ε ε is the NMS threshold
-
M M M predicted box with the highest score
相当于提升了阈值(保留的框框更多), ε + R D I o U ε+R_{DIoU} ε+RDIoU,在原来阈值的基础上,引入了部分距离信息(越近 R R R 越小越容易被抑制掉,越远 R R R 越大越容易被保留)作为阈值
5 Experiments
5.1 Datasets
PASCAL VOC
MS COCO
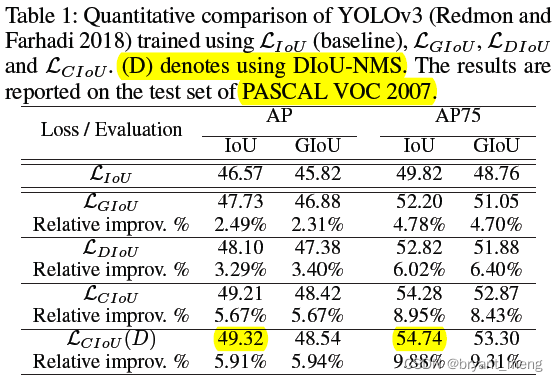
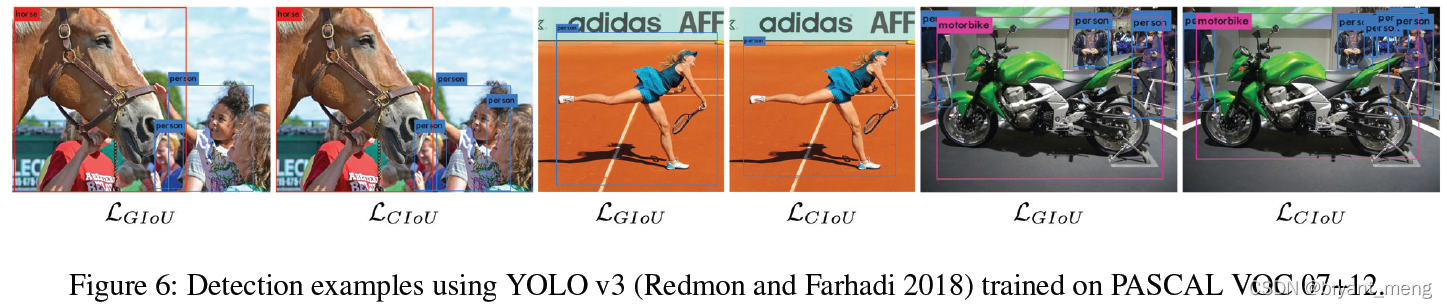
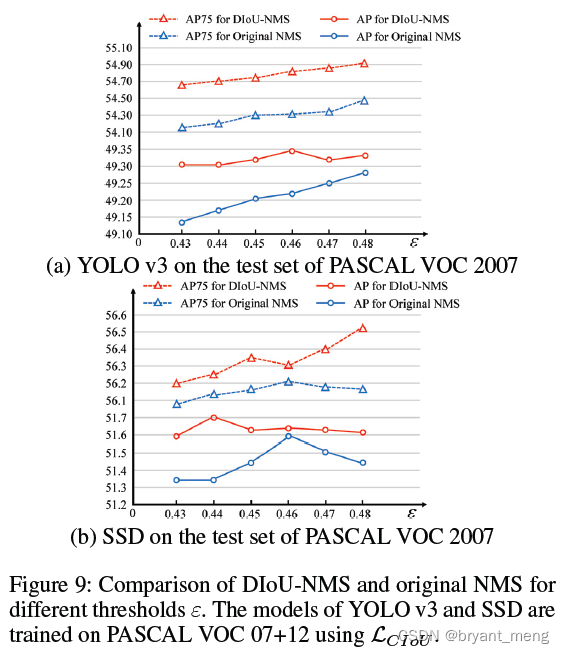
5.2 YOLO v3 on PASCAL VOC
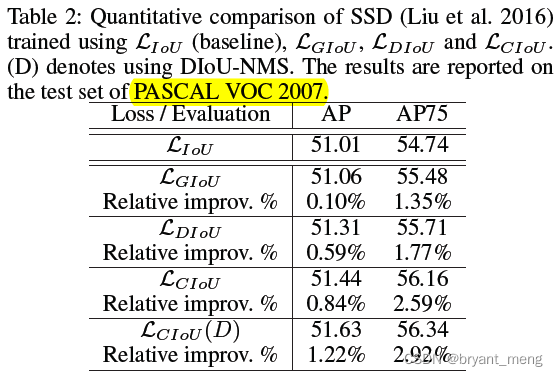
5.3 SSD on PASCAL VOC
We have observed that for dense anchor algorithms, increasing the regression loss properly can improve the performance.
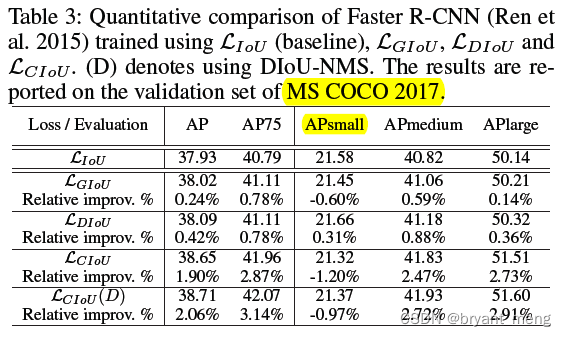
5.4 Faster R-CNN on MS COCO
作用到二阶段的时候,DIoU 没有那么给力了,作者的解释是
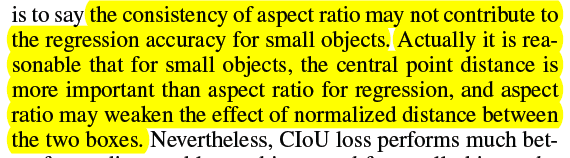
DIoU 小目标可以,CIoU 小目标不如 IoU,CIoU+DIoU-NMS 缓解了 CIoU 小目标的 adverse effects
为啥 CIoU 的小目标没有 DIoU 的猛,作者也解释了
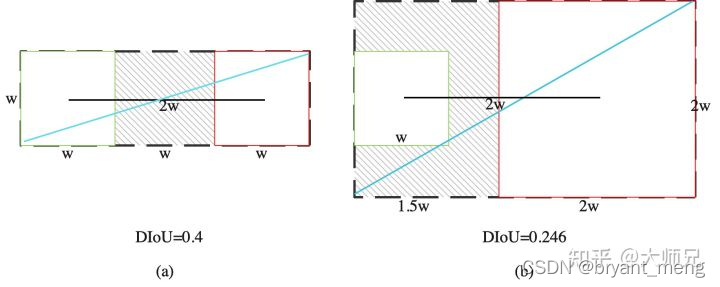
5.5 Discussion on DIoU-NMS
6 Conclusion(own) / Future work
- Without loss of generality, xxx 不失一般性
- DIoU-loss,CIoU-loss,DIoU-NMS
- l n l_n ln-norm loss is not a suitable choice to obtain the optimal IoU metric
- DIoU、CIoU、GIoU、IoU再理解结合代码(D 和 C 实现的时候出现了梯度)
- 用PyTorch实现CIoU NMS,DIoU NMS和GIoU NMS
- for dense anchor algorithms, increasing the regression loss properly can improve the performance.