本章将对springboot的数据库访问进行讲解。
3.1 springboot 数据访问概述
SpringData是spring提供的一个用于简化数据库访问,支持云服务的开源框架。能让我们快速简单地访问数据库地数据。springboot采用整合springdata的方式统一处理数据访问层,通过添加大量的自动配置,引入各种数据访问的模板,以及统一的Repository接口,从而达到简化数据访问层的操作。
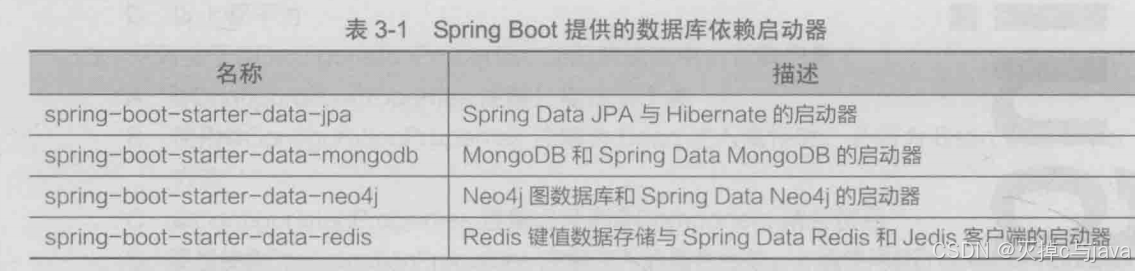
springdata提供啦多种类型数据库支持,springboot对其支持的数据库进行啦整合管理,提供对应的依赖启动器,如下表:
mybatis是操作数据库的框架,springboot没有给它的场景依赖,不过mybatis自己适配啦springboot,提供:mybatis-spring-boot-starter依赖启动器,实现数据访问操作。
3.2springboot整合mybatis
mybatis是优秀的持久层框架,支持定制化sql,存储过程以及高级映射,避免啦很多麻烦。mybatis可以用简单的xml或者注解配置和映射原生信息,将接口和java的pojos(普通java对象),映射成数据库的记录。
3.2.1 基础环境搭建
springboot与数据访问框架(mybatis)的整合非常简单,引入对应的依赖启动器,并且进行数据库相关参数设置就可以啦。下面我们来实操看:
1.数据准备
我们先新建springbootdata数据库,数据库里创建t_article和t_coomment,并且插入测试数据:
create DATABASE springbootdata;
USE springbootdata;
#创建t_article并插入相关数据
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS t_article;
#构建表t_article
CREATE TABLE t_article(
id int(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT cOMMENT '文章id',
title varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '文章标题',
content longtext COMMENT '文章内容',
PRIMARY KEY(id)
)ENGINE=InnODB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=UTF8;
INSERT INTO t_article VALUES('1','Spring Boot基础入门','从入门到精通讲解.');
INSERT INTO t_article VALUES('2','Spring Cloud基础入门','从入门到精通讲解..');
#构建表t_comment
CREATE TABLE t_comment(
id int(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '评论i',
content longtext COMMENT '评论内容',
author varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '评论作者',
a_id int(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '关联的文章id',
PRIMARY KEY(id)
)ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO t_comment VALUES ('1','很全、很详细','狂奔的蜗牛','1');
INSERT INTO t_comment VALUES ('2','赞一个','tom','1');
INSERT INTO t_comment VALUES ('3','很详细','tom2','1');
INSERT INTO t_comment VALUES ('4','赞','张山','1');
INSERT INTO t_comment VALUES ('5','很不错','张扬','2');2创建项目引入对应的启动器
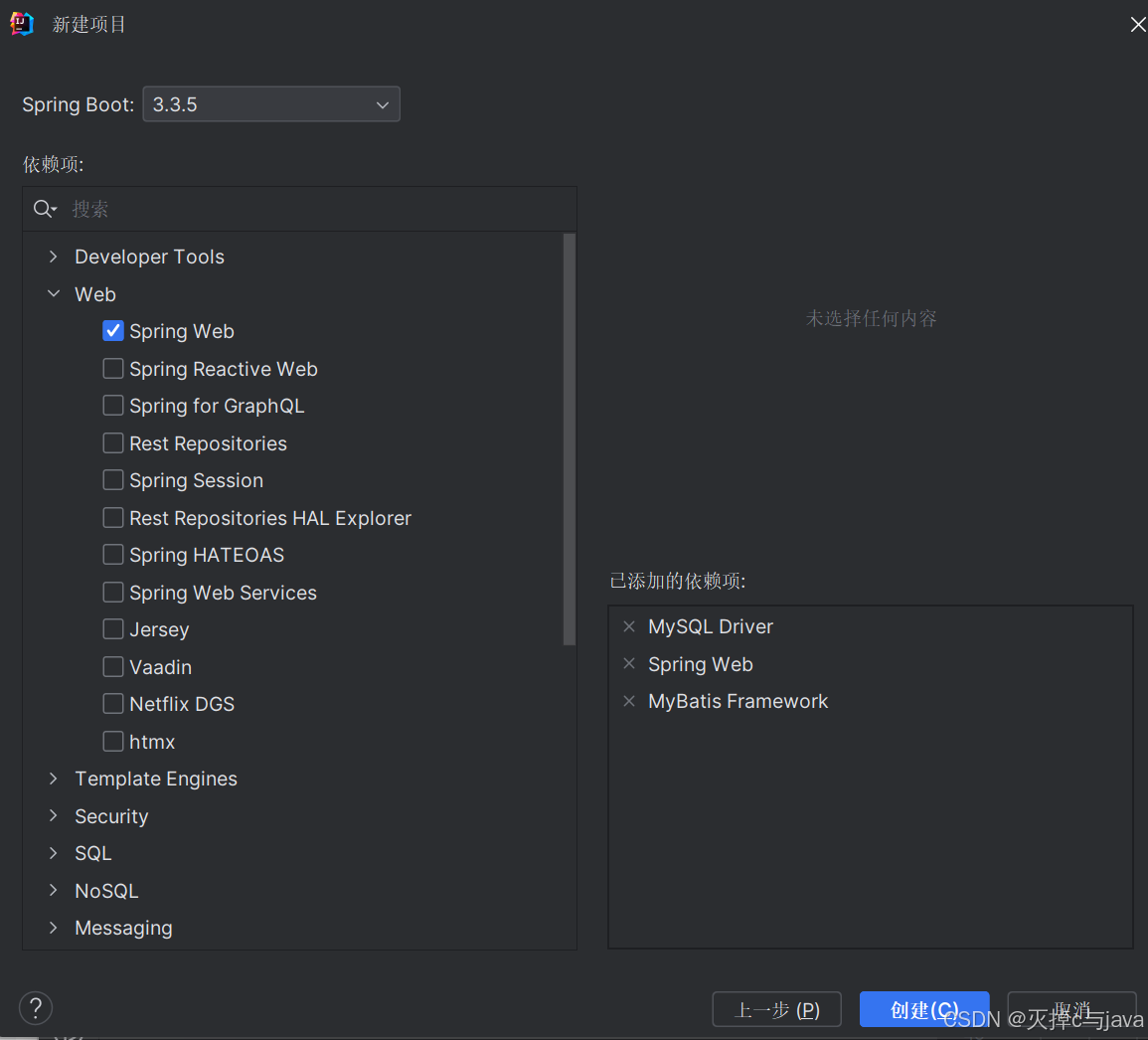
创建springboot项目时,选中依赖启动器:mysql和mybatis,springweb。
编写数据库的实体类:
package com.waiguoyu.chapter02.domain;
public class Comment {
private String content;
public Integer id;
public Integer aId;
private String author;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Comment{" +
"content='" + content + '\'' +
", id=" + id +
", aId=" + aId +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
'}';
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Integer getaId() {
return aId;
}
public void setaId(Integer aId) {
this.aId = aId;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
}
package com.waiguoyu.chapter02.domain;
import java.util.List;
public class Article {
private Integer id;
private String title;
private String content;
private List<Comment> commentsList;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Article{" +
"id=" + id +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
", commentsList=" + commentsList +
'}';
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public List<Comment> getCommentsList() {
return commentsList;
}
public void setCommentsList(List<Comment> commentsList) {
this.commentsList = commentsList;
}
}
这两个类中的属性分别对应数据库表中的字段。
3.编写配置文件
在全局配置文件中编写对应的mysql数据库连接配置:
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springbootdata?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
//数据库账号密码吗
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
这里的账号密码是 自己电脑数据库的账号密码。
数据库源选择配置:这里使用阿里巴巴的Druid数据源。引入启动依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.8</version>
</dependency>这个数据源启动器已经初始化啦一些运行参数,如果需要修改运行参数,要在配置文件中需改:
#添加并配置第三方数据源
spring.datasource,type = com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.initialSize=20
spring.datasource.minIdle=10
spring.datasource.maxActive=100上面实例啦修改数据源的:类型,初始化连接数,最小空闲数,最大连接数属性。如果需要修改其他的可以参照这样修改。
添加上述配置之后,springboot无法识别,需要编写自定义配置类,将这些属性注入到Druid数据源属性中。
注入方式完成啦第二章的目标就可以会啦:
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.waiguoyu.chapter02.mapper.CommentMapper;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration//标识该类为配置类,相当于创建啦xml配置文件
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Bean//向xml文件里面注入一个实例对象
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")//将全局配置文件中以spring.datasouce开头的注入到 该方法的 返回的 对象的属性中
public DataSource getDataSource() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
}上边不配置这些操作也可以进行,只是为啦模拟实际开发而已。
3.2.2 使用注解的方式整合mybatis
上面是环境搭建,在这里才是整合。
第一步:创建Mapper接口文件:
创建mapper包,然后创建对数据库表进行数据操作的接口:CommentMapper,
import com.waiguoyu.chapter02.domain.Comment;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
@Mapper//标识该类是mybatis接口文件,并且保证springboot能够扫描到它
public interface CommentMapper {
//接口内部通过注解和sql语句完成对表的增删改查
@Select("SELECT * FROM t_comment WHERE id= #{id}")
public Comment findById(Integer id);
@Insert("INSERT INTO t_comment(content,author,a_id)" + "values (#{content},#{author},#{aId})")
public int insertComment(Comment comment);
@Update("UPDATE t_comment set content = #{content} WHERE id = #{id}")
public int updateComment(Comment comment);
@Delete("DELETE FROM t_comment WHERE id=#{id}")
public int deleteComment(Integer id);
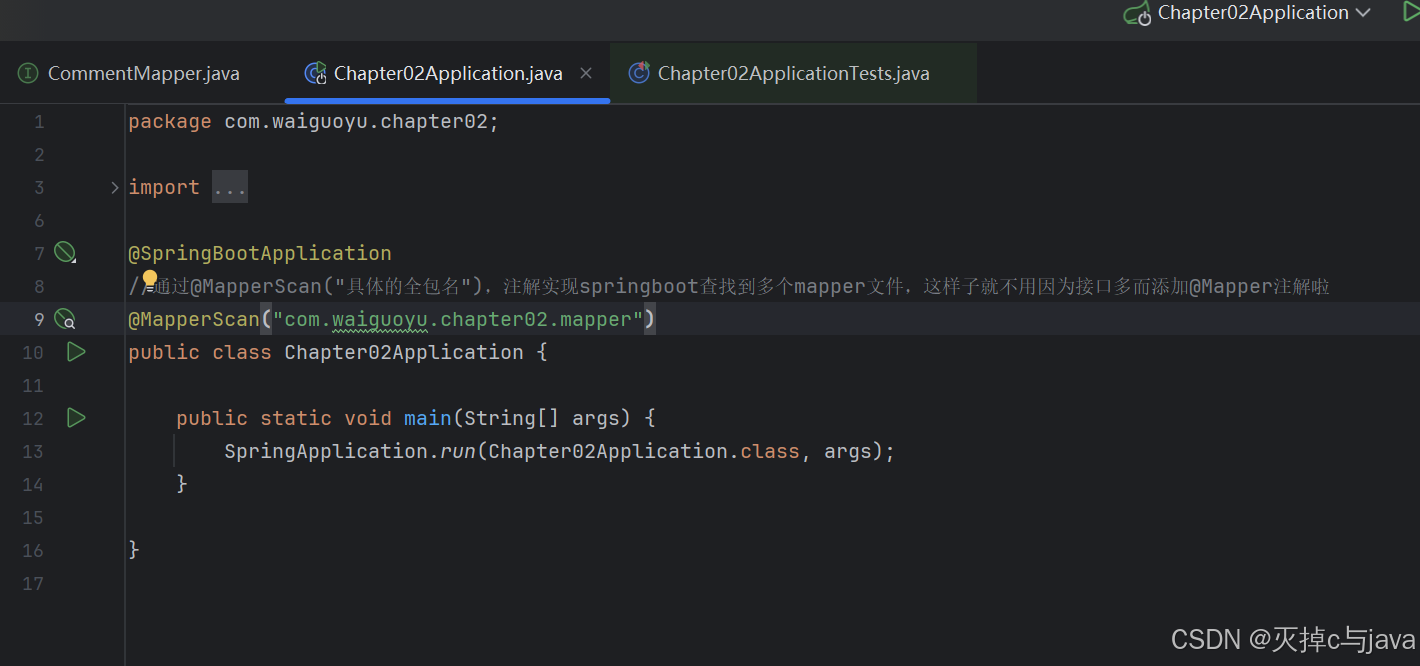
}注意:如果接口或者业务过多,需要重复添加大量的@Mapper注解,我们可以在sprin gboot启动类上添加:@MapperScan(“xxx”)注解,这样就不需要逐个添加@Mapper注解啦。xxx表示需要指定的具体包名。例如:
第二步:编写单元测试进行接口测试
在测试类引入Cm+ommentMapper接口,测试如下:
package com.waiguoyu.chapter02;
import com.waiguoyu.chapter02.domain.Comment;
import com.waiguoyu.chapter02.mapper.CommentMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
class Chapter02ApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
}
@Autowired
private CommentMapper commentMapper;
@Test
public void slectCommenttest(){
Comment comment = commentMapper.findById(1);
System.out.println(comment);
}
}
到这里就映入成功啦。
测试结果有一个数据没有映射成功,因为编写的实体类那个属性使用驼峰命名法,将数据表中的a_id设计成啦aId属性,所有无法正常映射。解决这个问题:
在springboot全局配置文件添加驼峰命名匹配映射配置就可以啦:
#开启驼峰命名匹配映射
mybatis.configuration.mapUnderscoreToCamelCase=true3.2.3 使用配置文件的方式整合Mybatis
通过案例来演示如何使用配置文件xml的方式整和mybatis
1.创建Mapper接口文件,用于操作数据库表:t_article
import com.waiguoyu.chapter02.domain.Article;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface ArticleMapper {
//查询数据
public ArticleMapper selectArticle(Integer id);
//更新数据操作
public int updataArticle(Article article);
}
这里声明啦查询和更新操作两个方法。
2.创建xml文件,创建一个统一映射文件ArticleMapper.xml:
这里是mybatis映射文件中的具体写法,详细请看mybaits官方文档。
3.配置xml映射文件路径:
上面的xml文件springboot无法扫描到,需要在全局配置文件里面添加这个映射文件路径的配置,同时还要添加实体类别名映射路径:
如果xml文件里面映射文件中实体类的数据映射配置,使用的是全路径名称,就不需要配置别名路径。
4.编写测试类进行测试:
实际开发中会混合使用这两种整合mybatis的方式。
3.3 springboot整合jpa
jpa:java持久化api,持久化规范,它提供:对象/关系映射 的 工具,管理java中的关系型数据库。
目的:简化持久化开发工作,整合orm(对象/关系映射)技术。
3.3.1 springData jap介绍
它是spring在Orm框架和jpa规范的基础上封装的一套jpa应用框架,让开发者用较少的代码完成数据的操作。我们先熟悉spring data jpa 的基本使用进行简单介绍
1.编写orm实体类
使用实体类前先编写实体类和数据表进行映射,并配置好映射关系,应为spring data jpa针对orm关系的数据进行的操作。
2.编写Repository接口
根据不同的 表数据操作 编写对应的Repository接口,并且根据需求编写对应的数据操作方法。
package com.waiguoyu.chapter02.mapper;
import com.waiguoyu.chapter02.domain.Discuss;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Modifying;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.List;
public interface DiscussRepository extends JpaRepository<Discuss, Integer> {
//基本的查询方法,不用注解,方法名是jpa支持的 方法名关键字 查询方法,方法的作用:查询author非空的Discuss数据
public List<Discuss> findByAuthorNotNull();
//该方法通过@Query注入sql语句,用于通过分页查询,查询discuss数据
@Query("SELECT c from t_comment c where c.aId=?1")
public List<Discuss> getDiscussPaged(Integer aid, Pageable pageable);
//与上面的方法同,nativeQuery = true 用来定义:编写原生的sql语句,
@Query(value = "SELECT * from t_comment where c.aId=?1",nativeQuery = true)
public List<Discuss> getDiscussPaged2(Integer aid, Pageable pageable);
@Transactional//支持事务管理,也就是要么都成功,如果更新数据不成功就退回全部操作,防止数据的丢失
@Modifying//支持数据变更
//通过注解注入sql语句,更新和删除需要配合使用上面两个注解。
@Query("update t_comment c set c.author = ?1 where c.id=?2")
public int updateDiscuss(String author,Integer id);
@Transactional
@Modifying
@Query("delete t_comment c where c.id=?1")
public int deleteDiscuss(Integer id);
}
下面对编写这种Repository接口进行具体的讲解:
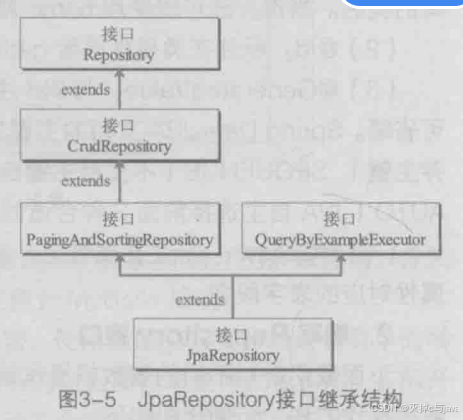
1.编写这类接口时,必须继承 XXRepository<T,ID>接口,T:表示要操作的实体类,ID表示实体类的主键的类型。上面的案例继承啦:JpaRepository接口。
下面讲解JpaRepository继承结构中的涉及到的接口:
1.repository接口没有方法,是spring Data JPA提供的用于自定义repository接口的顶级父接口。
2.CrudRepository接口:继承啦repository接口,包含一些基本的CRUD方法(比如)
3.PagingAndSortingRepository 接口继承CrudRepository接口,并且提供啦分页和排序两个方法。
4.QueryByExampleExecutor接口:能够进行条件封装查询,能通过Example实例执行复杂的条件查询。
5.JpaRepository接口:同时继承PagingAndSortingRepository 接口和QueryByExampleExecutor接口,并且还拥有一些数据操作方法,自定义Repository接口文件时一般会直接继承JpaRepository接口。
简而言之就是:JpaRepository接口接口有:一些基本的CRUD方法,分页和排序两个方法。能够进行条件封装查询,能通过Example实例执行复杂的条件查询。
使用springdatajpa进行数据操作时,可以有多种实现方式,下面进行说明:
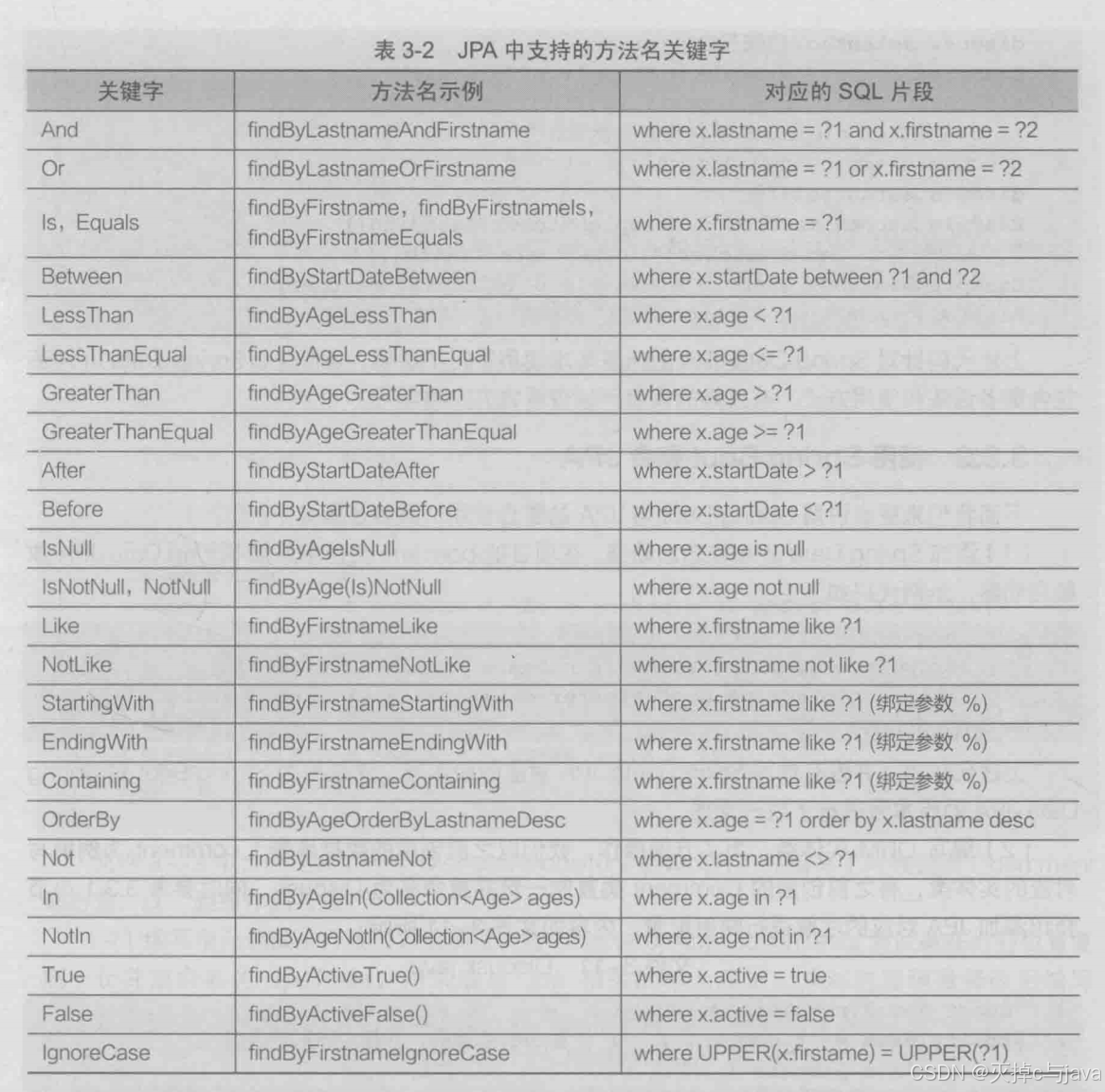
下图就是对应的springData Jpa中支持的方法名关键字对应的sql语句:
在自定义的Repository接口方法中,数据变更的操作方法上必须使用那两个注解(代码案例讲解那),不然会报错,如果在调用Repository接口的方法的service类上已经添加啦事务处理的注解
就不用在Repository接口上添加啦。
jpa还支持使用Example实例进行复杂的条件查询,spring Data Jpa的基本使用进行了解,详细可以去官方文档进行学习。
3.3.2 使用springboot整合jpa
了解完jpa之后,我们具体来整合jpa
1.在pom文件添加其依赖:
<!--springdatajpa的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>2.编写ORM实体类:
package com.waiguoyu.chapter02.domain;
import jakarta.persistence.Column;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
//定义springboot data jpa 实体类,将该类与数据库表进行映射
@Entity(name="t_comment")//标注一个 与数据库做映射的 实体类,用name属性指定映射的数据库表
public class Discuss {
@Id//可以用在类属性或者get方法上,用于绑定数据库表的主键
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)//与@id一起使用,确定主键的生成策略,比如TABLE;用一个特定的数据库表格来保存主键
// IDENTITY:主键自增,SEQUENCE:不支持主键自增的主键的生成策略,AUTO:由jpa自主选择前三个策略中的一个
private Integer id;
private String content;
private String author;
@Column(name = "a_id")//标注属性,当类属性和数据库表的对应字段名字不一样,就是用它来绑定
private Integer AId;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Discuss{" +
"id=" + id +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", AId=" + AId +
'}';
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public Integer getAId() {
return AId;
}
public void setAId(Integer AId) {
this.AId = AId;
}
}
3.编写respositry接口,类同上边得案例。
4.编写单元测试:
5.整体得测试:
3.4springboot整合redis
非关系型数据库的整合。
3.4.1redis介绍
redis介绍另看文章,接下来就i安装redis。
redis只需要解压缩好文件,运行redis-server.exe就启动可以啦。
再去下载redis desktop manager客户端连接用户端就可以啦。打开客户端根据下面的操作进行即可。
3.4.2 使用springboot整合redis
1.添加springbootdataredis依赖:
<!--redis的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>2.编写对应的实体类:
package com.waiguoyu.chapert03.domain;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisHash;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.index.Indexed;
import java.util.List;
@RedisHash("persons")//指定操作实体类在redis数据库中的存储空间,该类的数据操作都存储在redis数据库中名为persons的存储空间下
public class Person {
@Id //标识实体类主键。也可以在数据存储时指定id
private String id;
@Indexed //标识对应属性在redis数据库中生成二级索引。索引名称就是属性名
private String firstname;
@Indexed
private String lastname;
private Address address;
private List<Family> familyList;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", firstname='" + firstname + '\'' +
", lastname='" + lastname + '\'' +
", address=" + address +
", familyList=" + familyList +
'}';
}
public Person() {
}
public Person(String id, String firstname, String lastname, Address address, List<Family> familyList) {
this.id = id;
this.firstname = firstname;
this.lastname = lastname;
this.address = address;
this.familyList = familyList;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public List<Family> getFamilyList() {
return familyList;
}
public void setFamilyList(List<Family> familyList) {
this.familyList = familyList;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getLastname() {
return lastname;
}
public void setLastname(String lastname) {
this.lastname = lastname;
}
public String getFirstname() {
return firstname;
}
public void setFirstname(String firstname) {
this.firstname = firstname;
}
}
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.index.Indexed;
public class Family {
@Indexed
private String type;
@Indexed
private String username;
省略get,set,构造函数,以及tostringpublic class Address {
@Indexed
private String city;
@Indexed
private String country;3.编写Repository接口:
springboot给常用数据库提供啦一些自动化配置,
这些操作与上一节的一样。可以使用方法名关键字进行数据操作。
package com.waiguoyu.chapert03.repository;
import com.waiguoyu.chapert03.domain.Person;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import java.util.List;
//继承的CrudRepository接口定义啦很多查询方法,jpaRepository是springboot的jpa特有的,如果想使用这个接口操作redis数据库,可以同时导入redis和
//jpa依赖。
public interface PersonRepository extends CrudRepository<Person, Long> {
List<Person> findByLastName(String lastName);
Page<Person> findPersonByLastName(String lastName, Pageable page);
List<Person> findByFirstNameAAndLastname(String firstName, String lastName);
List<Person> findByAddress_City(String city);
List<Person> findByFamilyList_Username(String username);
}
4.连接redis数据库:
在配置文件配置信息:
#服务器连接密码默认为空 spring.data.redis.password= #redis服务器地址 spring.data.redis.host=localhost #连接的端口号 spring.data.redis.port=6379
也可以单独添加相关配置,跟之前的一样。
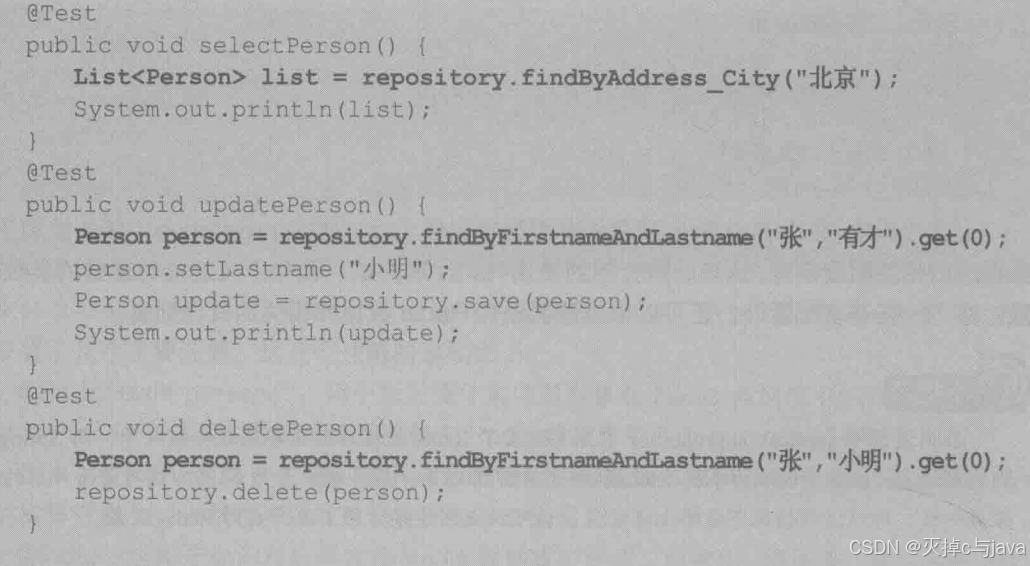
4.编写单元测试进行测试:
@Autowired
private PersonRepository personRepository;
@Test
public void savePerson() {
Person person = new Person("张","有才");
Person person1 = new Person("张","有才123");
Address address=new Address("北京","chinen");
person.setAddress(address);
//创建并添加家庭成员
List<Family> families=new ArrayList<>();
Family fan=new Family("父亲","母亲");
families.add(fan);
person.setFamilyList(families);
// 向redis数据库添加数据
Person save=personRepository.save(person);
Person save2=personRepository.save(person1);
System.out.println(save);
System.out.println(save2);
}bug:我这里打的代码连接不上redis数据库。
目前就是redis整合springboot以及进行数据库操作的方式啦。想了解更多redis知识请看官方文档。