1.问题描述
旅行商人要拜访n个城市,他必须选择所要走的路径,路径的限制是每个城市只能拜访一次,而且最后要回到原来出发的城市。路径的选择目标是要求得的路径路程为所有路径之中的最小值。矩阵cMatrix[i][j]代表从城市i到城市j的开销。
2.回溯法解题
解题思路
1.设置起始节点,开始递归(无论从哪个节点开始,最终开销都是一样的)
2.开始递归,判断是否经过所有城市
若已经经过所有城市
若可回到起始节点,判断开销是否小于已知的最小开销
若小于已知的最小开销,更新最小开销并更新最佳路径
若不小于已知的最小开销,什么也不做,返回上一层递归
若不可回到起始节点,什么也不做返回上一层递归
若尚未经过所有城市,从城市列表中选取第一个尚未经过且可达的城市更新临时变量并进入下一层递归
3.结束递归,输出结果
实现代码
package tsp;
/**
* 回溯法解TSP问题
* @author lzy
*
*/
public class TSPBack {
private int NoEdge = -1;
/* 邻接矩阵 */
private int[][] cMatrix;
/* 存储当前代价 */
private int cost = 0;
/* 当前最优代价 */
private int bestCost = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
/* 当前解 */
private int[] currentPath;
/* 当前最优解 */
private int[] bestPath;
/* 城市顶点个数 */
private int num = 0;
/**
* 回溯法遍历所有走法
*
* @param i 代表出发城市
* @param index 代表当前已经到达的城市个数,即当前解x的下标
*/
private void backtrack(int i, int index) {
/* index=n代表所有城市都走过了,进行代价判断 */
if (index == num) {
currentPath[index] = i;
/* 可以回到起点 */
if (cMatrix[currentPath[num]][currentPath[1]] != this.NoEdge) {
cost += cMatrix[currentPath[num]][currentPath[1]];
/* 若当前代价比已知的最优解小 */
if (cost < this.bestCost) {
/* 更新最优代价的值 */
this.bestCost = cost;
/* 更新最优路径 */
for (int j = 1; j <= index; j++) {
this.bestPath[j] = this.currentPath[j];
}
}
/* 不在继续往下递归,返回上一层 */
cost -= this.cMatrix[this.currentPath[this.num]][this.currentPath[1]];
}
} else {
/* 保存当前到达的城市 */
currentPath[index] = i;
/* 进行下一次递归 */
for (int j = 1; j <= this.num; j++) {
/* 判断是否重复城市 */
if (check(j, index + 1)) {
/* 判断能否到达 */
if (this.cMatrix[this.currentPath[index]][j] != this.NoEdge) {
/* 进入递归,记录到达代价 */
cost += this.cMatrix[this.currentPath[index]][j];
backtrack(j, index + 1);
/* 退出递归,清除到达代价 */
cost -= this.cMatrix[this.currentPath[index]][j];
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 判断当前点是否已经到达过
*
* @param pos 当前待判断城市节点
* @param index 当前已经到达过的城市个数
* @return 判断结果
*/
public boolean check(int pos, int index) {
/* 检查当前路径中是否有该节点 */
for (int i = 1; i < index; i++) {
if (pos == this.currentPath[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 获取问题的解
* @param cMatrix
* @param num
*/
public void solute(int[][] cMatrix, int num) {
this.num = num;
this.currentPath = new int[num + 1];
/* 起点 */
int start = 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= num; i++)
this.currentPath[i] = i;
this.bestPath = new int[num + 1];
this.cMatrix = cMatrix;
this.backtrack(start, 1);
this.printPath();
}
/**
* 输出最优路径
*/
public void printPath() {
System.out.print("The best path:");
for (int i = 1; i <= this.num; i++) {
System.out.print(this.bestPath[i] + "->");
}
System.out.println(this.bestPath[1]);
}
public int getBestCost() {
return bestCost;
}
public void setBestCost(int bestCost) {
this.bestCost = bestCost;
}
}
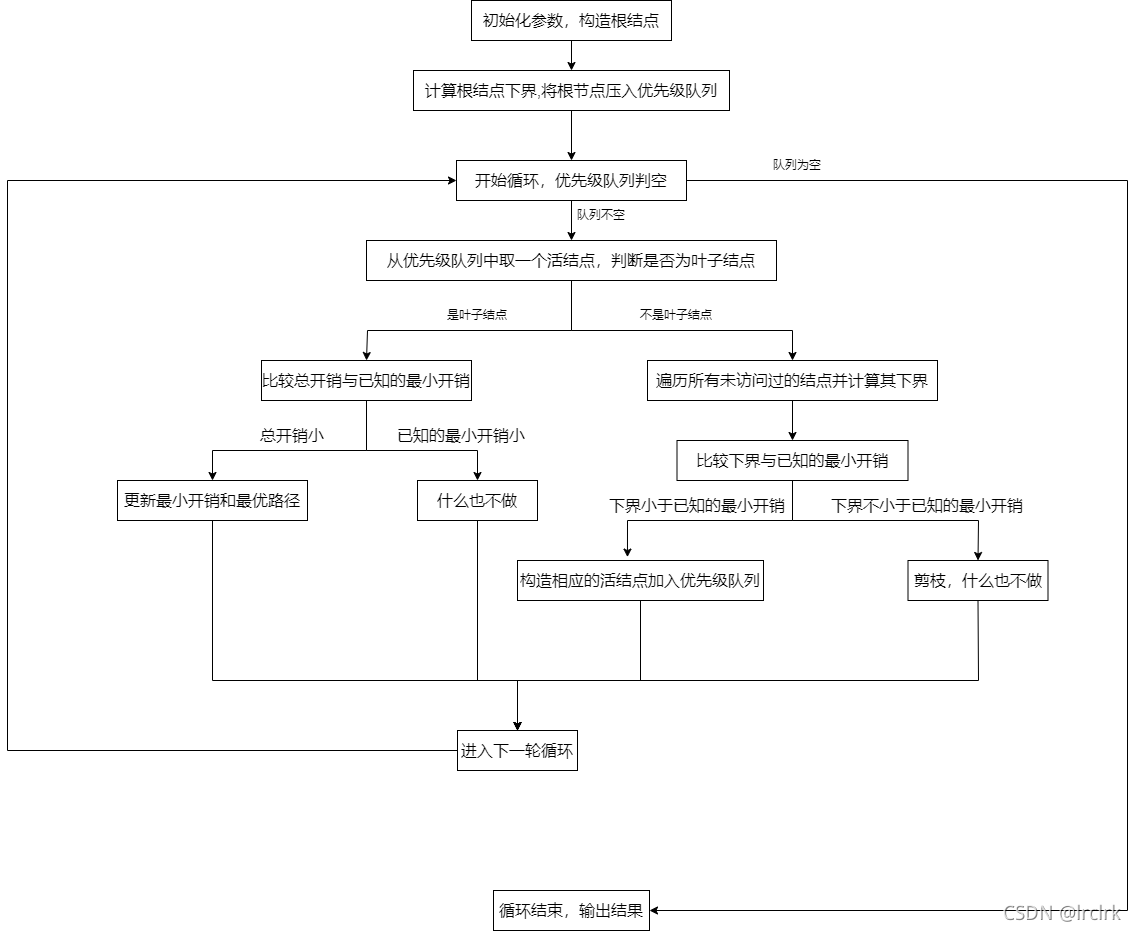
3.分支定界法
解题思路
1.初始化参数,构造根结点,以第一个城市作为出发点
2.计算根结点下界,下界计算函数描述如下: 获取已经走过的城市的边的集合,划去开销矩阵中这些边对应点所在的行和列,计算这些边的开销之和得sum1。在划去行列的矩阵中取每一行的最小值相加得sum2.返回sum1+sum2即为结点下界。
3.将根节点压入优先级队列
4.开始循环,优先级队列判空
若为空,结束循环
若不空,从优先级队列中取一个活结点,判断是否为叶子结点。
若为叶子结点,比较总开销与已知的最小开销
若总开销小于已知的最小开销,更新最小开销和最优路径
若总开销不小于已知的最小开销,什么也不做
若不为叶子结点,遍历所有未访问过且可达的结点并计算其下界
若下界小于已知的最小开销,构造相应的活结点加入优先级队列
若下界不小于已知的最小开销,剪枝
进入下一轮循环
5.结束循环,输出结果
实现代码
package tsp;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.Vector;
/**
* 分支限界法解TSP问题
*
* @author lzy
*
*/
public class TSPBB4 {
/* 表示没有边 */
private int NoEdge = -1;
/* 当前最小代价 */
private int minCost = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
/* 从大到小排序,开销越大的越先出队 */
Comparator<Node> cmp = new Comparator<Node>() {
public int compare(Node node1, Node node2) {
return node2.lcost - node1.lcost;
}
};
/* 优先级队列,存储活节点 */
private PriorityQueue<Node> queue = new PriorityQueue<Node>(100, cmp);
/* 最优路径 */
private Vector<Integer> bestPath;
public int getMinCost() {
return minCost;
}
public void setMinCost(int minCost) {
this.minCost = minCost;
}
public static class Node {
/* 城市排列 */
Vector<Integer> cityArrange = new Vector<Integer>();
/* 代价的下界 */
int lcost;
/* 0-level的城市是已经排好的,level代表已经访问过的城市个数 */
int level;
public Node(Vector<Integer> cities, int lcost, int level) {
cityArrange.addAll(0, cities);
this.lcost = lcost;
this.level = level;
}
}
/**
* 计算部分解的下界.
*
* @param cityArrange 城市的排列
*
* @param level 1-level的城市是已经排好的
* @param cMatrix 邻接矩阵,第0行,0列不算
*
* @exception IllegalArgumentException
*/
public int computeLB(Vector<Integer> cityArrange, int level, int[][] cMatrix) {
int cost = 0;
int length = cityArrange.size();
int temp;
/* 加上已有开销 */
for (int i = 1; i < level; i++) {
cost += cMatrix[cityArrange.get(i)][cityArrange.get(i + 1)];
}
/* 矩阵中经过边对应的点所在的行列需划去 */
Set<Integer> row = new HashSet<Integer>();
Set<Integer> column = new HashSet<Integer>();
for (int i = 1; i < level; i++) {
row.add(cityArrange.get(i));
}
for (int i = 2; i <= level; i++) {
column.add(cityArrange.get(i));
}
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
/* 不在已经过边对应的点所在的行列中 */
if (!row.contains(new Integer(i))) {
temp = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 1; j < length; j++) {
if (!column.contains(new Integer(j)) && cMatrix[i][j] != this.NoEdge) {
/* 取该行的最小值 */
if (temp > cMatrix[i][j]) {
temp = cMatrix[i][j];
}
}
}
/* 不为死路 */
if (temp != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
cost += temp;
}
}
}
return cost;
}
/**
* 计算TSP问题的最小代价的路径.
*
* @param cMatrix 邻接矩阵,第0行,0列不算
* @param n 城市个数.
* @exception IllegalArgumentException
*/
public int solute(int[][] cMatrix, int n) {
/* 构造根节点 */
/* 城市排列 */
Vector<Integer> cityArrange = new Vector<Integer>();
/* 空出一个城市,与cMatrix一致 */
cityArrange.add(0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cityArrange.add(i);
}
/* 1-level的城市是已经排好的 */
int level = 1;
/* 代价的下界 */
int lcost = computeLB(cityArrange, level, cMatrix);
this.bestPath = cityArrange;
/* 构造根结点,以第一个城市作为出发点 */
Node node = new Node(cityArrange, lcost, level);
Node temp = null;
queue.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
node = queue.poll();
/* 若结点为叶子结点 */
if (node.level == n) {
/* 若总开销小于已知最小开销,则更新最小开销并记录最佳路径 */
if (node.lcost < this.minCost) {
this.minCost = node.lcost;
this.bestPath = node.cityArrange;
}
} else {
/*
* 若不是叶子结点,遍历所有未访问过的结点 下界小于已知最小开销的构造结点加入优先级队列
*/
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!this.hasVisited(node.cityArrange, node.level, i)
&& cMatrix[node.cityArrange.get(node.level)][i] != this.NoEdge) {
cityArrange = new Vector<Integer>();
cityArrange.addAll(0, node.cityArrange);
cityArrange.set(node.level + 1, new Integer(i));
lcost = computeLB(cityArrange, node.level + 1, cMatrix);
/* 若下界大于已知的最小开销,剪枝 */
if (lcost < this.minCost && lcost != this.NoEdge) {
temp = new Node(cityArrange, lcost, node.level + 1);
queue.add(temp);
}
}
}
}
}
/* 输出最优路径 */
System.out.print("The best path:");
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
System.out.print(this.bestPath.get(i) + "->");
}
System.out.println(this.bestPath.get(1));
return this.minCost;
}
/**
* 判断是否到达过某指定城市
*
* @param cities
* @param level
* @param city
* @return
*/
public boolean hasVisited(Vector<Integer> cities, int level, int city) {
for (int i = 1; i <= level; i++) {
if (cities.get(i).intValue() == city) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
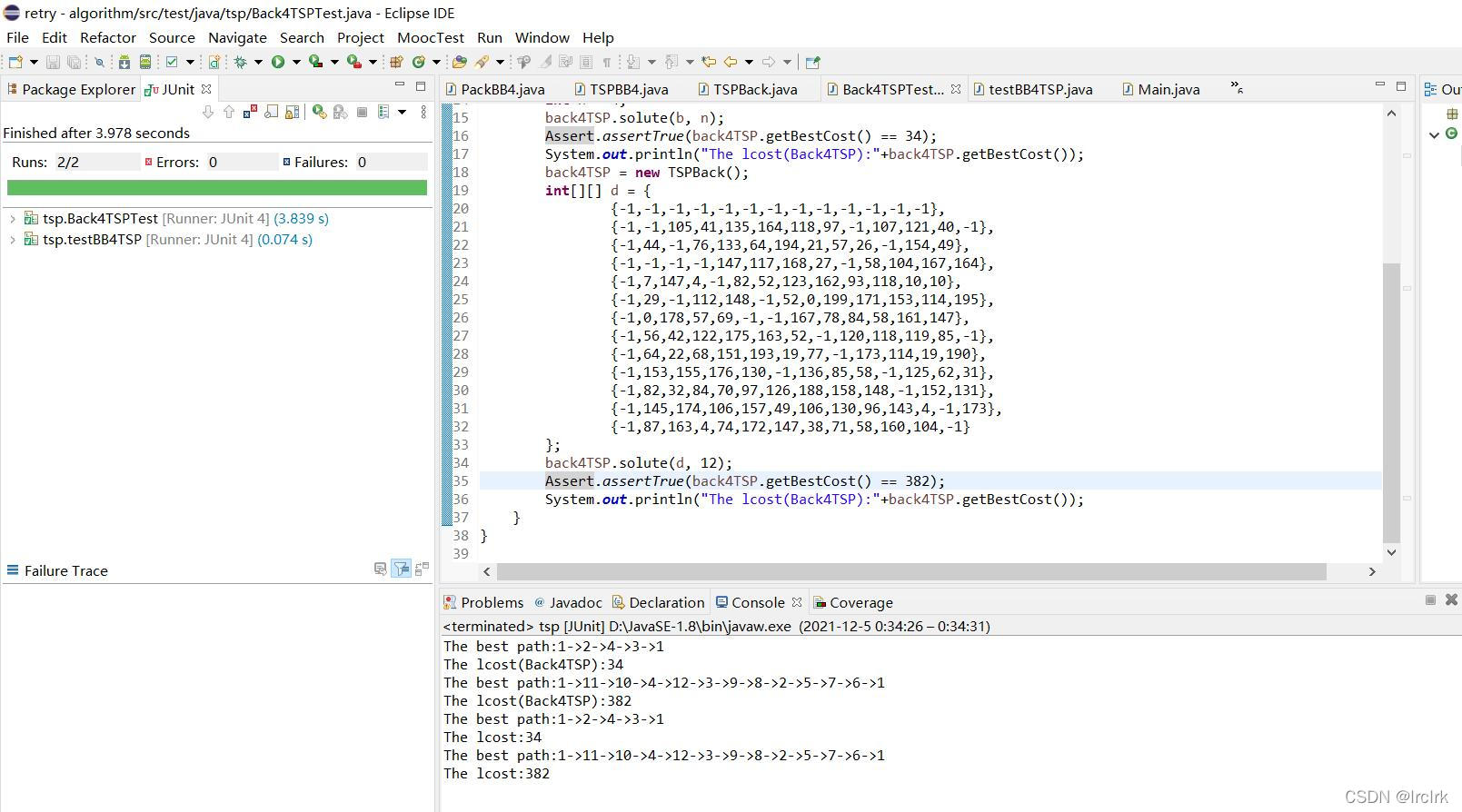
4.测试样例即结果
测试样例(两组)
int[][] d = {
{-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1},
{-1,-1,105,41,135,164,118,97,-1,107,121,40,-1},
{-1,44,-1,76,133,64,194,21,57,26,-1,154,49},
{-1,-1,-1,-1,147,117,168,27,-1,58,104,167,164},
{-1,7,147,4,-1,82,52,123,162,93,118,10,10},
{-1,29,-1,112,148,-1,52,0,199,171,153,114,195},
{-1,0,178,57,69,-1,-1,167,78,84,58,161,147},
{-1,56,42,122,175,163,52,-1,120,118,119,85,-1},
{-1,64,22,68,151,193,19,77,-1,173,114,19,190},
{-1,153,155,176,130,-1,136,85,58,-1,125,62,31},
{-1,82,32,84,70,97,126,188,158,148,-1,152,131},
{-1,145,174,106,157,49,106,130,96,143,4,-1,173},
{-1,87,163,4,74,172,147,38,71,58,160,104,-1}
};
int[][] b = {
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 },
{ -1, -1, 9, 19, 13 },
{ -1, 21, -1, -1, 14 },
{ -1, 1, 40, -1, 17 },
{ -1, 41, 80, 10, -1 }
};测试结果
写得很烂请见谅哈!