原github:GitHub - guusvanderham/artificial-motion-artifacts-for-ct
我转到了python 方法,方便使用
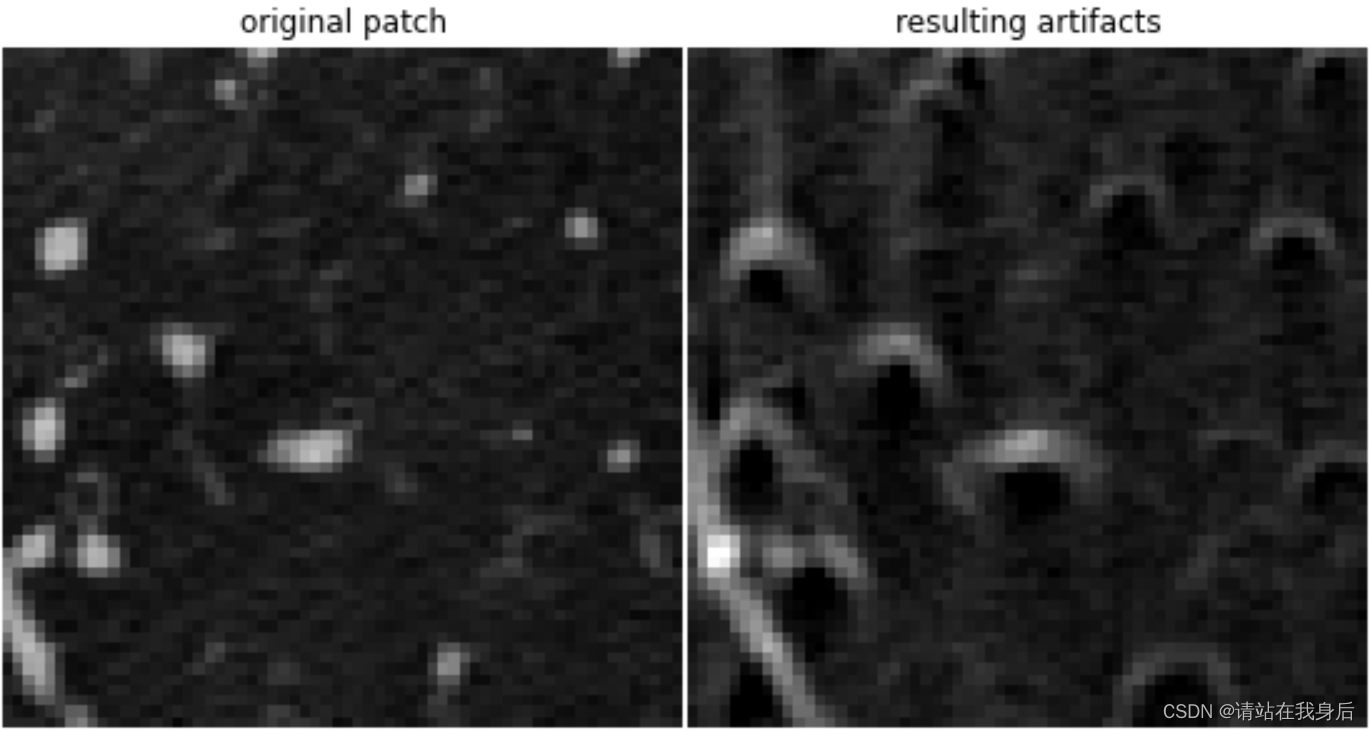
贴张模拟图
1、 读取、归一化,裁剪成patch
# load scan (as z,y,x)
path="data"
dcm_f = pydicom.read_file(path)
dcm = dcm_f.pixel_array
# normalize between 0 and 1
scan=normalize(dcm)
# show dimensions and example slice
# print(scan.shape)
# plt.imshow(scan[0, :, :], cmap='gray')
# plt.show()
# create a patch by specifying the topleft corner and patch size
x,y,z = (100,250,0)
patch_size = 128
patch = scan[z,y:y+patch_size,x:x+patch_size]2、需要一个mask,如果没有就全一
# binary mask specifying which pixels are lung tissue, lung masks can be generated from scans using e.g. https://github.com/JoHof/lungmask
# not using mask might result in lungborder artifacts or the simulation of a deforming ribcage (which is unrealistic)
# if no mask is available use:
patch_mask=np.ones((patch_size, patch_size))3、定义伪影的方向
# specify the motion direction in pixels
dir_x, dir_y=(9, 0)4、添加伪影
# specify the motion direction in pixels
dir_x, dir_y=(9, 0)def create_artifact_elasticdeform(img, mask, dir_x, dir_y, patch_size):
size_x, size_y=img.shape
width, height=patch_size
# padding
padsize=np.max((np.absolute(dir_x), np.absolute(dir_y)))
# coordinates of top-left corner of patch in background
x=int(size_x / 2 - width / 2)
y=int(size_y / 2 - height / 2)
background=np.zeros((size_x + 2 * padsize, size_y + 2 * padsize))
# copy of the original patch
temp=copy.copy(img)
# nr of angles in which the projector will take pictures
nr_angles=360
# the (radian) angles in which the projector will create a projection
angles=np.linspace(0, np.pi, nr_angles)
# get a random displacement vector grid
displacement=get_random_displacement(dir_x, dir_y)
# N, number of grid points for elastic deformation
order=5
# deform the lung mask to deal with lungborder artifacts later and create the movement mask
mask, movement_vectors_mask=deform_grid_py(mask, displacement, order=order)
# take the movement vectors for each pixel in the input image and compute the vector lengths(motion severity)
move_mask=np.linalg.norm(movement_vectors_mask, axis=0)
# make the mask binary again
mask=mask > 0.9
mask=mask * 1
# determine after which projection angles grid points need to move and the image in the scanner needs to be swapped
angles_idxs=np.array([])
angles_dict={}
for a in np.unique(displacement):
if np.abs(a) > 0:
angles_idxs=np.linspace(0, nr_angles, np.abs(a) + 2).astype(np.int32)
for angle in angles_idxs:
if not angle in angles_dict:
angles_dict[angle]=[a]
else:
angles_dict[angle].append(a)
# the indices of the angles in which the image needs to be moved
angles_x=np.linspace(0, nr_angles, np.absolute(dir_x) + 2).astype(np.int32)
angles_y=np.linspace(0, nr_angles, np.absolute(dir_y) + 2).astype(np.int32)
# remove 0 and pi as angles to move the image
angles_x=np.delete(angles_x, 0)
angles_x=np.delete(angles_x, len(angles_x) - 1)
angles_y=np.delete(angles_y, 0)
angles_y=np.delete(angles_y, len(angles_y) - 1)
# create one unique list after which indices of projection angles the image should be moved
angles_idx=np.concatenate((angles_x, angles_y))
angles_idx=np.unique(angles_idx)
# specify the number of detectors the scanner has
nr_detectors=np.max(img.shape) + 128
# initialize data for astra scanner
vol_geom=astra.creators.create_vol_geom(temp.shape[0], temp.shape[1])
sinogram=np.zeros((nr_angles, nr_detectors))
# Step 1: simulate acquisition of CT scan
# start simulation
for i, angle in enumerate(angles):
# create a new projector for each projection
projector_id=make_projector(angle, vol_geom, nr_detectors)
# if the current angle is in the dict, the image in the scanner needs to be moved slightly and replaced
if i in angles_dict:
# determine which grid points need to move by 1 pixel
idx=np.zeros(displacement.shape)
for j in angles_dict[i]:
idx+=displacement == j
idx=idx > 0
idx=idx * 1
idx[0, :, :]=idx[0, :, :] * np.sign(dir_y)
idx[1, :, :]=idx[1, :, :] * np.sign(dir_x)
# deform and update the image in the scanner
temp, _=deform_grid_py(temp, idx * 1.0, order=order)
# create artificial sinogram of one angle (add one column for the current projection)
(sino_id, sino)=astra.creators.create_sino(temp, projector_id, returnData=True, gpuIndex=None)
# store sinograms of all angles
sinogram[i, :]=sino
# remove the projector
astra.projector.delete(projector_id)
# clean up as the simulation of the scan is done
astra.projector.clear()
# Step 2: reconstruction of the patch given projection data
# create new projector for reconstruction
proj_geom=astra.create_proj_geom('parallel', 1, nr_detectors, np.linspace(0, np.pi, nr_angles))
projector_id=astra.creators.create_projector('line', proj_geom, vol_geom)
# load sinogram data as sinogram object
sinogram_id=astra.data2d.create('-sino', proj_geom, sinogram)
# create empty reconstruction volume
reconstruction_id=astra.data2d.create('-vol', vol_geom, data=0)
# initialize reconstruction algorithm
alg_cfg=astra.astra_dict('FBP')
alg_cfg['ProjectorId']=projector_id
alg_cfg['ProjectionDataId']=sinogram_id
alg_cfg['ReconstructionDataId']=reconstruction_id
algorithm_id=astra.algorithm.create(alg_cfg)
# create reconstruction from sinogram
astra.algorithm.run(algorithm_id)
reconstruction=astra.data2d.get(reconstruction_id)
# for extracting center patch of reconstruction
patch_x=int(reconstruction.shape[0] / 2 - width / 2)
patch_y=int(reconstruction.shape[1] / 2 - height / 2)
# for extracting center patch of original image for comparison
template_x=int(img.shape[0] / 2 - width / 2)
template_y=int(img.shape[1] / 2 - height / 2)
# extract center patch with given dimensions
patch=reconstruction[patch_x:patch_x + width, patch_y:patch_y + height]
# do the same for the lung mask
mask=mask[y:y + height, x:x + width]
# and the original patch for comparison
temp=temp[y:y + height, x:x + width]
# and the movement mask
move_mask=move_mask[y:y + height, x:x + width]
# set everyting outside of lung mask to 0 (also removes lungborder artifacts)
idxs=mask < 1
patch[idxs]=0
# apply a small amount of Gaussian filtering to deal with pixelation
patch=gaussian_filter(patch, sigma=0.5)
# for comparison also for the original
temp=gaussian_filter(temp, sigma=0.5)
# clip back the patch to a range of 0, 1
patch=np.clip(patch, 0, 1)
return patch, temp, move_maskdef show(img, title=""):
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
plt.title(title)
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.clim(0, 1)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
# create astra projector
def make_projector(angle, vol_geom, nr_detectors):
proj_geom=astra.create_proj_geom('parallel', 1, nr_detectors, [angle])
projector_id=astra.creators.create_projector('line', proj_geom, vol_geom)
return projector_id
# create a random displacement vector grid (fig 5a, 5b and 5c in thesis)
def get_random_displacement(dir_x, dir_y):
# create 2D Gaussian matrix
M=9
x, y=np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-1, 1, M), np.linspace(-1, 1, M))
d=np.sqrt(x * x + y * y)
# random sigma, high value creates uniform motion, low value creates motion focused around single grid point
sigma=np.random.uniform(0.1, 1.2)
mu=0
g=np.exp(-((d - mu) ** 2 / (2.0 * sigma ** 2)))
# N x N displacement vector grid
N=5
displacement=np.zeros((2, N, N))
# take random submatrix to simulate random motion source location
center_x=int(np.random.uniform(0, N - 1))
center_y=int(np.random.uniform(0, N - 1))
# displacement vectors x-values
displacement[1, :, :]=g[center_x:center_x + N, center_y:center_y + N] * dir_x + 1
# displacement vectors y-values
displacement[0, :, :]=g[center_x:center_x + N, center_y:center_y + N] * dir_y + 1
# clip back the motion vectors to the severity of the original motion direction
max_movement=np.max((dir_x, dir_y))
displacement=np.clip(displacement.astype(np.int32), -max_movement, max_movement)
return displacement
# adapted version of https://github.com/gvtulder/elasticdeform that also returns motion mask
def deform_grid_py(X, displacement, order=3, mode='constant', cval=0.0, crop=None, prefilter=True, axis=None):
if axis is None:
axis=tuple(range(X.ndim))
elif isinstance(axis, int):
axis=(axis,)
# compute number of control points in each dimension
points=[displacement[0].shape[d] for d in range(len(axis))]
# creates the grid of coordinates of the points of the image (an ndim array per dimension)
coordinates=np.meshgrid(*[np.arange(X.shape[d]) for d in axis], indexing='ij')
# creates the grid of coordinates of the points of the image in the "deformation grid" frame of reference
xi=np.meshgrid(*[np.linspace(0, p - 1, X.shape[d]) for d, p in zip(axis, points)], indexing='ij')
if crop is not None:
coordinates=[c[crop] for c in coordinates]
xi=[x[crop] for x in xi]
# crop is given only for the axes in axis, convert to all dimensions for the output
crop=tuple(crop[axis.index(i)] if i in axis else slice(None) for i in range(X.ndim))
else:
crop=(slice(None),) * X.ndim
move_mask=[]
# add the displacement to the coordinates
for i in range(len(axis)):
yd=scipy.ndimage.map_coordinates(displacement[i], xi, order=3)
move_mask.append(yd)
# adding the displacement
coordinates[i]=np.add(coordinates[i], yd)
out=np.zeros(X[crop].shape, dtype=X.dtype)
# iterate over the non-deformed axes
iter_axes=[range(X.shape[d]) if d not in axis else [slice(None)]
for d in range(X.ndim)]
for a in itertools.product(*iter_axes):
scipy.ndimage.map_coordinates(X[a], coordinates, output=out[a],
order=order, cval=cval, mode=mode, prefilter=prefilter)
return out, np.array(move_mask)5、展示
print(patch.shape)
print(result.shape)
show(result, 'resulting artifacts')
show(original, 'original patch')