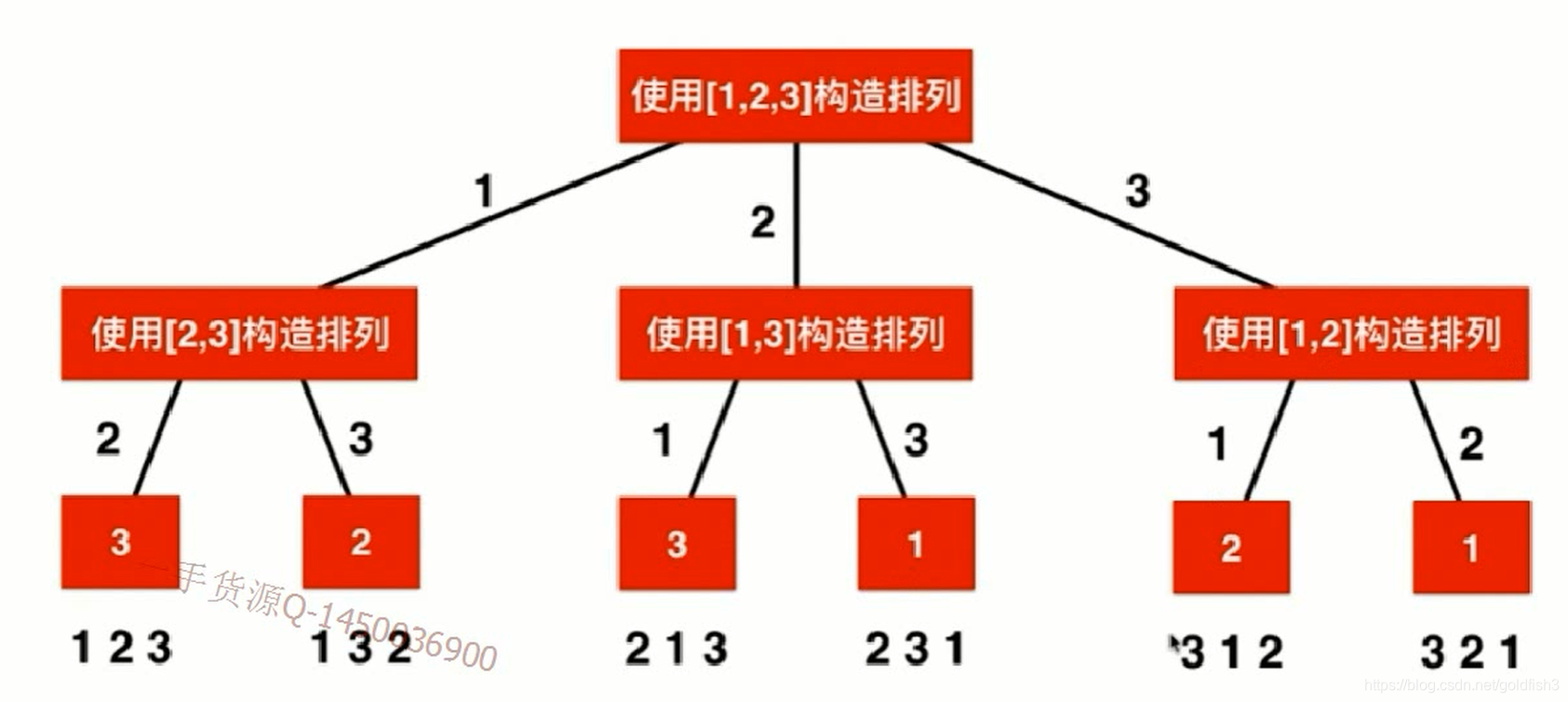
全排列问题
leetCode 46
使用回溯法解决 —— 解法1
如图:全排列问题是一个典型的树型问题:
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
private boolean[] flag;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main main = new Main();
int[] nums = {1,2,3};
List<List<Integer>> res = main.permute(nums);
for (List<Integer> l:res){
for (Integer i:l){
System.out.print(i);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public void premuteCore(int[] nums,ArrayList<Integer> tmp,int index){
if (index == nums.length){
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (Integer e : tmp){
res.add(e);
}
this.res.add(res);
return;
}
for (int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){
if (flag[i] != true){
tmp.add(nums[i]);
flag[i] = true;
premuteCore(nums,tmp,index+1);
tmp.remove(tmp.size()-1);
flag[i] = false;
}
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
flag = new boolean[nums.length];
premuteCore(nums, new ArrayList<Integer>(),0);
return res;
}
}
使用回溯法解决 —— 解法2
本质:任何一个组合都可以通过字符串的两两交换得到,这意味着,可以通过遍历所有的两两交换得到所有排列
这种解法比上面的解法效率高,缺点在于只能求全排列,不能求n个中取m个的排列情况
将第一个元素和后面的逐个交换,然后再第一个元素交换的基础上,将第二个元素和后面的逐个交换
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main main = new Main();
int[] nums = {1,2,3};
List<List<Integer>> res = main.permute(nums);
for (List<Integer> l:res){
for (Integer i:l){
System.out.print(i);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public void premuteCore(int[] nums,int index){
if (index == nums.length-1){
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i=0; i<nums.length; i++)
res.add(nums[i]);
this.res.add(res);
return;
}
for (int i=index; i<nums.length; i++){
if (i != index){
int tmp = nums[index];
nums[index] = nums[i];
nums[i] = tmp;
}
premuteCore(nums,index+1);
if (i != index){
int tmp = nums[index];
nums[index] = nums[i];
nums[i] = tmp;
}
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
premuteCore(nums,0);
return res;
}
}
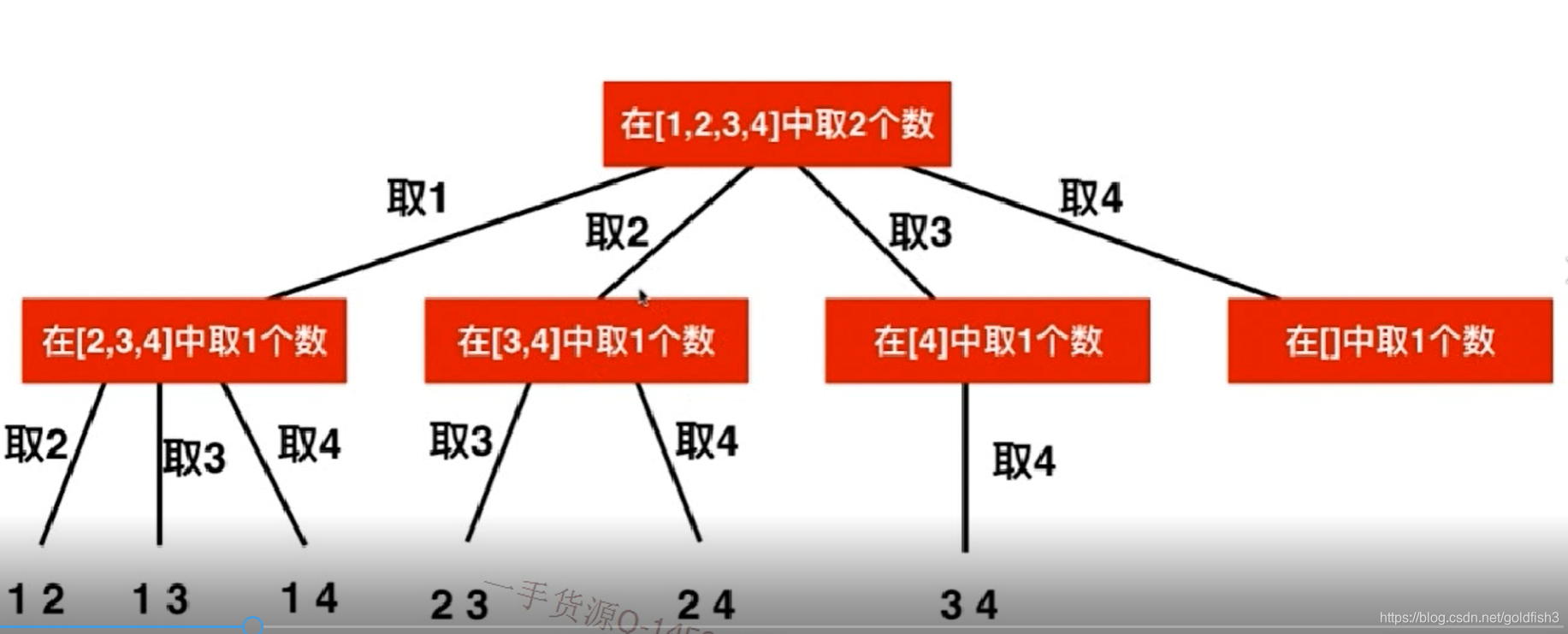
全组合问题
leetCode 77
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public void combineCore(int n,int k,int start,ArrayList<Integer> cres){
if(cres.size() == k){
ArrayList<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i=0; i<cres.size(); i++){
tmp.add(cres.get(i));
}
res.add(tmp);
return;
}
for(int i=start; i<=n; i++){
cres.add(i);
combineCore(n,k,i+1,cres);
cres.remove(cres.size()-1);
}
return;
}
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
if(n < 0 || k < 0 || k > n){
return this.res;
}
this.combineCore(n,k,1,new ArrayList<Integer>());
return this.res;
}
}
剪枝
注意在 combineCore 的循环中,如果传入递归中的值是i,那么下一次就是从
[i,n] 中查找 k-cres.size() 个元素
如果 (n-i)<(k-cres.size()) 就意味着后续元素没有足够的数量,让结果的长度等于k
因此,可以将循环的终止条件改为 i<n-(k-cres.size())+1
``java
class Solution {
private List<List> res = new ArrayList<List>();
public void combineCore(int n,int k,int start,ArrayList<Integer> cres){
if(cres.size() == k){
ArrayList<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i=0; i<cres.size(); i++){
tmp.add(cres.get(i));
}
res.add(tmp);
return;
}
for(int i=start; i<=n-(k-cres.size())+1; i++){
cres.add(i);
combineCore(n,k,i+1,cres);
cres.remove(cres.size()-1);
}
return;
}
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
if(n < 0 || k < 0 || k > n){
return this.res;
}
this.combineCore(n,k,1,new ArrayList<Integer>());
return this.res;
}
}
leetCode 39:组合总和
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:
所有数字(包括 target)都是正整数。
解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
输入: candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
所求解集为:
[
[7],
[2,2,3]
]
示例 2:
输入: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8,
所求解集为:
[
[2,2,2,2],
[2,3,3],
[3,5]
]
答案
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public void combinationCore(int[] candidates,ArrayList<Integer> cres, int start,int sum,int target){
if (sum > target){
return;
}
if (sum == target){
ArrayList<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (Integer e : cres){
tmp.add(e);
}
this.res.add(tmp);
return;
}
for (int i=start; i<candidates.length; i++){
cres.add(candidates[i]);
combinationCore(candidates,cres,i,sum+candidates[i],target);
cres.remove(cres.size()-1);
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
combinationCore(candidates,new ArrayList<Integer>(),0,0,target);
return this.res;
}
}
leetCode 78:子集
给定一组不含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
示例:
输入: nums = [1,2,3]
输出:
[
[3],
[1],
[2],
[1,2,3],
[1,3],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[]
]
答案
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
private void subsetsCore(int[] nums,ArrayList<Integer> cres,int start){
res.add(copyList(cres));
if(cres.size() == nums.length){
return;
}
for(int i=start; i<nums.length; i++){
cres.add(nums[i]);
subsetsCore(nums,cres,i+1);
cres.remove(cres.size()-1);
}
}
private List<Integer> copyList(List<Integer> list){
ArrayList<Integer> copyList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(Integer e : list){
copyList.add(e);
}
return copyList;
}
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
this.subsetsCore(nums,new ArrayList<Integer>(),0);
return this.res;
}
}