数据分析——numpy
1.numpy的定义
#使用numpy生成数组,得到ndarry的数据类型
#encoding='utf-8'
import numpy as np
import random
t1=np.array([1,2,3])
print(t1)
print(type(t1))
t2=np.array(range(10))
print(t2)
t3=np.arange(10)#可以发现t2和t3结果一致
print(t3)
print(t3.dtype)#返回的是默认的数据类型,也可以指定,具体见t4
t4=np.array(range(1,4),dtype=float)
print(t4.dtype)
#直接调整数据类型
t5=t4.astype("int8")
print(t5.dtype)
#numpy中的小数
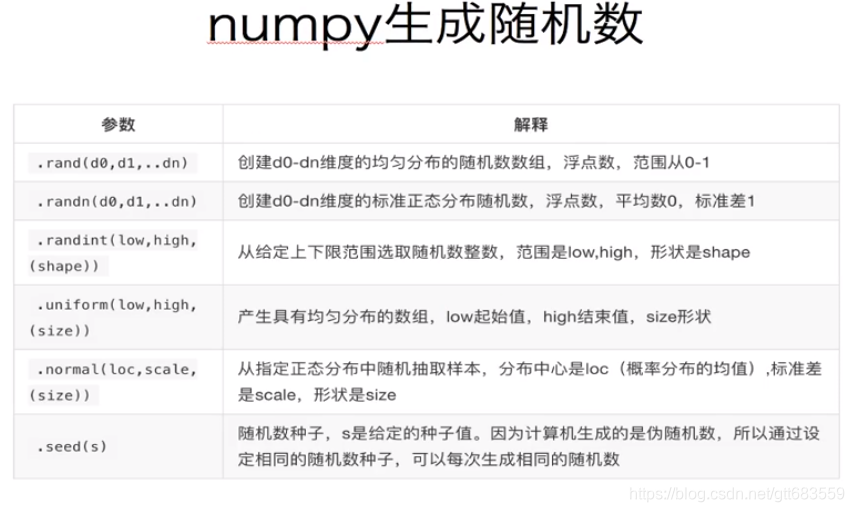
t6=np.array([random.random()for i in range(10)])
print(t6)
t7=np.round(t6,2)#保留两位小数
print(t7)
结果:
[1 2 3]
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
int32
float64
int8
[0.82247803 0.55364819 0.48687325 0.56505264 0.41843079 0.88040453
0.99396157 0.59593577 0.10335602 0.11364745]
[0.82 0.55 0.49 0.57 0.42 0.88 0.99 0.6 0.1 0.11]
进程已结束,退出代码0
2.数组计算
这里说明一下,0/0结果为nan,表示不是一个数字。非零数/0结果为inf,表示无穷无限
#encoding='utf-8'
import numpy as np
import random
t1=np.array([1,2,3])
print(t1.shape)#查看数组的形状,结果的括号里面有几个数就是几维数组
t2=np.arange(12)
print(t2)
t3=t2.reshape((3,4))#修改数组形状
print(t3)
t4=np.arange(24).reshape((2,3,4))
print(t4)
#转换为一维数组的方法
t5=t4.reshape((24,))#变回来
print(t5)
t6=t4.flatten()#返回一个折叠成一维的数组,但是该函数只能适用于numpy对象,即array或者mat,普通的list列表是不行的。
print(t6)
#广播机制
print(t4+2)#每一个数都加2
print(t4/2)#每一个数都除以2
print(t4/0)#报错
结果:
(3,)
[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11]
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
[[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
[[12 13 14 15]
[16 17 18 19]
[20 21 22 23]]]
[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23]
[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23]
[[[ 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9]
[10 11 12 13]]
[[14 15 16 17]
[18 19 20 21]
[22 23 24 25]]]
[[[ 0. 0.5 1. 1.5]
[ 2. 2.5 3. 3.5]
[ 4. 4.5 5. 5.5]]
[[ 6. 6.5 7. 7.5]
[ 8. 8.5 9. 9.5]
[10. 10.5 11. 11.5]]]
[[[nan inf inf inf]
[inf inf inf inf]
[inf inf inf inf]]
[[inf inf inf inf]
[inf inf inf inf]
[inf inf inf inf]]]
D:/pythonProject/hello.py:25: RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in true_divide
print(t4/0)
D:/pythonProject/hello.py:25: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in true_divide
print(t4/0)
进程已结束,退出代码0
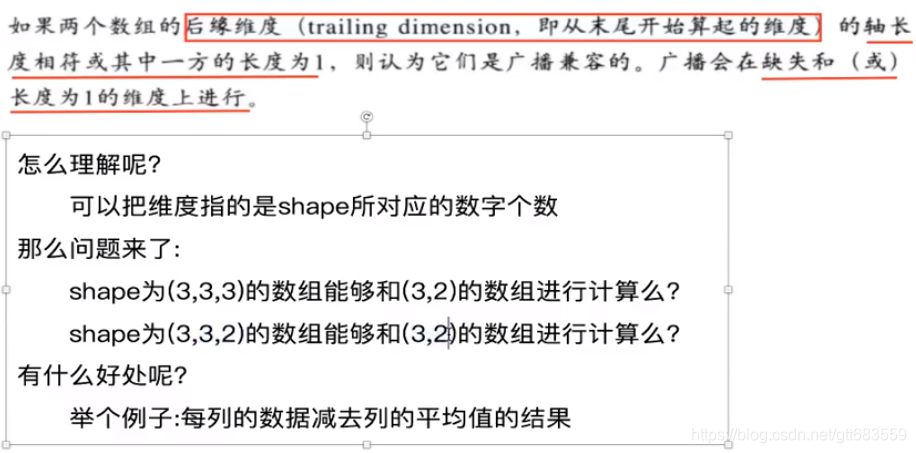
3.数组运算的广播原则,明显问题一不行,问题二是可以的,因为(3,3,2)可以理解为3块3行2列,和(3,2)在后缘维度(列的维度)一致。
import numpy as np
import random
t1=np.array([0,1,2,3])
print(t1.shape)
t4=np.arange(24).reshape((2,3,4))
print(t4)
t3=np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8])
print(t1-t4)#行或者列形状一致才可以计算
print(t3-t4)#否则就报错
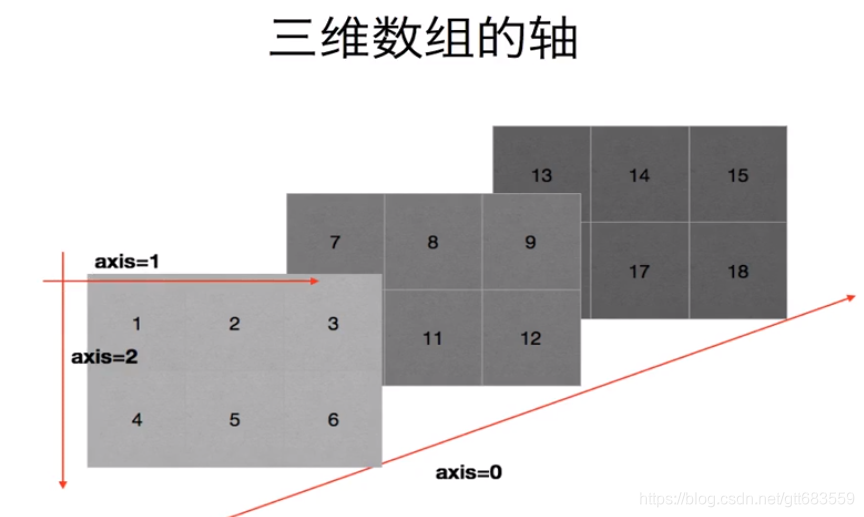
4.轴
5.numpy读取数据通常是CSV格式
unpack默认是False,True时实现交换轴,相当于转置。除此之外,t.transpose()和t.swapaxes(1,0)也能实现转置
6,numpy的索引和切片
import numpy as np
import random
t4=np.arange(12).reshape((3,4))
print(t4)
print(t4[1])#取一行
print(t4[1:])#取连续的多行,比如从一行开始
print(t4[[0,2]])#取不连续的多行
#取列
print(t4[:,0])
#取连续的多列,比如从一列开始
print(t4[:,1:])
#取不连续的多列
print(t4[:,[0,2]])
#取某行某列,结果是行列交叉的位置
print(t4[1,2])
#取多行多列,注意包头不包尾
print(t4[0:3,1:4])
#取多个不相邻的点,(0,0)和(2,1)位置上的点
print(t4[[0,2],[0,1]])
7.numpy中数值的修改
t4=np.arange(12).reshape((3,4))
print(t4)
print(t4<10)
#numpy中的数值修改
t4[t4<10]=3
print(t4)
#三元运算符,小于10的数全部赋值为0
t=np.where(t4<10,0,10)
print(t)
#clip操作,小于10的赋值为10,大于18的赋值为18
t5=t4.clip(10,18)
print(t5)
结果:
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
[[ True True True True]
[ True True True True]
[ True True False False]]
[[ 3 3 3 3]
[ 3 3 3 3]
[ 3 3 10 11]]
[[ 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 10 10]]
[[10 10 10 10]
[10 10 10 10]
[10 10 10 11]]
进程已结束,退出代码0
8.数组的拼接,行列交换
t1=np.arange(12).reshape((3,4))
t2=np.arange(13,25).reshape((3,4))
print(t1)
print(t2)
#拼接
t3=np.vstack((t1,t2))#竖直拼接
print(t3)
t4=np.hstack((t1,t2))#水平拼接
print(t4)
#交换
t1[[1,2],:]=t1[[2,1],:]
print(t1)#行交换
t2[:,[1,2]]=t2[:,[2,1]]
print(t2)#列交换
9,其他好用的方法
10.nan的注意点
11.常用统计函数
例子:均值填补nan
import numpy as np
def fill_ndarray(t1):
for i in range(t1.shape[1]):
temp_col = t1[:,i]
nan_num=np.count_nonzero(temp_col!=temp_col)
if nan_num!=0:
temp_not_nan_col=temp_col[temp_col==temp_col]
temp_col[np.isnan(temp_col)]=temp_not_nan_col.mean()
return t1
if __name__=='__main__':
t1=np.arange(24).reshape((4,6)).astype("float")
t1[1,2:]=np.nan
print(t1)
t1=fill_ndarray(t1)
print(t1)
结果:
[[ 0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.]
[ 6. 7. nan nan nan nan]
[12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17.]
[18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23.]]
[[ 0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.]
[ 6. 7. 12. 13. 14. 15.]
[12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17.]
[18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23.]]
进程已结束,退出代码0