参考线提供器: ReferenceLineProvider
本小节主要介绍参考线提供器的功能,参考线提供器主要完成的工作是计算车辆在规划路径上的短期可行路径。在控制规划地图Pnc Map中,有一个功能是路径段RouteSegments生成最终路径Path,这个Path就是车辆在规划路径上的可行路径,但是路径是以std::vector<common::math::LineSegment2d> segments_和std::vector<MapPathPoint> path_points_的离散形式存在的,如果还不了解,可以参考Pnc Map模块进行了解。而本节参考线提供器就是对上述的Path进行样条函数Spline插值,得到平滑的路径曲线。
对path_points_中的离散点进行样条函数插值,得到连续平滑的路径函数,主要的步骤包含有:
-
路径点采样与轨迹点矫正
-
knots分段与二次规划进行参考线平滑
除了参考线平,参考线提供器还提供参考线拼接的功能。参考线拼接是针对不同时刻的RawReference,如果两条原始的RawReference是相连并且有覆盖的,那么可以不需要重新去进行平滑,只要直接使用上时刻的平滑参考线,或者仅仅平滑部分anchor point即可。
功能1参考线平滑:路径点采样与轨迹点矫正
控制规划地图Pnc Map根据当前车辆状态与Routing模块规划路径响应可以得到当前情况下,车辆的可行驶方案Path的集合(每个RouteSegments生成对应的一个Path)。在Path中路径以std::vector<common::math::LineSegment2d> segments_和std::vector<MapPathPoint> path_points_存在,前者是段的形式,而后者是原始离散点的形式。那么这个Path其实就是路径的离散形式表示,在本节中,我们需要行驶路径(参考线)的连续表示法,也就是根据这些离散点拟合一个合理的连续函数。
路径点采样与轨迹点矫正阶段工作就是对路径做一个离散点采样,为什么不用知道的path_points_或者sample_points_,因为该阶段需要的条件不同,所以其实就是重新采样的过程,与sample_points_采样其实没太大区别,仅仅是采样的间隔不同。
首先,已知路径的长度length_,只需要给出采样的间距interval,就能完成采样。
/// file in apollo/modules/planning/reference_line/reference_line_provider.cc
void ReferenceLineProvider::GetAnchorPoints(const ReferenceLine &reference_line,
std::vector<AnchorPoint> *anchor_points) const {
// interval为采样间隔,默认max_constraint_interval=5.0,即路径累积距离每5m采样一个点。
const double interval = smoother_config_.max_constraint_interval();
// 路径采样点数量计算
int num_of_anchors = std::max(2, static_cast<int>(reference_line.Length() / interval + 0.5));
std::vector<double> anchor_s;
// uniform_slice函数就是对[0.0, reference_line.Length()]区间等间隔采样,每两个点之间距离为(length_-0.0)/(num_of_anchors - 1)
common::util::uniform_slice(0.0, reference_line.Length(), num_of_anchors - 1, &anchor_s);
// 根据每个采样点的累积距离s,以及Path的lane_segments_to_next_point_进行平滑插值,得到累积距离为s的采样点的坐标(x,y),并进行轨迹点矫正
for (const double s : anchor_s) {
anchor_points->emplace_back(GetAnchorPoint(reference_line, s));
}
anchor_points->front().longitudinal_bound = 1e-6;
anchor_points->front().lateral_bound = 1e-6;
anchor_points->front().enforced = true;
anchor_points->back().longitudinal_bound = 1e-6;
anchor_points->back().lateral_bound = 1e-6;
anchor_points->back().enforced = true;
}
在上述过程中能够,其实可以很清楚的看到路径点采样与轨迹点矫正的整个流程,其余代码都比较简单,我们这里分析GetAnchorPoint函数是如何完成采样点的坐标计算与轨迹点坐标矫正的。
auto ref_point = reference_line.GetReferencePoint(s);
首先采样点坐标计算与Pnc Map中Path::InitWidth采样点计算一致,虽然这里多了一层ReferenceLine::GetReferencePoint的函数包装,但是计算过程是一模一样的,可以参考Pnc Map模块
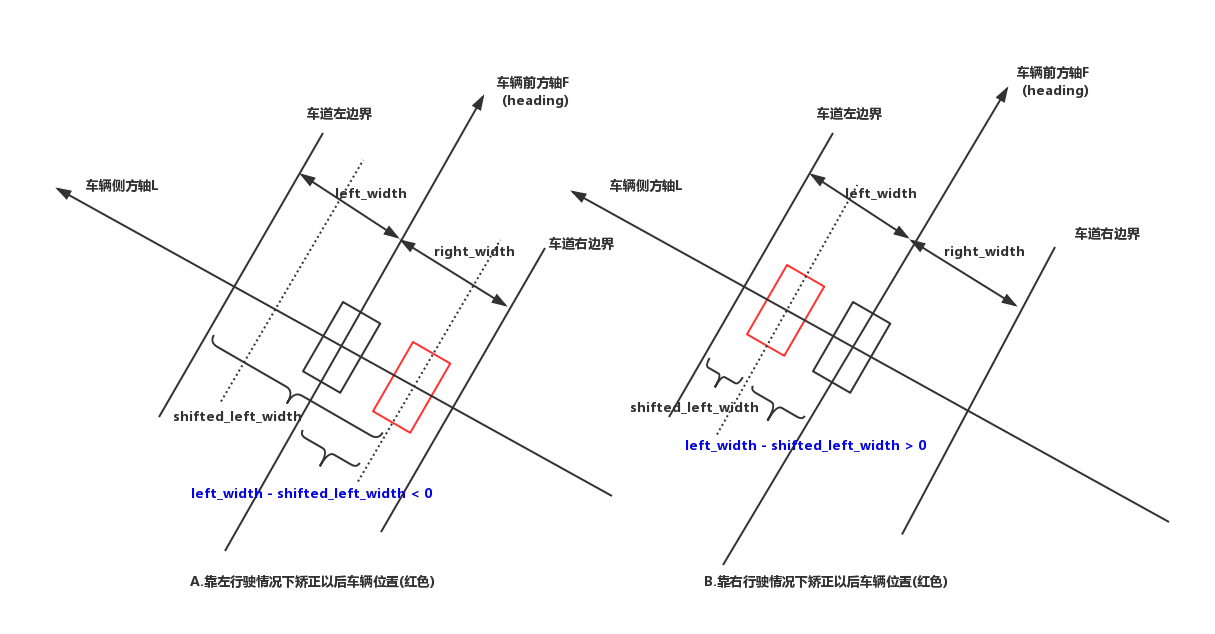
当完成采样点的计算以后,下一步就是采样点(也就是轨迹点)的坐标矫正。为什么需要坐标矫正?因为采样点坐标是在道路的中心线上,但当道路比较宽时,车辆不能一味的在中间行驶,需要考虑到其他车辆超车情况。在这种情况下,车辆需要靠右行驶(当然不同区域的模式不一样,部分地区是靠左形式),所以道路过宽时,需要将轨迹点向右或者向左矫正一段距离。
矫正的步骤如下:
- 计算车辆宽度adc_width和半宽adc_half_width
const double adc_width = VehicleConfigHelper::GetConfig().vehicle_param().width();
const double adc_half_width = adc_width / 2.0;
- 计算车道距左边界距离left_width和距右边界距离right_width
double left_width = 0.0;
double right_width = 0.0;
waypoint.lane->GetWidth(waypoint.s, &left_width, &right_width); // Hd Map中查询得到
double total_width = left_width + right_width; // 当前位置,车道总宽度
- 计算车辆应该右移或者左移(矫正)的距离
//如果车道宽度大于车辆宽度的wide_lane_threshold_factor倍,默认为2,则需要靠边行驶,因为存在其他车辆超车的可能性
// shift to left (or right) on wide lanes
if (!(waypoint.lane->lane().left_boundary().virtual_() ||
waypoint.lane->lane().right_boundary().virtual_()) &&
total_width > adc_width * smoother_config_.wide_lane_threshold_factor()) {
// 靠右行驶模式
if (smoother_config_.driving_side() == ReferenceLineSmootherConfig::RIGHT) {
shifted_left_width = adc_half_width + adc_width * smoother_config_.wide_lane_shift_remain_factor();
} else {
// 靠左形式模式
shifted_left_width = std::fmax(
adc_half_width,
total_width - (adc_half_width + adc_width * smoother_config_.wide_lane_shift_remain_factor()));
}
}
这部分代码可以从下面图中理解
纠正一下,上图中的下标错了,A:靠右行驶, B:靠左行驶
从代码可以看到,如果官方代码没有错误,那么:
- 当driving_side为RIGHT时
m = adc_half_width + adc_width * smoother_config_.wide_lane_shift_remain_factor()计算矫正后车辆与左边界距离
- 当driving_side为LEFT时
m = adc_half_width + adc_width * smoother_config_.wide_lane_shift_remain_factor()计算矫正后车辆与右边界距离
这样的方式在车道宽度差异比较大的时候,车联靠边行驶,距离边界的距离(total_width - m),这个距离不好控制。更不如使用一种更好的方法,同样是计算m,但是m的意义是距离最近边界线的距离,即靠边行驶与边界的距离,这个距离相对来说就比较好控制。只需要做一个更简单的改动,将上述代码的if-else判断条件交换一下即可,wide_lane_shift_remain_factor可以设置小于0.5的值。保证车辆边界与车到边界有一定距离(间隙)。
第二部分矫正是根据左右边界线是否是道路边界,如果车道左边界是道路边界线,那么shifted_left_width需要加上一个边界的缓冲距离curb_shift,默认0.2m,反之就是减去缓冲边界距离。
// shift away from curb boundary
auto left_type = hdmap::LeftBoundaryType(waypoint);
if (left_type == hdmap::LaneBoundaryType::CURB) {
shifted_left_width += smoother_config_.curb_shift();
}
auto right_type = hdmap::RightBoundaryType(waypoint);
if (right_type == hdmap::LaneBoundaryType::CURB) {
shifted_left_width -= smoother_config_.curb_shift();
}
最后矫正得到的平移距离就是shifted_left_width,如何根据这个平移距离求出车辆在世界坐标系中的矫正位置?
转换方法如下图,一目了然。
ref_point += left_vec * (left_width - shifted_left_width);
auto shifted_right_width = total_width - shifted_left_width;
anchor.path_point = ref_point.ToPathPoint(s);
double effective_width = std::min(shifted_left_width, shifted_right_width) -
adc_half_width - FLAGS_reference_line_lateral_buffer;
anchor.lateral_bound = std::max(smoother_config_.lateral_boundary_bound(), effective_width);
anchor.longitudinal_bound = smoother_config_.longitudinal_boundary_bound();
最后当使用二次规划来拟合轨迹点时,需要设置该点的约束,lateral_bound指的是预测的x值需要在ref_point的L轴的lateral_bound左右领域内,longitudinal_bound是预测的y值需要在ref_point的F轴的longitudinal_bound前后领域内
功能1参考线平滑:knots分段与二次规划进行参考线平滑
通过第一阶段路径点采样与轨迹点矫正,可以得到这条路径的anchor_point集合,里面是若干矫正过后的轨迹点,但还是离散形式。这个阶段我们需要对上述离散轨迹点进行多项式拟合。这部分内容也可以参考Apollo参考线平滑器。官方文档介绍的偏简单,在这里将从代码入手介绍一下参考线平滑过程。
这个过程目的是得到一条平滑的参考线,也就是运行轨迹,具体的做法是使用knots分段与QP二次规划。主要的思路是,将anchor_point分成n组,每组用一个多项式函数去拟合,可以得到n个多项式函数。
函数的输入和输出又是什么?我们现在只anchor_point中每个点的车道累积距离差s,以及世界系坐标(x,y)。想要拟合出轨迹曲线,只能是累积距离s作为自变量,世界系坐标作为应变量。计算函数为:
x = f i ( s ) = a i 0 + a i 1 s + a i 2 s 2 + a i 3 s 3 + a i 4 s 4 + a i 5 s 5 x = f_i(s) = a_{i0} + a_{i1}s + a_{i2}s^2 +a_{i3}s^3 + a_{i4}s^4 + a_{i5}s^5 x=fi(s)=ai0+ai1s+ai2s2+ai3s3+ai4s4+ai5s5
y = g i ( s ) = b i 0 + b i 1 s + b i 2 s 2 + b i 3 s 3 + b i 4 s 4 + b i 5 s 5 y = g_i(s) = b_{i0} + b_{i1}s + b_{i2}s^2 +b_{i3}s^3 + b_{i4}s^4 + b_{i5}s^5 y=gi(s)=bi0+bi1s+bi2s2+bi3s3+bi4s4+bi5s5
在这里是分别对x和y用多项式函数拟合,函数的参数a和b的下标i表示哪一个段(两个knots之间的anchor point)
A. 预处理:如何划分段,或者说设置knots?
简单,anchor point是对原始Path进行采样,采样间隔为smoother_config_.max_constraint_interval(),默认5m一个点。knots的采样其实也是相似的,采样间隔为config_.qp_spline().max_spline_length(),默认25m:
uint32_t num_spline = std::max(1u, static_cast<uint32_t>(length / config_.qp_spline().max_spline_length() + 0.5));
for (std::uint32_t i = 0; i <= num_spline; ++i) {
t_knots_.push_back(i * 1.0);
}
最后得到的knots节点有num_spline+1个。得到了所有的knots,也就意味着可到了所有的段,很明显这里就需要拟合num_spline个段,每个段有x和y两个多项式函数。
此外,还需要对anchor_point的自变量s做处理,本来s是从0到length_递增,现进行如下处理:
const double scale = (anchor_points_.back().path_point.s() -
anchor_points_.front().path_point.s()) /
(t_knots_.back() - t_knots_.front());
std::vector<double> evaluated_t;
for (const auto& point : anchor_points_) {
evaluated_t.emplace_back(point.path_point.s() / scale);
}
不难理解,就是将自变量s从[0,length_]区间按比例映射到[0,num_spline]区间,这样每个段内anchor point的s都属于[a,a+1]内,如果在减去knots[a]那么所有自变量的取值范围就是[0,1],事实上代码中也是这样做的。
同时还需要对应变量(x,y)做处理,处理方法如下
for (const auto& point : anchor_points_) {
const auto& path_point = point.path_point;
headings.push_back(path_point.theta());
longitudinal_bound.push_back(point.longitudinal_bound);
lateral_bound.push_back(point.lateral_bound);
xy_points.emplace_back(path_point.x() - ref_x_, path_point.y() - ref_y_);
}
可以看到x和y都需要减去Path第一个点的世界坐标系坐标,说白了2n个(2*num_spline)函数的坐标原点是Path的第一个点。
B. 如何设置约束条件?
在上一步预处理阶段,已经知道:
-
需要拟合的多项式函数数量为2*num_spline个,每两个knots之间会拟合x和y两个多项式
-
多项式最高阶数为5(qp_spline.spline_order: 5),所以每个多项式共6个参数,参数总和:(spline_order+1)*2*num_spline
-
使用每个段内的anchor point去拟合多项式函数,自变量范围[0,1],应变量相对于第一个anchor point的相对坐标。所以最后拟合出来的函数f和g的结果是相对于第一个anchor point的相对坐标。
那么在拟合过程中还需要满足一些约束,包括等式约束和不等式约束,例如:
- 预测的x’和y’需要保证在真实x和y的L轴lateral_bound、F轴longitudinal_bound领域内
- 第一个anchor point的heading和函数的一阶导方向需要一致,大小可以不一致,但是方向必需一致!
- x和y的n段函数之间,两两接壤部分应该是平滑的,两个函数值(位置)、一阶导(速度)、二阶导(加速度)必须一致。
B.1 边界约束
/// file in apollo/modules/planning/reference_line/qp_spline_reference_line_smoother.cc
bool QpSplineReferenceLineSmoother::AddConstraint() {
// all points (x, y) should not deviate anchor points by a bounding box
if (!spline_constraint->Add2dBoundary(evaluated_t, headings, xy_points,
longitudinal_bound, lateral_bound)) {
AERROR << "Add 2d boundary constraint failed.";
return false;
}
}
每个anchor point相对第一个点的相对参考系坐标为(x,y),方向为heading。而该点坐在的段拟合出来的相对参考系坐标为(x’,y’),坐标的计算方式为:
x ′ = f i ( s ) = a i 0 + a i 1 s + a i 2 s 2 + a i 3 s 3 + a i 4 s 4 + a i 5 s 5 x' = f_i(s) = a_{i0} + a_{i1}s + a_{i2}s^2 +a_{i3}s^3 + a_{i4}s^4 + a_{i5}s^5 x′=fi(s)=ai0+ai1s+ai2s2+ai3s3+ai4s4+ai5s5
y ′ = g i ( s ) = b i 0 + b i 1 s + b i 2 s 2 + b i 3 s 3 + b i 4 s 4 + b i 5 s 5 y' = g_i(s) = b_{i0} + b_{i1}s + b_{i2}s^2 +b_{i3}s^3 + b_{i4}s^4 + b_{i5}s^5 y′=gi(s)=bi0+bi1s+bi2s2+bi3s3+bi4s4+bi5s5
其中i是anchor point所在的knots段,i=1,2,…,n(n=num_spline)
- 真实点(x,y)F和L轴投影计算
如上图,实际情况下需要满足拟合坐标(x’,y’)在真实坐标(x,y)的领域内,真实点的投影计算方法比较简单,首先坐标在侧方L轴上的投影(天蓝色星星),投影点到原点的距离,也就是侧方距离计算方式为:
x p , l a t e r = ( c o s ( θ + π / 2 ) , s i n ( θ + π / 2 ) ) ⋅ ( x , y ) x_{p,later} = (cos(\theta+\pi/2), sin(\theta+\pi/2))·(x, y) xp,later=(cos(θ+π/2),sin(θ+π/2))⋅(x,y)
注意上述公式·为内积操作。这部分对应的代码为:
const double d_lateral = SignDistance(ref_point[i], angle[i]);
double Spline2dConstraint::SignDistance(const Vec2d& xy_point, const double angle) const {
return common::math::InnerProd(xy_point.x(), xy_point.y(), -std::sin(angle), std::cos(angle));
}
ref_point[i]是第i个anchor point的相对参考系坐标,angle[i]为该点的方向heading,也是公式中的theta。
注意一点,代码中的方向向量是(-sin(angle), cos(angle)),其实也可以等价为(cos(angle+pi/2), sin(angle+pi/2)),很明显,代码中的方向向量是在L轴的,所以在计算L轴上的投影距离是,直接将heading传入即可,不需要额外加上一个pi/2。最终代码的计算方式与公式是一致的。
真实点坐标在前方F轴上的投影(大红色星星),投影点到原点的距离,也就是前方距离计算方式为:
y p , l o n g i = ( c o s ( θ ) , s i n ( θ ) ) ⋅ ( x , y ) y_{p,longi} = (cos(\theta), sin(\theta))·(x, y) yp,longi=(cos(θ),sin(θ))⋅(x,y)
注意上述公式·为内积操作。对应的代码为:
const double d_longitudinal = SignDistance(ref_point[i], angle[i] - M_PI / 2.0);
从L轴到F轴的方向向量,需要减去一个pi/2。
- 函数预测点(x’,y’)F和L轴投影计算
根据多项式函数,可以简化出函数预测点(x’,y’)的计算方式为:
x = S A x = SA x=SA
y = S B y = SB y=SB
其中:
S = [ 1 , s , s 2 , s 3 , s 4 , s 5 ] S = [1, s, s^2, s^3, s^4, s^5] S=[1,s,s2,s3,s4,s5]
A = [ a i 0 , a i 1 , a i 2 , a i 3 , a i 4 , a i 5 ] T A = [a_{i0} ,a_{i1}, a_{i2}, a_{i3}, a_{i4}, a_{i5}]^T A=[ai0,ai1,ai2,ai3,ai4,ai5]T
B = [ b i 0 , b i 1 , b i 2 , b i 3 , b i 4 , b i 5 ] T B = [b_{i0} ,b_{i1}, b_{i2}, b_{i3}, b_{i4}, b_{i5}]^T B=[bi0,bi1,bi2,bi3,bi4,bi5]T
接下去我们从代码中验证一下正确性。
const uint32_t index = FindIndex(t_coord[i]);
const double rel_t = t_coord[i] - t_knots_[index];
const uint32_t index_offset = 2 * index * (spline_order_ + 1);
上述过程index是计算公式中的i,也就是计算n个拟合段中anchor point所属的段。rel_t是anchor point累积距离s相对于下界knots累积距离s的相对差,说白了就是自变量归一化到[0,1]之间。
index_offset是该段拟合函数对应的参数位置,我们可以知道n段拟合多项式函数的参数总和为 2*(spline_order+1)*n。所以第i个拟合函数的参数偏移位置为2*(spline_order+1)*i。
- [2*(spline_order+1)*i, 2*(spline_order+1)*i+(spline_order+1)]是x多项式函数的参数,共(spline_order+1)个,即向量A;
- [2*(spline_order+1)*i+(spline_order+1), 2*(spline_order+1)*(i+1)]是y多项式函数的参数,共(spline_order+1)个,即向量B
std::vector<double> longi_coef = AffineCoef(angle[i], rel_t);
std::vector<double> longitudinal_coef = AffineCoef(angle[i] - M_PI / 2, rel_t);
std::vector<double> Spline2dConstraint::AffineCoef(const double angle, const double t) const {
const uint32_t num_params = spline_order_ + 1;
std::vector<double> result(num_params * 2, 0.0);
double x_coef = -std::sin(angle);
double y_coef = std::cos(angle);
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < num_params; ++i) {
result[i] = x_coef;
result[i + num_params] = y_coef;
x_coef *= t;
y_coef *= t;
}
return result;
}
这部分longi_coef和longitudinal_coef也比较简单,一句话描述:
l o n g i c o e f = [ − s i n ( θ ) S , c o s ( θ ) S ] = [ c o s ( θ + π / 2 ) S , s i n ( θ + π / 2 ) S ] longicoef = [-sin(\theta)S, cos(\theta)S] = [cos(\theta+\pi/2)S, sin(\theta+\pi/2)S] longicoef=[−sin(θ)S,cos(θ)S]=[cos(θ+π/2)S,sin(θ+π/2)S]
l o n g i t u d i n a l c o e f = [ − s i n ( θ − π / 2 ) S , c o s ( θ − π / 2 ) S ] = [ c o s ( θ ) S , s i n ( θ ) S ] longitudinalcoef = [-sin(\theta-\pi/2)S, cos(\theta-\pi/2)S] = [cos(\theta)S, sin(\theta)S] longitudinalcoef=[−sin(θ−π/2)S,cos(θ−π/2)S]=[cos(θ)S,sin(θ)S]
两个系数分别是在L轴和F轴上的投影系数。但是longi_coef名字可能改成lateral_coef更合适。最后可以根据这两个值求解在F和L轴上的投影。
x q , l a t e r = ( c o s ( θ + π / 2 ) , s i n ( θ + π / 2 ) ) ⋅ ( x ′ , y ′ ) = ( c o s ( θ + π / 2 ) , s i n ( θ + π / 2 ) ) ⋅ ( S A , S B ) x_{q,later} = (cos(\theta+\pi/2), sin(\theta+\pi/2))·(x', y') = (cos(\theta+\pi/2), sin(\theta+\pi/2))·(SA, SB) xq,later=(cos(θ+π/2),sin(θ+π/2))⋅(x′,y′)=(cos(θ+π/2),sin(θ+π/2))⋅(SA,SB)
即
x q , l a t e r = [ − s i n ( θ ) S , c o s ( θ ) S ] ⋅ ( A , B ) = l o n g i c o e f ⋅ ( A , B ) x_{q,later} = [-sin(\theta)S, cos(\theta)S]·(A, B) = longicoef · (A, B) xq,later=[−sin(θ)S,cos(θ)S]⋅(A,B)=longicoef⋅(A,B)
y q , l o n g i = ( c o s ( θ ) , s i n ( θ ) ) ⋅ ( x ′ , y ′ ) = ( c o s ( θ ) , s i n ( θ ) ) ⋅ ( S A , S B ) y_{q,longi} = (cos(\theta), sin(\theta))·(x', y') = (cos(\theta), sin(\theta))·(SA, SB) yq,longi=(cos(θ),sin(θ))⋅(x′,y′)=(cos(θ),sin(θ))⋅(SA,SB)
即
y q , l o n g i = [ − s i n ( θ − π / 2 ) S , c o s ( θ − π / 2 ) S ] ⋅ ( A , B ) = l o n g i t u d i n a l c o e f ⋅ ( A , B ) y_{q,longi} = [-sin(\theta-\pi/2)S, cos(\theta-\pi/2)S]·(A, B) = longitudinalcoef · (A, B) yq,longi=[−sin(θ−π/2)S,cos(θ−π/2)S]⋅(A,B)=longitudinalcoef⋅(A,B)
- 约束条件设置
现在可以计算真实点和拟合点在F轴L轴的投影,那么就有约束条件:
|d_lateral - longi_coef·(A, B)| <= lateral_bound
|d_longitudinal - longitudinal_coef(A, B)| <= longitudinal_bound
最后得到四个约束不等式:
- L轴上界不等式
d_lateral - longi_coef·(A, B) <= lateral_bound
整理得到:longi_coef·(A, B) >= d_lateral - lateral_bound
- L轴下界不等式
d_lateral - longi_coef·(A, B) >= -lateral_bound
整理得到: -longi_coef·(A, B) >= -d_lateral - lateral_bound
- F轴上界不等式
d_longitudinal - longitudinal_coef·(A, B) <= longitudinal_bound
整理得到:longitudinal_coef·(A, B) >= d_longitudinal - longitudinal_bound
- F轴下界不等式
d_longitudinal - longitudinal_coef·(A, B) >= -longitudinal_bound
整理得到:-longitudinal_coef·(A, B) >= -d_longitudinal - longitudinal_bound
for (uint32_t j = 0; j < 2 * (spline_order_ + 1); ++j) {
// upper longi,设置L轴上界不等式系数
affine_inequality(4 * i, index_offset + j) = longi_coef[j];
// lower longi,设置L轴下界不等式系数
affine_inequality(4 * i + 1, index_offset + j) = -longi_coef[j];
// upper longitudinal,设置F轴上界不等式系数
affine_inequality(4 * i + 2, index_offset + j) = longitudinal_coef[j];
// lower longitudinal,设置F轴下界不等式系数
affine_inequality(4 * i + 3, index_offset + j) = -longitudinal_coef[j];
}
affine_boundary(4 * i, 0) = d_lateral - lateral_bound[i]; //设置L轴上界不等式的边界
affine_boundary(4 * i + 1, 0) = -d_lateral - lateral_bound[i]; //设置L轴下界不等式的边界
affine_boundary(4 * i + 2, 0) = d_longitudinal - longitudinal_bound[i]; //设置F轴上界不等式的边界
affine_boundary(4 * i + 3, 0) = -d_longitudinal - longitudinal_bound[i]; //设置L轴下界不等式的边界
配合代码和上述的公式可以不难看出不等式系数的设置和边界设置。经过上述赋值:
affine_inequality等同于: [longi_coef, -longi_coef, longitudinal_coef, -longitudinal_coef]
affine_boundary等同于: [d_lateral-lateral_bound, -d_lateral-lateral_bound, d_longitudinal-longitudinal_bound, -d_longitudinal-longitudinal_bound]
最后不等式约束:
affine_inequality * [A1,B1,A2,B2,..An,Bn] >= affine_boundary
B.2 方向约束
/// file in apollo/modules/planning/reference_line/qp_spline_reference_line_smoother.cc
bool QpSplineReferenceLineSmoother::AddConstraint() {
// the heading of the first point should be identical to the anchor point.
if (!spline_constraint->AddPointAngleConstraint(evaluated_t.front(),
headings.front())) {
AERROR << "Add 2d point angle constraint failed.";
return false;
}
}
第一个anchor point的heading应该和第一段的多项式函数f1和g1的偏导数方向一致,大小可以不一致。也就是: heading = argtan(g1’(s), f1’(s))。从上述代码可以看到,参入的参数是第一个点。
/// file in apollo/modules/planning/math/smoothing_spline/spline_2d_constraint.cc
bool Spline2dConstraint::AddPointAngleConstraint(const double t,
const double angle) {
const uint32_t index = FindIndex(t);
const uint32_t num_params = spline_order_ + 1;
const uint32_t index_offset = index * 2 * num_params;
const double rel_t = t - t_knots_[index];
}
第一步还是计算第一个anchor point所属的函数索引index,index_offset是该段函数参数(Ai,Bi)所在的位置偏移,rel_t是第一个点的自变量,归一化到[0,1]。为了确保方向一致,代码中使用两个约束来保证这个方向一致的约束问题:
- L轴分量为0,保证方向相同或者相反
- 验证同向性
- L轴分量为0,保证方向相同或者相反
bool Spline2dConstraint::AddPointAngleConstraint(const double t,
const double angle) {
// add equality constraint
Eigen::MatrixXd affine_equality = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(1, total_param_);
Eigen::MatrixXd affine_boundary = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(1, 1);
std::vector<double> line_derivative_coef = AffineDerivativeCoef(angle, rel_t);
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < line_derivative_coef.size(); ++i) {
affine_equality(0, i + index_offset) = line_derivative_coef[i];
}
}
std::vector<double> Spline2dConstraint::AffineDerivativeCoef(
const double angle, const double t) const {
const uint32_t num_params = spline_order_ + 1;
std::vector<double> result(num_params * 2, 0.0);
double x_coef = -std::sin(angle);
double y_coef = std::cos(angle);
std::vector<double> power_t = PolyCoef(t);
for (uint32_t i = 1; i < num_params; ++i) {
result[i] = x_coef * power_t[i - 1] * i;
result[i + num_params] = y_coef * power_t[i - 1] * i;
}
return result;
}
等式约束还是那句话,第一个点的方向heading和多项式曲线在该点的斜率(一阶导)方向必须一致,大小可以不一致。方向一致等价于:斜率在L轴方向上的分量为0
代码中通过Spline2dConstraint::AffineDerivativeCoef函数计算得到的系数矩阵line_derivative_coef为:
微分矩阵 $ D = [0, 1, 2s, 3s^2, 4s^3, 5s^4] $
line_derivative_coef = [-sin(theta)D, cos(theta)D]
可以得到L轴方向分量的计算方式为 line_derivative_coef · (A, B) = 0
从代码我们可以看到一个问题:只是限制了L轴分量为零,但是不保证同向性。
- 验证同向性
真实点的方向为heading,拟合多项式在该点的一阶导数为 (D·A, D·B)。代码中对heading做一个处理,规则化到[0, 2*pi]
计算heading的方向向量sgn = [x_sign, y_sign],计算方法为:
- 如果正则化heading在[0, pi/2]: sgn = [1, 1]
- 如果正则化heading在[pi/2, pi]: sgn = [-1, 1]
- 如果正则化heading在[pi,3*pi/2]: sgn = [-1, -1]
- 如果正则化heading在[3*pi/2, 2*pi]: sgn = [1, -1]
只需要最后的内积 sgn·(D·A, D·B) > 0表明方向一致。
其实有更加简单地方式,heading方向对应的单位向量为(cos(heading), sin(heading)),所以需要要如下代码就可以:
x_sign = std::cos(angle)
y_sign = std::sin(angle)
也不需要去计算normalized_angle这些,代码量明显减少了。但是代码这样的写法有一个明显的优势:系数为1或者-1,优化变得简单。
B.3 各函数接壤处平滑约束
边界约束和方向约束是对每个多项式拟合函数的约束,而相邻多项式函数之间也需要进行约束,需要保证函数间是连续可微的。具体包括:
-
两个函数接壤部分函数值相同,保证连续。(位置一致)
-
两个函数接壤部分一阶和二阶导相同,保证可微。(速度,加速度一致)
所以从上述可以得知,平滑约束共6个不等式。
f i ( k n o t s [ i + 1 ] . s − k n o t s [ i ] . s ) − f i + 1 ( 0 ) = 0 f_i(knots[i+1].s-knots[i].s) - f_{i+1}(0) = 0 fi(knots[i+1].s−knots[i].s)−fi+1(0)=0
g i ( k n o t s [ i + 1 ] . s − k n o t s [ i ] . s ) − g i + 1 ( 0 ) = 0 g_i(knots[i+1].s-knots[i].s) - g_{i+1}(0) = 0 gi(knots[i+1].s−knots[i].s)−gi+1(0)=0
f ( 1 ) _ i ( k n o t s [ i + 1 ] . s − k n o t s [ i ] . s ) − f ( 1 ) _ i + 1 ( 0 ) = 0 f^{(1)}\_i(knots[i+1].s-knots[i].s) - f^{(1)}\_{i+1}(0) = 0 f(1)_i(knots[i+1].s−knots[i].s)−f(1)_i+1(0)=0
f ( 2 ) _ i ( k n o t s [ i + 1 ] . s − k n o t s [ i ] . s ) − f ( 2 ) _ i + 1 ( 0 ) = 0 f^{(2)}\_i(knots[i+1].s-knots[i].s) - f^{(2)}\_{i+1}(0) = 0 f(2)_i(knots[i+1].s−knots[i].s)−f(2)_i+1(0)=0
g ( 1 ) _ i ( k n o t s [ i + 1 ] . s − k n o t s [ i ] . s ) − g ( 1 ) _ i + 1 ( 0 ) = 0 g^{(1)}\_i(knots[i+1].s-knots[i].s) - g^{(1)}\_{i+1}(0) = 0 g(1)_i(knots[i+1].s−knots[i].s)−g(1)_i+1(0)=0
g ( 2 ) _ i ( k n o t s [ i + 1 ] . s − k n o t s [ i ] . s ) − g ( 2 ) _ i + 1 ( 0 ) = 0 g^{(2)}\_i(knots[i+1].s-knots[i].s) - g^{(2)}\_{i+1}(0) = 0 g(2)_i(knots[i+1].s−knots[i].s)−g(2)_i+1(0)=0
以x的多项式拟合函数f为例,函数的一阶导和二阶导分别为
x ′ = f ( 1 ) _ i ( s ) = 0 + a i 1 + 2 a i 2 s + 3 a i 3 s 2 + 4 a i 4 s 3 + 5 a i 5 s 4 x' = f^{(1)}\_i(s) = 0 + a_{i1} + 2a_{i2}s + 3a_{i3}s^2 + 4a_{i4}s^3 + 5a_{i5}s^4 x′=f(1)_i(s)=0+ai1+2ai2s+3ai3s2+4ai4s3+5ai5s4
x ′ ′ = f ( 2 ) _ i ( s ) = 0 + 0 + 2 a i 2 + 6 a i 3 s + 12 a i 4 s 2 + 20 a i 5 s 3 x'' = f^{(2)}\_i(s) = 0 + 0 + 2a_{i2} + 6a_{i3}s + 12a_{i4}s^2 + 20a_{i5}s^3 x′′=f(2)_i(s)=0+0+2ai2+6ai3s+12ai4s2+20ai5s3
函数值系数: $ Ds_0 = [1, s, s^2, s^3, s^4, s^5] $
一阶导系数: $ Ds_1 = [0, 1, 2s, 3s^2, 4s^3, 5s^4] $
二阶导系数: $ Ds_2 = [0, 0, 2, 6s, 12s^2, 20s^3] $
最终简化后的6个等式约束为:
D s 0 A i − [ 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ] A i + 1 = 0 Ds_0A_i - [1,0,0,0,0,0]A_{i+1} = 0 Ds0Ai−[1,0,0,0,0,0]Ai+1=0
D s 1 A i − [ 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ] A i + 1 = 0 Ds_1A_i - [0,1,0,0,0,0]A_{i+1} = 0 Ds1Ai−[0,1,0,0,0,0]Ai+1=0
D s 2 A i − [ 0 , 0 , 2 , 0 , 0 , 0 ] A i + 1 = 0 Ds_2A_i - [0,0,2,0,0,0]A_{i+1} = 0 Ds2Ai−[0,0,2,0,0,0]Ai+1=0
D s 0 B i − [ 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ] B i + 1 = 0 Ds_0B_i - [1,0,0,0,0,0]B_{i+1} = 0 Ds0Bi−[1,0,0,0,0,0]Bi+1=0
D s 1 B i − [ 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ] B i + 1 = 0 Ds_1B_i - [0,1,0,0,0,0]B_{i+1} = 0 Ds1Bi−[0,1,0,0,0,0]Bi+1=0
D s 2 B i − [ 0 , 0 , 2 , 0 , 0 , 0 ] B i + 1 = 0 Ds_2B_i - [0,0,2,0,0,0]B_{i+1} = 0 Ds2Bi−[0,0,2,0,0,0]Bi+1=0
代码如下
// guarantee upto second order derivative are joint
bool Spline2dConstraint::AddSecondDerivativeSmoothConstraint() {
if (t_knots_.size() < 3) {
return false;
}
// 6个等式,affine_equality是系数,affine_boundary是值。约束函数数量:6 * (n-1), n=t_knots_.size()-1
Eigen::MatrixXd affine_equality = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(6 * (t_knots_.size() - 2), total_param_);
Eigen::MatrixXd affine_boundary = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(6 * (t_knots_.size() - 2), 1);
// 相邻两个knots对之间的多项式拟合函数进行约束
for (uint32_t i = 0; i + 2 < t_knots_.size(); ++i) {
// 计算第一个曲线的自变量:t_knots[i+1].s-t_knots[i].s
const double rel_t = t_knots_[i + 1] - t_knots_[i];
const uint32_t num_params = spline_order_ + 1;
const uint32_t index_offset = 2 * i * num_params;
// 函数值系数: [1, s, s^2, s^3, s^4, s^5]
std::vector<double> power_t = PolyCoef(rel_t);
// 一阶导系数: [0, 1, 2s, 3s^2, 4s^3, 5s^4]
std::vector<double> derivative_t = DerivativeCoef(rel_t);
// 二阶导系数: [0, 0, 2, 6s, 12s^2,20s^3]
std::vector<double> second_derivative_t = SecondDerivativeCoef(rel_t);
for (uint32_t j = 0; j < num_params; ++j) {
affine_equality(6 * i, j + index_offset) = power_t[j]; // 第一个多项式x曲线终点函数值
affine_equality(6 * i + 1, j + index_offset) = derivative_t[j]; // 第一个多项式x曲线终点一阶导
affine_equality(6 * i + 2, j + index_offset) = second_derivative_t[j]; // 第一个多项式x曲线终点二阶导
affine_equality(6 * i + 3, j + index_offset + num_params) = power_t[j]; // 第二个多项式y曲线终点函数值
affine_equality(6 * i + 4, j + index_offset + num_params) = derivative_t[j]; // 第二个多项式y曲线终点一阶导
affine_equality(6 * i + 5, j + index_offset + num_params) = second_derivative_t[j];// 第二个多项式y曲线终点二阶导
}
affine_equality(6 * i, index_offset + 2 * num_params) = -1.0; // 第一个多项式x曲线终点函数值 - 第二个多项式x曲线起点函数值
affine_equality(6 * i + 1, index_offset + 2 * num_params + 1) = -1.0; // 第一个多项式x曲线终点一阶导 - 第二个多项式x曲线起点一阶导(速度一致)
affine_equality(6 * i + 2, index_offset + 2 * num_params + 2) = -2.0; // 第一个多项式x曲线终点二阶导 - 第二个多项式x曲线起点二阶导(加速度一致)
affine_equality(6 * i + 3, index_offset + 3 * num_params) = -1.0; // 第一个多项式y曲线终点函数值 - 第二个多项式y曲线起点函数值
affine_equality(6 * i + 4, index_offset + 3 * num_params + 1) = -1.0; // 第一个多项式y曲线终点一阶导 - 第二个多项式y曲线起点一阶导(速度一致)
affine_equality(6 * i + 5, index_offset + 3 * num_params + 2) = -2.0; // 第一个多项式y曲线终点二阶导 - 第二个多项式y曲线起点二阶导(加速度一致)
}
return AddEqualityConstraint(affine_equality, affine_boundary);
}
C. 如何设置cost函数?
由reference_line_smoother可以看到Apollo使用的cost函数:
$$ cost = \sum_{i=1}^{n} \Big( \int\limits_{0}^{t_i} (f_i''')^2(t) dt + \int\limits_{0}^{t_i} (g_i''')^2(t) dt \Big) $$
/// file in apollo/modules/planning/conf/qp_spline_smoother_config.pb.txt
qp_spline {
spline_order: 5
max_spline_length : 25.0
regularization_weight : 1.0e-5
second_derivative_weight : 200.0 // 二阶导cost函数权重
third_derivative_weight : 1000.0 // 三阶导cost函数权重
}
实际上,从代码和配置文件中可以看到,其实cost函数用了二阶导和三阶导,下面我们以三阶导和第k段多项式x曲线fk为例,描述cost函数的计算过程。可知fk多项式函数的0,1,2,3阶导函数分别为:
x = f k ( s ) = a k 0 + a k 1 s + a k 2 s 2 + a k 3 s 3 + a k 4 s 4 + a k 5 s 5 x = f_k(s) = a_{k0} + a_{k1}s + a_{k2}s^2 + a_{k3}s^3 + a_{k4}s^4 + a_{k5}s^5 x=fk(s)=ak0+ak1s+ak2s2+ak3s3+ak4s4+ak5s5
x ′ = f k ( 1 ) ( s ) = 0 + a k 1 + 2 a k 2 s + 3 a k 3 s 2 + 4 a k 4 s 3 + 5 a k 5 s 4 x' = f_k^{(1)}(s) = 0 + a_{k1} + 2a_{k2}s + 3a_{k3}s^2 + 4a_{k4}s^3 + 5a_{k5}s^4 x′=fk(1)(s)=0+ak1+2ak2s+3ak3s2+4ak4s3+5ak5s4
x ′ ′ = f k ( 2 ) ( s ) = 0 + 0 + 2 + 6 a k 3 s + 12 a k 4 s 2 + 20 a k 5 s 3 x'' = f_k^{(2)}(s) = 0 + 0 + 2 + 6a_{k3}s + 12a_{k4}s^2 + 20a_{k5}s^3 x′′=fk(2)(s)=0+0+2+6ak3s+12ak4s2+20ak5s3
x ′ ′ ′ = f k ( 3 ) ( s ) = 0 + 0 + 0 + 6 + 24 a k 4 s 1 + 60 a k 5 s 2 x''' = f_k^{(3)}(s) = 0+ 0 + 0 + 6 + 24a_{k4}s^1 + 60a_{k5}s^2 x′′′=fk(3)(s)=0+0+0+6+24ak4s1+60ak5s2
先做如下标记:
D s 0 = [ 1 , s , s 2 , s 3 , s 4 , s 5 ] Ds_0 = [1, s, s^2, s^3, s^4, s^5] Ds0=[1,s,s2,s3,s4,s5]
D s 1 = [ 0 , 1 , 2 s , 3 s 2 , 4 s 3 , 5 s 4 ] Ds_1 = [0, 1, 2s, 3s^2, 4s^3, 5s^4] Ds1=[0,1,2s,3s2,4s3,5s4]
D s 2 = [ 0 , 0 , 2 , 6 s , 12 s 2 , 20 s 3 ] Ds_2 = [0, 0, 2, 6s, 12s^2, 20s^3] Ds2=[0,0,2,6s,12s2,20s3]
D s 3 = [ 0 , 0 , 0 , 6 , 24 s , 60 s 2 ] Ds_3 = [0, 0, 0, 6, 24s, 60s^2] Ds3=[0,0,0,6,24s,60s2]
A k = [ a k 0 , a k 1 , a k 2 , a k 3 , a k 4 , a k 5 ] T A_k = [a_{k0}, a_{k1}, a_{k2}, a_{k3}, a_{k4}, a_{k5}]^T Ak=[ak0,ak1,ak2,ak3,ak4,ak5]T
B k = [ b k 0 , b k 1 , b k 2 , b k 3 , b k 4 , b k 5 ] T B_k = [b_{k0}, b_{k1}, b_{k2}, b_{k3}, b_{k4}, b_{k5}]^T Bk=[bk0,bk1,bk2,bk3,bk4,bk5]T
最终cost可以变为:
$$ cost = \sum_{k=1}^{n} \Big( \int\limits_{0}^{t_k} (Ds_3A_k)^T(Ds_3A_k) dt + \int\limits_{0}^{t_k} (Ds_3B_k)^T(Ds_3B_k) dt \Big) $$
$$ cost = \sum_{k=1}^{n} \Big( \int\limits_{0}^{t_k} {A_k}^T{Ds_3}^TDs_3A_k dt + \int\limits_{0}^{t_k} {B_k}^T{Ds_3}^TDs_3B_k dt \Big) $$
以第k段多项式函数fk为例,接下来的难点就是如何求解
∫ 0 t k A k T D s 3 T D s 3 A k d t = A k T ( ∫ 0 t k D s 3 T D s 3 d t ) A k \int\limits_{0}^{t_k} {A_k}^T{Ds_3}^TDs_3A_k dt = {A_k}^T\Big(\int\limits_{0}^{t_k} {Ds_3}^TDs_3 dt\Big)A_k 0∫tkAkTDs3TDs3Akdt=AkT(0∫tkDs3TDs3dt)Ak
等价于求解
P P k = ∫ 0 t k D s 3 T D s 3 d t PP_k = \int\limits_{0}^{t_k} {Ds_3}^TDs_3 dt PPk=0∫tkDs3TDs3dt
上述公式就跟上述的约束一样,也是一个系数矩阵。
现令:$Pk = {Ds_3}^TDs_3 $ 可以思考一下,Pk中的任意一个元素 P k i j Pk_{ij} Pkij,他的完整计算方式为:
KaTeX parse error: Undefined control sequence: \[ at position 16: Pk_{ij} = Ds_3\̲[̲i\] * Ds_3\[j\]…
上述公式中的参数 $ c = i*(i-1)*(i-2)*j*(j-1)*(j-2) $
那么对于这个选一项积分,可以得到:
∫ 0 t k P k i j d t = ∫ 0 t k c s i + j − 6 d t = c i + j − 5 s i + j − 5 ∣ _ s = t k − c i + j − 5 s i + j − 5 ∣ _ s = 0 = c i + j − 5 s i + j − 5 ∣ _ s = t k \int\limits_{0}^{t_k} Pk_{ij} dt = \int\limits_{0}^{t_k} cs^{i+j-6} dt = \left. \frac{c}{i+j-5}s^{i+j-5} \right| \_{s=t_k} - \left. \frac{c}{i+j-5}s^{i+j-5} \right| \_{s=0} = \left. \frac{c}{i+j-5}s^{i+j-5} \right| \_{s=t_k} 0∫tkPkijdt=0∫tkcsi+j−6dt=i+j−5csi+j−5∣∣∣∣_s=tk−i+j−5csi+j−5∣∣∣∣_s=0=i+j−5csi+j−5∣∣∣∣_s=tk
上述公式需要满足条件: i, j必须都大于等于3
所以最终的积分系数矩阵Pk可以分别成两部分:
PPk = Qk(同kernel_third_order_derivative_) · Rk(同term_matrix)(注意这里是点乘,并非矩阵乘法)
上述中kernel_third_order_derivative_是积分三阶导系数矩阵,term_matrix是s的多项式矩阵。
C.1 积分导数系数矩阵Q计算
- 在三阶导系数矩阵中,每个位置元素的计算方式为:
KaTeX parse error: Undefined control sequence: \* at position 19: …{i,j} = \frac{i\̲*̲(i-1)\*(i-2)\*j…
公式必须保证i和j都要大于等于3,因为低阶项(第0,1,2项)不存在3次导;或者说低阶项的三阶导为0,积分过后的系数矩阵依旧为0。
/// file in apollo/modules/planning/math/smoothing_spline/spline_seg_kernel.cc
void SplineSegKernel::CalculateThirdOrderDerivative(const uint32_t num_params) {
kernel_third_order_derivative_ = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(num_params, num_params);
for (int r = 3; r < kernel_third_order_derivative_.rows(); ++r) {
for (int c = 3; c < kernel_third_order_derivative_.cols(); ++c) {
kernel_third_order_derivative_(r, c) =
(r * r - r) * (r - 2) * (c * c - c) * (c - 2) / (r + c - 5.0);
}
}
}
从代码可以不难验证我们推理的正确性。
- 在二阶导系数矩阵中,每个位置元素的计算方式为:
KaTeX parse error: Undefined control sequence: \* at position 19: …{i,j} = \frac{i\̲*̲(i-1)\*j\*(j-1)…
公式必须保证i和j都要大于等于2,因为低阶项(第0,1项)不存在2次导;或者说低阶项的二阶导为0,积分过后的系数矩阵依旧为0。
/// file in apollo/modules/planning/math/smoothing_spline/spline_seg_kernel.cc
void SplineSegKernel::CalculateSecondOrderDerivative(const uint32_t num_params) {
kernel_second_order_derivative_ = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(num_params, num_params);
for (int r = 2; r < kernel_second_order_derivative_.rows(); ++r) {
for (int c = 2; c < kernel_second_order_derivative_.cols(); ++c) {
kernel_second_order_derivative_(r, c) =
(r * r - r) * (c * c - c) / (r + c - 3.0);
}
}
}
C.2 多项式矩阵R计算
对于三阶导cost函数,原本多项式矩阵R计算为:
R = [ 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , s , s 2 ] T [ 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , s , s 2 ] R = [0, 0, 0, 1, s, s^2]^T[0, 0, 0, 1, s, s^2] R=[0,0,0,1,s,s2]T[0,0,0,1,s,s2]
但是由于积分后,每个元素的多项式次数需要加一,所以最后的R为:
R = s ⋅ [ 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , s , s 2 ] T [ 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , s , s 2 ] R = s · [0, 0, 0, 1, s, s^2]^T[0, 0, 0, 1, s, s^2] R=s⋅[0,0,0,1,s,s2]T[0,0,0,1,s,s2]
/// file in apollo/modules/planning/math/smoothing_spline/spline_seg_kernel.cc
void SplineSegKernel::IntegratedTermMatrix(const uint32_t num_params,
const double x,
const std::string& type,
Eigen::MatrixXd* term_matrix) const {
if (term_matrix->rows() != term_matrix->cols() ||
term_matrix->rows() != static_cast<int>(num_params)) {
term_matrix->resize(num_params, num_params);
}
std::vector<double> x_pow(2 * num_params + 1, 1.0);
for (uint32_t i = 1; i < 2 * num_params + 1; ++i) {
x_pow[i] = x_pow[i - 1] * x;
}
if (type == "fx") {
...
} else if (type == "derivative") {
...
} else if (type == "second_order") {
...
} else {
for (uint32_t r = 3; r < num_params; ++r) {
for (uint32_t c = 3; c < num_params; ++c) {
(*term_matrix)(r, c) = x_pow[r + c - 5]; // 每个元素本来为 r-3+c-3,积分过后指数加1,变成r+c-5
}
}
(*term_matrix).block(0, 0, num_params, 3) = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(num_params, 3); // 前三列置0
(*term_matrix).block(0, 0, 3, num_params) = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(3, num_params); // 前三行置0
}
}
C.3 cost函数计算
代码也是一目了然,最后的cost函数等价于:
$$ cost = \sum_{k=1}^{n} \Big( {A_k}^T(Q_k·R_k)A_k + {B_k}^T(Q_k·R_k)B_k \Big) $$
上述公式Qk·Rk是点乘,不是矩阵乘法
/// file in apollo/modules/planning/math/smoothing_spline/spline_2d_kernel.cc
// AddNthDerivativeKernelMatrix是计算cost函数的总系数矩阵,对应上述公式中的sigma,一共n-1段函数
// n = num_spline = t_knots_.size() - 1
void Spline2dKernel::AddNthDerivativeKernelMatrix(const uint32_t n, const double weight) {
for (uint32_t i = 0; i + 1 < t_knots_.size(); ++i) {
const uint32_t num_params = spline_order_ + 1;
Eigen::MatrixXd cur_kernel =
SplineSegKernel::instance()->NthDerivativeKernel(
n, num_params, t_knots_[i + 1] - t_knots_[i]) *
weight;
kernel_matrix_.block(2 * i * num_params, 2 * i * num_params, num_params,
num_params) += cur_kernel;
kernel_matrix_.block((2 * i + 1) * num_params, (2 * i + 1) * num_params,
num_params, num_params) += cur_kernel;
}
}
/// file in apollo/modules/planning/math/smoothing_spline/spline_seg_kernel.cc
// SecondOrderDerivativeKernel是计算每一个段的多项式拟合函数的系数矩阵 Q_i · R_i
Eigen::MatrixXd SplineSegKernel::SecondOrderDerivativeKernel(
const uint32_t num_params, const double accumulated_x) {
if (num_params > reserved_order_ + 1) {
CalculateSecondOrderDerivative(num_params);
}
Eigen::MatrixXd term_matrix;
IntegratedTermMatrix(num_params, accumulated_x, "second_order", &term_matrix);
return kernel_second_order_derivative_.block(0, 0, num_params, num_params)
.cwiseProduct(term_matrix); // 计算Q·R,点乘
}
在Apollo中将n段多项式曲线的参数合并在一起形成一个大的参数向量x,最终需要优化的系数为:
x = [ A 0 , B 0 , A 1 , B 1 , . . . , A n − 1 , B n − 1 ] x = [A_0,B_0,A_1,B_1,...,A_{n-1},B_{n-1}] x=[A0,B0,A1,B1,...,An−1,Bn−1]
参数的个数一共:2 * (spline_order + 1) * num_spline
所以无论在设置约束条件还是计算cost函数时,都是将n段函数并在一起,方便计算。
此外,Apollo还设置了2,3阶复合cost函数,同样的每一段的cost系数(Qk · Rk) * weight,将所有的cost系数即2*num_spline个方阵排列在主对角线,每个方阵维度为spline_order+1。最后的三阶导数cost值就为 x^T * kernel_matrix_ * x
Apollo中使用2,3阶导共同构建cost,最终的cost为:
c o s t = x T ∗ H 1 ∗ x + x T ∗ H 2 ∗ x cost = x^T * H_1 * x + x^T * H_2 * x cost=xT∗H1∗x+xT∗H2∗x
公式中,H_1为二阶导系数矩阵,权值为second_derivative_weight(200); H_2为二阶导系数矩阵,权值为third_derivative_weight(1000)。
最后一个问题,cost函数为什么设置成这样?暂时没想明白
C.4 正则化项
加入正则化项是对参数进行惩罚,常见的有:
- L1正则:$ fx $
- L2正则:$ x^Tfx $
qp_spline {
spline_order: 5
max_spline_length : 25.0
regularization_weight : 1.0e-5 // L2正则系数
second_derivative_weight : 200.0
third_derivative_weight : 1000.0
}
两者区别在于L1用于参数的稀疏,L2正则是防止过拟合,Apollo采用后者作为惩罚项。F的值取1e-5。所以得到最后的F矩阵是对角阵,对角每个元素为1e-5.
// customized input output
void Spline2dKernel::AddRegularization(const double regularization_param) {
Eigen::MatrixXd id_matrix = Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(kernel_matrix_.rows(), kernel_matrix_.cols());
kernel_matrix_ += id_matrix * regularization_param;
}
经过上述C.1-C.4处理,最终的优化目标函数等于cost加上正则化项,形式为:
1 2 ⋅ x T ⋅ H ⋅ x + f T ⋅ x s . t . L B ≤ x ≤ U B A e q x = b e q A x ≤ b \frac{1}{2} \cdot x^T \cdot H \cdot x + f^T \cdot x \\ s.t. LB \leq x \leq UB \\ A_{eq}x = b_{eq} \\ Ax \leq b 21⋅xT⋅H⋅x+fT⋅xs.t.LB≤x≤UBAeqx=beqAx≤b
D. 如何优化求解系数
请参考开源软件qpOASES
求解完这个QP问题就可以得到系数矩阵,也变相得到了x和y的这n段平滑曲线,最后的工作就是包装秤一条ReferenceLine,如何包装?答案是采样,用更细的细度去采样离散保存这条基准线。
/// file in apollo/modules/planning/reference_line/qp_spline_reference_line_smoother.cc
bool QpSplineReferenceLineSmoother::Smooth(
const ReferenceLine& raw_reference_line,
ReferenceLine* const smoothed_reference_line) {
// Step A
// mapping spline to reference line point
const double start_t = t_knots_.front(); // 原始ReferenceLine的起点,第一个anchor point,也是平滑后的ReferenceLine起点
const double end_t = t_knots_.back(); // 原始ReferenceLine的终点,最后一个anchor point,也是平滑后的ReferenceLine终点
const double resolution = (end_t - start_t) / (config_.num_of_total_points() - 1); // 采样精度,一共采样500个点。
double t = start_t;
std::vector<ReferencePoint> ref_points; // 采样点保存
const auto& spline = spline_solver_->spline();
...
}
上述代码就可以看到采样的起点、终点、精度和采样数量。
/// file in apollo/modules/planning/reference_line/qp_spline_reference_line_smoother.cc
bool QpSplineReferenceLineSmoother::Smooth(
const ReferenceLine& raw_reference_line,
ReferenceLine* const smoothed_reference_line) {
// Step A
...
// Step B
for (std::uint32_t i = 0; i < config_.num_of_total_points() && t < end_t; ++i, t += resolution) {
const double heading = std::atan2(spline.DerivativeY(t), spline.DerivativeX(t)); // 采样点速度大小
const double kappa = CurveMath::ComputeCurvature( // 采样点曲率,弧线越直曲率越小;弧线越弯,曲率越大
spline.DerivativeX(t), spline.SecondDerivativeX(t),
spline.DerivativeY(t), spline.SecondDerivativeY(t));
const double dkappa = CurveMath::ComputeCurvatureDerivative( // 曲率导数,描述曲率变化
spline.DerivativeX(t), spline.SecondDerivativeX(t),
spline.ThirdDerivativeX(t), spline.DerivativeY(t),
spline.SecondDerivativeY(t), spline.ThirdDerivativeY(t));
std::pair<double, double> xy = spline(t); // 求解累积距离为t时曲线的坐标,也是相对与第一个点的偏移坐标
xy.first += ref_x_; // 加上第一个anchor point的世界系坐标,变成世界系坐标
xy.second += ref_y_;
common::SLPoint ref_sl_point;
if (!raw_reference_line.XYToSL({xy.first, xy.second}, &ref_sl_point)) {
return false;
}
if (ref_sl_point.s() < -kEpsilon || ref_sl_point.s() > raw_reference_line.Length()) {
continue;
}
ref_sl_point.set_s(std::max(ref_sl_point.s(), 0.0));
// 将点封装成ReferencePoint,并加入向量
ReferencePoint rlp = raw_reference_line.GetReferencePoint(ref_sl_point.s());
auto new_lane_waypoints = rlp.lane_waypoints();
for (auto& lane_waypoint : new_lane_waypoints) {
lane_waypoint.l = ref_sl_point.l();
}
ref_points.emplace_back(ReferencePoint(
hdmap::MapPathPoint(common::math::Vec2d(xy.first, xy.second), heading,
new_lane_waypoints), kappa, dkappa));
}
// 去除过近的冗余点,最终将vector<ReferencePoint>封装成ReferenceLine
ReferencePoint::RemoveDuplicates(&ref_points);
if (ref_points.size() < 2) {
AERROR << "Fail to generate smoothed reference line.";
return false;
}
*smoothed_reference_line = ReferenceLine(ref_points);
return true;
}
上述平滑ReferenceLine的生成过程其实也比较简单,分别采集每个点,计算坐标,速度,曲率,曲率导数等信息;然后修正采样点的累积距离便可以得到平滑后参考线的采样点。最后对所有的采样点封装变成平滑的参考线。
至此,knots分段与二次规划进行参考线平滑阶段已经全部完成,可以看到平滑参考线其实依旧是一个采样的过程,为什么不对原始的参考线直接进行更细粒度的采样(与anchor point和knots采样一样)?这里的理解是使用平滑参考线可以实时计算参考线上每个点的速度,曲率,曲率导数等信息,可以进一步描述车辆的运动状态信息。例如,车辆在平坦或者弯道部分(查询kappa)?车辆正要进入弯道还是脱离弯道(查询dkappa)?
在得到平滑参考线以后一定要做一个校验:对平滑参考线SmoothReferenceLine上的点(可以采样,比如累积距离每10m采样),投影到原始参考线RawReferenceLine的距离为l,l不能太大,否则两条参考线有较大的偏移。这也是IsReferenceLineSmoothValid的工作。
/// file in apollo/modules/planning/reference_line/reference_line_provider.cc
bool ReferenceLineProvider::IsReferenceLineSmoothValid(
const ReferenceLine &raw, const ReferenceLine &smoothed) const {
constexpr double kReferenceLineDiffCheckStep = 10.0;
for (double s = 0.0; s < smoothed.Length();
s += kReferenceLineDiffCheckStep) {
auto xy_new = smoothed.GetReferencePoint(s);
common::SLPoint sl_new;
if (!raw.XYToSL(xy_new, &sl_new)) {
AERROR << "Fail to change xy point on smoothed reference line to sl "
"point respect to raw reference line.";
return false;
}
const double diff = std::fabs(sl_new.l());
if (diff > FLAGS_smoothed_reference_line_max_diff) {
AERROR << "Fail to provide reference line because too large diff "
"between smoothed and raw reference lines. diff: "
<< diff;
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
功能2:平滑参考线的拼接
平滑参考线拼接是针对不同时刻的RawReference,如果两条原始的RawReference是相连并且有覆盖的,那么可以不需要重新去进行平滑,只要直接使用上时刻的平滑参考线,或者仅仅平滑部分anchor point即可。
例如上时刻得到的平滑参考线reference_prev,这时刻由RouteSegments得到的原始费平滑参考线reference_current。由于RouteSegments生成有一个look_forward_distance的前向查询距离,所以这时候车辆的位置很可能还在前一时刻的平滑参考线reference_prev,这时候就可以复用上时刻的参考线信息,下面我们直接从代码来理解参考线拼接的流程和逻辑。
/// file in apollo/modules/planning/reference_line/reference_line_provider.cc
bool ReferenceLineProvider::CreateReferenceLine(
std::list<ReferenceLine> *reference_lines,
std::list<hdmap::RouteSegments> *segments) {
if (!CreateRouteSegments(vehicle_state, look_backward_distance, look_forward_distance, segments)) {
return false;
}
// A. 参考线平滑,条件enable_reference_line_stitching设置为False,也就是不允许参考线拼接操作
if (is_new_routing || !FLAGS_enable_reference_line_stitching) {
for (auto iter = segments->begin(); iter != segments->end();) {
reference_lines->emplace_back();
if (!SmoothRouteSegment(*iter, &reference_lines->back())) {
AERROR << "Failed to create reference line from route segments";
reference_lines->pop_back();
iter = segments->erase(iter);
} else {
++iter;
}
}
return true;
} else { // B. 允许参考线拼接
for (auto iter = segments->begin(); iter != segments->end();) {
reference_lines->emplace_back();
if (!ExtendReferenceLine(vehicle_state, &(*iter), &reference_lines->back())) {
AERROR << "Failed to extend reference line";
reference_lines->pop_back();
iter = segments->erase(iter);
} else {
++iter;
}
}
}
return true;
}
下面我们将深入ExtendReferenceLine参考线扩展/拼接函数,查看逻辑,通过代码我们将逻辑整理如下:
- 根据历史缓存信息,查询当前RouteSegments是否在某条(Smoothed)ReferenceLine上,如果不是就直接进行平滑参考线操作
bool ReferenceLineProvider::ExtendReferenceLine(const VehicleState &state,
RouteSegments *segments,
ReferenceLine *reference_line) {
// Case A
RouteSegments segment_properties;
segment_properties.SetProperties(*segments);
auto prev_segment = route_segments_.begin();
auto prev_ref = reference_lines_.begin();
while (prev_segment != route_segments_.end()) {
if (prev_segment->IsConnectedSegment(*segments)) {
break;
}
++prev_segment;
++prev_ref;
}
if (prev_segment == route_segments_.end()) {
return SmoothRouteSegment(*segments, reference_line);
}
查询路径段prev_segment是否连接到segments整个路径上的函数IsConnectedSegment其实很简单,无非以下四种情况:
- segments整个路径的起点在prev_segment段内
- segments整个路径的终点在prev_segment段内
- prev_segment路径段的起点落在segments路径上
- prev_segment路径段的终点落在segments路径上
- 如果在同一个平滑参考线(历史平滑参考线)上,计算车辆当前位置和历史平滑参考线终点的距离,如果距离超过了阈值,则可以复用这条历史参考线;否则长度不够需要拼接。
bool ReferenceLineProvider::ExtendReferenceLine(const VehicleState &state,
RouteSegments *segments,
ReferenceLine *reference_line) {
// Case A
...
// Case B
common::SLPoint sl_point;
Vec2d vec2d(state.x(), state.y());
LaneWaypoint waypoint;
if (!prev_segment->GetProjection(vec2d, &sl_point, &waypoint)) { // 计算车辆当前位置在历史平滑参考线上的位置
return SmoothRouteSegment(*segments, reference_line);
}
const double prev_segment_length = RouteSegments::Length(*prev_segment); // 历史平滑参考线总长度
const double remain_s = prev_segment_length - sl_point.s(); // 历史平滑参考线前方剩下的距离
const double look_forward_required_distance = LookForwardDistance(state); // 前向查询距离
if (remain_s > look_forward_required_distance) { // 如果剩下的距离足够长,那么直接复用这条历史平滑参考线。
*segments = *prev_segment;
segments->SetProperties(segment_properties);
*reference_line = *prev_ref;
return true;
}
- 如果2种情况历史参考线遗留长度不够,那么久需要先对RouteSegments进行扩展,这部分在Pnc Map后接车道处理中有相关介绍。如果扩展失败直接进行平滑操作;如果扩展以后长度仍然不够,说明死路没有后继车道,只能复用历史平滑参考线。
bool ReferenceLineProvider::ExtendReferenceLine(const VehicleState &state,
RouteSegments *segments,
ReferenceLine *reference_line) {
// Case A
...
// Case B
...
// Case C
double future_start_s =
std::max(sl_point.s(), prev_segment_length - FLAGS_reference_line_stitch_overlap_distance);
double future_end_s = prev_segment_length + FLAGS_look_forward_extend_distance; // 向后额外扩展look_forward_extend_distance的距离,默认50m
RouteSegments shifted_segments;
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(pnc_map_mutex_);
if (!pnc_map_->ExtendSegments(*prev_segment, future_start_s, future_end_s, &shifted_segments)) {
lock.unlock();
AERROR << "Failed to shift route segments forward";
return SmoothRouteSegment(*segments, reference_line); // C.1 扩展操作失败,直接对新的RouteSegments进行平滑得到平滑参考线
}
lock.unlock();
if (prev_segment->IsWaypointOnSegment(shifted_segments.LastWaypoint())) {
*segments = *prev_segment; // C.2 扩展操作成功,但是扩招以后长度没有太大变化,死路,直接使用历史平滑参考线
segments->SetProperties(segment_properties);
*reference_line = *prev_ref;
ADEBUG << "Could not further extend reference line";
return true;
}
- 如果3情况下扩展成功,并且额外增加了一定长度,得到了新的Path(也即新的RouteSegments),接下来对新的路径进行平滑然后与历史平滑参考线进行拼接,就可以得到一条更长的平滑参考线。
bool ReferenceLineProvider::ExtendReferenceLine(const VehicleState &state,
RouteSegments *segments,
ReferenceLine *reference_line) {
// Case A
...
// Case B
...
// Case C
...
// Case D
hdmap::Path path;
hdmap::PncMap::CreatePathFromLaneSegments(shifted_segments, &path);
ReferenceLine new_ref(path);
if (!SmoothPrefixedReferenceLine(*prev_ref, new_ref, reference_line)) { // SmoothPrefixedReferenceLine过程和普通的拼接其实没多大差异
AWARN << "Failed to smooth forward shifted reference line";
return SmoothRouteSegment(*segments, reference_line);
}
if (!reference_line->Stitch(*prev_ref)) { // 两条平滑车道线拼接
AWARN << "Failed to stitch reference line";
return SmoothRouteSegment(*segments, reference_line);
}
if (!shifted_segments.Stitch(*prev_segment)) { // 两条平滑车道线对应的RouteSegments拼接
AWARN << "Failed to stitch route segments";
return SmoothRouteSegment(*segments, reference_line);
}
拼接过程也是非常简单,我们可以直接看Apollo给出的定义
- Stitch current reference line with the other reference line
- The stitching strategy is to use current reference points as much as
- possible. The following two examples show two successful stitch cases.
- Example 1
- this: |--------A-----x-----B------|
- other: |-----C------x--------D-------|
- Result: |------A-----x-----B------x--------D-------|
- In the above example, A-B is current reference line, and C-D is the other
- reference line. If part B and part C matches, we update current reference
- line to A-B-D.
- Example 2
- this: |-----A------x--------B-------|
- other: |--------C-----x-----D------|
- Result: |--------C-----x-----A------x--------B-------|
- In the above example, A-B is current reference line, and C-D is the other
- reference line. If part A and part D matches, we update current reference
- line to C-A-B.
- @return false if these two reference line cannot be stitched
- 当在4完成参考线的拼接以后,就可以得到一条更长的参考线,前向查询距离经过限制不会超出要求,但是随着车辆的前进,车后参考线的长度会变得很大,所以最后一步就是对车后的参考线进行收缩,保证车辆前后都有合理长度的参考线
bool ReferenceLineProvider::ExtendReferenceLine(const VehicleState &state,
RouteSegments *segments,
ReferenceLine *reference_line) {
// Case A
...
// Case B
...
// Case C
...
// Case D
...
// Case E
*segments = shifted_segments;
segments->SetProperties(segment_properties);
common::SLPoint sl;
if (sl.s() > FLAGS_look_backward_distance * 1.5) { // 如果车后参考线的距离大于后向查询距离1.5倍,就需要收缩
if (!reference_line->Shrink(vec2d, FLAGS_look_backward_distance, // E.1 拼接参考线收缩
std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity())) {
AWARN << "Failed to shrink reference line";
}
if (!segments->Shrink(vec2d, FLAGS_look_backward_distance, // E.2 对应的RouteSegments收缩
std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity())) {
AWARN << "Failed to shrink route segment";
}
}
收缩参考线ReferenceLine的操作很简单,就是删除查询距离1.5倍之后的ReferencePoint即可。
/// file in apollo/modules/planning/reference_line/reference_line.cc
bool ReferenceLine::Shrink(const common::math::Vec2d& point,
double look_backward, double look_forward) {
common::SLPoint sl;
if (!XYToSL(point, &sl)) {
return false;
}
const auto& accumulated_s = map_path_.accumulated_s();
size_t start_index = 0;
if (sl.s() > look_backward) { // 查询收缩下界
auto it_lower = std::lower_bound(accumulated_s.begin(), accumulated_s.end(), sl.s() - look_backward);
start_index = std::distance(accumulated_s.begin(), it_lower);
}
size_t end_index = reference_points_.size();
if (sl.s() + look_forward < Length()) { // 查询收缩上界
auto start_it = accumulated_s.begin();
std::advance(start_it, start_index);
auto it_higher = std::upper_bound(start_it, accumulated_s.end(), sl.s() + look_forward);
end_index = std::distance(accumulated_s.begin(), it_higher);
}
// 删除上界和下界以外的点,完成收缩
reference_points_.erase(reference_points_.begin() + end_index, reference_points_.end());
reference_points_.erase(reference_points_.begin(), reference_points_.begin() + start_index);
map_path_ = MapPath(std::vector<hdmap::MapPathPoint>(
reference_points_.begin(), reference_points_.end()));
return true;
}
注意在ReferenceLineProvider::ExtendReferenceLine中不论是ReferenceLine还是RouteSegments的Shrink函数,look_forward参数都设置为无穷大,所以只是后向收缩,前向不收缩。
如有侵权,请联系本人删除!
参考资料:https://github.com/YannZyl/Apollo-Note/blob/master/docs/planning/reference_line_provider.md