1、缓存核心接口
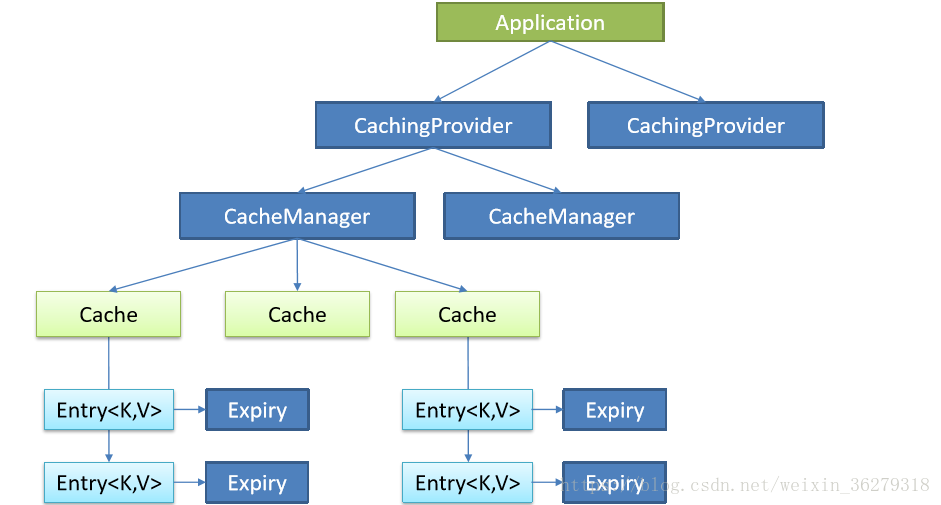
Java Caching定义了5个核心接口,分别是CachingProvider, CacheManager, Cache, Entry 和 Expiry。
- CachingProvider定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager。一个应用可 以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。
- CacheManager定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,这些Cache 存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅被一个CachingProvider所拥有。
- Cache是一个类似Map的数据结构并临时存储以Key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个 CacheManager所拥有。
- Entry是一个存储在Cache中的key-value对。
- Expiry 每一个存储在Cache中的条目有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期 的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。
示意图:
2、Spring缓存抽象
Spring定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术; 并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们开发。(跟面向JDBC编程是一个道理,统一一个规范,统一面向jdbc编程。)
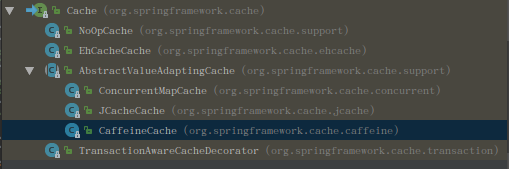
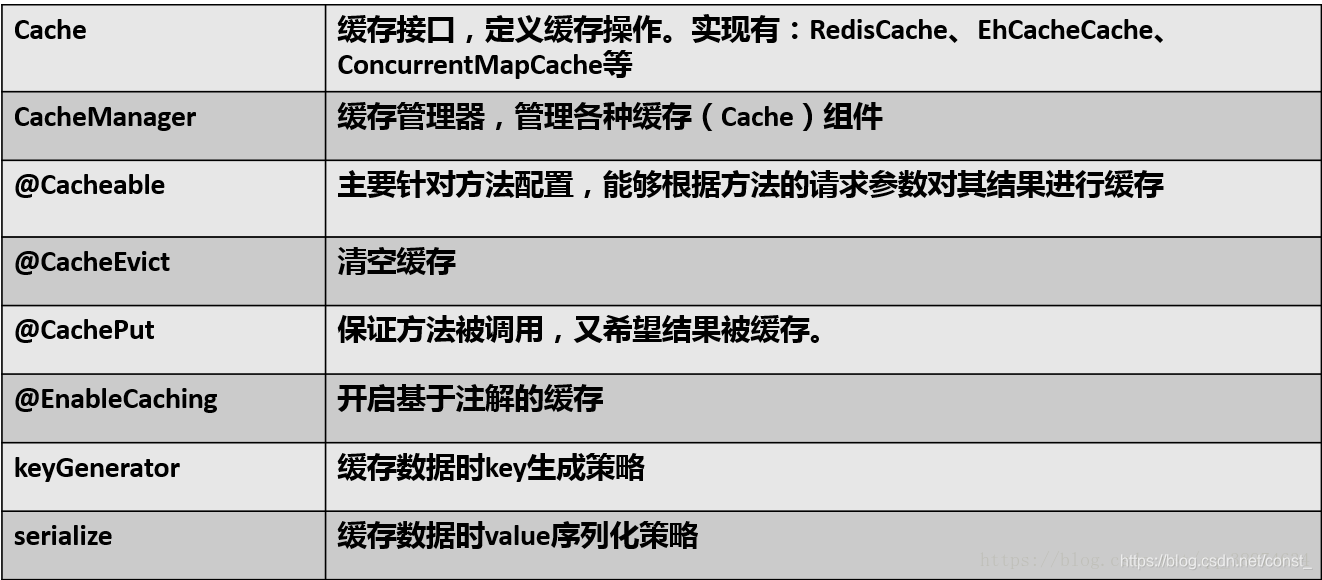
- Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合。
- Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现:
- 每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查检查指定参数的指定的目标方法是否已经被调用过;如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法并缓存结果后返回给用户。下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
- 使用Spring缓存抽象时我们需要关注以下两点:
1、确定方法需要被缓存以及他们的缓存策略
2、从缓存中读取之前缓存存储的数据
缓存注解。
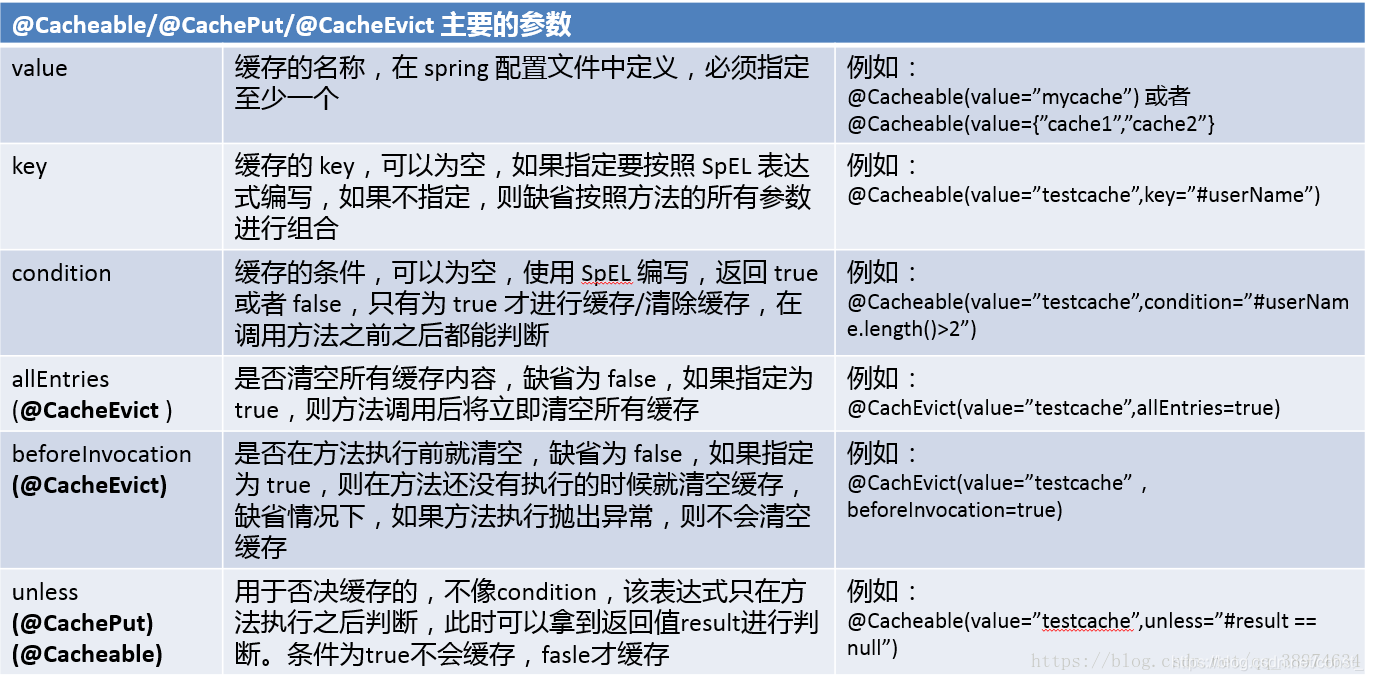
@Cacheable/@CachePut/@CacheEvict 主要的参数。
参数值支持支持SpEL表达式。
3、SpringBoot缓存工作原理
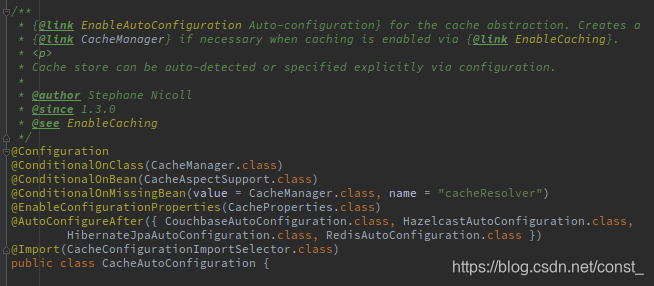
1、首先分析自动配置类:CacheAutoConfiguration
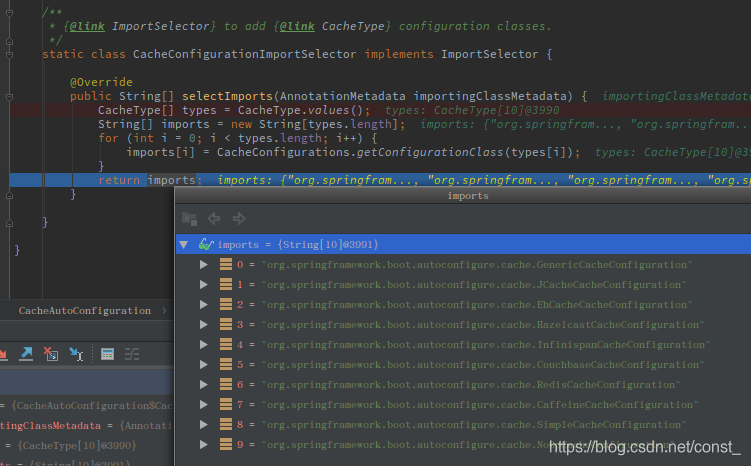
2、这个自动配置中导入了一个类CacheConfigurationImportSelector,这个类会引入一些缓存配置类。
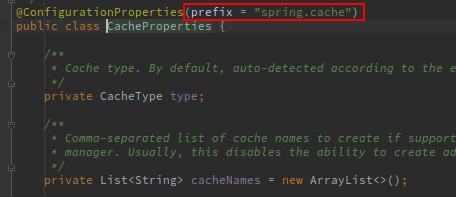
3、缓存配置类:CacheProperties
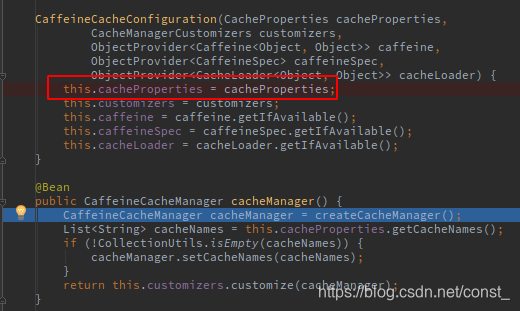
4、CaffeineCacheConfiguration这个配置类给容器中注册了一个CacheManager。
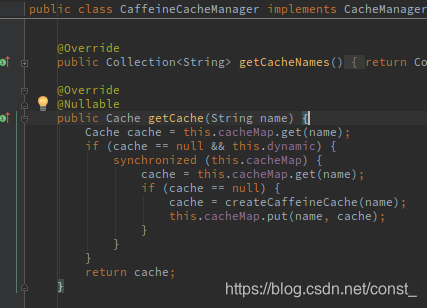
5、缓存方法运行之前,先按照cacheNames查询缓存组件,第一次获取缓存如果没有缓存创建一个。
4、SpringBoot中Cache缓存的使用
1、导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId>
<artifactId>caffeine</artifactId>
</dependency>
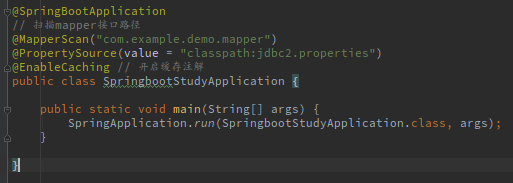
2、在主程序中开启缓存注解
3、@Cacheable缓存注解的使用 (标注在service业务层方法上)
执行流程:先执行@Cacheable注解中的getCache(String name)方法,根据name判断ConcurrentMap中是否有此缓存,如果没有缓存那么创建缓存并保存数据,另外service层的方法也会执行。如果有缓存不再创建缓存,另外service层的方法也不会执行。
总结:先执行@Cacheable----->再执行service层的方法
service层代码:
第一次查询数据库打印service类方法日志,并把数据保存到Cahce中。
第二次传入相同参数不再执行service类方法,不会打印日志,查询的数据直接从缓存中获取。
/*1. @Cacheable的几个属性详解:
* cacheNames/value:指定缓存组件的名字。
* key:缓存数据使用的key,可以用它来指定,默认使用方法参数的值。
* keyGenerator:作用和key一样,二选一。
* cacheManager和cacheResolver作用相同:指定缓存管理器,二选一。
* condition:指定符合条件才缓存。
* 比如:condition="#id>3"(也就是说传入的参数id>3才缓存数据)
* unless:否定缓存,当unless为true时不缓存,可以获取方法结果进行判断。
* sync:是否使用异步模式。
*/
//@Cacheable(cacheNames= "person")
//@Cacheable(cacheNames= "person",key="#id",condition="#id>3")
@Cacheable(cacheNames= "person",key="#id")
public Person query(Long id) {
log.info("查询数据库。id = {}", id);
return dao.query(id);
}
4、@CachePut必须结合@Cacheable一起使用,否则没什么意义
@CachePut的作用:即调用方法,又更新缓存数据 ,修改了数据库中的数据,同时又更新了缓存。
// @CachePut(value = "person", key = "#person.id")
@CachePut(value = "person", key = "#result.id")
public Person update(Person person) {
dao.update(person);
return person;
}
5、@CacheEvict也是结合@Cacheable一起使用才有意义
@CacheEvict的作用:清除缓存中的指定数据或清除缓存中所有数据
/**
* @CacheEvict:清除缓存
* 1.key:指定要清除缓存中的某条数据
* 2.allEntries=true:删除缓存中的所有数据
* beforeInvocation=false:默认是在方法之后执行清除缓存
* 3.beforeInvocation=true:现在是在方法执行之前执行清除缓存,
* 作用是:只清除缓存、不删除数据库数据
*/
//@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "person",key = "#id")
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "person",allEntries=true)
public void delete(Long id) {
dao.delete(id);
}
6、@Caching是@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict注解的组合
@Caching的作用:此注解用于复杂的缓存操作
/**
* @Caching是 @Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict注解的组合
* 以下注解的含义:
* 1.当使用指定名字查询数据库后,数据保存到缓存
* 2.现在使用id、age就会直接查询缓存,而不是查询数据库
*/
@Caching(
cacheable = { @Cacheable(value = "person", key = "#name") },
put = {
@CachePut(value = "person", key = "#result.id"),
@CachePut(value = "person", key = "#result.age")
}
)
public Person queryByName(String name) {
Person person = dao.queryByName(name);
return person;
}
7、@CacheConfig主要用于配置该类中会用到的一些共用的缓存配置
@CacheConfig的作用:抽取@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict的公共属性值
@Service
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "person") //将cacheNames抽取出来
public class PersonService {
@Cacheable(key="#id")
public Person query(Long id) {
log.info("查询数据库。id = {}", id);
return personMap.get(id);
}
@CachePut(key = "#result.id")
public Person update(Person person) {
System.out.println(person.toString());
personMap.put(person.getId(), person);
return person;
}
}
5、Spring Boot缓存配置
在缓存配置中,比如spring.cache.caffeine.spec=maximumSize=500,expireAfterWrite=10s,所有的缓存的到期策略都是一样的,如果我们要实现不同数据的缓存到期时间不一致,可以用自定义CacheManager。
1、application.yml
caching:
specs:
student:
timeout: 2
person:
timeout: 5
上面配置中,缓存person是10秒过期,student是2秒过期。
2、CacheConfiguration
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Caffeine;
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Ticker;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.caffeine.CaffeineCache;
import org.springframework.cache.support.SimpleCacheManager;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "caching")
@Data
@Slf4j
public class CacheConfiguration {
@Data
public static class CacheSpec {
private Integer timeout;
private Integer max = 200;
}
private Map<String, CacheSpec> specs;
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(Ticker ticker) {
SimpleCacheManager manager = new SimpleCacheManager();
if (specs != null) {
List<CaffeineCache> caches = specs.entrySet()
.stream()
.map(entry -> buildCache(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue(), ticker))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
manager.setCaches(caches);
}
return manager;
}
private CaffeineCache buildCache(String name, CacheSpec cacheSpec, Ticker ticker) {
log.info("Cache {} specified timeout of {} min, max of {}", name, cacheSpec.getTimeout(), cacheSpec.getMax());
final Caffeine<Object, Object> caffeineBuilder = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(cacheSpec.getTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.maximumSize(cacheSpec.getMax())
.ticker(ticker);
return new CaffeineCache(name, caffeineBuilder.build());
}
// 指定时间源
@Bean
public Ticker ticker() {
return Ticker.systemTicker();
}
}