利用Prompt工程为LLM提升推理能力
众所周知,一个精心设计的Prompt能够显著增强大型语言模型(LLMs)的推理能力,助力AI应用更高效地解决实际问题。本文将深入探讨如何通过有效的Prompt工程技术,实现这一目标。【⭐文章结尾附全部代码⭐】
有效的Prompt工程技术对于帮助大型语言模型(LLMs)产生更可靠、结构化且推理严谨的回答至关重要。通常,这些Prompt技术都是基于以下几个关键原则写出来的:
- 任务分解:将复杂任务细分为更小、更易管理的步骤,帮助LLMs更系统地进行信息处理,减少错误,提升逻辑一致性。
- 清晰格式:制定明确的输出结构,引导LLMs有序组织思路,以更易懂的方式呈现信息。
- 自我反思:鼓励LLMs回顾自身推理过程,有助于发现潜在错误,考量多元观点。
- 情境模拟:设定特定框架,如“利弊分析”或“多角度考量”,助力模型从不同维度解决问题。
这些原则构成了我们编写Prompt的基石,每种策略都充分发挥了LLMs的不同能力,确保回答的一致性和可靠性。
基于策略的推理详解
虽然白板的LLM也可以直接处理任务,但是要是想让LLM有高级推理能力的话,就需要设计结构化的解决问题方法。为此,我们首先定义了一个策略模式父类,进而派生出多种推理策略。接下来,让我们一探究竟:
class ExecutionStrategy(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def build_prompt(self, task: str, instruction: Optional[str] = None) -> str:
"""Build the prompt according to the strategy."""
pass
@abstractmethod
def process_response(self, response: str) -> str:
"""Process the LLM response according to the strategy."""
pass
这个抽象的父类为实现各种推理策略提供了基础。每种策略都提供了一种独特的方法来:
- 构建问题解决过程;
- 分解复杂任务;
- 组织代理的思考过程;
- 确保对问题进行彻底考虑。
下面让我们更深入地看看三种不同的技术:ReAct、思维链和反思。
ReAct: 推理与行动
ReAct策略(Reasoning和Action)实现了一个思考、行动和观察三个行为的循环执行,这样可以使LLM的决策过程变得清晰且可追溯。下面是实现代码:
class ReactStrategy(ExecutionStrategy):
def build_prompt(self, task: str, instruction: Optional[str] = None) -> str:
base_prompt = """Approach this task using the following steps:
1) Thought: Analyze what needs to be done
2) Action: Decide on the next action
3) Observation: Observe the result
4) Repeat until task is complete
Follow this format for your response:
Thought: [Your reasoning about the current situation]
Action: [The action you decide to take]
Observation: [What you observe after the action]
... (continue steps as needed)
Final Answer: [Your final response to the task]
Task: {task}"""
这个策略确保了:
- 明确推理:每一步思考过程都表达得清晰明了。
- 行动导向:决策与具体行动紧密相连。
- 迭代优化:通过循环观察和调整,逐步完善解决方案。
思维链:逐步解决问题
思维链策略将复杂问题分解成可管理的步骤,使推理过程更加透明和可验证。下面是它的工作原理:
class ChainOfThoughtStrategy(ExecutionStrategy):
def build_prompt(self, task: str, instruction: Optional[str] = None) -> str:
base_prompt = """Let's solve this step by step:
Task: {task}
Please break down your thinking into clear steps:
1) First, ...
2) Then, ...
(continue with your step-by-step reasoning)
Final Answer: [Your conclusion based on the above reasoning]"""
这种方法提供了:
- 线性进展:通过步骤化推进复杂问题。
- 清晰联系:步骤与结论之间逻辑清晰。
- 易于验证:推理过程更简单易懂。
- 深度理解:更好地把握结论的来龙去脉。
反思:深入分析和自我审查
反思策略增加了一个元认知层,鼓励代理检查自己的假设并考虑替代方法。代码如下:
class ReflectionStrategy(ExecutionStrategy):
def build_prompt(self, task: str, instruction: Optional[str] = None) -> str:
base_prompt = """Complete this task using reflection:
Task: {task}
1) Initial Approach:
- What is your first impression of how to solve this?
- What assumptions are you making?
2) Analysis:
- What could go wrong with your initial approach?
- What alternative approaches could you consider?
3) Refined Solution:
- Based on your reflection, what is the best approach?
- Why is this approach better than the alternatives?"""
与代理架构的集成
这些策略通过工厂模式和策略设置器,与代理架构实现了无缝集成。
class Agent:
@property
def strategy(self) -> Optional[ExecutionStrategy]:
return self._strategy
@strategy.setter
def strategy(self, strategy_name: str):
"""Set the execution strategy by name."""
self._strategy = StrategyFactory.create_strategy(strategy_name)
执行流程包含了所选策略:
def execute(self, task: Optional[str] = None) -> str:
if task is not None:
self._task = task
messages = self._build_messages()
try:
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model=self._model,
messages=messages
)
response_content = response.choices[0].message.content
# Process response through strategy if set
if self._strategy:
response_content = self._strategy.process_response(response_content)
实际应用
下面以一个实际的例子,展示如何在实际中使用这些策略:
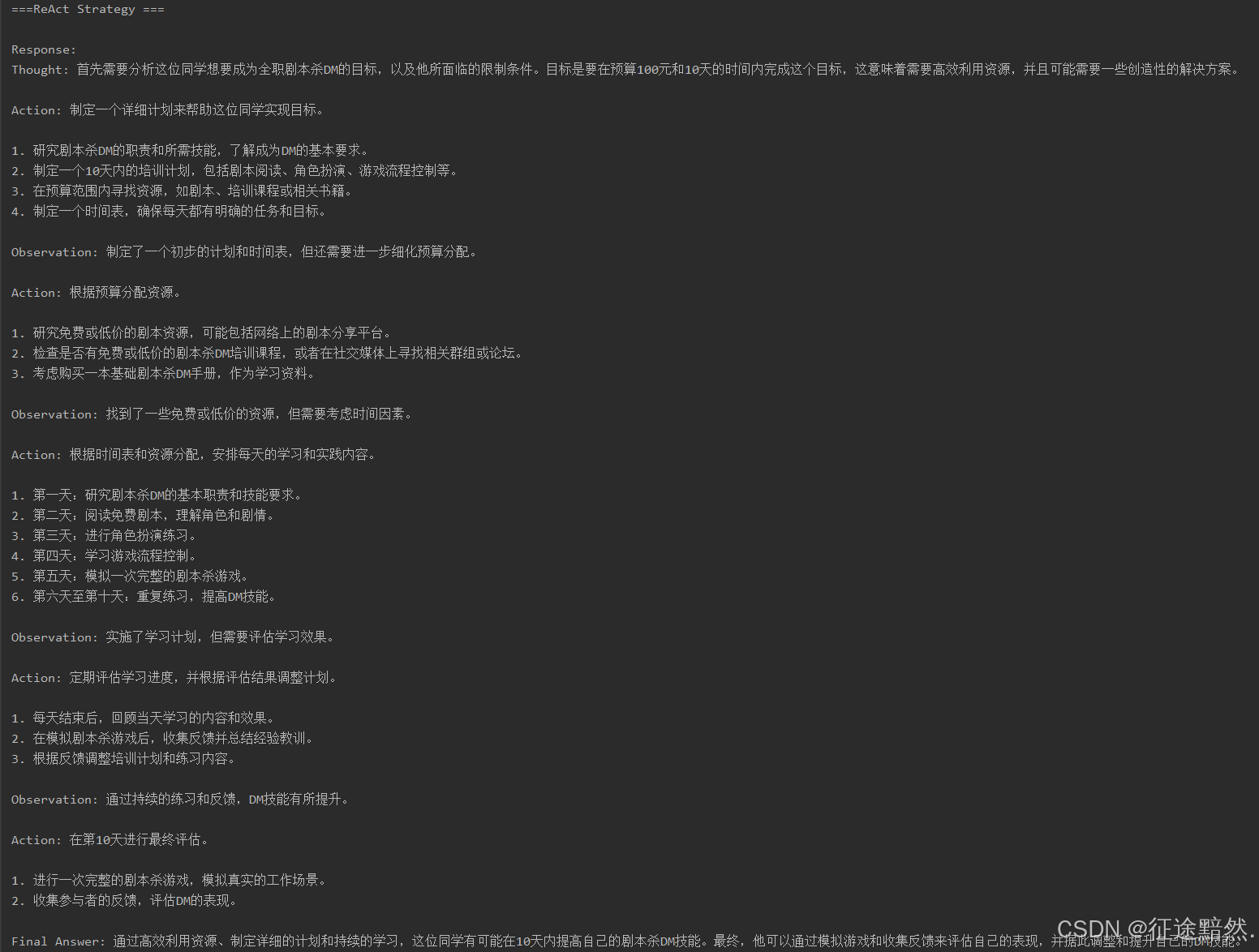
task = """一位同学想成为全职剧本杀DM,他有如下限制条件:
预算:100元
限时:10天
他们应该如何完成这个白日梦?"""
print("\n===ReAct Strategy ===")
agent.strategy = "ReactStrategy"
agent.task = task
response = agent.execute()
print("\nResponse:")
print(response)
print("\n===Chain of Thought Strategy ===")
agent.strategy = "ChainOfThoughtStrategy"
agent.task = task
response = agent.execute()
print("\nResponse:")
print(response)
print("\n===Reflection Strategy ===")
agent.strategy = "ReflectionStrategy"
agent.task = task
response = agent.execute()
print("\nResponse:")
print(response)
三种策略的效果如下所示:
在实际应用中,这些策略展现了显著优势:
- 灵活选择:针对不同任务,灵活选用适宜的推理方法。
- 一致格式:无论采用何种策略,输出都保持结构化。
- 清晰路径:问题解决过程记录透明,易于追踪。
- 策略对比:方便评估同一问题的不同解决方法。
代码附录
from abc import abstractmethod, ABC
from typing import Optional, List, Dict
from openai import OpenAI
class ExecutionStrategy(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def build_prompt(self, task: str, instruction: Optional[str] = None) -> str:
"""Build the prompt according to the strategy."""
pass
@abstractmethod
def process_response(self, response: str) -> str:
"""Process the LLM response according to the strategy."""
pass
class ReactStrategy(ExecutionStrategy):
def build_prompt(self, task: str, instruction: Optional[str] = None) -> str:
base_prompt = """Approach this task using the following steps:
1) Thought: Analyze what needs to be done
2) Action: Decide on the next action
3) Observation: Observe the result
4) Repeat until task is complete
Follow this format for your response:
Thought: [Your reasoning about the current situation]
Action: [The action you decide to take]
Observation: [What you observe after the action]
... (continue steps as needed)
Final Answer: [Your final response to the task]
Task: {task}"""
if instruction:
base_prompt += f"\nAdditional Instruction: {instruction}"
return base_prompt.format(task=task)
def process_response(self, response: str) -> str:
"""Process the LLM response according to the strategy."""
return response
class ChainOfThoughtStrategy(ExecutionStrategy):
def build_prompt(self, task: str, instruction: Optional[str] = None) -> str:
base_prompt = """Let's solve this step by step:
Task: {task}
Please break down your thinking into clear steps:
1) First, ...
2) Then, ...
(continue with your step-by-step reasoning)
Final Answer: [Your conclusion based on the above reasoning]"""
if instruction:
base_prompt += f"\nAdditional Instruction: {instruction}"
return base_prompt.format(task=task)
def process_response(self, response: str) -> str:
"""Process the LLM response according to the strategy."""
return response
class ReflectionStrategy(ExecutionStrategy):
def build_prompt(self, task: str, instruction: Optional[str] = None) -> str:
base_prompt = """Complete this task using reflection:
Task: {task}
1) Initial Approach:
- What is your first impression of how to solve this?
- What assumptions are you making?
2) Analysis:
- What could go wrong with your initial approach?
- What alternative approaches could you consider?
3) Refined Solution:
- Based on your reflection, what is the best approach?
- Why is this approach better than the alternatives?"""
if instruction:
base_prompt += f"\nAdditional Instruction: {instruction}"
return base_prompt.format(task=task)
def process_response(self, response: str) -> str:
"""Process the LLM response according to the strategy."""
return response
class StrategyFactory:
"""Factory class for creating execution strategies."""
_strategies = {
'ReactStrategy': ReactStrategy,
'ChainOfThoughtStrategy': ChainOfThoughtStrategy,
'ReflectionStrategy': ReflectionStrategy
}
@classmethod
def create_strategy(cls, strategy_name: str) -> ExecutionStrategy:
"""Create a strategy instance based on the strategy name."""
strategy_class = cls._strategies.get(strategy_name)
if not strategy_class:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown strategy: {strategy_name}")
return strategy_class()
@classmethod
def available_strategies(cls) -> List[str]:
"""Return a list of available strategy names."""
return list(cls._strategies.keys())
class Agent:
def __init__(self, name: str, system_prompt: str, instruction: str, api_key: str, url: str, model_name: str):
self.task = None
self.name = name
self.system_prompt = system_prompt
self.instruction = instruction
self._strategy = None
self.model_name = model_name
self.client = OpenAI(
api_key=api_key,
base_url=url
)
@property
def strategy(self) -> Optional[ExecutionStrategy]:
return self._strategy
@strategy.setter
def strategy(self, strategy_name: str):
"""Set the execution strategy by name."""
self._strategy = StrategyFactory.create_strategy(strategy_name)
def execute(self, task: Optional[str] = None) -> str:
if task is not None:
self.task = task
messages = self._build_messages()
try:
completion = self.client.chat.completions.create(
model=self.model_name,
messages=messages
)
response_content = completion.choices[0].message.content
if self._strategy:
response_content = self._strategy.process_response(response_content)
return response_content
except Exception as e:
return f"An error occurred: {str(e)}"
def _build_messages(self) -> List[Dict[str, str]]:
messages = [{"role": "system", "content": self.system_prompt}]
if self.instruction:
messages.append({
"role": "user",
"content": f"Global Instruction: {self.instruction}"
})
current_task = self._strategy.build_prompt(self.task, self.instruction)
if current_task:
messages.append({"role": "user", "content": current_task})
return messages
system_prompt = """你是一个分析解决问题的助手。你擅长分解复杂的问题并解释你的思维过程。你的解释透彻、有逻辑、清晰。"""
instruction = "确保你的回答清晰、详细、结构合理。始终保持以中文回答。"
url = "https://open.bigmodel.cn/api/paas/v4/"
api_key = "xxx"
agent = Agent(
name="难题粉碎机",
system_prompt=system_prompt,
instruction=instruction,
api_key=api_key,
url=url,
model_name="glm-4-flash"
)
task = """一位同学想成为全职剧本杀DM,他有如下限制条件:
预算:100元
限时:10天
他们应该如何完成这个白日梦?"""
print("\n===ReAct Strategy ===")
agent.strategy = "ReactStrategy"
agent.task = task
response = agent.execute()
print("\nResponse:")
print(response)
print("\n===Chain of Thought Strategy ===")
agent.strategy = "ChainOfThoughtStrategy"
agent.task = task
response = agent.execute()
print("\nResponse:")
print(response)
print("\n===Reflection Strategy ===")
agent.strategy = "ReflectionStrategy"
agent.task = task
response = agent.execute()
print("\nResponse:")
print(response)