一、基础语法
1、代码块靠缩进
-
Python 不用
{},而是用 4个空格或 Tab 表示代码属于哪个块。
if 3 > 2:
print("对了!") # 缩进表示属于 if 的代码2、注释
-
单行注释用
#,多行用'''注释'''或"""注释"""。
# 这是单行注释
'''
这是
多行注释
'''二、变量和数据类型
1、变量直接赋值
-
不用声明类型,直接写名字和值。
name = "小明" # 字符串
age = 18 # 整数
height = 1.75 # 浮点数
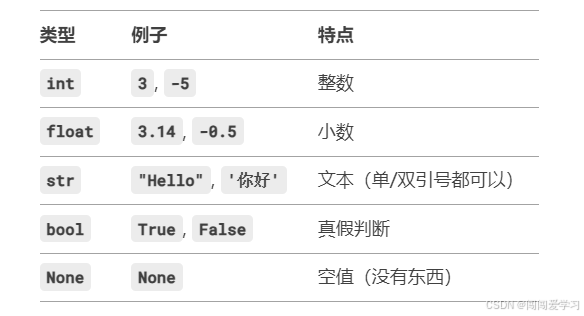
is_student = True # 布尔值(True/False)2、常见数据类型
三、运算符
1、算术运算符
print(3 + 2) # 5(加)
print(5 - 3) # 2(减)
print(2 * 3) # 6(乘)
print(10 / 3) # 3.333...(除)
print(10 // 3) # 3(整除,只保留整数部分)
print(10 % 3) # 1(取余数)
print(2 ** 3) # 8(2的3次方)2、比较和逻辑运算符
-
比较:
==(等于)、!=(不等于)、>、<、>=、<= -
逻辑:
and(与)、or(或)、not(非)
print(3 == 3) # True
print(3 > 5 or 5 > 3) # True(只要有一个对就True)
print(not False) # True四、控制流程
1、条件判断(if-elif-else)
score = 85
if score >= 90:
print("优秀")
elif score >= 60:
print("及格")
else:
print("不及格")2、循环
-
for 循环:遍历列表、字符串等
for i in [1, 2, 3]:
print(i) # 输出 1, 2, 3-
while 循环:条件满足时重复执行
count = 0
while count < 3:
print(count)
count += 1 # 输出 0, 1, 2五、数据结构
1、列表(List)
-
可变的有序集合,用
[]表示。
fruits = ["苹果", "香蕉", "橘子"]
fruits.append("葡萄") # 添加元素
print(fruits[0]) # 输出 "苹果"2、字典(Dict)
-
键值对集合,用
{}表示。
person = {"name": "小明", "age": 18}
print(person["name"]) # 输出 "小明"3、元组(Tuple)
-
不可变的有序集合,用
()表示。
colors = ("红", "绿", "蓝")
print(colors[1]) # 输出 "绿"4、集合(Set)
-
无序且不重复的元素集合,用
{}或set()创建。
nums = {1, 2, 3}
nums.add(3) # 不会重复添加
print(nums) # {1, 2, 3}六、函数
1、定义函数
def add(a, b):
return a + b
print(add(2, 3)) # 输出 52、默认参数
-
参数可以设置默认值,调用时可不传。
def greet(name="朋友"):
print(f"你好,{name}!")
greet() # 输出 "你好,朋友!"
greet("小明") # 输出 "你好,小明!"七、常用技巧
1、文件读写
# 写入文件
with open("test.txt", "w") as f:
f.write("Hello World")
# 读取文件
with open("test.txt", "r") as f:
content = f.read()
print(content) # 输出 "Hello World"2、异常处理
try:
num = int(input("输入一个数字:"))
except ValueError:
print("这不是数字!")