涉及基本的http知识,可参阅(4.1.28.4)HTTP协议的报文浅析
一、概述
AndServer是一个Android平台的WebServer服务器和WebServer开发框架,作为Web服务器它支持了IP、端口的绑定,以及SSL自定义证书。作为Web开发框架它支持静态网站部署、动态Http接口、文件的上传下载。
作为一个平台框架,它的最核心的功能应该是对Web开发的支持,它的这些特性可能是你喜欢的:
- Request拦截器
- RequestHandler过滤器
- 全局异常处理者
1.1 基本Api:单服务器多站点
从AndServer1.1.0版本开始,有了站点这个概念。每一个Android机器看作一台服务器,一台服务器可以搭建多个站点,也就是下文中要提到的Server。
从某种意义而言,可以理解为:一台服务器可以部署多个网站,不同的网站绑定不同的端口监听,也就是单服务器多站点;当前站点内,会对当前 IP:Port/Path的Path做响应
下述代码除了端口必须要指定外,几乎所有的Api都不是必须的,开发者选择自己需要的进行设置即可。一般情况下,我们至少会注册一个Http接口的路径和对应的处理器。
如果不绑定IP地址,从mServer.getInetAddress()拿到的IP地址可能是0.0.0.0,这种情况下,服务器默认监听了本机当前局域网IP,例如192.168.1.11
Server mServer;
...
mServer = AndServer.serverBuilder()
// 服务器设置部分:
.sslContext() // 设置SSLConext,加载SSL证书。
.sslSocketInitializer() // 对SSLServerSocket进行一些初始化设置。
.inetAddress() // 设置服务器要监听的网络地址。
.port() // 设置服务器要监听的端口。
.timeout() // Socket的超时时间。
.listener() // 服务器监听。
// Web框架设置部分:
.interceptor() // Request/Response对的拦截器。
.website() // 设置网站。
.registerHandler() // 注册一个Http Api路径和对应的处理器。
.filter() // RequestHandler的过滤器。
.exceptionResolver() // 异常解决者。
.build();
...
mServer.start(); // 启动服务器。
mServer.shutdown(); // 关闭服务器。
boolean isRunnging = mServer.isRunning(); // 服务器是否在运行。
InetAddress address = mServer.getInetAddress(); // 拿到服务器监听的网络地址
二、Socket通信承载功能一览
AndServer的底层依赖并不是直接写了Socket,而是使用了封装的框架[Apache HttpCore]
可以参看(4.2.46)AndroidGodEye源码整体结构分析 中的原生写法
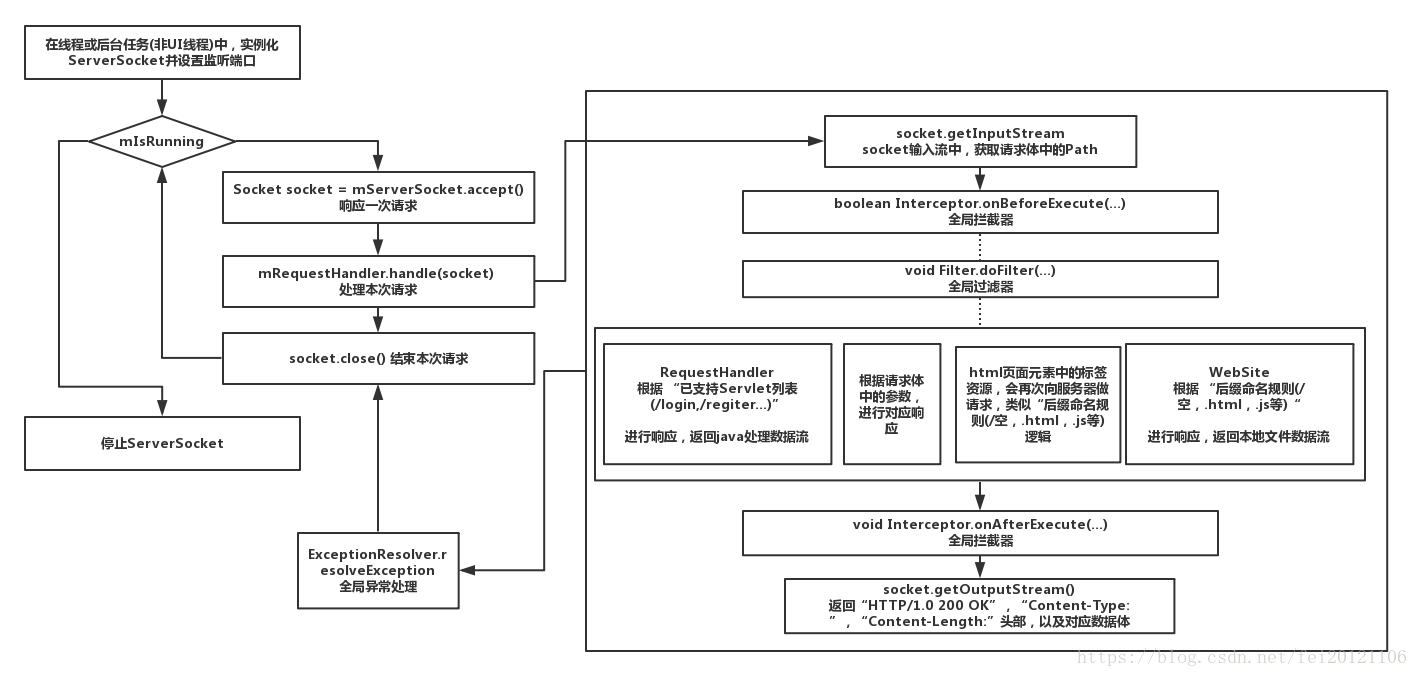
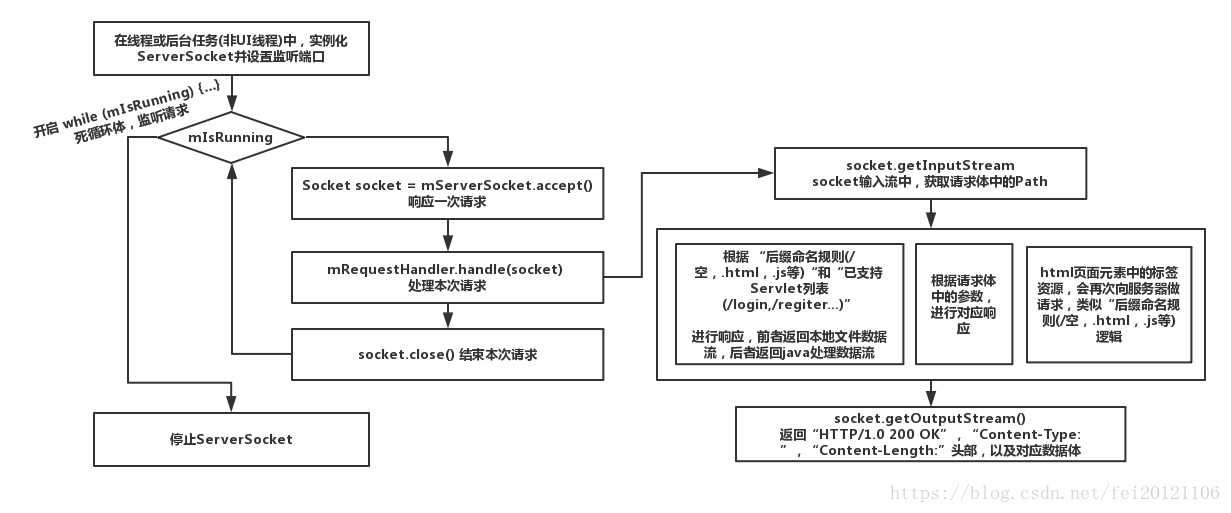
- 在线程或后台任务(非UI线程)中,实例化socket并设置监听端口;
- 开启 while (mIsRunning) {…}死循环体,监听请求
循环体内:
2.1 Socket socket = mServerSocket.accept();响应一次请求
2.2 mRequestHandler.handle(socket) 处理本次请求
2.2.1 获取请求体中的Path
2.2.2 根据 “后缀命名规则(/空,.html,.js等)“和“已支持Servlet列表(/login,/regiter…)”进行响应,前者返回本地文件数据流,后者返回java处理数据流
2.2.2 根据请求体中的参数,进行对应响应
2.2.2 html页面元素中的标签资源,会再次向服务器做请求,类似“后缀命名规则(/空,.html,.js等)逻辑
2.2.3 返回“HTTP/1.0 200 OK”,“Content-Type: ”,“Content-Length:”头部,以及对应数据体
2.3 socket.close() 结束本次请求
【图1 processon】
在承载功能的基础上,我们对AndServer涉及的基本API进行下字面解读:
服务器设置部分:
- inetAddress(InetAddress var1) 设置服务器要监听的网络地址,默认是本机内网IP
- port(int var1) 设置服务器要监听的端口
- timeout(int var1, TimeUnit var2) Socket的超时时间
- listener(Server.ServerListener var1) 服务器启动、停止及异常监听
- void onStarted();
- void onStopped();
- void onError(Exception var1);
Web框架设置部分:
- registerHandler(String var1, RequestHandler var2) 可多次调用,配置2.2.2中描述的“指定Path”对应的“处理handler,其实就是servlet声明”
- website(WebSite webSite) 单次调用,实现2.2.2中描述,根据指定后缀命名规则,返回本地文件的数据流
- WebSite其实就是一种特殊的RequestHandler,它自带拦截规则(),满足拦截规则的Path就被直接截停
- interceptor(Interceptor interceptor) 单次调用,包裹2.2过程的收尾,在请求进入和请求出去时进行拦截,如果某个请求被拦截,那么所有的Website或者RequestHandler都将收不到任何请求
- boolean onBeforeExecute(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context) throws HttpException, IOException;
进行逻辑判断是否要拦截,返回true将拦截,返回false不拦截 - void onAfterExecute(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context) throws HttpException, IOException;
如果不拦截将在请求处理完毕后会调用onAfterExecute
- boolean onBeforeExecute(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context) throws HttpException, IOException;
- filter(Filter filter) 单次调用,仅处理请求过程,用于过滤RequestHandler
- void doFilter(RequestHandler handler, HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context) throws HttpException, IOException;
exceptionResolver(ExceptionResolver resolver) 单次调用,用来处理在每一个request/response对中发生的所有异常,包括Interceptor、RequestHandler、Filter等的处理过程
- 相当于服务器异常时,应该如何返回数据给客户端
【图2 processon】
三、管理器 Server
- AndServer 暴露给外部使用的server构建器
- Server 管理器能力接口
- 启动、停止、判断运行中、获取ip
- Builder接口能力,配置API
- ServerListener 服务器操作生命周期回调
- Core:真正的管理器实现
3.1 AndServer
暴露给外部使用的server构建器
public class AndServer {
private AndServer() {
}
public static Server.Builder serverBuilder() {
return Core.newBuilder();
}
}3.2 Server
管理器能力接口
- 启动、停止、判断运行中、获取ip
- Builder接口能力,配置API
- ServerListener 服务器操作生命周期回调
public interface Server {
//启动、停止、判断运行中、获取ip
boolean isRunning();
void startup();
InetAddress getInetAddress();
void shutdown();
//Builder接口能力,配置API
interface Builder {
Builder inetAddress(InetAddress inetAddress);
Builder port(int port);
Builder timeout(int timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit);
Builder sslContext(SSLContext sslContext);
Builder sslSocketInitializer(SSLSocketInitializer initializer);
Builder interceptor(Interceptor interceptor);
Builder website(WebSite webSite);
Builder registerHandler(String path, RequestHandler handler);
Builder filter(Filter filter);
Builder exceptionResolver(ExceptionResolver resolver);
Builder listener(ServerListener listener);
Server build();
}
//ServerListener 服务器操作生命周期回调
interface ServerListener {
/**
* When the server is started.
*/
void onStarted();
/**
* When the server stops running.
*/
void onStopped();
/**
* An error occurred while starting the server.
*/
void onError(Exception e);
}
}3.3 Core
AndServer核心依赖于HttpCore的HttpServer
自己的业务实现主要在DispatchRequestHandler
- 启动、停止、判断运行中、获取ip
- 配置API,持有相关配置参数
- bulider模式实现 (不再列出,具体看源码)
- ServerListener 服务器操作生命周期回调
3.3.1 持有变量
/**
* 服务器设置部分
*/
private final InetAddress mInetAddress;//服务器要监听的网络地址
private final int mPort; // 服务器要监听的端口
private final int mTimeout;//Socket的超时时间
private final SSLContext mSSLContext;//SSLConext,加载SSL证书
private final SSLSocketInitializer mSSLSocketInitializer;//对SSLServerSocket进行一些初始化设置
private final ServerListener mListener;//服务器监听
/**
* Web框架设置部分
*/
private final Map<String, RequestHandler> mRequestHandlerMap;//servlets列表,Path:Servlet的映射关系
private final WebSite mWebSite;//本地网站
private final Interceptor mInterceptor;//全局Request/Response拦截器
private final Filter mFilter;//全局请求过滤器
private final ExceptionResolver mExceptionResolver;//全局异常处理器
/**
* 数据:AndServer核心依赖于HttpCore的HttpServer
*/
private HttpServer mHttpServer;
private boolean isRunning;3.3.2 启动
- 【步骤1】为AndServer配置一个全部路径的HttpRequestHandler处理器,AndServer的相关过滤逻辑通过DispatchRequestHandler实现
- 【步骤2】构建HttpServer
- 【步骤3】标示启动状态
- 【步骤4】启动服务器
- 【步骤5】触发启动生命周期
- 【步骤6】虚拟机关闭时的调用钩子,在虚拟机关闭的时候调用这些钩子线程
@Override
public void startup() {
if (isRunning) return;
Executors.getInstance().submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//AndServer底层依赖于HttpCore
//【步骤1】为AndServer配置一个全部路径的HttpRequestHandler处理器,AndServer的相关过滤逻辑通过DispatchRequestHandler实现
DispatchRequestHandler handler = new DispatchRequestHandler();
handler.setInterceptor(mInterceptor);
handler.setWebSite(mWebSite);
if (mRequestHandlerMap != null && mRequestHandlerMap.size() > 0) {
for (Map.Entry<String, RequestHandler> handlerEntry : mRequestHandlerMap.entrySet()) {
String path = handlerEntry.getKey();
RequestHandler requestHandler = handlerEntry.getValue();
handler.registerRequestHandler(path, requestHandler);
}
}
handler.setFilter(mFilter);
handler.setExceptionResolver(mExceptionResolver);
//【步骤2】构建HttpServer
mHttpServer = ServerBootstrap.bootstrap()
.setSocketConfig(
SocketConfig.custom()
.setSoKeepAlive(true)
.setSoReuseAddress(false)
.setSoTimeout(mTimeout)
.setTcpNoDelay(false)
.build()
)
.setConnectionConfig(
ConnectionConfig.custom()
.setBufferSize(4 * 1024)
.setCharset(Charset.defaultCharset())
.build()
)
.setLocalAddress(mInetAddress)
.setListenerPort(mPort)
.setSslContext(mSSLContext)
.setSslSetupHandler(new SSLSocketInitializer.SSLSocketInitializerWrapper(mSSLSocketInitializer))
.setServerInfo("AndServer")
.registerHandler("*", handler)
.setExceptionLogger(ExceptionLogger.STD_ERR)
.create();
try {
isRunning = true;//【步骤3】标示启动状态
mHttpServer.start();//【步骤4】启动服务器
Executors.getInstance().post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mListener != null)
mListener.onStarted();//【步骤5】触发启动生命周期
}
});
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
//【步骤6】虚拟机关闭时的调用钩子,在虚拟机关闭的时候调用这些钩子线程
mHttpServer.shutdown(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
});
} catch (final Exception e) {
Executors.getInstance().post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mListener != null)
mListener.onError(e);//【步骤5】触发启动生命周期
}
});
}
}
});
}
3.3.3 停止与判断
@Override
public boolean isRunning() {
return isRunning;
}
@Override
public InetAddress getInetAddress() {
if (isRunning)
return mHttpServer.getInetAddress();
return null;
}
/**
* Stop core server.
*/
@Override
public void shutdown() {
if (!isRunning) return;
Executors.getInstance().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mHttpServer != null)
mHttpServer.shutdown(3, TimeUnit.MINUTES);//【步骤1】停止
Executors.getInstance().post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mListener != null)
mListener.onStopped();//【步骤2】触发启动生命周期
}
});
}
});
}3.4 DispatchRequestHandler请求分发器
其实就是HttpServer的请求处理器,虽然HttpServer也支持针对Path的处理,但是在这里AndServer进行了包装,所有的URL都由该请求处理器处理,并在该处理器内部实现自己的业务分发
3.4.1 持有变量
private Map<String, RequestHandler> mRequestHandlerMapper = new LinkedHashMap<>();//servlets列表,Path:Servlet的映射关系
private WebSite mWebSite;//本地网站
private Interceptor mInterceptor;//全局Request/Response拦截器
private Filter mFilter;//全局请求过滤器
private ExceptionResolver mExceptionResolver = sDefaultExceptionResolver;//全局异常处理器
private static ExceptionResolver sDefaultExceptionResolver = new SimpleExceptionResolver();//默认的全局处理器
/*****************************get | set*********************************************/
void setInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
mInterceptor = interceptor;
}
void setWebSite(WebSite webSite) {
this.mWebSite = webSite;
}
void registerRequestHandler(String path, RequestHandler handler) {
mRequestHandlerMapper.put(path, handler);
}
void setFilter(Filter filter) {
this.mFilter = filter;
}
void setExceptionResolver(ExceptionResolver exceptionResolver) {
mExceptionResolver = exceptionResolver;
}
3.4.2 核心分发功能
- 【步骤1:触发全局拦截器的拦截事件】
- 【步骤2:处理请求】
- 【步骤2.1:获取本次请求对应的RequestHandler处理器】
- 获取Path
- 判断是否被 WebSite(特殊的RequestHandler处理器)拦截
2.1 是,则返回该WebSite
2.2 不是,则从 《Path:Servlet的映射表》中获取对应处理器
- 【步骤2.2:本次请求无对应的RequestHandler处理器,抛出异常,进入异常处理器】
- 【步骤2.3:对应的RequestHandler处理器 准备处理请求】
【步骤2.3.1:校验本次请求请求方式是否满足 当前处理器限定】
【步骤2.4:全局过滤器不为null,则进入过滤器(内部进行响应处理)】
【步骤2.5:全局过滤器为null,则直接调用处理器处理】
- 【步骤2.1:获取本次请求对应的RequestHandler处理器】
- 【步骤3:触发全局拦截器的拦截事件】
- 【步骤4:触发全局异常处理器的异常处理】
【图3 】
/*****************************核心:分发与过滤*******************************************/
@Override
public void handle(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context) throws HttpException, IOException {
try {
//【步骤1:触发全局拦截器的拦截事件】
if (mInterceptor != null && mInterceptor.onBeforeExecute(request, response, context))
return;
//【步骤2:处理请求】
//【步骤2.1:获取本次请求对应的RequestHandler处理器】
RequestHandler handler = getRequestHandler(request, context);
if (handler == null) {//【步骤2.2:本次请求无对应的RequestHandler处理器,抛出无对应处理器异常,进入异常处理器】
String path = getRequestPath(request);
throw new NotFoundException(path);
} else {
//【步骤2.3:对应的RequestHandler处理器 准备处理请求】
handleRequest(handler, request, response, context);
}
//【步骤3:触发全局拦截器的拦截事件】
if (mInterceptor != null)
mInterceptor.onAfterExecute(request, response, context);
} catch (Exception e) {
//【步骤4:触发全局异常处理器的异常处理】
try {
mExceptionResolver.resolveException(e, request, response, context);
} catch (Exception ee) {
sDefaultExceptionResolver.resolveException(e, request, response, context);
}
}
}
/**
* 【步骤2.1:获取本次请求对应的RequestHandler处理器】
* 1. 获取Path
* 2. 判断是否被 WebSite(特殊的RequestHandler处理器)拦截
* 2.1 是,则返回该WebSite
* 2.2 不是,则从 《Path:Servlet的映射表》中获取对应处理器
*/
private RequestHandler getRequestHandler(HttpRequest request, HttpContext context) throws HttpException, IOException {
String path = HttpRequestParser.getRequestPath(request);
if (mWebSite != null && mWebSite.intercept(request, context)) {
return mWebSite;
}
return mRequestHandlerMapper.get(path);
}
/**
* Handle Request with handler.
* 【步骤2.3:对应的RequestHandler处理器 准备处理请求】
*/
private void handleRequest(RequestHandler handler, HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context) throws HttpException, IOException {
//【步骤2.3.1:校验本次请求请求方式是否满足 当前处理器限定】
verifyHandler(request, handler);
if (mFilter != null) {
//【步骤2.3.2:全局过滤器不为null,则进入过滤器(内部进行响应处理)】
mFilter.doFilter(handler, request, response, context);
} else {
//【步骤2.3.3:全局过滤器为null,则直接调用处理器处理】
handler.handle(request, response, context);
}
}
//【步骤2.3.1:校验本次请求请求方式是否满足 当前处理器限定】
private void verifyHandler(HttpRequest request, RequestHandler handler) throws BaseException {
RequestMethod requestMethod = RequestMethod.reverse(request.getRequestLine().getMethod());
Class<?> clazz = handler.getClass();
try {
Method handlerMethod = clazz.getMethod("handle", HttpRequest.class, HttpResponse.class, HttpContext.class);
RequestMapping requestMapping = handlerMethod.getAnnotation(RequestMapping.class);
if (requestMapping != null) {
RequestMethod[] requestMethods = requestMapping.method();
List<RequestMethod> requestMethodList = Arrays.asList(requestMethods);
if (!requestMethodList.contains(requestMethod)) {
throw new MethodNotSupported(requestMethod);
}
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ignored) {
}
}四、RequestHandler请求处理器
DispatchRequestHandler请求分发器会将一次具体的请求,转交给处理器处理。
在AndServer中,每一个Http的path就对应一个RequestHandler。它好比SpringMVC中Controller的某一个方法上加了RequestMapping注解一样,但是很遗憾AndServer目前没有提供像SpringMVC那样的注解来实现path注册(它是我的计划,AndServer2.0将会用编译时注解来实现)
public interface RequestHandler {
/**
* When is the client request is triggered.
*
* @param request {@link HttpRequest}.
* @param response {@link HttpResponse}.
* @param context {@link HttpContext}.
* @throws HttpException may be.
* @throws IOException read data.
*/
void handle(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context) throws HttpException, IOException;
}实现一个RequestHandler步骤:
- 实现RequestHandler接口
- 读取客户端提交的参数
- 处理业务
- 返回业务数据
4.1 登录接口示例
HttpRequestParser是一系列工具类方法,能快速帮我们从HttpRequest抽取相关配置参数
public class LoginHandler implements RequestHandler {
@Override
public void handle(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context)
throws HttpException, IOException {
Map<String, String> params = HttpRequestParser.parseParams(request);
if (!params.containsKey("username") || !params.containsKey("password")) {
StringEntity stringEntity = new StringEntity("缺少参数", "utf-8");
response.setStatusCode(400);
response.setEntity(stringEntity);
return;
}
String userName = URLDecoder.decode(params.get("username"), "utf-8");
String password = URLDecoder.decode(params.get("password"), "utf-8");
if ("123".equals(userName) && "123".equals(password)) {
StringEntity stringEntity = new StringEntity("登录成功", "utf-8");
response.setStatusCode(200);
response.setEntity(stringEntity);
} else {
StringEntity stringEntity = new StringEntity("登录失败", "utf-8");
response.setStatusCode(400);
response.setEntity(stringEntity);
}
}
}4.2 SimpleRequestHandler 快捷处理器
AndServer还提供了一个简单的RequestHandler的实现SimpleRequestHandler,子类只需要:
- 快速继承SimpleRequestHandler
- 覆盖handle方法,并返回View即可
- SimpleRequestHandler会将放回的View自动拆解,并设置到Response中
public class SimpleRequestHandler implements RequestHandler {
@Override
public final void handle(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context) throws HttpException, IOException {
View view = handle(request, response);
response.setStatusCode(view.getHttpCode());
response.setEntity(view.getHttpEntity());
response.setHeaders(view.getHeaders());
}
protected View handle(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response) throws HttpException, IOException {
return handle(request);
}
protected View handle(HttpRequest request) throws HttpException, IOException {
return new View(200);
}
}我们来看下修改后的Login接口:
public class LoginHandler extends SimpleRequestHandler {
@Override
public View handle(HttpRequest request) throws HttpException, IOException {
Map<String, String> params = HttpRequestParser.parseParams(request);
if (!params.containsKey("username") || !params.containsKey("password")) {
return new View(400, "缺少参数");
}
String userName = URLDecoder.decode(params.get("username"), "utf-8");
String password = URLDecoder.decode(params.get("password"), "utf-8");
if ("123".equals(userName) && "123".equals(password)) {
return new View(400, "登录成功");
} else {
return new View(400, "帐号或者密码错误");
}
}
}4.2.1 View响应中间件
- View被用在一些接口的简单实现类中,比如RequestHandler的简单实现类SimpleRequestHandler,减少了入参,可以直接返回View对象
- View会被类SimpleRequestHandler拆解,并设置到Response中
public class View {
private int mHttpCode;
private HttpEntity mHttpEntity; //HttpCore支持的数据类型,Response数据体
private HeaderGroup mHeaderGroup;//HttpCore支持的数据类型,Response数据头部
/**
* 直接传入响应码,没有包体。
*/
public View(int httpCode);
/**
* 传入响应码,用String作为包体。
*/
public View(int httpCode, String httpBody);
/**
* 传入响应码,用制定的HttpEntity作为包体。
*/
public View(int httpCode, HttpEntity httpEntity);
/**
* 设置某个响应头。
*/
public void setHeader(String key, String value);
/**
* 添加某个相应头。
*/
public void addHeader(String key, String value);
}HttpEntity :HttpCore支持的数据类型,Response数据体,底层用数据流实现
- AbstractHttpEntity
- BasicHttpEntity
- ByteArrayEntity
- EntityTemplate
- FileEntity
- InputStreamEntity
- SerializableEntity
- StringEntity
- HttpEntityWrapper
- BufferedHttpEntity
4.2.1.1OkView 成功响应的快捷方式
public class OkView extends View {
public OkView() {
super(200);
}
public OkView(String httpBody) {
super(200, httpBody);
}
public OkView(HttpEntity httpEntity) {
super(200, httpEntity);
}
}使用如下:
return new OkView("成功")
return new OkView(JSON.toJSONString(user))4.2.1.2 RedirectView 重定向响应
public class RedirectView extends View {
private static final String LOCATION = "Location";
public RedirectView(String path) {
super(302);
setHeader(LOCATION, path);
}
}使用如下:
return new RedirectView("/user/admin")
return new RedirectView("http://www.yanzhenjie.com")4.3 Reponse响应
HttpEntity :HttpCore支持的数据类型,Response数据体,底层用数据流实现
- AbstractHttpEntity
- BasicHttpEntity
- ByteArrayEntity
- EntityTemplate
- FileEntity
- InputStreamEntity
- SerializableEntity
- StringEntity
- HttpEntityWrapper
- BufferedHttpEntity
4.3.1 返回图片
返回图片的方式有很多种,最终我们都要返回HttpEntity这个对象,所以图片可以来自assets,drawable、SD卡,下面是一个来自SD卡的图片示例:
public class ImageHandler extends SimpleRequestHandler {
private File mFile = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(), "xxx.jpg");
@Override
protected View handle(HttpRequest request) throws HttpException, IOException {
HttpEntity httpEntity = new FileEntity(mFile);
return new View(200, httpEntity);
}
}4.3.2 下载文件
public class FileHandler extends SimpleRequestHandler {
@Override
public View handle(HttpRequest request) throws HttpException, IOException {
// 为了示例,创建一个临时文件。
File file = File.createTempFile("AndServer", ".txt", App.get().getCacheDir());
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
IOUtils.write("天上掉下个林妹妹。", outputStream, Charset.defaultCharset());
HttpEntity httpEntity = new FileEntity(file);
View view = new View(200, httpEntity);
view.addHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=AndServer.txt");
return view;
}
}这里其实和返回图片章节没啥却别,唯一值得注意的是:
view.addHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=AndServer.txt");这里我们添加了一个Content-Disposition的响应头,attachment的意思是告诉浏览器,这个文件应该被下载,filename=AndServer.txt的意思是告诉浏览器,这个文件默认被命名为AndServer.txt。
如果不添加上述相应头,比如没有attachment大部分浏览器会直接打开自己可以直接打开的文件,没有filename=AndServer.txt浏览器将会用自己的算法给文件取一个默认名称。
4.3.3 上传图片
作为服务器,在某些情况下可能会接受客户端上传文件的请求。
上传文件涉及到文件保存,所以代码稍微多几行:
public class UploadHandler implements RequestHandler {
/**
* 保存文件的文件夹。
*/
private File mDirectory = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory();
@Override
public void handle(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context)
throws HttpException, IOException {
if (!HttpRequestParser.isMultipartContentRequest(request)) { // 是否Form传文件的请求。
response(403, "说好的文件呢", response);
} else {
try {
processFileUpload(request);
response(200, "上传成功", response);
} catch (Exception e) {
response(500, "保存文件失败", response);
}
}
}
private void response(int responseCode, String message, HttpResponse response)
throws HttpException, IOException {
response.setStatusCode(responseCode);
response.setEntity(new StringEntity(message, "utf-8"));
}
/**
* 保存文件和参数处理。
*/
private void processFileUpload(HttpRequest request) throws Exception {
FileItemFactory factory = new DiskFileItemFactory(1024 * 1024, mDirectory);
HttpFileUpload fileUpload = new HttpFileUpload(factory);
// 你还可以监听上传进度:
// fileUpload.setProgressListener(new ProgressListener(){...});
HttpUploadContext context = new HttpUploadContext((HttpEntityEnclosingRequest) request);
List<FileItem> fileItems = fileUpload.parseRequest(context);
for (FileItem fileItem : fileItems) {
if (fileItem.isFormField()) { // 普通参数。
String key = fileItem.getName(); // 表单参数名。
String value = fileItem.getString(); // 表单参数值。
...;
} else { // 文件。
// fileItem.getFieldName(); // 表单参数名。
// fileItem.getName(); // 客户端指定的文件名。
// fileItem.getSize(); // 文件大小。
// fileItem.getContentType(); // 文件的MimeType。
// 把流写到文件夹。
File uploadedFile = new File(mDirectory, fileItem.getName());
fileItem.write(uploadedFile);
}
}
}
}4.3.4 返回Json
返回JSON就比较简单了,其实JSON就是把实体对象转为JSON字符串发送给客户端,归根结底就是发送字符串。
这里我们只要把实体对象转为JSON字符串解决即可:
public class LoginHandler extends SimpleRequestHandler {
@Override
public View handle(HttpRequest request) throws HttpException, IOException {
User user = new User();
user.setName("林妹妹");
user.setSex("女");
String json = JSON.toJSONString(user);
return new OkView(json);
}
}4.4 请求方法限制
对应 《【步骤2.3.1:校验本次请求请求方式是否满足 当前处理器限定】》
很多时候我们需要限制某个接口的请求方法,比如POST、PUT、GET,为了避免每个接口都需要我们检查请求方法,AndServer提供了注解来简化它。
我们只需要在RequestHandler#handle()上加上@RequestMapping()注解即可,例如我们限制某个接口只能用POST请求:
public class LoginHandler implements RequestHandler {
@RequestMapping(method = {RequestMethod.POST, RequestMethod.PUT, RequestMethod.GET})
@Override
public void handle(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context)
throws HttpException, IOException {
...;
}
}注意:如果使用注解必须要在RequestHandler#handle()方法上,因为《【步骤2.3.1:校验本次请求请求方式是否满足 当前处理器限定】》是从handler中读取注解的,也就是说它不支持SimpleRequestHandler的Handle(View)实现,但是你可以通过重写类似SimpleGetRequestHandler的基类来实现
五、WebSite 站点响应器
其实WebSite就是一种特殊的RequestHandler,全局唯一,它自带一个intercept函数。
业务请求在到达后会,先触发boolean WebSiete.intercept(HttpRequest request, HttpContext context),如果被拦截,则不再由RequestHandler处理
我们可以理解为:RequestHandle主要用于返回java运算的数据,而WebSite主要用于返回本地资源(.html/.js等)所转化的数据
public interface WebSite extends RequestHandler {
boolean intercept(HttpRequest request, HttpContext context) throws HttpException, IOException;
}5.1 SimpleWebsite 基类站点响应器
- 快捷View响应支持,类似SimpleRequestHandler
- Path的”/”操作Utils
public abstract class SimpleWebsite implements WebSite {
protected static final String INDEX_FILE_PATH = "/index.html";
@Override
public void handle(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context) throws HttpException, IOException {
View view = handle(request, response);
response.setStatusCode(view.getHttpCode());
response.setEntity(view.getHttpEntity());
response.setHeaders(view.getHeaders());
}
protected View handle(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response) throws HttpException, IOException {
return handle(request);
}
protected View handle(HttpRequest request) throws HttpException, IOException {
throw new NotFoundException(getRequestPath(request));
}
protected String addStartSlash(String target) {
if (!target.startsWith(File.separator)) target = File.separator + target;
return target;
}
protected String addEndSlash(String target) {
if (!target.endsWith(File.separator)) target = target + File.separator;
return target;
}
protected String trimStartSlash(String target) {
while (target.startsWith(File.separator)) target = target.substring(1);
return target;
}
protected String trimEndSlash(String target) {
while (target.endsWith(File.separator)) target = target.substring(0, target.length() - 1);
return target;
}
protected String trimSlash(String target) {
target = trimStartSlash(target);
target = trimEndSlash(target);
return target;
}
}5.2 自定义站点
- 实现Website接口,或者继承SimpleWebsite基类
- 在Website中拦截要处理的请求
- 处理Request并返回内容
public class MyWeibsite implement Website {
private List<String> mPathList;
...
@Override
public boolean intercept(HttpRequest request, HttpContext context)
throws HttpException, IOException {
// 拿到http的路径。
String httpPath = HttpRequestParser.getRequestPath(request);
// 判断是否要拦截。
if(mPathList.contains(httpPath)) { // 这里可以写一些判断逻辑。
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
...
// 如果真是这么简单的判断逻辑,简单点
return mPathList.contains(httpPath);
}
@Override
public void handle(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context)
throws HttpException, IOException {
// 这里和RequestHandler的处理方式完全相同,请参考RequestHandler一章。
}
}5.3 AssetsWebsite 基于Assets站点
AssetsWebsite可以部署assets中的内容为网站,只要传入你要部署的网站在assets中的路径即可。比如我的网站放在/assets/web/webiste目录下,那么我可以这么写:
AssetManager assetsManager = context.getAssets();
Website website = new AssetsWebsite(assetsManager, "assets/web/website");AssetsWebsite会扫描根路径下的全部文件,并形成HttpRequestPath:FilePath的映射表;收到相关请求后,根据FilePath获取到FIle并转换为对应数据流返回
这里值得注意的是,因为assets比较特殊,所以在路径的前后不要带上/,不然将无法解析。
- 例如/assets/web下的网站:new AssetsWebsite(getAssets(), “web”);
- 例如/assets下的网站:new AssetsWebsite(getAssets(), “”);
注意:AssetsWebsite不支持热插拔
5.3.1 网站首页和index.html
传入的目录中如果存在index.html将作为网站的首页,每一个目录中如果存在index.html,将作为这个目录路径的默认页面。
例如我们把assets根目录作为网站部署目录:
assets
├─index.html
├─user
│ ├─index.html
│ └─admin.html
├─shop
│ └─index.html
└─items
└─index.html假设我们在某个手机上部署new AssetsWebsite(getAssets(), “assets”);为网站,这个手机的本机局域网IP是192.168.1.11,我们指定AndServer监听的端口是8080。那么对于上方这个结构
- 默认首页是http://192.168.1.11:8080或者http://192.168.1.11:8080/index.html,那么访问到的资源就是/assets/index.html
- 访问http://192.168.1.11:8080/user访问到的资源是/assets/user/index.html
5.4 实现
- 持有变量:
private final AssetsReader mAssetsReader;//Android Asset文件访问Utils
private boolean isScanned;//是否已经扫描统计过 “根路径下的所有资源文件”
private final String mRootPath;//根路径
private final Map<String, String> mPatternMap;//httppath---filePath的Map
public AssetsWebsite(AssetManager assetManager, String rootPath) {
this.mAssetsReader = new AssetsReader(assetManager);
this.mRootPath = rootPath;
this.mPatternMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
}- 拦截判断:“资源文件列表”中是否存在
@Override
public boolean intercept(HttpRequest request, HttpContext context) {
tryScanFile();
String httpPath = getRequestPath(request);
return mPatternMap.containsKey(httpPath);
}
private void tryScanFile() {
if (!isScanned) {
synchronized (AssetsWebsite.class) {
if (!isScanned) {
onScanFile(mRootPath, mAssetsReader, mPatternMap);
isScanned = true;
}
}
}
}
protected void onScanFile(String rootPath, AssetsReader assetsReader, Map<String, String> patternMap) {
List<String> fileList = assetsReader.scanFile(rootPath);
if (fileList.size() > 0) {
for (String filePath : fileList) {
String httpPath = trimStartSlash(filePath);
httpPath = httpPath.substring(rootPath.length(), httpPath.length());
httpPath = addStartSlash(httpPath);
patternMap.put(httpPath, filePath);
if (filePath.endsWith(INDEX_FILE_PATH)) {
httpPath = httpPath.substring(0, httpPath.indexOf(INDEX_FILE_PATH));
patternMap.put(httpPath, filePath);
patternMap.put(addEndSlash(httpPath), filePath);
}
}
}
}- 数据响应:返回指定文件
@Override
public View handle(HttpRequest request) throws HttpException, IOException {
String httpPath = getRequestPath(request);//获取HTTPPath
String filePath = mPatternMap.get(httpPath);//获取FilePath
InputStream source = mAssetsReader.getInputStream(filePath);//获取字符流
if (source == null)
throw new NotFoundException(httpPath);
int length = source.available();
String mimeType = getMimeType(filePath);
HttpEntity httpEntity = new InputStreamEntity(source, length, ContentType.create(mimeType, Charset.defaultCharset()));
return new View(200, httpEntity);
}- 示例:
inPath:web
filePath out:
web/css/login.css
web/image/logo.png
web/index.html
web/login.html
httppath---filePath:
"/css/login.css" -> "web/css/login.css"
"/image/logo.png" -> "web/image/logo.png"
"/index.html" -> "web/index.html"
"" -> "web/index.html"
"/" -> "web/index.html" //http://192.200.36.43:8080/
"/login.html" -> "web/login.html"5.5 StorageWebsite 基于SD卡
StorageWebsite可以部署SD卡中的内容为网站,只要传入你要部署的网站在SD卡中的路径即可。比如我的网站放在/sdcard/andserver/webiste目录下,那么我可以这么写:
Website website = new StorageWebsite("/sdcard/andserver/website");这里值得注意的是因为SD卡也是磁盘,所以路径必须是绝对路劲。
注意:StorageWebsite支持热插拔
5.5.1 网站首页和index.html
传入的目录中如果存在index.html将作为网站的首页,每一个目录中如果存在index.html,将作为这个目录路径的默认页面。
例如我们把/sdcard/andserver/webiste目录作为网站部署目录:
...
├─index.html
├─user
│ ├─index.html
│ └─admin.html
├─shop
│ └─index.html
└─items
└─index.html假设我们在某个手机上部署new StorageWebsite(“/sdcard/andserver/webiste”);为网站,这个手机的本机局域网IP是192.168.1.11,我们指定AndServer监听的端口是8080。
那么对于上方这个结构,默认首页是http://192.168.1.11:8080或者http://192.168.1.11:8080/index.html,那么访问到的资源就是/sdcard/andserver/webiste/index.html。
5.5.2 实现
- 持有变量:
private final String mRootPath;
public StorageWebsite(String rootPath) {
this.mRootPath = rootPath;
}- 拦截:指定路径的文件是否存在
@Override
public boolean intercept(HttpRequest request, HttpContext context) throws HttpException, IOException {
String httpPath = getRequestPath(request);
httpPath = "/".equals(httpPath) ? "/" : trimEndSlash(getRequestPath(request));//生成httpPath
File source = findPathSource(httpPath);
return source != null;
}
//查找指定路径的文件
private File findPathSource(String httpPath) {
if ("/".equals(httpPath)) {
File indexFile = new File(mRootPath, INDEX_FILE_PATH);
if (indexFile.exists() && indexFile.isFile()) {
return indexFile;
}
} else {
File sourceFile = new File(mRootPath, httpPath);
if (sourceFile.exists()) {
if (sourceFile.isFile()) {
return sourceFile;
} else {
File childIndexFile = new File(sourceFile, INDEX_FILE_PATH);
if (childIndexFile.exists() && childIndexFile.isFile()) {
return childIndexFile;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}- 响应:返回指定的文件
@Override
public View handle(HttpRequest request) throws HttpException, IOException {
String httpPath = trimEndSlash(getRequestPath(request));
File source = findPathSource(httpPath);
if (source == null)
throw new NotFoundException(httpPath);
return generateSourceView(source);
}
private View generateSourceView(File source) throws IOException {
String mimeType = getMimeType(source.getAbsolutePath());
HttpEntity httpEntity = new FileEntity(source, ContentType.create(mimeType, Charset.defaultCharset()));
return new View(200, httpEntity);
}5.6 FileBrowse文件浏览器
FileBrowse可以部署SD卡中的内容供别人以文件的形式浏览。
Website website = new FileBrowser("/sdcard");这里值得注意的是因为SD卡也是磁盘,所以路径必须是绝对路劲。
注意:FileBrowser支持热插拔。
5.6.1 路径说明
如我们把/sdcard目录作为部署目录:
假设我们在某个手机上部署new FileBrowse(“/sdcard”);目录,这个手机的本机局域网IP是192.168.1.11,我们指定AndServer监听的端口是8080
当用户在地址栏输入http://192.168.1.11:8080时并访问后,用户将看到一个网页,网页上面会列出/sdcard下的所有文件和目录,并且在文件和目录上加上超链接。当用户点击文件时,浏览器可能会直接打开这个文件或者让用户下载这个文件;当用户点击目录时,用户将会看到一个新页面中列出了他点击的目录中的所有目录和文件
5.6.2 实现
- 持有变量:
private final String mRootPath;
public FileBrowser(String rootPath) {
this.mRootPath = rootPath;
}- 拦截:指定路径的文件或文件夹是否存在
@Override
public boolean intercept(HttpRequest request, HttpContext context) throws HttpException, IOException {
String httpPath = getRequestPath(request);
httpPath = "/".equals(httpPath) ? "/" : trimEndSlash(getRequestPath(request));
File source = findPathSource(httpPath);
return source != null;
}
private File findPathSource(String httpPath) {
if ("/".equals(httpPath)) {
return new File(mRootPath);
} else {
File sourceFile = new File(mRootPath, httpPath);
if (sourceFile.exists()) {
return sourceFile;
}
}
return null;
}- 返回:返回指定路径的文件数据流或文件夹html
@Override
public View handle(HttpRequest request) throws HttpException, IOException {
String httpPath = trimEndSlash(getRequestPath(request));
File source = findPathSource(httpPath);
if (source == null)
throw new NotFoundException(httpPath);
return generatePageView(source);
}
private View generatePageView(File source) throws IOException {
if (source.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = source.listFiles();
File tempFile = File.createTempFile("file_browser", ".html");
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(tempFile);
String folderName = source.getName();
String prefix = String.format(FOLDER_HTML_PREFIX, folderName, folderName);
outputStream.write(prefix.getBytes("utf-8"));
if (files != null && files.length > 0) {
for (File file : files) {
String filePath = file.getAbsolutePath();
int rootIndex = filePath.indexOf(mRootPath);
String httpPath = filePath.substring(rootIndex + mRootPath.length());
httpPath = addStartSlash(httpPath);
String fileItem = String.format(FOLDER_ITEM, httpPath, file.getName());
outputStream.write(fileItem.getBytes("utf-8"));
}
}
outputStream.write(FOLDER_HTML_SUFFIX.getBytes("utf-8"));
return generateSourceView(tempFile);
} else {
return generateSourceView(source);
}
}
private View generateSourceView(File source) throws IOException {
String mimeType = getMimeType(source.getAbsolutePath());
HttpEntity httpEntity = new FileEntity(source, ContentType.create(mimeType, Charset.defaultCharset()));
return new View(200, httpEntity);
}
private static final String FOLDER_HTML_PREFIX
= "<!DOCTYPE html>"
+ "<html>"
+ "<head>"
+ "<meta http-equiv=\"content-type\" content=\"text/html; charset=UTF-8\"/>"
+ "<meta name=\"viewport\" content=\"width=device-width, initial-scale=1, user-scalable=no\">"
+ "<meta name=\"format-detection\" content=\"telephone=no\"/>"
+ "<title>%1$s</title>"
+ "<style>"
+ ".center_horizontal{margin:0 auto;text-align:center;}"
+ "*,*::after,*::before {"
+ "box-sizing: border-box;"
+ "margin: 0;"
+ "padding: 0;"
+ "}"
+ "a:-webkit-any-link {"
+ "color: -webkit-link;"
+ "cursor: auto;"
+ "text-decoration: underline;"
+ "}"
+ "ul {"
+ "list-style: none;"
+ "display: block;"
+ "list-style-type: none;"
+ "-webkit-margin-before: 1em;"
+ "-webkit-margin-after: 1em;"
+ "-webkit-margin-start: 0px;"
+ "-webkit-margin-end: 0px;"
+ "-webkit-padding-start: 40px;"
+ "}"
+ "li {"
+ "display: list-item;"
+ "text-align: -webkit-match-parent;"
+ "margin-bottom: 5px;"
+ "}"
+ "</style>"
+ "</head>"
+ "<body>"
+ "<h1 class=\"center_horizontal\">%2$s</h1>"
+ "<ul>";
private static final String FOLDER_ITEM = "<li><a href=\"%1$s\">%2$s</a></li>";
private static final String FOLDER_HTML_SUFFIX
= "</ul>"
+ "</body>"
+ "</html>";六、拦截器
拦截器的功能是在请求进入和请求出去时进行拦截,如果某个请求被拦截,那么所有的Website或者RequestHandler都将收不到任何请求。
拦截器是作用于全局的
public interface Interceptor {
/**
* When receiving a request, first ask if you intercept,
* if intercepted it will not be distributed to any {@code RequestHandler}.
*/
boolean onBeforeExecute(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context) throws HttpException, IOException;
/**
* Called after any {@code RequestHandler} response.
*/
void onAfterExecute(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context) throws HttpException, IOException;
}
6.1 拦截登录示例
假如我们要拦截某些接口的用户登录,我们可以用注解和反射实现。
- 思路:
- 定义一个需要登录的注解
- 需要登录的接口处理器的handle()方法上加上该注解
- 拦截器是作用于全局的,那么在onBeforeExecute中获取到指定的Handler,然后通过反射读取函数注解进行拦截
//定义注解:
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface NeedLogin {
boolean need() default true;
}
// 需要拦截登录的handle:
public class AdminHandler implement RequestHandler {
@NeedLogin()
@ovrride
public void handle(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context)
throws HttpException, IOException {
}
}
// 拦截登录:
@Override
public boolean onBeforeExecute(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context)
throws HttpException, IOException {
Class<?> clazz = handler.getClass();
Method method = clazz.getMethod("handle", HttpRequest.class,
HttpResponse.class, HttpContext.class);
NeedLogin needLogin = method.getAnnotation(NeedLogin.class);
if (needLogin != null) {
if(needLogin.need()) {
String token = request.getHeader("Token");
if(verifyToken(token)) { // 假设这里验证Token是否有效。
response.setStatus(401);
... // 返回一些数据。
return true; // 拦截掉。
}
}
}
return false;
}如果你读完了异常解决者一章的文档,那么我们可以简化一下我们的拦截器:
//定义自定义异常
public class NotLoginException extends BaseException {
...
}
//抛出的异常,会被全局的异常处理器hold
@Override
public boolean onBeforeExecute(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context)
throws HttpException, IOException {
Class<?> clazz = handler.getClass();
Method method = clazz.getMethod("handle", HttpRequest.class, HttpResponse.class,
HttpResponse.class, HttpContext.class);
NeedLogin needLogin = method.getAnnotation(NeedLogin.class);
if (needLogin != null) {
if(needLogin.need()) {
String token = request.getHeader("Token");
if(verifyToken(token)) { // 假设这里验证Token是否有效。
new throw NotLoginException("请您先登录");
}
}
}
return false;
}七、过滤器
- Inteceptor是拦截请求/响应的,也就是拦截Request/Response对的。每一个Request/Response对都会经过拦截器
- Filter是过滤RequestHandler的。
- 当服务器接受到一个请求后,先经过Inteceptor拦截,如果没有被拦截,会根据Request匹配对应的RequestHandler,如果没有找到则抛出NotFoundException异常
- 如果找到对应的RequestHandler,如果开发者设置了Filter,那么把RequestHandler和Request/Response对交给Filter处理,如果没有设置Filter,则由对应的RequestHandler处理
7.1 简单示例
- 实现Filter接口
- 需要时,主动调用handler的处理方法
public class MyFilter implement Filter {
@Ovrride
public void doFilter(RequestHandler handler, HttpRequest request, HttpContext context)
throws HttpException, IOException {
boolean isFilted = ... // 一些处理逻辑,过滤器是否处理。
if(!isFitler) { // 如果过滤器没处理则交给handler处理。
handler.hande(request, response, context);
}
}
}7.2 Http缓存过滤器
过滤器是非常有用的,比如Http缓存协议的实现就可以基于过滤器来做。
在AndServer中,有一个HttpCacheFilter类,它实现了Http缓存协议部分,下面是它实现的几个关键头:
- Cache-Control
- Last-Modified
- If-Modified-Since
- If-Unmodified-Since
- ETag
- If-None-Match
7.2.1 内置缓存过滤器
100%建议开启Website的缓存,它能提高用来提高服务器性能,尤其像AndServer这种运行在手机端的服务器。
Server server = AndServer.serverBuilder()
...
.filter(new HttpCacheFilter())
.build();
...如上述代码即可打开AndServer自带的几个Website的缓存:
- AssetsWebsite
- StorageWebsite
但是自己的RequestHandler必须通过实现对应接口来实现,可以参考AssetsWebsite
7.2.2 LastModified背景
在浏览器首次请求某个资源时,服务器端返回的状态码是200 (ok),内容是你请求的资源,同时有一个Last-Modified的属性标记(Reponse Header),标识此文件在服务期端最后被修改的时间,格式:Last-Modified:Tue, 24 Feb 2009 08:01:04 GMT
浏览器第二次请求该资源时,根据HTTP协议的规定,浏览器会向服务器传送If-Modified-Since报头(Request Header),询问该文件是否在指定时间之后有被修改过,格式为:If-Modified-Since:Tue, 24 Feb 2009 08:01:04 GMT
如果服务器端的资源没有变化,则服务器返回304状态码(Not Modified),内容为空,这样就节省了传输数据量。当服务器端代码发生改变,则服务器返回200状态码(ok),内容为请求的资源,和第一次请求资源时类似。从而保证在资源没有修改时不向客户端重复发出资源,也保证当服务器有变化时,客户端能够及时得到最新的资源。
7.2.3 ETag背景
当浏览器首次请求资源的时候,服务器会返回200的状态码(ok),内容为请求的资源,同时response header会有一个ETag标记,该标记是服务器端根据容器(IIS或者Apache等等)中配置的ETag生成策略生成的一串唯一标识资源的字符串,ETag格式为 ETag:”856247206”
当浏览器第2次请求该资源时,浏览器会在传递给服务器的request中添加If-None-Match报头,询问服务器改文件在上次获取后是否修改了,报头格式:If-None-Match:”856246825”
服务器在获取到浏览器的请求后,会根据请求的资源查找对应的ETag,将当前服务器端指定资源对应的Etag与request中的If-None-Match进行对比,如果相同,说明资源没有修改,服务器返回304状态码(Not Modified),内容为空;如果对比发现不相同,则返回200状态码,同时将新的Etag添加到返回浏览器的response中
7.2.4 过滤器实现
public class HttpCacheFilter implements Filter {
private static final String CACHE_CONTROL = "Cache-Control";
private static final String LAST_MODIFIED = "Last-Modified";
private static final String IF_MODIFIED_SINCE = "If-Modified-Since";
private static final String IF_UNMODIFIED_SINCE = "If-Unmodified-Since";
private static final String E_TAG = "ETag";
private static final String IF_NONE_MATCH = "If-None-Match";
@Override
public void doFilter(RequestHandler handler, HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context) throws HttpException, IOException {
boolean isLastModified;
long sourceLastModified = -1;//指定资源最后修改时间
if (isLastModified = handler instanceof LastModified) {//处理器支持 LastModified标签头
sourceLastModified = ((LastModified) handler).getLastModified(request);
}
boolean isETag;
String sourceETag = null;//指定资源的唯一标示
if (isETag = handler instanceof ETag) {//处理器支持 ETag标签头
sourceETag = ((ETag) handler).getETag(request);
}
Header ifUnmodifiedSinceHeader = request.getFirstHeader(IF_UNMODIFIED_SINCE);
if (isLastModified && ifUnmodifiedSinceHeader != null) {
if (!validateIfUnmodifiedSince(request, sourceLastModified)) {
response.setStatusCode(412);
return;
}
}
Header ifModifiedSinceHeader = request.getFirstHeader(IF_MODIFIED_SINCE);
Header ifNoneMatchHeader = request.getFirstHeader(IF_NONE_MATCH);
if (isLastModified && isETag) {
if (ifModifiedSinceHeader != null && ifNoneMatchHeader != null) {
if (validateIfModifiedSince(request, sourceLastModified) && validateIfNoneMatch(request, sourceETag)) {
response.setStatusCode(304);
response.addHeader(CACHE_CONTROL, "public");
response.addHeader(LAST_MODIFIED, generateLastModified(sourceLastModified));
response.addHeader(E_TAG, generateETag(sourceETag));
return;
}
}
}
if (isLastModified && ifModifiedSinceHeader != null) {
if (validateIfModifiedSince(request, sourceLastModified)) {
response.setStatusCode(304);
response.addHeader(CACHE_CONTROL, "public");
response.addHeader(LAST_MODIFIED, generateLastModified(sourceLastModified));
return;
}
}
handler.handle(request, response, context);
if (isLastModified && sourceLastModified >= 0) {
response.addHeader(LAST_MODIFIED, generateLastModified(sourceLastModified));
}
if (isETag && sourceETag != null) {
response.addHeader(E_TAG, generateETag(sourceETag));
}
if (isLastModified) {
response.addHeader(CACHE_CONTROL, "public");
}
}
} 7.2.5 接口实现
我们以FileBrowser为例
@Override
public long getLastModified(HttpRequest request) throws IOException {
String httpPath = trimEndSlash(getRequestPath(request));
File source = findPathSource(httpPath);
if (source != null && source.isFile())
return source.lastModified();
return -1;
}
@Override
public String getETag(HttpRequest request) throws IOException {
String httpPath = trimEndSlash(getRequestPath(request));
File source = findPathSource(httpPath);
if (source != null && source.isFile()) {
long sourceSize = source.length();
String sourcePath = source.getAbsolutePath();
long lastModified = source.lastModified();
return sourceSize + sourcePath + lastModified;
}
return null;
}八、ExceptionResolver异常解决者
异常解决者全局唯一,用来处理在每一个request/response对中发生的所有异常,包括Interceptor、RequestHandler、Filter等的处理过程。
它好比SpringMVC中的HandlerExceptionResolver或者@ControllerAdvice + @ExceptionHandler。
我们来看看它的代码:
public interface ExceptionResolver {
void resolveException(Exception e, HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response,
HttpContext context);
}8.1 默认异常及其处理器
8.1.1 BaseException 基本类型异常
AndServer中定义了一个基本的异常BaseException:
public class BaseException extends HttpException {
private int mHttpCode;
private HttpEntity mHttpBody;
public BaseException() {
this(500, "Unknown exception occurred on server.");
}
public BaseException(int httpCode, String httpBody) {
super(httpBody);
this.mHttpCode = httpCode;
this.mHttpBody = new StringEntity(httpBody, ContentType.TEXT_PLAIN);
}
public int getHttpCode() {
return mHttpCode;
}
public HttpEntity getHttpBody() {
return mHttpBody;
}
}它包含了返回给客户端的响应码和数据,如果不需要添加响应头等信息时,我们的自定义异常可以继承它。
例如,在Http接口章节提到的请求方法中,AndServer会检查请求方法和handle()的注解的请求方法是否匹配,如果不匹配则会抛出一个MethodNotSupported异常,这个异常就是继承自BaseException。
AndServer中在处理请求时会抛出的两个异常:
- NotFoundException,path指定的资源没有找到
- MethodNotSupported,接口不支持的请求方法
8.1.2 默认异常处理器
默认的异常解决者先判断异常是否是自定义异常,如果是那么返回自定义的响应码和响应数据;如果不是则返回500响应码,并告诉客户端哪一个接口出了问题
public class SimpleExceptionResolver implements ExceptionResolver {
@Override
public final void resolveException(Exception e, HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response, HttpContext context) {
View view = resolveException(e, request, response);
response.setStatusCode(view.getHttpCode());
response.setEntity(view.getHttpEntity());
response.setHeaders(view.getHeaders());
}
public View resolveException(Exception e, HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response) {
return resolveException(e);
}
protected View resolveException(Exception e) {
if (e instanceof BaseException) {
BaseException exception = (BaseException) e;
return new View(exception.getHttpCode(), exception.getHttpBody());
}
String message = String.format("Server error occurred:\n%1$s", e.getMessage());
HttpEntity httpEntity = new StringEntity(message, ContentType.TEXT_PLAIN);
return new View(500, httpEntity);
}
}8.2 自定义异常及其处理器
自定义异常解决者可以实现ExceptionResolver接口或者继承SimpleExceptionResolver类。
为了方便,我们这里以继承SimpleExceptionResolver类为例
先定义一个异常的基类:
public class MyException extends HttpException {
private int code;
private String message;
public MyException(int code, String message) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
}定义异常解决者
public class MyResolver extends SimpleExceptionResolver {
@ovrride
protected View resolveException(Exception e) {
if (e instanceof MyException) {
MyException exception = (MyException) e;
String json = JSON.toJSONString(exception);
return new View(exception.getCode(), json);
}
// 其它未知异常处理。
String message = String.format("服务器发生异常:\n%1$s", e.getMessage());
MyException exception = new MyException(500, message);
return new View(exception.getCode(), json);
}
}这样处理后,当服务器抛出异常后,客户端接收到的数据将是JSON格式:
{
"code":"401",
"message":"请您先登录"
}未知异常:
{
"code":"500",
"message":"服务器发生异常:/user/admin"
}九、其他
9.1 Request解析
这里介绍一个比较有用的帮助类HttpRequestParser:
public class HttpRequestParser {
/**
* 解析当前Request的请求参数。
*/
public static Map<String, String> parseParams(HttpRequest request);
/**
* 解析当前Request的请求参数,可控制是否把参数名转为小写。
*/
public static Map<String, String> parseParams(HttpRequest request, boolean lowerCaseNames);
/**
* 拿到当前Request的path。
*/
public static String getRequestPath(HttpRequest request);
/**
* 当前Requst是否是允许带有Body的。
*/
public static boolean isAllowRequestBody(HttpRequest request);
/**
* 拿到当前Request的请求方法。
*/
public static RequestMethod getRequestMethod(HttpRequest request);
/**
* 当期Request是否带有表单Body。
*/
public static boolean isMultipartContentRequest(HttpRequest request);
/**
* 解析Request的某个Date类型的头为毫秒,如果不存在则为-1。
*/
public static long parseDateHeader(HttpRequest request, String headerName);
}还有其它几个方法,几乎不会用到,这里不做介绍,有兴趣的开发者可以自行看源码。
官方网站笔误
20180315采集
官方说明中:new AssetsWebsite(getAssets(), “web”);
源码中:HttpRequestParser.getRequestPath 多解析了一个/
能否一个端口同时配置多种类型的WebSite站点?
在逻辑上其实是支持,但是目前的写法是FileBrowse、StorageWebsite、AssetsWebsite不能共存,完全可以通过写一个自定义的WebSite来实现,也可以通过修改框架,将单WebSite改为多WebSite