目录
1. 封装一个函数--利用冒泡排序,实现对整型数组的升序排序
一、输出
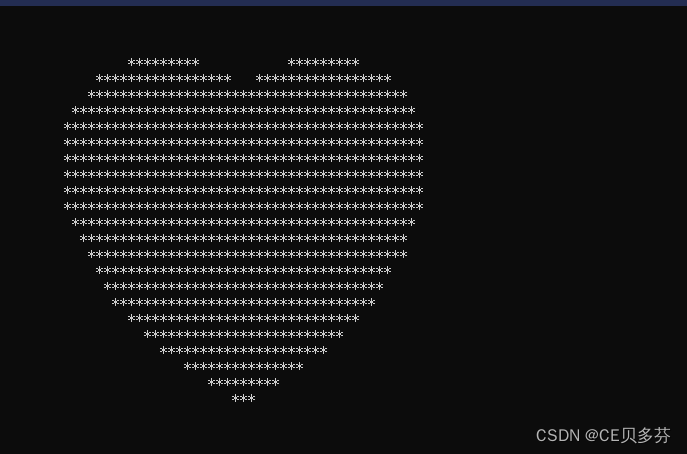
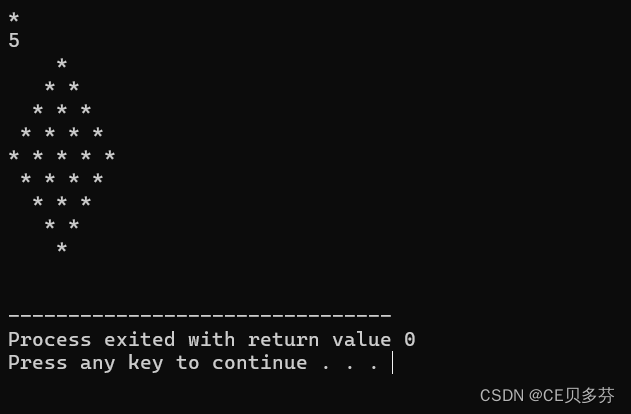
1. 用for循环写一个爱心代码
说明,在控制台输出一个由 “*” 组成的爱心。
#include<stdio.h>
int main ()
{
float x,y,a;
for( y=1.5f; y> -1.5f ;y -=0.1f){
for ( x=-1.5f;x<1.5f;x+=0.05f){
float a=x*x+y*y-1;
putchar(a*a*a-x*x*y*y*y<=0.0f?'*':' ');
}
putchar ('\n');
}
return 0;
}运行结果:
2. 在爱心的基础上,做一些高级的表白爱心
说明:在控制台输出
遇到你
我才发现
曾经所有的条件
似乎都成了我等你的借口
我对你的感情已经决堤
所以
请允许我,从今往后映入你
明媚的眼
我
想和你
耳鬓厮磨,相濡以沫!答应我吧!
输入yes,你可以看到我的真心
控制所有字体改变颜色。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define I 20
#define R 340
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char answer[4];
printf("遇到你\n我才发现\n曾经所有的条件\n似乎都成了我等你的借口\n\n");
printf("我对你的感情已经决堤\n所以\n请允许我,从今往后映入你\n明媚的眼\n");
printf("我\n想和你\n耳鬓厮磨,相濡以沫!");
printf("答应我吧!\n输入yes,你可以看到我的真心\n");
scanf("%s",&answer);
float y, x, z, f;
for (y = 1.5f; y > -1.5f; y-=0.1f){
for (x = -1.5f; x < 1.5f; x += 0.05f){
z = x*x + y*y -1;
f = z*z*z - x*x*y*y*y;
putchar(f <= 0.0f ? "*********"[(int)(f*-8.0f)]:' ');
}
putchar('\n');
}
long time;
for(; ;)
{
system("color a");
for(time=0;time<99999999;time++);
system("color b");
for(time=0;time<99999999;time++);
system("color c");
for(time=0;time<99999999;time++);
system("color d");
for(time=0;time<99999999;time++);
system("color e");
for(time=0;time<99999999;time++);
system("color f");
for(time=0;time<99999999;time++);
system("color 0");
for(time=0;time<99999999;time++);
system("color 1");
for(time=0;time<99999999;time++);
system("color 2");
for(time=0;time<99999999;time++);
system("color 3");
for(time=0;time<99999999;time++);
system("color 4");
for(time=0;time<99999999;time++);
system("color 5");
for(time=0;time<99999999;time++);
system("color 6");
for(time=0;time<99999999;time++);
system("color 7");
for(time=0;time<99999999;time++);
system("color 8");
for(time=0;time<99999999;time++);
system("color 9");
}
getchar();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
D
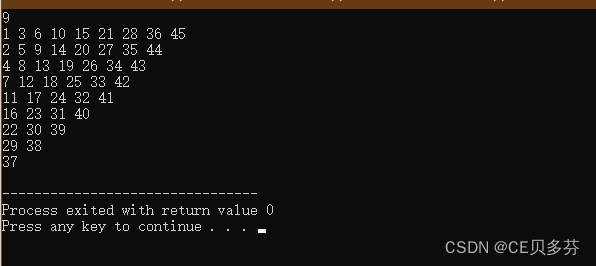
3. 蛇形矩阵
说明:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int N;
scanf("%d", &N);
int i, j, down = 1, right;
for(i = 0; i < N; i++){
down += i; // 记录第一列的数字
right = down; // 记录某一行应该从哪个数值开始加
printf("%d ", down); // 打印每一列的第一个数字
for(j = i+1; j < N; j++){
right = right + j+1; // 记录每一行相加后的值
printf("%d",right);
if(j!=N-1) printf(" "); // 最后一个数字后不用空格
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
运行结果:
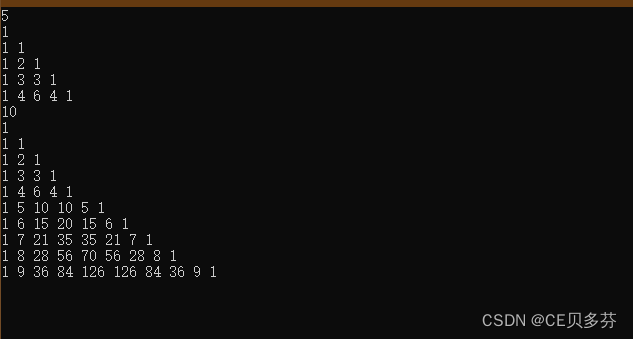
4. 杨辉三角
#include<stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int i,j,n;
int a[100][100];
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
for (i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
a[0][0]=1;
if(i==j||j==0)
a[i][j]=1;
else
a[i][j]=a[i-1][j-1]+a[i-1][j];
printf("%d ",a[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}运行结果:
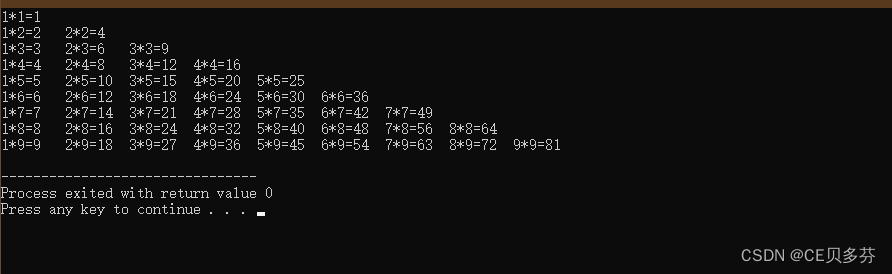
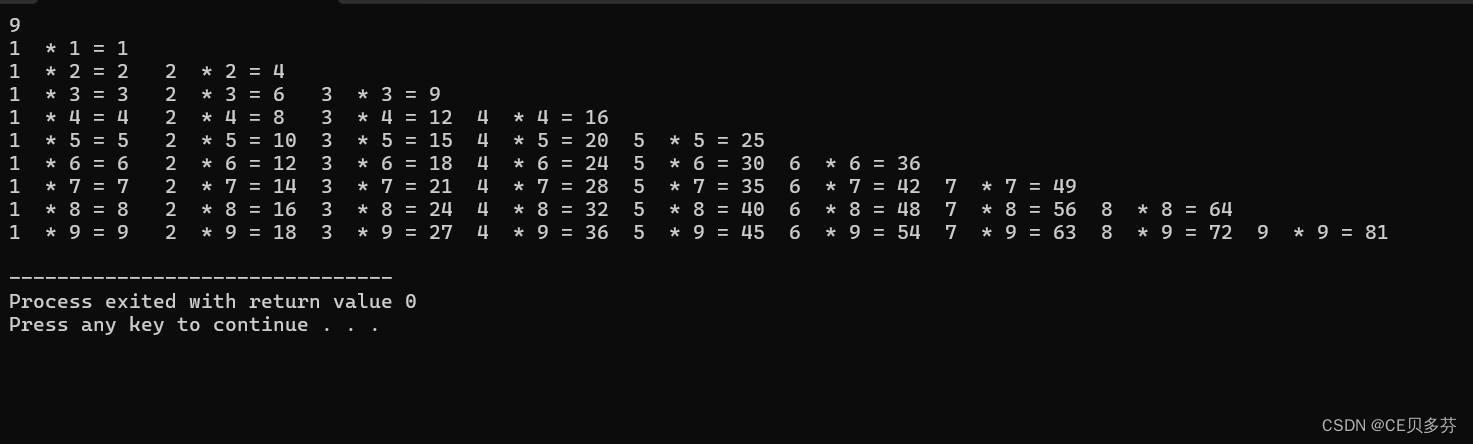
5. 9×9乘法表
说明:就是我们从小背的9×9乘法表
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h> // 万能
#include<string.h>
#include<ctype.h> // 字符串字母大小写函数
#include<iomanip> // 保留小数位数
#include<math.h> // 数学
#include <time.h> // 时间函数库
//clock_t clock(void)
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
for(int i=1;i<10;i++)
{
for( int j=1;j<i+1;j++)
{
cout<<j<<"*"<<i<<"="<<j*i<<"\t";
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}运行结果:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n;
int i = 1,j;
scanf("%d",&n);
while( i <= n ){
j = 1;
while( j <= i ){
printf("%d * %d = %d",j,i,i*j);
if( i*j < 10 ){
printf(" ");
}else{
printf(" ");
}
j++;
}
printf("\n");
i++;
}
return 0;
}运行结果:
6. 水仙花数
说明:
水仙花数(Narcissistic number)也被称为超完全数字不变数(pluperfect digital invariant, PPDI)、自恋数、自幂数、阿姆斯壮数或阿姆斯特朗数(Armstrong number),水仙花数是指一个 3 位数,它的每个位上的数字的 3次幂之和等于它本身。例如:1^3 + 5^3+ 3^3 = 153。
输出100~1000内的水仙花数。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a,b,c;
for(int i=100;i<1000;i++){
a=i/100;
b=i/10%10;
c=i%10;
if(a*a*a+b*b*b+c*c*c==i){
cout<<i<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}运行结果:
do-while循环
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a,b,c;
int num=100;
do{
a=num/100;
b=num/10%10;
c=num%10;
if(a*a*a+b*b*b+c*c*c==num){
cout<<num<<endl;
}
num++;
}while(num<1000);
return 0;
}
运行结果
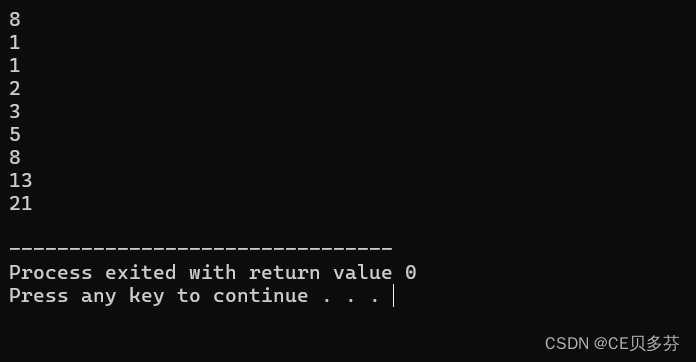
7. 递归--斐波那契数列
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int fib(int n)
{
if(n==0||n==1)
return 1;
else
return fib(n-1)+fib(n-2);
}
int main ()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
cout<<fib(n)<<endl;
return 0;
}
//1 1 2 3 5 8 13运行结果:
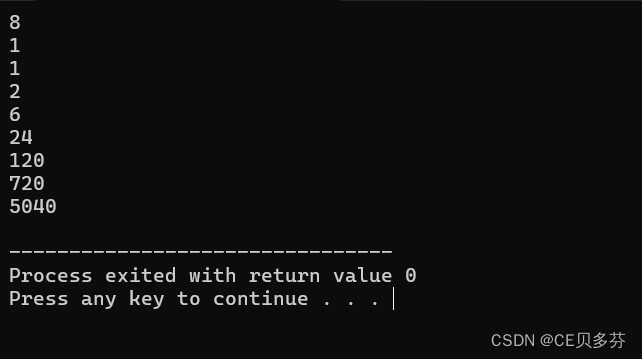
8. 递归--数的阶乘
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
long fac(int n)
{
if(n==0)
return 1;
else
return(n*fac(n-1));
}
int main ()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cout<<fac(i)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}运行结果:
9. 进制转化
常用的八进制,十进制和十六进制的转化
// %d —— 以十进制形式打印一个整型值
// %o —— 八进制
// %x —— 十六进制
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
int num;
scanf("%d", &num);
printf("%o\n", num);
printf("%x\n",num);
return 0;
}运行结果:
10. 输出菱形
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str;
int n;
cin>>str>>n;
//输出上半部分
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
//输出空格
for(int j=0;j<n-1-i;j++){
cout<<" ";
}
//输出字符
for(int k=0;k<i+1;k++){
cout<<str<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
//输出下半部分
for(int i=0;i<=n-1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<i+1;j++){
cout<<" ";
}
for(int k=0;k<n-1-i;k++){
cout<<str<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}运行结果:
二、循环+数组
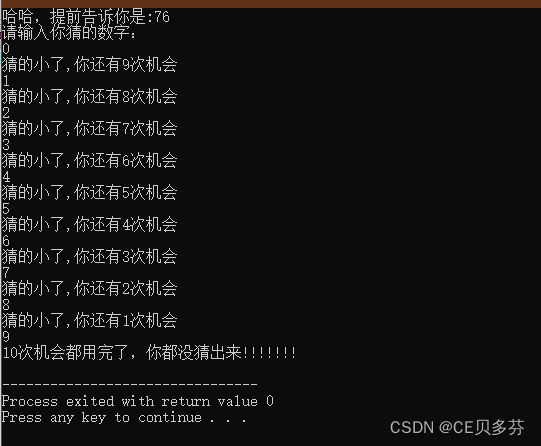
1. while循环猜数组
说明:随机一个100以内的数字,共10次机会,每次猜测都反馈偏大还是偏小,猜对后显示所用次数,10次机会用完后结束。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h> // 万能
#include<string.h>
#include<ctype.h> // 字符串字母大小写函数
#include<iomanip> // 保留小数位数
#include<math.h> // 数学
#include <time.h> // 时间函数库
//clock_t clock(void)
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
int num = rand()%100+1;
cout<<"哈哈,提前告诉你是:"<<num<<endl;
int value;
int count=0;
cout<<"请输入你猜的数字:"<<endl;
while(true)
{
cin>>value;
if(value>num&&count<9)
{
count++;
cout<<"猜的大了,你还有"<<10-count<<"次机会"<<endl;
}
else if(value<num&&count<9)
{
count++;
cout<<"猜的小了,你还有"<<10-count<<"次机会"<<endl;
}
else if(value==num&&count<9)
{
count++;
cout<<"猜对了,用了"<<count<<"次机会"<<endl;
break;
}
else if(count==9||9-count==0)
{
cout<<"10次机会都用完了,你都没猜出来!!!!!!!"<<endl;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
运行结果:
2. for循环敲桌子游戏
说明:0~100内的数字,逢到7的倍数(7,14,21...)或者含有7的数字(17,27,37...)必须用敲桌子代替。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h> // 万能
#include<string.h>
#include<ctype.h> // 字符串字母大小写函数
#include<iomanip> // 保留小数位数
#include<math.h> // 数学
#include <time.h> // 时间函数库
//clock_t clock(void)
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
for(int i=0;i<100;i++)
{
if(i>10)
{
if(i%7==0 || i/10==7 || i%10==7)
{
cout<<"敲桌子"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<i<<endl;
}
}
else
{
if(i%7==0)
{
cout<<"敲桌子"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<i<<endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
运行结果:
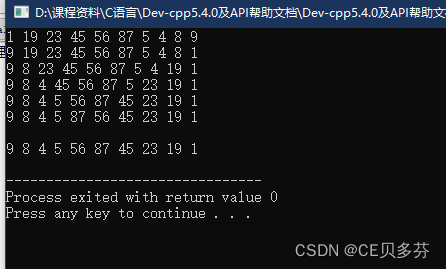
3. 一维数组--元素逆置
说明:将一维数组中的元素排序反转输出
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// 元素逆置
int arr[10]={1,19,23,45,56,87,5,4,8,9};
int start=0;
int end=sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
for(int i=0;i<=end/2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<end;j++){
cout<<arr[j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
int temp=arr[start+i];
arr[start+i]=arr[end-1-i];
arr[end-1-i]=temp;
}
cout<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<end;i++){
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
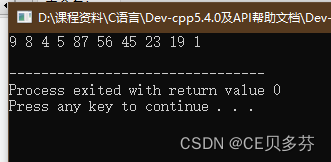
方法二:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// 元素逆置
int arr[10]={1,19,23,45,56,87,5,4,8,9};
int start=0;
int end=sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);// 结束下标
while(start<end-1){
int temp=arr[start];
arr[start]=arr[end-1];
arr[end-1]=temp;
start++;
end--;
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
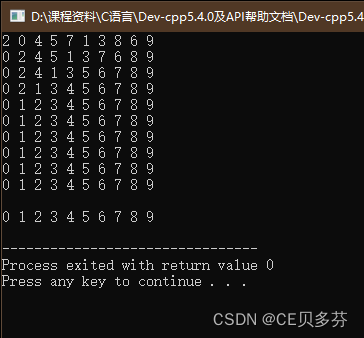
4. 冒泡排序
作用:最常用的排序算法,对数组内元素进行排序
过程:
- 比较相邻的元素。如果第一个比第二个大,就交换他们两个。
- 对每一对相邻元素做同样的工作,执行完毕后,找到第一个最大值。
- 重复以上的步骤,每次比较次数-1,直到不需要比较
图示:
示例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int arr[10]={2,4,0,5,8,7,1,3,9,6};
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
for(int j=0;j<10-i-1;j++){
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]){
int temp=arr[j];
arr[j]=arr[j+1];
arr[j+1]=temp;
}
}
for(int k=0;k<10;k++){
cout<<arr[k]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
三、字符--字符串
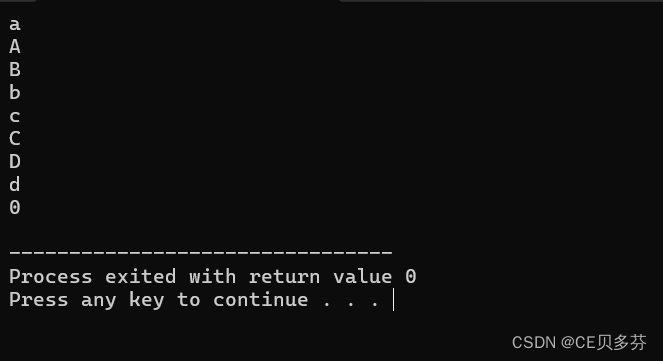
1. 字符的大小写转化(c语言版)
利用ASCLL码对字符进行转化
#include<stdio.h>
int main ()
{
char a[30];
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<30;i++)
{
while(scanf("%c",&a[i])!=EOF)
if(a[i]>='a'&&a[i]<='z')
{
a[i]-=32;
printf("%c",a[i]);
}
else if(a[i]>='A'&&a[i]<='Z')
printf("%c",a[i]+=32);
else if(a[i]=='0'){ // 按0退出
i=31;
break;
}
else
printf("%c",a[i]);
}
return 0;
}运行结果:
四、函数
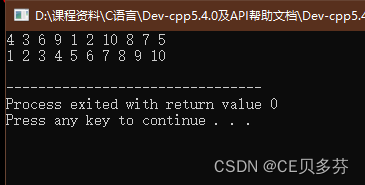
1. 封装一个函数--利用冒泡排序,实现对整型数组的升序排序
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
void bubbleSort(int *arr,int len)
{
for(int i=0;i<len-1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<len-1-i;j++){
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]){
int temp=arr[j];
arr[j]=arr[j+1];
arr[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
}
void printArr(int *arr,int len)
{
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
int arr[10]={4,3,6,9,1,2,10,8,7,5};
// 数组长度
int len=sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
printArr(arr,len);
bubbleSort(arr,len);
printArr(arr,len);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
五、switch--case
1. 模拟计算器(switch case)
利用switch-case,模拟计算器的功能。
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int a,b;
char c;
while(scanf("%d %c %d",&a,&c,&b)!=EOF)
switch(c)// 用于判读符号
{
case '+':
printf("%d%c%d=%d ",a,c,b,a+b);
break;
case '-':
printf("%d%c%d=%d ",a,c,b,a-b);
break;
case '*':
printf("%d%c%d=%d ",a,c,b,a*b);
break;
case '/':
printf("%d%c%d=%d ",a,c,b,a/b);
break;
case '%':
printf("%d%c%d=%d ",a,c,b,a%b);
break;
}
}运行结果:
六、结构体
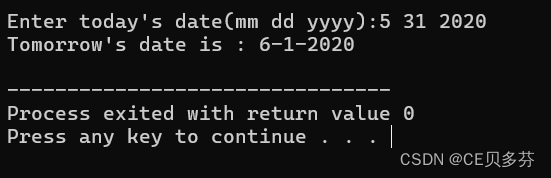
1. 结构体案例:查看明天的日期
说明:结构体中存放年月日三个变量,根据传入的日期,判断明天的日期
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
struct date {
int month;
int day;
int year;
};
bool isleap(struct date d);
int numberofdays(struct date d);
int main (int argc,char const *argv[])
{
struct date today;
struct date tomorrow;
// 定义两个结构体
printf("Enter today's date(mm dd yyyy):");
scanf("%d %d %d",&today.month,&today.day,&today.year);
if( today.day != numberofdays(today) ){
tomorrow.day = today.day + 1;
tomorrow.month = today.month;
tomorrow.year = today.year;
// 普通年份普通月份,日期加一;
}else if( today.month == 12 ){
tomorrow.day = 1;
tomorrow.month = 1;
tomorrow.year = today.year + 1;
// 一年中最后一天,直接到下一年第一天;
}else{
tomorrow.day = 1;
tomorrow.month = today.month +1;
tomorrow.year = today.year;
// 某一年的某月的最后一天;所以第二天是下一个月的第一天;
}
printf("Tomorrow's date is : %i-%i-%i\n",
tomorrow.month,tomorrow.day,tomorrow.year);
return 0;
}
int numberofdays(struct date d)
{
int days;
const int dayspermonth[12] = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if( d.month == 2 && isleap(d) )
// 判断2月是否是闰年;
days = 29;
else
days = dayspermonth[d.month-1]; // 数组从0开始,所以要减一
return days;
}
bool isleap(struct date d)
{
bool leap = false;
if( ( d.year %4 == 0 && d.year %100 ==0 ) || ( d.year %400 ==0 ))
// if语句用于判断是否是闰年;
leap = true;
return leap;
}运行结果:
2. 结构体嵌套结构体
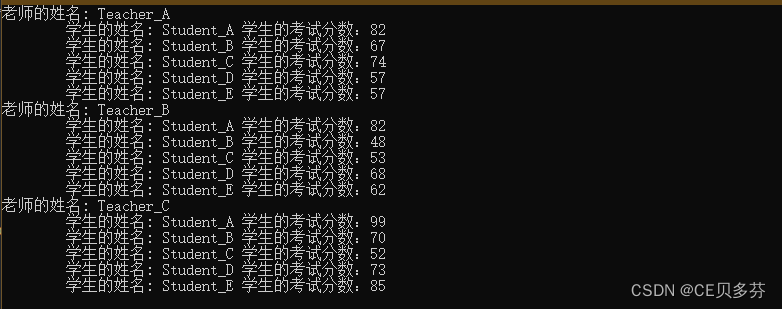
说明:三个老师的结构体数组,下面带五个学生结构体数组,给五个学生打随机分数
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
struct students {
string name;
int score;
};
struct teachers {
string name;
struct students student[5];
};
// 给老师和学生赋值函数
void space(struct teachers teacher[], int len)
{
string nameseed = "ABCDE";
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
teacher[i].name = "Teacher_";
teacher[i].name += nameseed[i];
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
teacher[i].student[j].name = "Student_";
teacher[i].student[j].name += nameseed[j];
int random = rand() % 61 + 40;
teacher[i].student[j].score = random;
}
}
}
void printinfo(struct teachers teacher[], int len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << "老师的姓名: " << teacher[i].name << endl;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
cout << "\t学生的姓名: " << teacher[i].student[j].name
<< " 学生的考试分数:" << teacher[i].student[j].score << endl;
}
}
}
int main()
{
// 随机种子
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
teachers teacher[3];
int len = sizeof(teacher) / sizeof(teacher[0]);
space(teacher, len);
printinfo(teacher, len);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
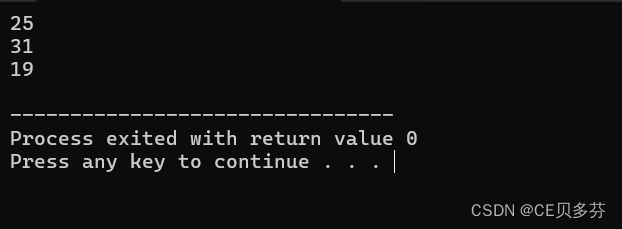
3. 结构体排序
说明:
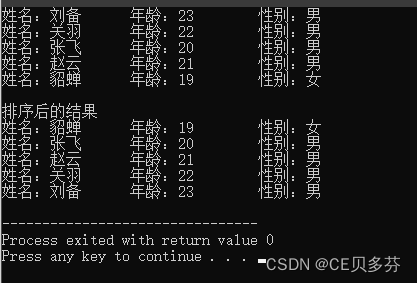
设计一个英雄的结构体,包括成员姓名,年龄,性别;创建结构体数组,数组中存放5名英雄。
通过冒泡排序的算法,将数组中的英雄按照年龄进行升序排列,最终打印排序后的结果。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// 英雄结构体
struct Hero
{
string name; // 姓名
int age; // 年龄
string sex; // 性别
};
// 通过冒泡排序进行排序,按照年龄进行升序排列
void bubbleSort(struct Hero heroArr[],int len)
{
for(int i=0;i<len-1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<len-i-1;j++){
if(heroArr[j].age>heroArr[j+1].age){
struct Hero temp =heroArr[j];
heroArr[j]=heroArr[j+1];
heroArr[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
}
// 输出函数
void printArr(struct Hero heroArr[],int len)
{
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
cout<<"姓名:"<<heroArr[i].name<<"\t年龄:"<<heroArr[i].age<<"\t性别:"<<heroArr[i].sex<<endl;
}
}
int main()
{
struct Hero heroArr[5]={
{"刘备",23,"男"},
{"关羽",22,"男"},
{"张飞",20,"男"},
{"赵云",21,"男"},
{"貂蝉",19,"女"},
};
int len=sizeof(heroArr)/sizeof(heroArr[0]);
printArr(heroArr,len);
// 排序
bubbleSort(heroArr,len);
cout<<endl<<"排序后的结果"<<endl;
printArr(heroArr,len);
return 0;
}
运行结果: