转载自 http://blog.csdn.net/hguisu/article/details/7418161
2.数据流的基本概念
4 数据流分类:
1) 字节流:数据流中最小的数据单元是字节
2) 字符流:数据流中最小的数据单元是字符, Java中的字符是Unicode编码,一个字符占用两个字节。
3. 标准I/O
Java程序可通过命令行参数与外界进行简短的信息交换,同时,也规定了与标准输入、输出设备,如键盘、显示器进行信息交换的方式。而通过文件可以与外界进行任意数据形式的信息交换。
1. 命令行参数
运行命令:java Java C VB
运行结果:
args[0] is <Java>
args[1] is <C>
args[2] is <VB>
2. 标准输入,输出数据流
java系统自带的标准数据流:java.lang.System:
注意:
(1)System类不能创建对象,只能直接使用它的三个静态成员。
(2)每当main方法被执行时,就自动生成上述三个对象。
1) 标准输出流 System.out
System.out向标准输出设备输出数据,其数据类型为PrintStream。方法:
2)标准输入流 System.in
System.in读取标准输入设备数据(从标准输入获取数据,一般是键盘),其数 据类型为InputStream。方法:

3)标准错误流
System.err输出标准错误,其数据类型为PrintStream。可查阅API获得详细说明。
标准输出通过System.out调用println方法输出参数并换行,而print方法输出参数但不换行。println或print方法都通 过重载实现了输出基本数据类型的多个方法,包括输出参数类型为boolean、char、int、long、float和double。同时,也重载实现 了输出参数类型为char[]、String和Object的方法。其中,print(Object)和println(Object)方法在运行时将调 用参数Object的toString方法。
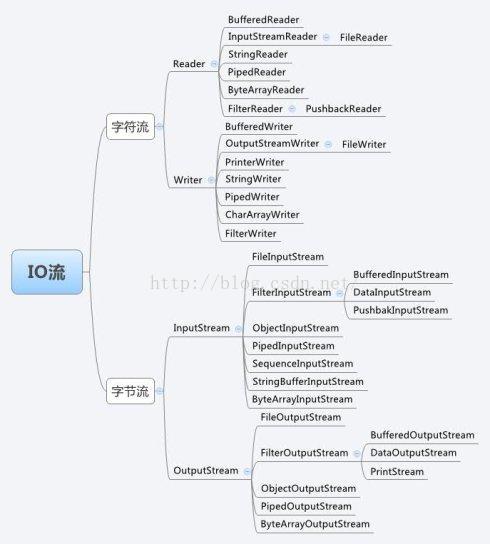
6. Java.IO流类库
1. io流的四个基本类
java.io包中包含了流式I/O所需要的所有类。在java.io包中有四个基本类:InputStream、OutputStream及Reader、Writer类,它们分别处理字节流和字符流:
基本数据流的I/O
| 输入/输出 | 字节流 | 字符流 |
| 输入流 | Inputstream | Reader |
| 输出流 | OutputStream | Writer |
Java中其他多种多样变化的流均是由它们派生出来的:
JDK1.4版本开始引入了新I/O类库,它位于java.nio包中,新I/O类库利用通道和缓冲区等来提高I/O操作的效率。
在java.io包中, java.io.InputStream 表示字节输入流, java.io.OutputStream表示字节输出流,处于java.io包最顶层。这两个类均为抽象类,也就是说它们不能被实例化,必须生成子类之后才能实现一定的功能。
7. 字节流InputStream/OutputStream
1. InputStream抽象类
InputStream 为字节输入流,它本身为一个抽象类,必须依靠其子类实现各种功能,此抽象类是表示字节输入流的所有类的超类。 继承自InputStream 的流都是向程序中输入数据的,且数据单位为字节(8bit);
InputStream是输入字节数据用的类,所以InputStream类提供了3种重载的read方法.Inputstream类中的常用方法:
(1) public abstract int read( ):读取一个byte的数据,返回值是高位补0的int类型值。若返回值=-1说明没有读取到任何字节读取工作结束。
(2) public int read(byte b[ ]):读取b.length个字节的数据放到b数组中。返回值是读取的字节数。该方法实际上是调用下一个方法实现的
(3) public int read(byte b[ ], int off, int len):从输入流中最多读取len个字节的数据,存放到偏移量为off的b数组中。
(4) public int available( ):返回输入流中可以读取的字节数。注意:若输入阻塞,当前线程将被挂起,如果InputStream对象调用这个方法的话,它只会返回0,这个方法必须由继承InputStream类的子类对象调用才有用,
(5) public long skip(long n):忽略输入流中的n个字节,返回值是实际忽略的字节数, 跳过一些字节来读取
(6) public int close( ) :我们在使用完后,必须对我们打开的流进行关闭.
主要的子类:
1) FileInputStream把一个文件作为InputStream,实现对文件的读取操作
2) ByteArrayInputStream:把内存中的一个缓冲区作为InputStream使用
3) StringBufferInputStream:把一个String对象作为InputStream
4) PipedInputStream:实现了pipe的概念,主要在线程中使用
5) SequenceInputStream:把多个InputStream合并为一个InputStream
2.OutputStream抽象类
OutputStream提供了3个write方法来做数据的输出,这个是和InputStream是相对应的。1. public void write(byte b[ ]):将参数b中的字节写到输出流。
2. public void write(byte b[ ], int off, int len) :将参数b的从偏移量off开始的len个字节写到输出流。
3. public abstract void write(int b) :先将int转换为byte类型,把低字节写入到输出流中。
4. public void flush( ) : 将数据缓冲区中数据全部输出,并清空缓冲区。
5. public void close( ) : 关闭输出流并释放与流相关的系统资源。
主要的子类:
1) ByteArrayOutputStream:把信息存入内存中的一个缓冲区中
2) FileOutputStream:把信息存入文件中
3) PipedOutputStream:实现了pipe的概念,主要在线程中使用
4) SequenceOutputStream:把多个OutStream合并为一个OutStream
流结束的判断:方法read()的返回值为-1时;readLine()的返回值为null时。
3. 文件输入流: FileInputStream类
FileInputStream可以使用read()方法一次读入一个字节,并以int类型返回,或者是使用read()方法时读入至一个byte数组,byte数组的元素有多少个,就读入多少个字节。在将整个文件读取完成或写入完毕的过程中,这么一个byte数组通常被当作缓冲区,因为这么一个byte数组通常扮演承接数据的中间角色。

作用:以文件作为数据输入源的数据流。或者说是打开文件,从文件读数据到内存的类。
使用方法(1)
File fin=new File("d:/abc.txt");
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream( fin);
使用方法(2)
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(“d: /abc.txt”);
程序举例:
将InputFromFile.java的程序的内容显示在显示器上
4.文件输出流:FileOutputStream类
作用:用来处理以文件作为数据输出目的数据流;或者说是从内存区读数据入文件
FileOutputStream类用来处理以文件作为数据输出目的数据流;一个表示文件名的字符串,也可以是File或FileDescriptor对象。
创建一个文件流对象有两种方法:
方式1:
File f=new File (“d:/myjava/write.txt ");
FileOutputStream out= new FileOutputStream (f);
方式2:
FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream(“d:/myjava/write.txt ");
方式3:构造函数将 FileDescriptor()对象作为其参数。
FileDescriptor() fd=new FileDescriptor();
FileOutputStream f2=new FileOutputStream(fd);
方式4:构造函数将文件名作为其第一参数,将布尔值作为第二参数。
FileOutputStream f=new FileOutputStream("d:/abc.txt",true);
注意: (1)文件中写数据时,若文件已经存在,则覆盖存在的文件;(2)的读/写操作结束时,应调用close方法关闭流。

计算机访问外部设备非常耗时。访问外存的频率越高,造成CPU闲置的概率就越大。为了减少访问外存的次数,应该在一次对外设的访问中,读写更多的数据。为此,除了程序和流节点间交换数据必需的读写机制外,还应该增加缓冲机制。缓冲流就是每一个数据流分配一个缓冲区,一个缓冲区就是一个临时存储数据的内存。这样可以减少访问硬盘的次数,提高传输效率。
BufferedInputStream:当向缓冲流写入数据时候,数据先写到缓冲区,待缓冲区写满后,系统一次性将数据发送给输出设备。
BufferedOutputStream :当从向缓冲流读取数据时候,系统先从缓冲区读出数据,待缓冲区为空时,系统再从输入设备读取数据到缓冲区。
将BufferedInputStream与FileInputStream相接
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream( “file1.txt ” );
BufferedInputStream bin=new BufferedInputStream( in);
2)将内存写入文件:
将BufferedOutputStream与 FileOutputStream相接
FileOutputStreamout=new FileOutputStream(“file1.txt”);
BufferedOutputStream bin=new BufferedInputStream(out);
3)键盘输入流读到内存
从键盘读入字符,并写入到文件中 BufferedReader类的方法: String readLine()
作用:读一行字符串,以回车符为结束。
BufferedWriter类的方法: bout.write(String s,offset,len)
作用:从缓冲区将字符串s从offset开始,len长度的字符串写到某处。
Java中字符是采用Unicode标准,一个字符是16位,即一个字符使用两个字节来表示。为此,JAVA中引入了处理字符的流。
1. Reader抽象类
用于读取字符流的抽象类。子类必须实现的方法只有 read(char[], int, int) 和 close()。但是,多数子类将重写此处定义的一些方法,以提供更高的效率和/或其他功能。

1) FileReader :与FileInputStream对应
主要用来读取字符文件,使用缺省的字符编码,有三种构造函数:
(1)将文件名作为字符串 :FileReader f=new FileReader(“c:/temp.txt”);
(2)构造函数将File对象作为其参数。
File f=new file(“c:/temp.txt”);
FileReader f1=new FileReader(f);
(3) 构造函数将FileDescriptor对象作为参数
FileDescriptor() fd=new FileDescriptor()
FileReader f2=new FileReader(fd);
(1) 用指定字符数组作为参数:CharArrayReader(char[])
(2) 将字符数组作为输入流:CharArrayReader(char[], int, int)
读取字符串,构造函数如下: public StringReader(String s);
2) CharArrayReader:与ByteArrayInputStream对应
3) StringReader : 与StringBufferInputStream对应
4) InputStreamReader
从输入流读取字节,在将它们转换成字符:Public inputstreamReader(inputstream is);
5) FilterReader: 允许过滤字符流
protected filterReader(Reader r);
6) BufferReader :接受Reader对象作为参数,并对其添加字符缓冲器,使用readline()方法可以读取一行。
Public BufferReader(Reader r);
主要方法:
(1) public int read() throws IOException; //读取一个字符,返回值为读取的字符
(2) public int read(char cbuf[]) throws IOException; /*读取一系列字符到数组cbuf[]中,返回值为实际读取的字符的数量*/
(3) public abstract int read(char cbuf[],int off,int len) throws IOException;
/*读取len个字符,从数组cbuf[]的下标off处开始存放,返回值为实际读取的字符数量,该方法必须由子类实现*/
2. Writer抽象类
写入字符流的抽象类。子类必须实现的方法仅有 write(char[], int, int)、flush() 和 close()。但是,多数子类将重写此处定义的一些方法,以提供更高的效率和/或其他功能。 其子类如下:
1) FileWrite: 与FileOutputStream对应
将字符类型数据写入文件,使用缺省字符编码和缓冲器大小。
Public FileWrite(file f);
2) chararrayWrite:与ByteArrayOutputStream对应 ,将字符缓冲器用作输出。
Public CharArrayWrite();
3) PrintWrite:生成格式化输出
public PrintWriter(outputstream os);
4) filterWriter:用于写入过滤字符流
protected FilterWriter(Writer w);
5) PipedWriter:与PipedOutputStream对应
6) StringWriter:无与之对应的以字节为导向的stream
主要方法:
(1) public void write(int c) throws IOException; //将整型值c的低16位写入输出流
(2) public void write(char cbuf[]) throws IOException; //将字符数组cbuf[]写入输出流
(3) public abstract void write(char cbuf[],int off,int len) throws IOException; //将字符数组cbuf[]中的从索引为off的位置处开始的len个字符写入输出流
(4) public void write(String str) throws IOException; //将字符串str中的字符写入输出流
(5) public void write(String str,int off,int len) throws IOException; //将字符串str 中从索引off开始处的len个字符写入输出流
(6) flush( ) //刷空输出流,并输出所有被缓存的字节。
(7)close() 关闭流 public abstract void close() throws IOException
3 .InputStream与Reader差别 OutputStream与Writer差别
InputStream和OutputStream类处理的是字节流,数据流中的最小单位是字节(8个bit)
Reader与Writer处理的是字符流,在处理字符流时涉及了字符编码的转换问题

Reader类能够将输入流中采用其他编码类型的字符转换为Unicode字符,然后在内存中为其分配内存
Writer类能够将内存中的Unicode字符转换为其他编码类型的字符,再写到输出流中。
构造方法:FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(String fileName);//创建字符输出流类对象和已存在的文件相关联。文件不存在的话,并创建。
如: FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("C:\\1.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(String fileName,boolean append);//创建字符输出流类对象和已存在的文件相关联,并设置该该流对文件的操作是否为续写。
如:FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("C:\\1.txt",ture); //表示在fw对文件再次写入时,会在该文件的结尾续写,并不会覆盖掉。
主要方法:
void write(String str) //写入字符串。当执行完此方法后,字符数据还并没有写入到目的文件中去。此时字符数据会保存在缓冲区中。此时在使用刷新方法就可以使数据保存到目的文件中去。
viod flush() //刷新该流中的缓冲。将缓冲区中的字符数据保存到目的文件中去。
viod close() //关闭此流。在关闭前会先刷新此流的缓冲区。在关闭后,再写入或者刷新的话,会抛IOException异常。
1)确定是数据源和数据目的(输入还是输出)
源:输入流 InputStream Reader
目的:输出流 OutputStream Writer
2)明确操作的数据对象是否是纯文本
是:字符流Reader,Writer
否:字节流InputStream,OutputStream
3)明确具体的设备。
是硬盘文件:File++:
读取:FileInputStream,, FileReader,
写入:FileOutputStream,FileWriter
是内存用数组
byte[]:ByteArrayInputStream, ByteArrayOutputStream
是char[]:CharArrayReader, CharArrayWriter
是String:StringBufferInputStream(已过时,因为其只能用于String的每个字符都是8位的字符串), StringReader, StringWriter
是网络用Socket流
是键盘:用System.in(是一个InputStream对象)读取,用System.out(是一个OutoutStream对象)打印
3)是否需要转换流是,就使用转换流,从Stream转化为Reader,Writer:InputStreamReader,OutputStreamWriter
4)是否需要缓冲提高效率
是就加上Buffered:BufferedInputStream, BufferedOuputStream, BuffereaReader, BufferedWriter
5)是否需要格式化输出
例:将一个文本文件中数据存储到另一个文件中。
1)数据源和数据目的:读取流,InputStream Reader 输出:OutputStream Writer
2)是否纯文本:是!这时就可以选择Reader Writer。
3)设备:是硬盘文件。Reader体系中可以操作文件的对象是 FileReader FileWriter。
FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("b.txt");
4)是否需要提高效率:是,加Buffer
BufferedReader bfr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("a.txt"); );
BufferedWriter bfw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("b.txt"); );
1.public class EOFException :
非正常到达文件尾或输入流尾时,抛出这种类型的异常。
2.public class FileNotFoundException:
当文件找不到时,抛出的异常。
3.public class InterruptedIOException:
当I/O操作被中断时,抛出这种类型的异常。