一、Linux命令和windows区别?
1、Linux命令全部严格区分大小写;而windows命令大小写都识别。
2、Linux所有的文件都是没有扩展名的,而windows是文件是有扩展名的。
创建一个新用户
[root@localhost mxh]# useradd mxh2 # 创建一个user
[root@localhost mxh]# password mxh2 #12345678
[root@localhost xxx]# groupadd mxhgrp #创建一个组mxhgrp
[root@localhost xxx]# passwd mxhgrp #12345678
passwd 命令用于更改密码
管理员可以更改任何人的密码;而普通用户只能更改自己的密码;
查找命令使用方法
1、man ls
2、 ls --helptab命令用于补全文件名
二、使用命令
命令格式
命令 [-选项] [参数] []->指可选参数,不加这两个参数的命令也可以单独执行,例如ls
例如: ls -la /etc
ls:命令; -la:选项;/etc:操作对象
文件用户分为三类:所有者、用户组、其他人
1、所有者:只能有一个,而且身份可能是会变换的;比如我的电脑,我就是所有者,卖给别人后,那个卖买的人就是所有者,而我不是所有者了。
2、所属组:我的电脑可以给办公室里的美女使用,多个美女就是一个所属组,而我还是所有者
3、其他人:除了以上两个身份外的用户
| 目录处理命令 | |
| ls -a | 查看目录下所有文件,包括隐藏的文件 |
| ls -l | 查看目录下文件的详细信息(包括权限) |
| ls -lh | 人性化查看目录下文件的详细信息(包括权限) |
| ls -ld | 查看文件详细信息(包括权限) |
| ls -li | 查看文件的ID序号 |
1、ls:主要查看当前目录下有什么文件,并没有定位到那个目录下
[root@localhost ~]# ls /
bin dev home lib64 mnt proc run srv tmp var
boot etc lib media opt root sbin sys usr
2、cd:用于定位到那个目录下
[root@localhost ~]# ls /
bin dev home lib64 mnt proc run srv tmp var
boot etc lib media opt root sbin sys usr
[root@localhost ~]# ls /run
auditd.pid dbus initramfs plymouth tmpfiles.d
blkid dhclient-ens33.pid lock sepermit tuned
chrony dmeventd-client log setrans udev
console dmeventd-server lvm sshd.pid user
crond.pid ebtables.lock mount sudo utmp
cron.reboot faillock netreport syslogd.pid vmware
cryptsetup firewalld NetworkManager systemd xtables.lock
[root@localhost ~]# cd /run
[root@localhost run]# ls
auditd.pid dbus initramfs plymouth tmpfiles.d
blkid dhclient-ens33.pid lock sepermit tuned
chrony dmeventd-client log setrans udev
console dmeventd-server lvm sshd.pid user
crond.pid ebtables.lock mount sudo utmp
cron.reboot faillock netreport syslogd.pid vmware
cryptsetup firewalld NetworkManager systemd xtables.lock
[root@localhost run]#
3、ls -a:显示当前目录下所有文件,包括隐藏的文件,隐藏的文件是以 .开头的
[root@localhost ~]# ls -a
. .. anaconda-ks.cfg .bash_logout .bash_profile .bashrc .cshrc .tcshrc
4、ls -l(l->long) :文件以一个详细的信息列出来显示
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l
总用量 4
-rw-------. 1 root root 1216 10月 22 21:38 anaconda-ks.cfg
#1->引用计数; root->所有者(rw权限); root->所属组(无权限); 1216B->文件大小;10.22是文件修改时间
ls -lh(h->human人性化显示)
[root@localhost ~]# ls -lh
总用量 4.0K
-rw-------. 1 root root 1.2K 10月 22 21:38 anaconda-ks.cfg文件类型:区分软连接、文件、目录
-:表示一个文件
d开头:表示一个目录
l:开头表示一个软连接
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /
总用量 20
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 10月 22 21:29 bin -> usr/bin #软连接
dr-xr-xr-x. 5 root root 4096 10月 23 09:23 boot #目录
[root@localhost ~]# ls -a
. .. anaconda-ks.cfg .bash_logout .bash_profile .bashrc .cshrc .tcshrc
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /run #查看run目录下所有文件权限
总用量 24
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 4 10月 23 09:21 auditd.pid
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 80 10月 23 09:22 blkid #所有者:rw、x、r权限;所属组:x、r权限
drwxr-x---. 2 chrony chrony 80 10月 23 09:23 chrony #是一个目录
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 40 10月 23 09:21 console
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 09:23 crond.pid #是一个文件
X执行权限最大;
5、ls -ld :查看文件权限,不是目录下文件的权限;注意与ls -l的区别;
[root@localhost ~]# ls -ld /run
drwxr-xr-x. 26 root root 740 10月 23 09:23 /run #run这个文件:所有者rw、x、r权限
5、ls -li:查看文件的id序号(最前面的是ID号)
[root@localhost ~]# ls -li /run
总用量 24
15072 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 4 10月 23 09:21 auditd.pid
16995 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 80 10月 23 09:22 blkid
24830 drwxr-x---. 2 chrony chrony 80 10月 23 09:23 chrony
15035 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 40 10月 23 09:21 console
26891 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 09:23 crond.pid
28110 ----------. 1 root root 0 10月 23 09:23 cron.reboot
15034 drwx------. 2 root root 40 10月 23 09:21 cryptsetup
24213 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 60 10月 23 09:23 dbus
27608 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 11:31 dhclient-ens33.pid
13853 prw-------. 1 root root 0 10月 23 09:19 dmeventd-client
13852 prw-------. 1 root root 0 10月 23 09:19 dmeventd-server
28868 -rw-------. 1 root root 0 10月 23 09:23 ebtables.lock
15024 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 40 10月 23 09:21 faillock
27614 drwxr-x---. 2 root root 40 10月 23 09:23 firewalld
10562 drwxr-xr-x. 4 root root 120 10月 23 09:19 initramfs
1085 drwxr-xr-x. 5 root root 120 10月 23 10:30 lock
10566 drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 60 10月 23 09:19 log
| 文件处理命令 | |
| mkdir | 创建文件mkdir /tmp/mxh 在tmp目录下创建mxh文件夹 |
| mkdir -p | 递归创建多个文件夹 |
| cd | 定位到某个目录下 |
| cd.. | 返回上一级目录 |
| pwd | 打印当前所在的完整目录 |
| rmdir | 删除命令(只能删除空目录) |
| cp | 复制命令:将文件复制到其他目录下的操作 |
| cp -r | 复制命令:将目录复制到其他目录下的操作 |
| cp -p | 复制文件时保留其属性,修改时间不变,特别是日志 |
| cp | 进行复制的同时还可以改名字 |
1、mkdir 创建文件
mkdir +文件位置 这个只能在原有的目录下创建一个文件夹,不能连续创建多个子目录
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /tmp/mxh
[root@localhost ~]# ls /tmp
ks-script-IAr5pa
mxh #这个是我创建的文件夹
vmware-root_724-2965906890
vmware-root_7527-3853947382
yum.log
2、mkdir -p 加目录:可连续创建多个子目录
[root@localhost tmp]# mkdir -p /tmp/mxh/mxh1/mxh2 #连续创建两个子目录mxh1、mxh2
[root@localhost tmp]# ls /tmp/mxh
mxh1
[root@localhost tmp]# ls /tmp/mxh/mxh1
mxh2
3、mkdir 同时创建多个并行目录文件夹
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /tmp/mxh/AK1 /tmp/mxh/AK2 #两个目录中间是用空格隔开
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /tmp
总用量 4
-rwx------. 1 root root 836 10月 22 21:38 ks-script-IAr5pa
drwxr-xr-x. 5 root root 40 10月 23 13:00 mxh
drwx------. 3 root root 17 10月 23 09:23 systemd-private-4b41272e80d041ceb75a8d4cc2b1d4a6-chronyd.service-KlCaFC
drwx------. 3 root root 17 10月 22 21:41 systemd-private-4d581edd37154b6cb14d94ae0babdd78-chronyd.service-dubJHv
drwx------. 2 root root 6 10月 22 21:41 vmware-root_724-2965906890
drwx------. 2 root root 6 10月 23 09:23 vmware-root_7527-3853947382
-rw-------. 1 root root 0 10月 22 21:28 yum.log
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /tmp/mxh
总用量 0
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 10月 23 13:00 AK1 #在/tmp/mxh下创建AK1
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 10月 23 13:00 AK2 #在/tmp/mxh下创建AK2
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 18 10月 23 12:52 mxh1
4、pwd
[root@localhost ~]# cd /tmp/mxh/AK1
[root@localhost AK1]# ls
[root@localhost AK1]# pwd
/tmp/mxh/AK1
5、cd用法,返回上一级命令
[root@localhost tmp]# cd /tmp/mxh/AK1
[root@localhost AK1]# pwd
/tmp/mxh/AK1
[root@localhost AK1]# cd ..
[root@localhost mxh]# cd ..
[root@localhost tmp]# cd ..
[root@localhost /]# cd ..
[root@localhost /]# ls /
bin dev home lib64 mnt proc run srv tmp var
boot etc lib media opt root sbin sys usr
6、rmdir 删除命令使用(只能删除空目录)
[root@localhost /]# ls /tmp/mxh
AK1 AK2 mxh1
[root@localhost /]# rmdir /tmp/mxh/AK2 #删除AK2
[root@localhost /]# ls /tmp/mxh
AK1 mxh1
7、cp复制命令:#这个是将文件复制到其他目录下的操作
#这个是将文件复制到其他目录下的操作
[root@localhost tmp]# cp /run/auditd.pid /tmp/mxh/test #将auditd.pid复制到test目录下
[root@localhost tmp]# ls /tmp/mxh/test
auditd.pid
8、将目录复制到其他目录下操作
[root@localhost tmp]# ls /tmp
ks-script-IAr5pa
mxh
systemd-private-4b41272e80d041ceb75a8d4cc2b1d4a6-chronyd.service-KlCaFC
systemd-private-4d581edd37154b6cb14d94ae0babdd78-chronyd.service-dubJHv
test1 #将test1这个目录复制到麦mxh这个目录下
vmware-root_724-2965906890
vmware-root_7527-3853947382
yum.log
[root@localhost tmp]# cp -r /tmp/test1 /tmp/mxh
[root@localhost tmp]# ls /tmp/mxh
test test1
9、cp同时复制多个文件到其他目录 cp 目标文件1 目标文件2 。。。。 目的目录
#将/run下的crond.pid、cron.reboot复制到test1目录下
[root@localhost tmp]# cp /run/crond.pid /run/cron.reboot /tmp/mxh/test1
[root@localhost tmp]# ls /tmp/mxh/test1
crond.pid cron.reboot
10、cp -p :复制文件时保留其属性不变
[root@localhost tmp]# ls /run
auditd.pid dbus initramfs plymouth tmpfiles.d
blkid dhclient-ens33.pid lock sepermit tuned
chrony dmeventd-client log setrans udev
console dmeventd-server lvm sshd.pid user
crond.pid ebtables.lock mount sudo utmp
cron.reboot faillock netreport syslogd.pid vmware
cryptsetup firewalld NetworkManager systemd xtables.lock
[root@localhost tmp]# ls -l /run/crond.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 09:23 /run/crond.pid
[root@localhost tmp]# cp -p /run/crond.pid /tmp/mxh/test1
cp:是否覆盖"/tmp/mxh/test1/crond.pid"? y
[root@localhost tmp]# ls -l /tmp/mxh/test1
总用量 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 09:23 crond.pid 时间和修改前不变
11、cp进行复制的同时还可以改名字
[root@localhost tmp]# ls /tmp/mxh
test test1
[root@localhost tmp]# ls /tmp/mxh/test1
crond.pid cron.reboot
[root@localhost tmp]# cp -r /tmp/mxh/test1 /tmp/mxh/test/gaiming #将test1这个目录复制到test目录下,并同时将test1这个目录名称改为gaiming这个名称
[root@localhost tmp]# ls /tmp/mxh/test
auditd.pid gaiming
[root@localhost tmp]# ls /tmp/mxh/test/gaiming
crond.pid cron.reboot
| mv | 剪切功能:mv 剪切目标 剪切目的(可直接剪切文件或目录,不需要像cp -r 来复制目录) |
| mv | 该文件或文件夹名称 |
1、mv 剪切功能(可直接剪切文件或目录,不需要像cp -r 来复制目录)
[root@localhost ~]# ls /tmp/mxh/test1
crond.pid cron.reboot
[root@localhost ~]# mv /tmp/mxh/test1/crond.pid /tmp/mxh #将crond.pid剪切到mxh目录下
[root@localhost ~]# ls /tmp/mxh
crond.pid test1
[root@localhost ~]# ls /tmp/mxh/test1
cron.reboot
2、mv 剪切功能同时改名(可直接剪切文件或目录,不需要像cp -r 来复制目录)
[root@localhost ~]# ls /tmp/mxh
test1
[root@localhost ~]# ls /tmp/mxh/test1
crond.pid cron.reboot
[root@localhost ~]# cp /tmp/mxh/test1/crond.pid /tmp/mxh/test1/1.pid
[root@localhost ~]# ls /tmp/mxh/test1
1.pid crond.pid cron.reboot
[root@localhost ~]# mv /tmp/mxh/test1/1.pid /tmp/mxh/2.pid #将1.pid 剪切并改名为2.pid到mxh目录下
[root@localhost ~]# ls /tmp/mxh/test1
crond.pid cron.reboot
[root@localhost ~]# ls /tmp/mxh
2.pid test1
3、mv 直接改文件夹或文件名称
[root@localhost ~]# ls /tmp/mxh
2.pid test1
[root@localhost ~]# cd /tmp/mxh
[root@localhost mxh]# mv 2.pid 3.pid
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
3.pid test1
| rm | 删除文件(每次删除会带有问你是否删除) |
| rm -f | 强制删除 (不会带有询问) |
| rm -rf | 删除目录文件夹 |
1、rm删除文件
[root@localhost ~]# ls /tmp/mxh
1.pid test1
[root@localhost ~]# cp /tmp/mxh/1.pid /tmp/mxh/2.pid
[root@localhost ~]# ls /tmp/mxh #绝对路经下复制
1.pid 2.pid test1
[root@localhost ~]# cd /tmp/mxh
[root@localhost mxh]# cp 2.pid 3.pid
[root@localhost mxh]# ls #进到路径下复制
1.pid 2.pid 3.pid test1
[root@localhost mxh]# rm 1.pid #删除文件
rm:是否删除普通文件 "1.pid"?y
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
2.pid 3.pid test1
[root@localhost mxh]# cp 2.pid 1.pid
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid 2.pid 3.pid test1
[root@localhost mxh]# mv 3.pid 4.pid
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid 2.pid 4.pid test1
2、rm -f 强制删除 (不会带有询问)
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid 2.pid 4.pid test1
[root@localhost mxh]# cd
[root@localhost ~]# rm -f /tmp/mxh/1.pid /tmp/mxh/2.pid #删除1.pid 2.pid
[root@localhost ~]# ls /tmp/mxh
4.pid test1
3、rm -rf 强制删除目录文件夹
[root@localhost mxh]# mkdir test
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid 2.pid 3.pid 4.pid test test1
[root@localhost mxh]# cp 1.pid 2.pid 3.pid 4.pid test
[root@localhost mxh]# ls test
1.pid 2.pid 3.pid 4.pid
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid 2.pid 3.pid 4.pid test test1
[root@localhost mxh]# ls test
1.pid 2.pid 3.pid 4.pid
[root@localhost mxh]# rm test
rm: 无法删除"test": 是一个目录
[root@localhost mxh]# rm -r test
rm:是否进入目录"test"? y
rm:是否删除普通文件 "test/1.pid"?y
rm:是否删除普通文件 "test/2.pid"?y
rm:是否删除普通文件 "test/3.pid"?y
rm:是否删除普通文件 "test/4.pid"?y
rm:是否删除目录 "test"?y
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid 2.pid 3.pid 4.pid test1
[root@localhost mxh]# mkdir test
[root@localhost mxh]# cp 1.pid 2.pid 3.pid 4.pid test
[root@localhost mxh]# ls test
1.pid 2.pid 3.pid 4.pid
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid 2.pid 3.pid 4.pid test test1
[root@localhost mxh]# rm -rf test
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid 2.pid 3.pid 4.pid test1
文件处理命令
| touch | 新建一个文件(mkdir是创建一个目录,不一样) |
| cat | 直接浏览文件的具体内容(适合小文档内容查看) |
| cat -n | 显示内容的行号 |
| more | 查看大文件很多内容的方法 |
| less | 查看大文件很多内容的方法,比more好用(less只能区分大小写查找,要想找到只能输入的单词完全正确才行,与后面的grep 查找文档内容有区别) |
| head -n 行数m | 查看文件的前m行 |
| tail -n 行数m | 查看文件的最后的m行 |
| tail -f | 动态显示日志的后10行内容,日志变化显示也跟着变化 |
1、touch创建文件命令
[root@localhost mxh]# touch 7.pid
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid 2.pid 3.pid 4.pid 7.pid test1
2、连续新建文档(适合小文档内容查看)
[root@localhost mxh]# touch 5.pid 6.pid
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid 2.pid 3.pid 4.pid 5.pid 6.pid 7.pid test1
3、cat直接浏览文件的具体内容,cat -n 显示内容的行数
[root@localhost mxh]# cat 1.pid
7565
[root@localhost mxh]# cat -n 1.pid
1 7565
4、more:查看一个文件里有很多内容方法
[root@localhost ~]# more /etc/services
# /etc/services:
# $Id: services,v 1.55 2013/04/14 ovasik Exp $
#
# Network services, Internet style
# IANA services version: last updated 2013-04-10
#
# Note that it is presently the policy of IANA to assign a single well-known
# port number for both TCP and UDP; hence, most entries here have two entries
# even if the protocol doesn't support UDP operations.
# Updated from RFC 1700, ``Assigned Numbers'' (October 1994). Not all ports
# are included, only the more common ones.
#
# The latest IANA port assignments can be gotten from
# http://www.iana.org/assignments/port-numbers
# The Well Known Ports are those from 0 through 1023.
# The Registered Ports are those from 1024 through 49151
# The Dynamic and/or Private Ports are those from 49152 through 65535
#
# Each line describes one service, and is of the form:
#
# service-name port/protocol [aliases ...] [# comment]
tcpmux 1/tcp # TCP port service multiplexer
--More--(0%)
空格或f 往下翻页
Enter 一行一行的翻页
b 往上一页一页的往回翻页
ctrl +C 退出
5、more的用法
tcpmux 1/udp # TCP port service multiplexer
[root@localhost ~]# less /etc/services
[root@localhost ~]#
[root@localhost ~]# less /etc/services
# /etc/services:
# $Id: services,v 1.55 2013/04/14 ovasik Exp $
#
# Network services, Internet style
# IANA services version: last updated 2013-04-10
#
# Note that it is presently the policy of IANA to assign a single well-known
# port number for both TCP and UDP; hence, most entries here have two entries
# even if the protocol doesn't support UDP operations.
# Updated from RFC 1700, ``Assigned Numbers'' (October 1994). Not all ports
# are included, only the more common ones.
PgDn向上翻页
PgDn向下翻页
q 退出
#
# The latest IANA port assignments can be gotten from
# http://www.iana.org/assignments/port-numbers
# The Well Known Ports are those from 0 through 1023.
# The Registered Ports are those from 1024 through 49151
# The Dynamic and/or Private Ports are those from 49152 through 65535
#
# Each line describes one service, and is of the form:
#
# service-name port/protocol [aliases ...] [# comment]
tcpmux 1/tcp # TCP port service multiplexer
/service #写入/ +要查找的关键字 就会帮你找出来
#写入"/" +要查找的关键字 就会帮你找出来
按键 n(next) 会帮你查找下一个关键字
6、head -n 行数m:查看文件内容的前m行
[root@localhost ~]# head -n 10 /etc/services
# /etc/services:
# $Id: services,v 1.55 2013/04/14 ovasik Exp $
#
# Network services, Internet style
# IANA services version: last updated 2013-04-10
#
# Note that it is presently the policy of IANA to assign a single well-known
# port number for both TCP and UDP; hence, most entries here have two entries
# even if the protocol doesn't support UDP operations.
# Updated from RFC 1700, ``Assigned Numbers'' (October 1994). Not all ports
7、tail -n 行数m:查看文件内容的后m行(工作中查看日志常用)
[root@localhost ~]# tail -n 5 /etc/services
com-bardac-dw 48556/tcp # com-bardac-dw
com-bardac-dw 48556/udp # com-bardac-dw
iqobject 48619/tcp # iqobject
iqobject 48619/udp # iqobject
matahari 49000/tcp # Matahari Broker
8、tail -f 动态显示日志的后10行内容,日志变化显示也跟着变化
链接命令:软链接命令相当于windows的快捷方式
| ln(link) | ln -s [源文件] [目标文件] 生成链接文件 针对的是文件,不是目录 软链接 |
| ln [源文件] [目标文件] 生成链接文件 针对的是文件,不是目录,生成硬链接 |
1、ln -s [源文件] [目标文件] 生成链接文件 针对的是文件,不是目录 生成软链接
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid 2.pid 3.pid 4.pid 5.pid 6.pid 7.pid mxhtest test1
[root@localhost mxh]# ln -s mxhtest mxhtest.soft 生成软链接
[root@localhost mxh]# ls -l
总用量 16
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 22:18 1.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 22:18 2.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 22:18 3.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 22:18 4.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 23 23:17 5.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 23 23:17 6.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 23 23:07 7.pid
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 10月 24 10:00 mxhtest
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 10月 24 10:01 mxhtest.soft -> mxhtest #软连接
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 42 10月 23 21:51 test1
2、ln [源文件] [目标文件] 生成链接文件 针对的是文件,不是目录 生成硬链接
[root@localhost mxh]# ln mxhtest mxhtest.hard
[root@localhost mxh]# ls -l
总用量 16
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 22:18 1.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 22:18 2.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 22:18 3.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 22:18 4.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 23 23:17 5.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 23 23:17 6.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 23 23:07 7.pid
-rw-r--r--. 2 root root 0 10月 24 10:07 mxhtest
-rw-r--r--. 2 root root 0 10月 24 10:07 mxhtest.hard
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 10月 24 10:07 mxhtest.soft -> mxhtest #注意软链接的特点
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 42 10月 23 21:51 test1
权限管理命令
权限: r读 、w写、x执行
权限对象:所有者、所属组、其他人
只有所有者或超级管理员才能更改权限
r -> 4 w->2 x->1
| chmod | 权限管理命令chmod 754 文件名称 |
| chmod -R | 递归修改,就是如果、a/b/c,执行chmod -r 777 /a ,那么,、b/c的权限也会和/a的权限一样被修改 |
1、chmod修改文件目录权限
[root@localhost mxh]# ls -l 1.pid
-rwxr--r--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 22:18 1.pid
假设1.pid 原本的权限是 所有者rwx(4+2+1=7) ;所属者r(4+0+0=4) ;其他人 r(4+0+0=4) 1.pid的权限是744;我想要改成rwxrxw--(拆分就是754)
[root@localhost mxh]# ls -l 1.pid
-rwxr-xr--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 22:18 1.pid #修改后
2、chmod -R递归修改文件目录权限,递归修改,就是如果、a/b/c,执行chmod -R 777 /a ,那么,、b/c的权限也会和/a的权限一样被修改
[root@localhost mxh]# ls -l
总用量 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 24 10:07 mxhtest
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 10月 24 10:07 mxhtest.soft -> mxhtest
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 42 10月 23 21:51 test1
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 32 10月 24 12:55 xxx #未修改前
[root@localhost mxh]# ls -l xxx
总用量 8
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 22:18 2.pid #未修改前
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 5 10月 23 22:18 3.pid #未修改前
[root@localhost mxh]# chmod -R 777 xxx #递归修改xxx目录后,其底下的两个文件权限也跟着变
[root@localhost mxh]# ls -l
总用量 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 24 10:07 mxhtest
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 10月 24 10:07 mxhtest.soft -> mxhtest
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 42 10月 23 21:51 test1
drwxrwxrwx. 2 root root 32 10月 24 12:55 xxx #修改后
[root@localhost mxh]# ls -l xxx
总用量 8
-rwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 5 10月 23 22:18 2.pid #修改后
-rwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 5 10月 23 22:18 3.pid #修改后
目录权限
对于目录来说,有以下权限就可以执行相应的操作:
r -> ls查看
w->mkdir\rm\rmdir\touch 删除和增加文件
x-> cd 进入到目录下
有r权一定有x权限,不然查看不了目录的文件,进不去目录
| chown | chown 用户名 目标文件 更改目标文件的所有者 |
| chgrp | chgrp 用户名 目标文件 更改目标文件的所属组 |
| umask -S | 查看当前创建目录有哪一些权限 |
1、chown 用户名 目标文件 更改目标文件的所有者
[root@localhost xxx]# ls -l
总用量 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 24 17:18 1.pid #第一个root是所有者(一般是谁创建谁就是所有者) 第二个root是所属者
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 24 17:18 2.pid
[root@localhost xxx]# useradd mxh2
useradd:用户“mxh2”已存在
[root@localhost xxx]# chown mxh2 1.pid #把所有者的身份从root转移到mxh2上
[root@localhost xxx]# ls -l
总用量 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 mxh2 root 0 10月 24 17:18 1.pid #1.pid的所有者是mxh2
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 24 17:18 2.pid
2、chgrp 用户名 目标文件 更改目标文件的所属组
[root@localhost xxx]# ls -l
总用量 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 mxh2 root 0 10月 24 17:18 1.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 24 17:18 2.pid
[root@localhost xxx]# chgrp mxhgrp 1.pid #将1.pid所属者的身份从root变为mxhgrp用户
[root@localhost xxx]# ls -l
总用量 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 mxh2 mxhgrp 0 10月 24 17:18 1.pid #成功修改权限
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 24 17:18 2.pid
3、chmod更改所有者和所属组的权限(这个是最好用的)
[root@localhost xxx]# ls -l
总用量 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 mxh2 mxhgrp 0 10月 24 17:18 1.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 24 17:18 2.pid
[root@localhost xxx]# ^C
[root@localhost xxx]# chmod 777 1.pid
[root@localhost xxx]# ls -l
总用量 0
-rwxrwxrwx. 1 mxh2 mxhgrp 0 10月 24 17:18 1.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 24 17:18 2.pid
3、umask -S查看当前创建目录有哪一些权限
[root@localhost xxx]# ls
[root@localhost xxx]# umask -S #针对创建目录查看其权限
u=rwx,g=rx,o=rx
[root@localhost xxx]# mkdir test
[root@localhost xxx]# touch 1.pid
[root@localhost xxx]# ls -l
总用量 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 24 18:48 1.pid #为了安全性,一般新建的文件不具有可执行性
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 10月 24 18:48 test #与umask -S 的权限一致
umask创建目录时的权限是怎么得来的:
[root@localhost ~]# umask
0022
#第一个0 :特殊权限
#022 对应一下:
# ----w--w- 然后与777异或取值
# rwxrwxrwx
----------------------
# rwxr-xr-x 所以看到创建的目录是rwxr-xr-x文件搜索命令
| find | find会占用服务器大量的系统资源,尽量少用 |
| find 目录范围 -name 文件名 (区分大小写查找) | find 目录范围 -name 文件名 (精准查找)或 find 目录范围 -name *文件名* (只要有这个文件名的都找出来) |
| find 目录范围 -iname 文件名 (不区分大小写查找) | 不区分大小写进行查找 |
1、find 目录范围 -name 文件名 (区分大小写查找) 精准查找和广泛查找(区分大小写查找)
[root@localhost ~]# find /etc -name init
/etc/sysconfig/init
/etc/selinux/targeted/active/modules/100/init
[root@localhost ~]# find /etc -name *init*
/etc/systemd/system/sysinit.target.wants
/etc/inittab
/etc/sysconfig/init
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/init.ipv6-global
/etc/init.d
/etc/rc.d/init.d
/etc/selinux/targeted/active/modules/100/init
/etc/selinux/targeted/contexts/initrc_context
/etc/security/namespace.init
2、find 目录范围 -iname 文件名 (不区分大小写查找)
[root@localhost mxh]# cd xxx
[root@localhost xxx]# touch INIT
[root@localhost xxx]# ls
1.pid INIT test #在这里创建一个INIt文件
[root@localhost xxx]# find / -name init #查找不到INIT
/sys/fs/selinux/initial_contexts/init
/etc/sysconfig/init
/etc/selinux/targeted/active/modules/100/init
/usr/sbin/init
/usr/libexec/os-probes/init
[root@localhost xxx]# find / -iname init #不区分大小写查找,查到了INIT文件
/sys/fs/selinux/initial_contexts/init
/etc/sysconfig/init
/etc/selinux/targeted/active/modules/100/init
/tmp/mxh/xxx/INIT #这里
/usr/sbin/init
/usr/libexec/os-probes/init
| find /目录 -size +n(大于)/-n(小于)/n(等于) | 根据文件大小来查找 |
| find /目录 -user/-group 文件名 | 根据用户来查找文件 |
| find /目录 -amin -n分钟 | 查找在n分钟访问过的文件目录 |
| find /目录 -cmin -n分钟 | 根据在n分钟内更改过的文件来查找 |
| find /目录 -mmin -n分钟 | 根据在n分钟内文件内容被修改来查找 |
1、根据文件大小来查找
[root@localhost ~]# find /tmp -size -1k
/tmp/yum.log
/tmp/mxh/test1/cron.reboot
/tmp/mxh/mxhtest
/tmp/mxh/xxx/1.pid
/tmp/mxh/xxx/INIT
2、根据用户来查找 find /目录 -user/-group 文件名
[root@localhost ~]# find / -user mxh2 #查找用户mxh2的所有文件
/run/user/1000
/var/spool/mail/mxh2
/home/mxh2
/home/mxh2/.bash_logout
/home/mxh2/.bash_profile
/home/mxh2/.bashrc
/home/mxh2/.lesshst
/home/mxh2/.bash_history
3、find /目录 -amin -n分钟 查找在n分钟访问过的文件目录
[root@localhost ~]# find /tmp -amin -100
/tmp/mxh/test1
4、find /目录 -cmin -n分钟 根据在n分钟内更改过的文件来查找
[root@localhost ~]# find /tmp -cmin -200
/tmp/mxh/xxx
/tmp/mxh/xxx/INIT
5、find /目录 -mmin -n分钟 根据在n分钟内文件内容被修改来查找
[root@localhost ~]# find /tmp -mmin -300
/tmp
/tmp/mxh/xxx
/tmp/mxh/xxx/test
/tmp/mxh/xxx/1.pid
/tmp/mxh/xxx/INIT
/tmp/systemd-private-e90722c3e92448538e73ca7ff7af2bf4-chronyd.service-UmZK4C
/tmp/systemd-private-e90722c3e92448538e73ca7ff7af2bf4-chronyd.service-UmZK4C/tmp
/tmp/vmware-root_713-4290166671
| find /目录 -type f | 查找文件(f是文件) |
| find /目录 -type d | 查找目录(d是目录) |
| find /目录 -type l | 查找软连接(l是软连接) |
| 连接符:-a | 条件同时满足 |
| 连接符:-o | 条件满足其中之一 |
| find /目录 -iname 文件名 -exec ls -l {} \; | 解读:可以把ls -l 改成其他命令的组合;意思就是找到这些文件后你要操作什么步骤 |
1、find /目录 -type f 查找文件(f是文件)
[root@localhost ~]# find /tmp -type f
/tmp/yum.log
/tmp/ks-script-IAr5pa
/tmp/mxh/test1/cron.reboot
/tmp/mxh/test1/crond.pid
/tmp/mxh/mxhtest
/tmp/mxh/xxx/1.pid
/tmp/mxh/xxx/INIT
2、find /目录 -type d 查找目录(d是目录)
[root@localhost ~]# find /tmp -type d
/tmp
/tmp/.XIM-unix
/tmp/.font-unix
/tmp/.X11-unix
/tmp/.ICE-unix
/tmp/.Test-unix
3、find /目录 -type l 查找软连接(l是软连接)
[root@localhost ~]# find /tmp -type l
/tmp/mxh/mxhtest.soft
4、连接符:-a 条件同时满足
oot@localhost ~]# find /etc -iname *init* -a -type f
/etc/inittab
/etc/sysconfig/init
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/init.ipv6-global
/etc/selinux/targeted/contexts/initrc_context
/etc/security/namespace.init
[root@localhost ~]# find /etc -iname *init* -a -type l
/etc/init.d
[root@localhost ~]# find /etc -iname *init* -a -type d
/etc/systemd/system/sysinit.target.wants
/etc/rc.d/init.d
/etc/selinux/targeted/active/modules/100/init
5、find /目录 -iname 文件名 -exec ls -l {} \; {}表示前面找到的内容的一个集合
解读:可以把ls -l 改成其他命令的组合;意思就是找到这些文件后你要操作什么步骤
[root@localhost ~]# find /etc -iname init -a -type f
/etc/sysconfig/init
[root@localhost ~]# find /etc -iname init -a -type f -exec ls -l {} \;
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 798 10月 13 2020 /etc/sysconfig/init
6、find和cp命令结合使用 {}表示前面找到的内容的一个集合
[root@localhost ~]# find /etc -iname init -a -type f -exec cp {} /tmp/mxh/xxx \;
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /tmp/mxh/xxx
总用量 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 24 18:48 1.pid
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 798 10月 24 22:44 init
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 24 19:21 INIT
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 10月 24 18:48 test
7、find . -inum 序号 -exec rm {} \; {}表示前面找到的内容的一个集合
[root@localhost xxx]# touch 1.pid
[root@localhost xxx]# ls -il
总用量 0
33583818 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 25 13:04 1.pid
[root@localhost xxx]# find . -inum 33583818 -exec rm -rf {} \;
[root@localhost xxx]# ls -il
总用量 0
| locate | 查找命令,首先安装yum install mlocate ;再更新库 updatedb;再进行 locate 文件名 进行查找 (基于数据库检索) |
| locate -i 文件名 | 不区分大小写进行查找 |
1、locate 文件名 基于数据库查找 ;但是,存在临时文件的查找不了
[root@localhost ~]# yum install mlocate #安装
已加载插件:fastestmirror
[root@localhost ~]# updatedb #更新数据库
[root@localhost ~]# locate mxh #关键字查找
/home/mxh2
/home/mxh2/.bash_history
/home/mxh2/.bash_logout
/home/mxh2/.bash_profile
/home/mxh2/.bashrc
/home/mxh2/.lesshst
/var/spool/mail/mxh2
2、临时文件下面的查找不到
[root@localhost ~]# ls /tmp/mxh
mxhtest mxhtest.soft test1 xxx
[root@localhost ~]# locate test1
[root@localhost ~]#
3、locate -i 文件名 不区分大小写进行查找
[root@localhost home]# ls -il
总用量 0
33583836 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 25 19:38 MXh1
51042340 drwx------. 2 mxh2 mxh2 99 10月 24 17:30 mxh2
[root@localhost home]# updatedb
[root@localhost home]# locate -i mxh1
/home/MXh1
| which 命令 | 快速查找命令所在位置 |
| whereis 命令 | 快速查找命令和帮助文档所在位置 |
| grep -i 关键词 文件目录 | 可以不区分关键词大小写来进行查找文档内容 |
1、which 命令 快速查找命令所在位置
[root@localhost ~]# which groupadd
/usr/sbin/groupadd
[root@localhost ~]# which ls
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
/usr/bin/ls
2、whereis 命令 同样能找到命令所在位置,还能知道帮助文件所在位置,whereis路径多出来的部分就是帮助文档的路径 以下:/usr/share/man/man1/ls.1.gz 就是帮助文档位置。
[root@localhost ~]# whereis ls
ls: /usr/bin/ls /usr/share/man/man1/ls.1.gz
[root@localhost ~]# which ls
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
/usr/bin/ls
3、grep -i 关键词 文件目录 可以不区分关键词大小写来进行查找文档内容
[root@localhost ~]# more /etc/fstab
#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Fri Oct 22 21:28:51 2021
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
/dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=57a167f9-7601-4c24-93e7-d2916c3a2445 /boot xfs defaults 0
0
/dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults 0 0
[root@localhost ~]# grep -i created /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Fri Oct 22 21:28:51 2021 #检索结果直接打出关键词的这一行
[root@localhost ~]# grep -i create /etc/fstab #不完全输入完也能找出来
# Created by anaconda on Fri Oct 22 21:28:51 2021
帮助命令
| man 命令 | man 命令 查看命令的帮助信息 |
| man 配置文件 | 查看配置文件的帮助内容 |
| 命令 --help | 也是可以查看帮助命令 |
安装man命令前要提前安装好库,一共一条语句:
、sudo yum install man-pape
1、man 命令 查看命令的帮助信息
[root@localhost ~]# man ls #就能查看ls这个命令的使用法内容2、man 配置文件 查看配置文件的帮助内容
[root@localhost ~]# man services #就能查看services这个文档的帮助内容
3、
[root@localhost ~]# whereis passwd
passwd: /usr/bin/passwd /etc/passwd /usr/share/man/man1/passwd.1.gz /usr/share/man/man5/passwd.5.gz
# 1.gz 是指命令帮助信息
# 5.gz 是指配置文件帮助信息3.1 如果直接man passwd 它就会优先显示passwd的命令帮助信息
[root@localhost ~]# man passwd3.2 想要显示配置文件信息可以这样做
[root@localhost ~]# man 5 passwd #因为5是配置文件信息,声明一下4、命令 --help 查看命令帮助
[root@localhost ~]# ls --help
用户管理命令
管理员可以更改任何人的密码;而普通用户只能更改自己的密码;
| useradd | 增加用户 |
| passwd | 更改密码 |
| who | 查看有谁在登陆linux |
1、who 查看谁登陆服务器
[yangmi@localhost ~]$ who
root tty1 2021-10-25 19:19 #tty1 表示本地登录
root pts/0 2021-10-25 19:19 (192.168.32.1) #pts1 表示远程登陆1 登录时间 登陆ip地址
yangmi pts/1 2021-10-25 21:41 (192.168.32.1) #pts2 表示远程登陆2 登录时间 登陆ip地址
2、w 这个命令可以详细查看用户登录信息
[yangmi@localhost ~]$ w
21:56:38 up 2:41, 3 users, load average: 0.08, 0.03, 0.05 #
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
root tty1 19:19 2:37m 0.12s 0.12s -bash
root pts/0 192.168.32.1 19:19 12:30 6.73s 6.73s -bash
yangmi pts/1 192.168.32.1 21:41 6.00s 1.56s 1.20s w
文件压缩命令
在linux和windows之间共用的压缩后缀名是 .zip
| gzip 文件 | 文件压缩命令(压缩后源文件没有了,只有压缩包) 不可压缩目录 gz 文件名 |
| gunzip 压缩文件 | 解压文件 |
| tar 可以压缩文件和目录(能保留源文件) | tar -cvzf 文件名.tar.gz 要打包的目录(打包并压缩目录或文件) -c 表示打包;-v 表示打包什么内容; -z 表示打包后并压缩;-f 表示指定文件名(f一定要放在最后) |
| tar 可以压缩文件和目录(能保留源文件) | tar -xvzf 文件名.tar.gz -x表示解压;-v 表示打包什么内容; -z 表示打包后并压缩;-f 表示指定文件名(f一定要放在最后) |
| zip 压缩(能保留源文件) | zip 文件名.zip 要压缩的文件 (压缩目录:zip -r 文件名.zip 要压缩的文件) |
| unzip 解压(能保留源文件) | unzip 压缩包 |
| bzip2 | bzip2 -k 文件名 -k保留原文件压缩 |
| bunzip2 解压 | bunzip 文件名.bz2 |
| bzip2 (一般用于压缩大文件) | tar -cvjf 文件名.tar.bz2 文件名 (与tar对比就是 -cvzf变成了-cvjf) |
| bunzip2 解压 | tar -xvjf 文件名.tar.bz2 |
| du -sh 文件或目录 | 查看文件或目录大小 |
1、gzip 文件 文件压缩命令 不可压缩目录
[root@localhost mxh]# gzip mxhtest
[root@localhost mxh]# ls -il
总用量 4
51042136 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 28 10月 24 10:07 mxhtest.gz
2、gunzip 压缩文件 解压文件
[root@localhost mxh]# ls -l
总用量 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 26 10月 26 19:08 1.pid.gz
[root@localhost mxh]# gunzip 1.pid.gz
[root@localhost mxh]# ls -l
总用量 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 10月 26 19:08 1.pid
3、tar (打包并压缩)
-c 表示打包;-v 表示打包什么内容; -z 表示打包后并压缩;-f 表示指定文件名(f一定要放在最后)
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid Mxh3 mxhtest.soft test1 xxx xxx.tar.gz
[root@localhost mxh]# ls xxx
1 2 3.4
[root@localhost mxh]# tar -cvzf xxx.tar.gz xxx
xxx/ 打包后的文件名 要打包的文件
xxx/1/
xxx/1/2/
xxx/1/2/3/
xxx/2/
xxx/3.4/
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid Mxh3 mxhtest.soft test1 xxx xxx.tar.gz
4、tar (解压) -x表示解压;-v 表示打包什么内容; -z 表示打包后并压缩;-f 表示指定文件名(f一定要放在最后)
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid Mxh3 mxhtest.soft test1 xxx.tar.gz
[root@localhost mxh]# tar -xvzf xxx.tar.gz # x表示解压
xxx/
xxx/1/
xxx/1/2/
xxx/1/2/3/
xxx/2/
xxx/3.4/
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid Mxh3 mxhtest.soft test1 xxx xxx.tar.gz
[root@localhost mxh]# ls xxx
1 2 3.4
5、zip zip 文件名.zip 要压缩的文件 (压缩目录:zip -r 文件名.zip 要压缩的文件)(能保留源文件) 安装zip命令:yum install zip
[root@localhost mxh]# ls #压缩
1.pid Mxh3 mxhtest.soft test1 xxx
[root@localhost mxh]# zip -r xxx.zip xxx
adding: xxx/ (stored 0%)
adding: xxx/1/ (stored 0%)
adding: xxx/1/2/ (stored 0%)
adding: xxx/1/2/3/ (stored 0%)
adding: xxx/1/2/3/1.pid (stored 0%)
adding: xxx/1/2/2.pid (stored 0%)
adding: xxx/2/ (stored 0%)
adding: xxx/3.4/ (stored 0%)
[root@localhost mxh]# unzip xxx.zip #解压
Archive: xxx.zip
creating: xxx/
creating: xxx/1/
creating: xxx/1/2/
creating: xxx/1/2/3/
extracting: xxx/1/2/3/1.pid
extracting: xxx/1/2/2.pid
creating: xxx/2/
creating: xxx/3.4/
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid Mxh3 mxhtest.soft test1 xxx xxx.zip
6、bzip2 (一般用于压缩大文件) tar -cvjf 文件名.tar.bz2 文件名(与tar对比就是 -cvzf变成了-cvjf) 先安装bzip2命令:yum install bzip2
1.pid Mxh3 mxhtest.soft test1 xxx xxx.tar.gz #压缩xxx
[root@localhost mxh]# tar -cvjf xxx.tar.bz2 xxx
xxx/
xxx/1/
xxx/1/2/
xxx/1/2/3/
xxx/1/2/3/1.pid
xxx/1/2/2.pid
xxx/2/
xxx/3.4/
[root@localhost mxh]# ls
1.pid Mxh3 mxhtest.soft test1 xxx xxx.tar.bz2 xxx.tar.gz
7、du -sh 文件或目录 查看文件或目录大小
[root@localhost mxh]# du -sh xxx
704K xxx
网络命令
| write 用户名 | write 用户名 直接写信给用户 ,ctrl+D进行保存 |
| wall 写信内容 | 直接进行所有用户广播 |
| ping | ping -c 次数 IP |
1、write 用户名 直接写信给用户 ,ctrl+D进行保存
[mxh2@localhost ~]$ write root #写给超级用户
write: root is logged in more than once; writing to pts/1
maixiuhu
[root@localhost ~]# #超级用户这边已经收到
Message from [email protected] on pts/0 at 22:26 ...
maixiuhu
EOF
2、wall 写信内容 直接进行所有用户广播
[root@localhost ~]# wall mxh yijing you nanpy!
[root@localhost ~]#
Broadcast message from [email protected] (pts/1) (Tue Oct 26 22:35:03 2021):
mxh yijing you nanpy! #首先自己也能收到
[mxh2@localhost ~]$ #mxh2这个用户也能收到
Broadcast message from [email protected] (pts/1) (Tue Oct 26 22:35:03 2021):
mxh yijing you nanpy!
3、ping -c 次数 IP
[mxh2@localhost ~]$ ping -c 4 192.168.32.1
PING 192.168.32.1 (192.168.32.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.32.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=128 time=2.67 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.32.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=128 time=1.31 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.32.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=128 time=0.852 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.32.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=128 time=0.931 ms
--- 192.168.32.1 ping statistics ---
4 packets transmitted, 4 received, 0% packet loss, time 3005ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.852/1.441/2.670/0.731 ms
| last | last命令能够查看登录用户,以及重启时间 |
| lastlog | 查看所有用户最后一次登陆的时间 |
| netstat -ltun | 查看本机监听的端口 |
| netstat -an | 查看本机连接的所有网络连接 |
| netstat -rn | 查看本机路由表 |
1、last命令查看用户登录详细情况,包括系统重启时间
[mxh2@localhost ~]$ last
mxh2 pts/2 192.168.32.3 Wed Oct 27 21:32 still logged in
yangmi pts/4 192.168.32.3 Wed Oct 27 21:27 - 21:30 (00:03)
root pts/3 192.168.32.3 Wed Oct 27 21:18 still logged in
mxh2 pts/2 192.168.32.3 Wed Oct 27 21:18 - 21:30 (00:12)
mxh2 pts/1 192.168.32.3 Wed Oct 27 19:05 still logged in
root pts/0 192.168.32.3 Wed Oct 27 19:05 still logged in
root tty1 Wed Oct 27 19:04 still logged in
reboot system boot 3.10.0-1160.el7. Wed Oct 27 19:03 - 21:33 (02:29)
mxh2 pts/0 192.168.32.3 Wed Oct 27 11:31 - crash (07:32)
root pts/2 192.168.32.3 Wed Oct 27 11:30 - crash (07:32)
mxh2 pts/1 192.168.32.3 Wed Oct 27 11:23 - 11:30 (00:07)
root pts/0 192.168.32.3 Wed Oct 27 11:23 - 11:30 (00:07)
root tty1 Wed Oct 27 11:22 - crash (07:40)
reboot system boot 3.10.0-1160.el7. Wed Oct 27 11:21 - 21:33 (10:11)
2、lastlog 查看所有用户最后一次登陆的时间
[mxh2@localhost ~]$ lastlog
用户名 端口 来自 最后登陆时间
root pts/3 192.168.32.3 三 10月 27 21:18:25 +0800 2021
bin **从未登录过**
daemon **从未登录过**
adm **从未登录过**
mxh2 pts/2 192.168.32.3 三 10月 27 21:32:38 +0800 2021
yangmi pts/4 192.168.32.3 三 10月 27 21:27:28 +0800 2021
3、netstat -ltun 查看本机监听的端口(TCP 相当于打电话;UDP相当于发短信;TCP有监听,PDp没有监听)
[root@localhost ~]# netstat -ltun
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN
udp 0 0 127.0.0.1:323 0.0.0.0:*
udp6 0 0 ::1:323 :::*
4、netstat -an 查看本机所有的网络连接
[root@localhost ~]# netstat -an
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 192.168.32.111:22 192.168.32.3:10190 ESTABLISHED #表示正在连接 和netstat -lutn的区别就在这
tcp 0 0 192.168.32.111:22 192.168.32.3:4371 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 192.168.32.111:22 192.168.32.3:7340 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 192.168.32.111:22 192.168.32.3:4376 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 192.168.32.111:22 192.168.32.3:9658 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 192.168.32.111:22 192.168.32.3:4377 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 48 192.168.32.111:22 192.168.32.3:10189 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 192.168.32.111:22 192.168.32.3:7337 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 192.168.32.111:22 192.168.32.3:4370 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 192.168.32.111:22 192.168.32.3:8178 ESTABLISHED
tcp 0 0 192.168.32.111:22 192.168.32.3:9656 ESTABLISHED
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN
udp 0 0 192.168.32.111:47888 84.16.73.33:123 ESTABLISHED
udp 0 0 127.0.0.1:323 0.0.0.0:*
udp6 0 0 ::1:323 :::*
raw6 0 0 :::58 :::* 5、netstat -rn 查看路由表
[root@localhost ~]# netstat -rn
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface
0.0.0.0 192.168.32.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 ens33
192.168.32.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 ens33
| mount -t 文件系统 设备文件名 挂载点 | |
1、mount -t 文件系统 设备文件名 挂载点
(1)先在/mnt目录下建立一个空目录cdrom ; /mnt这个目录用于挂载的目录
[root@localhost mnt]# mkdir cdrom
[root@localhost mnt]# ls
cdrom
(2)# mount -t iso9660 /dev/sr0 /mnt/新建的目录 只有新建的目录要改,其他都是固定格式
[root@localhost mnt]# mount -t iso9660 /dev/sr0 /mnt/cdrom
mount: /dev/sr0 写保护,将以只读方式挂载
# mount -t iso9660 /dev/sr0 /mnt/新建的目录 只有新建的目录要改,其他都是固定格式(3)打开挂载好的目录后可以看见iso文件里的东西
[root@localhost mnt]# ls -l cdrom
总用量 696
-rw-r--r--. 3 root root 14 10月 30 2020 CentOS_BuildTag
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 2048 10月 27 2020 EFI
-rw-rw-r--. 21 root root 227 8月 30 2017 EULA
-rw-rw-r--. 21 root root 18009 12月 10 2015 GPL
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 2048 10月 27 2020 images
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 2048 11月 3 2020 isolinux
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 2048 10月 27 2020 LiveOS
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 673792 11月 4 2020 Packages
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 11月 4 2020 repodata
-rw-rw-r--. 21 root root 1690 12月 10 2015 RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
-rw-rw-r--. 21 root root 1690 12月 10 2015 RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-Testing-7
-r--r--r--. 1 root root 2883 11月 4 2020 TRANS.TBL
关机和重启命令
| shutdown -h now | 现在关机 |
| shutdown -h 20:30 | 20:30关机 |
| shutdown -r now | 现在重启 |
| exit | 退出登录 |
Vim文本编辑器使用
1、vim插入模式(编写文本模式)
[root@localhost mxh]# vi 1 #vi 文件名 进入到文件内
mxh is a gril!
~
~
~
~
~
~
"1" 3L, 17C #进入后是这样子 还不是编辑文本模式
2、按下键盘小写字母 :a 或 i 或 o 即可进入编辑文本模式
mxh is a gril!
~
~
~
~
~
~
-- INSERT -- #按下a\i\o后进入后是这样子 是编辑文本模式这时就可以上下左右移动光标进行编写文件内容了。
3、编写完成后按下esc键退出编写模式,回到命令模式
1 mxh is a gril!
2 wqdqdcdsavsvdsdcascse
3
~
~
~
~
:set nu
命令模式下,输入:号,再进行输入命令执行操作。如果再想回到编辑文本模式下,再次按下a 或 i 或 o 即可进入编辑文本模式。
4、保存退出命令: ":wq"
定位命令:
| :set nu | 设置行号 |
| :set nonu | 取消行号 |
| gg | 定位到第一行 |
| G | 定位到最后一行 |
| :n | 定位到第n行 |
| $ | 定位到行尾 |
| 0 | 定位到行首 |
| dd | 直接删除光标所在的一行 |
| :n1,n2d | 删除n1到n2 的行数 |
| 数字n+dd | 删除光标所在位置以下的n行 |
1、设置行号和取消行号
1 mxh is a gril!
2 wq dq dcdsavsvdsdca
3
~
:set nu #设置行号
mxh is a gril!
wq dq dcdsavsvdsdca
~
:set nonu #取消行号
2、:n1,n2d 定位到第n行
196 mobilip-mn 435/udp
197 https 443/tcp # http protocol over TLS/SSL
198 https 443/udp # http protocol over TLS/SSL
199 https 443/sctp # http protocol over TLS/SSL
200 snpp 444/tcp # Simple Network Paging Protocol
201 snpp 444/udp # Simple Network Paging Protocol
202 microsoft-ds 445/tcp
203 microsoft-ds 445/udp
204 kpasswd 464/tcp kpwd # Kerberos "passwd"
205 kpasswd 464/udp kpwd # Kerberos "passwd"
206 photuris 468/tcp
207 photuris 468/udp
208 saft 487/tcp # Simple Asynchronous File Transfer
209 saft 487/udp # Simple Asynchronous File Transfer
210 gss-http 488/tcp
211 gss-http 488/udp
212 pim-rp-disc 496/tcp
213 pim-rp-disc 496/udp
:200 #表示定位到200行
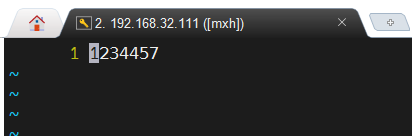
3、删除n1到n2 的行数
1 akndsajcnbjncjd #删除前
2 kncjanbjcbsd
3 asncjabckjbckjbd
4 skjkcdcknd
5 snmkncxksanc
6 askncjnsabc
7 nsaknc
~
1 akndsajcnbjncjd
7 nsaknc
~
5 fewer lines
:2,6d
#删除2-6行的文字
以下命令都是在命令模式下进行:
| 复制n yy | 复制光标所在及以下的n行内容,按下p即可粘贴复制的n行,复制一行的话直接yy即可 |
| 剪切 n dd | dd同时是删除,也同时是剪切,剪切n行的内容,后面按下按键p即可进行粘贴 |
| 撤销功能:小写字母u | 撤销功能 |
| r | 取代光标所在字符 |
| R | 从光标所在位置开始进行后面的替换,esc退出 |
| 查找 | 在命令模式下输入 / 关键字 按下n进行下一个查找(这个方式是区分大小写来查找的) |
| 查找 | 不区分大小写来查找 :set ic 回车后再 / 关键词进行查找 |
| 全文替换功能 | %s : 表示全文替换 用法: ": %s/ftp/mxh/g" 就会把全文的ftp替换成mxh |
| 范围内替换功能 | :n1,n2s/ftp/mxh/g 在n1,n2这个范围内就会把全文的ftp替换成mxh |
1、在命令模式下输入 / 关键字 按下n进行下一个查找(这个方式是区分大小写来查找的)
/FTP #/关键字
2、不区分大小写来查找 :set ic 回车后再 / 关键词进行查找
:set ic
/ftp此时就不会区分大小写来查找了。
取消的话是 :set noic
注意:在set ic 模式下替换全文的话,是不区分大小写来进行替换的;如果已经输入命令set noic下,是区分大小写来进行替换的
3、全文替换功能,%s : 表示全文替换
用法: ": %s/ftp/mxh/g" 就会把全文的ftp替换成mxh
回车后:
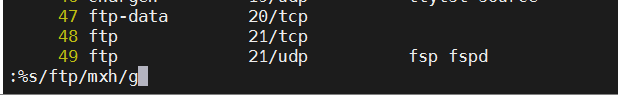
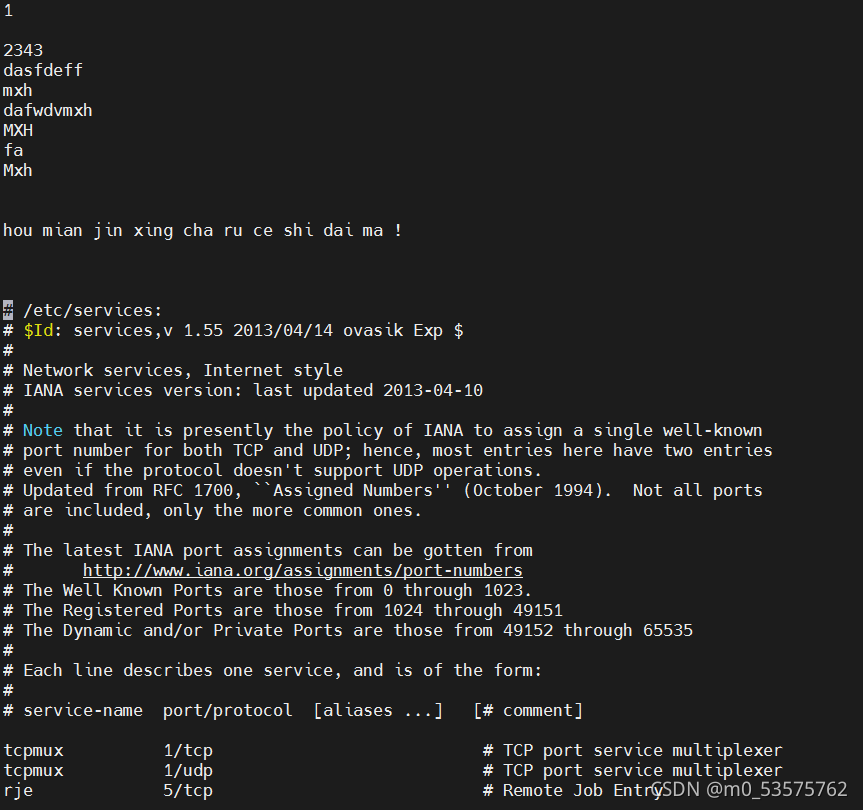
4、范围内替换功能 :n1,n2s/ftp/mxh/g 在n1,n2这个范围内就会把全文的ftp替换成mxh
19 12343
20 dasfdeff
21 mxh
22 dafwdvmxh
23 MXH
24 fa
25 Mxh
:21,23s/mxh/yamgmi/g #在21到23之间把mxh替换成杨幂
回车后
19 12343
20 dasfdeff
21 yangmi
22 dafwdvyangmi
23 MXH #回车后,只有21,22行的mxh变成了yangmi,因为我设置了set noic模式
24 fa
25 Mxh
:21,23s/mxh/yangmi/g
| :w | 只保存 |
| :q! | 不保存修改退出 |
| :wq | 保存修改并退出 |
| :wq! | 没有读写权限的时候也可以保存退出(只有所有者和root可以) |
[root@localhost xxx]# chmod 444 /tmp/mxh/xxx/test222 #把这个文件只允许读操作
[root@localhost xxx]# ls -il
51217784 -r--r--r--. 1 root root 58 10月 31 12:22 test222
打开文件后:
12343
dasfdeff
mxh
dafwdvmxh
MXH
fa
Mxh
#原本的文件代码量输入:wq
12343
dasfdeff
mxh
dafwdvmxh
MXH
fa
Mxh
hou mian jin xing cha ru ce shi dai ma ! #这个是插入的代码
E45: 'readonly' option is set (add ! to override) #输入:wq 提示这个文件只读
换成:wq! 就能进行保存和退出了!
| :r /tmp/mxh/xx/services | 在命令模式下执行此操作,可以把目录下的services文件下的内容写在光标下处,相当于导入功能 |
| :!which ls | 在vi里面查找ls 命令的位置所在处,与不是在vim里面查找多了一个 ! 号 |
| :r !date | 把当前时间导入到光标处 |
1、:r /tmp/mxh/xx/services 在命令模式下执行此操作,可以把目录下的services文件下的内容写在光标下处,相当于导入功能
:r /tmp/mxh/xxx/services
2、:!which ls 查找ls 命令位置目录
:!which ls
[root@localhost xxx]# which ls
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
/usr/bin/ls
[root@localhost xxx]# vi test222
/usr/bin/ls
Press ENTER or type command to continue
/usr/bin/ls
Press ENTER or type command to continue #按下回车会进入到刚才vim编辑里面
3、:r !date 把当前时间导入到光标处
:r !date
2021年 10月 31日 星期日 13:06:29 CST
vim里自定义快捷键:
| :map ^P I#<ESC> 表示在行首插入注释符号#,然后按下快捷键ctrl+p即可调用 | ^P :同时按下ctrl+V+P I: 表示定位到行首并插入# 然后退出 |
| :n1,n2s/^/#/g 表示在n1,n2行进行注释 | ^:表示行首的意思和查找替换命令一样 |
| :n1,n2s/^#//g 表示在n1,n2行去掉注释符号 | ^:表示标记行首位置,不然不是行首的#也会被删除 |
| ab a b | 相当于你输入a时,b的内容就会替换a |
1、:map ^K I#<ESC> 表示在行首插入注释符号#,然后按下快捷键ctrl+p即可调用 ;^K :同时按下ctrl+V+K (也可把P改为其他字母)
:map ^k I#<ESC>
1 #a2343
2 #dasfdeff #把光标移动,ctrl+p就会在最前面的位置插入注释符号#
3 #mxh
4 #dafwdvmxh
5 #MXH
6 #fa
7 #Mxh
2、:n1,n2s/^/#/g 表示在n1,n2行进行注释;^:表示行首的意思和查找替换命令一样
1 #a2343
2 #dasfdeff
3 #mxh
4 #dafwdvmxh
5 #MXH
6 #fa
7 #Mxh
:1,7s/^/#/g
3、:n1,n2s/^#//g ;^:表示标记行首位置,不然不是行首的#也会被删除
1 a2343
2 dasfdeff
3 mxh
4 dafwdvmxh
5 MXH
6 fa
7 Mxh
:1,7s/^#//g #删除首行的注释符号
4、ab a b 相当于你输入a时,b的内容就会替换a
:ab baba mxh
输入:baba
回车:12345
5、将一些常用的命令写在配置文件下:root: /root/.vimrc
其他用户名:/home/username/.vimrc
没有这个.vimrc文件就自己创建。
1 set nu #打开任何文件有设置好行号=:set nu
2 map ^K I#<ESC> #ctrl+K 行首插入一个注释符号
3 map ^L 0x #ctrl+L 行首去掉一个注释符号
~
软件包管理
1、源码包
脚本安装包,可以看见源代码
2、二进制包
(RPM包、系统默认包) 指编译过的文件包看不见源代码
RPM包管理命令
1、RPM命名规则:
RPM包命名原则
httpd-2.2.15-15.el6.centos.1.i686.rpm (包全名)
httpd 软件包名
2.2.15 软件版本
15 软件发布的次数
el6.centos 适合的Linux平台
i686 适合的硬件平台
rpm rpm包扩展名
包全名和包名:
包全名:操作的包没有安装软件包时
包名:操作已安装的软件包使用包名,在/var/lib/rpm 中的数据库
2、RPM包依赖性
树形依赖 a->b->c
环形依赖 a->b->c->a
模块依赖查询网站:www.rpmfind.net
3、RPM安装
| rpm -ivh 包全名(安装) | -i:安装,-v显示详细信息,-h:显示进度(这个复杂,了解一下) |
| rpm -e 包名 (卸载) | -e:卸载 |
| rpm -q 包名 | 查询这个包是否安装 |
| rpm -qa | 查询所有已安装的包 |
| rpm -qi | 查询安装包的详细信息(q和i不能颠倒位置) |
| rpm -qip 包全名 | 查询未安装包的详细信息 |
| rpm -ql 包名 | 查询包下的文件都安装在哪里 |
| rpm -qlp 包全名 | 查看未安装的包中的文件将要安装的位置在哪里 |
| rpm -qf 系统文件名 | 查询这个系统文件名属于哪一个包 |
| rpm -qR 包名 | 查询安装包的依赖性 |
| rpm -qRp 包全名 | 查询未安装包的依赖性 |
(1)rpm -q 包名,查询这个包是否安装
[root@localhost Packages]# rpm -q yum
yum-3.4.3-168.el7.centos.noarch
[root@localhost Packages]# rpm -q zip
zip-3.0-11.el7.x86_64
(2)rpm -qa,查询所有已安装的包
[root@localhost Packages]# rpm -qa
yum-3.4.3-168.el7.centos.noarch
grub2-common-2.02-0.86.el7.centos.noarch
firewalld-filesystem-0.6.3-11.el7.noarch
setup-2.8.71-11.el7.noarch
kbd-1.15.5-15.el7.x86_64
basesystem-10.0-7.el7.centos.noarch
NetworkManager-team-1.18.8-1.el7.x86_64
ncurses-base-5.9-14.20130511.el7_4.noarch
NetworkManager-tui-1.18.8-1.el7.x86_64
tzdata-2020a-1.el7.noarch
selinux-policy-targeted-3.13.1-268.el7.noarch
glibc-common-2.17-317.el7.x86_64
kexec-tools-2.0.15-51.el7.x86_64
nspr-4.21.0-1.el7.x86_64
openssh-clients-7.4p1-21.el7.x86_64
libstdc++-4.8.5-44.el7.x86_64
audit-2.8.5-4.el7.x86_64
bash-4.2.46-34.el7.x86_64
kernel-3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64
pcre-8.32-17.el7.x86_64
microcode_ctl-2.1-73.el7.x86_64
zlib-1.2.7-18.el7.x86_64
[root@localhost Packages]# rpm -qa | grep yum #列出所有安装的包,再查询有关yum的包
yum-3.4.3-168.el7.centos.noarch
yum-plugin-fastestmirror-1.1.31-54.el7_8.noarch
yum-metadata-parser-1.1.4-10.el7.x86_64
(3)rpm -qi查询安装包的详细信息(q和i不能颠倒位置)
[root@localhost Packages]# rpm -qi yum
Name : yum
Version : 3.4.3
Release : 168.el7.centos
Architecture: noarch
Install Date: 2021年10月22日 星期五 21时30分45秒
Group : System Environment/Base
Size : 5829237
License : GPLv2+
Signature : RSA/SHA256, 2020年10月15日 星期四 03时21分12秒, Key ID 24c6a8a7f4a80eb5
Source RPM : yum-3.4.3-168.el7.centos.src.rpm
Build Date : 2020年10月02日 星期五 01时03分49秒
Build Host : x86-02.bsys.centos.org
Relocations : (not relocatable)
Packager : CentOS BuildSystem <http://bugs.centos.org>
Vendor : CentOS
URL : http://yum.baseurl.org/
Summary : RPM package installer/updater/manager
(4)rpm -qip 包全名 :查询未安装包的信息
#进到目录Packages下
[root@localhost Packages]# rpm -qip zziplib-0.13.62-12.el7.x86_64.rpm
Name : zziplib
Version : 0.13.62
Release : 12.el7
Architecture: x86_64
Install Date: (not installed)
Group : Applications/Archiving
Size : 216046
License : LGPLv2+ or MPLv1.1
Signature : RSA/SHA256, 2020年04月04日 星期六 05时10分34秒, Key ID 24c6a8a7f4a80eb5
Source RPM : zziplib-0.13.62-12.el7.src.rpm
Build Date : 2020年04月01日 星期三 13时04分24秒
Build Host : x86-01.bsys.centos.org
Relocations : (not relocatable)
Packager : CentOS BuildSystem <http://bugs.centos.org>
Vendor : CentOS
URL : http://zziplib.sourceforge.net/
Summary : Lightweight library to easily extract data from zip files
(5)rpm -ql 包名 查询包下的文件都安装在哪里
[root@localhost Packages]# rpm -ql yum
/etc/logrotate.d/yum
/etc/yum
/etc/yum.conf
/etc/yum.repos.d
/etc/yum/fssnap.d
/etc/yum/pluginconf.d
/etc/yum/protected.d
/etc/yum/vars
/etc/yum/version-groups.conf
/usr/bin/yum
/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/rpmUtils
/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/rpmUtils/__init__.py
/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/rpmUtils/__init__.pyc
(6)rpm -qlp 包全名 查看未安装的包中的文件将要安装的位置在哪里
[root@localhost Packages]# rpm -qlp zziplib-0.13.62-12.el7.x86_64.rpm
/usr/lib64/libzzip-0.so.10
/usr/lib64/libzzip-0.so.11
/usr/lib64/libzzip-0.so.12 #这些位置是将要安装的位置
/usr/lib64/libzzip-0.so.13
/usr/lib64/libzzip-0.so.13.0.62
/usr/lib64/libzzipfseeko-0.so.10
/usr/lib64/libzzipfseeko-0.so.11
/usr/lib64/libzzipfseeko-0.so.12
/usr/lib64/libzzipfseeko-0.so.13
/usr/lib64/libzzipfseeko-0.so.13.0.62
/usr/lib64/libzzipmmapped-0.so.10
/usr/lib64/libzzipmmapped-0.so.11
/usr/lib64/libzzipmmapped-0.so.12
/usr/lib64/libzzipmmapped-0.so.13
/usr/lib64/libzzipmmapped-0.so.13.0.62
/usr/lib64/libzzipwrap-0.so.13
(7)rpm -qf 系统文件名 查询这个系统文件名属于哪一个包(只能查包的文件,不能查自己创建的和系统临时生成的文件)
/var/lib/yum/uuid #已知这个文件名
[root@localhost Packages]# rpm -qf /var/lib/yum/uuid
yum-3.4.3-168.el7.centos.noarch #查出来是yum这个包的文件
(8)rpm -qR 包名 查询已安装包的依赖性
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -qR yum #不需要进入到/mnt/cdrom/Packages 里面
#表示yum包下的文件都安装在哪一些地方
/usr/bin/python
config(yum) = 3.4.3-168.el7.centos
cpio
diffutils
pygpgme
pyliblzma
python >= 2.4
python(abi) = 2.7
python-iniparse
python-sqlite
python-urlgrabber >= 3.10-8
pyxattr
rpm >= 0:4.11.3-22
rpm-python
rpmlib(CompressedFileNames) <= 3.0.4-1
rpmlib(FileDigests) <= 4.6.0-1
rpmlib(PayloadFilesHavePrefix) <= 4.0-1
yum-metadata-parser >= 1.1.0
yum-plugin-fastestmirror
rpmlib(PayloadIsXz) <= 5.2-1
(9)rpm -qRp 包全名 查询未安装的包的文件的依赖性
[root@localhost Packages]# rpm -qRp yum-3.4.3-168.el7.centos.noarch.rpm
/usr/bin/python
config(yum) = 3.4.3-168.el7.centos #这些依赖包和上面一段代码结果一模一样
cpio
diffutils
pygpgme
pyliblzma
python >= 2.4
python(abi) = 2.7
python-iniparse
python-sqlite
python-urlgrabber >= 3.10-8
pyxattr
rpm >= 0:4.11.3-22
rpm-python
rpmlib(CompressedFileNames) <= 3.0.4-1
rpmlib(FileDigests) <= 4.6.0-1
rpmlib(PayloadFilesHavePrefix) <= 4.0-1
yum-metadata-parser >= 1.1.0
yum-plugin-fastestmirror
rpmlib(PayloadIsXz) <= 5.2-1
yum在线管理工具(yum这里没有包全名,只有包名)
| yum search 包名 | yum search 包名 |
| yum -y install 包名 | 包安装,-y是为了防止它一个一个的询问 |
| yum -y update 包名 | 升级包(后面一定要加包名,不然全部升级,导致服务器崩溃!谨慎使用) |
| yum -y remove 包名 | 卸载(尽量别卸载,有一些依赖不仅仅是这个包的依赖,还有可能是系统的依赖,yum直接卸载也可能把系统的依赖给卸载掉,导致系统崩溃,所以升级和卸载尽量少用!) |
1、yum search 包名,yum search 包名
[root@localhost ~]# yum search httpd
已加载插件:fastestmirror
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirror.lzu.edu.cn
* epel: mirrors.bfsu.edu.cn
* extras: mirror.lzu.edu.cn
* updates: mirrors.aliyun.com
=================================== N/S matched: httpd ====================================
dmlite-apache-httpd.x86_64 : Apache HTTPD frontend for dmlite
iipsrv-httpd-fcgi.noarch : Apache HTTPD files for iipsrv
keycloak-httpd-client-install.noarch : Tools to configure Apache HTTPD as Keycloak client
libmicrohttpd-devel.i686 : Development files for libmicrohttpd
libmicrohttpd-devel.x86_64 : Development files for libmicrohttpd
libmicrohttpd-doc.noarch : Documentation for libmicrohttpd
2软件么、yum -y install 包名,包安装,-y是为了防止它一个一个的询问
yum -y install httpd安装gcc
yum install gcc源码包安装位置
系统给我们一个位置来安装外来软件源码包 /usr/local/软件名 软件么自己创建一个文件夹
注意:如果是自己手动安装外来的软件,就要安装到、usr/local 目录下,启动程序时需要绝对路径来启动:
如果是用yum来安装的话,可以使用service httpd start来启动程序,如以下的程序:
| service httpd start | 启动Apache命令: |
| service httpd status | 查看Apache 状态 |
| service httpd stop | 停止服务 |
1、启动Apache命令:service httpd start
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl status httpd.service
● httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since 一 2021-11-01 21:48:41 CST; 3s ago
Docs: man:httpd(8)
man:apachectl(8)
Main PID: 1680 (httpd)
Status: "Processing requests..."
CGroup: /system.slice/httpd.service
├─1680 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─1681 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─1682 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─1683 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─1684 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
└─1685 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
2、查看Apache 状态service httpd status
[root@localhost ~]# service httpd status
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl status httpd.service
● httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
Docs: man:httpd(8)
man:apachectl(8)
3、service httpd stop停止服务
[root@localhost ~]# service httpd stop
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl stop httpd.service
[root@localhost ~]# service httpd status
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl status httpd.service
● httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
Docs: man:httpd(8)
man:apachectl(8)
11月 01 21:48:40 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server...
11月 01 21:48:41 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Started The Apache HTTP Server.
11月 01 21:56:15 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Stopping The Apache HTTP Server...
11月 01 21:56:17 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Stopped The Apache HTTP Server.
| service firewalld start | linux防火墙开启 |
| service firewalld stop | linux防火墙关闭 |
|
| 在这个目录下新建一个index.html文件,在这个文件里随便写点东西,在你的linux服务器上的网页上就会显示出来,比如我的服务器:192.168.32.11 |
1、[root@localhost ~]# cd /var/www/html
脚本安装包
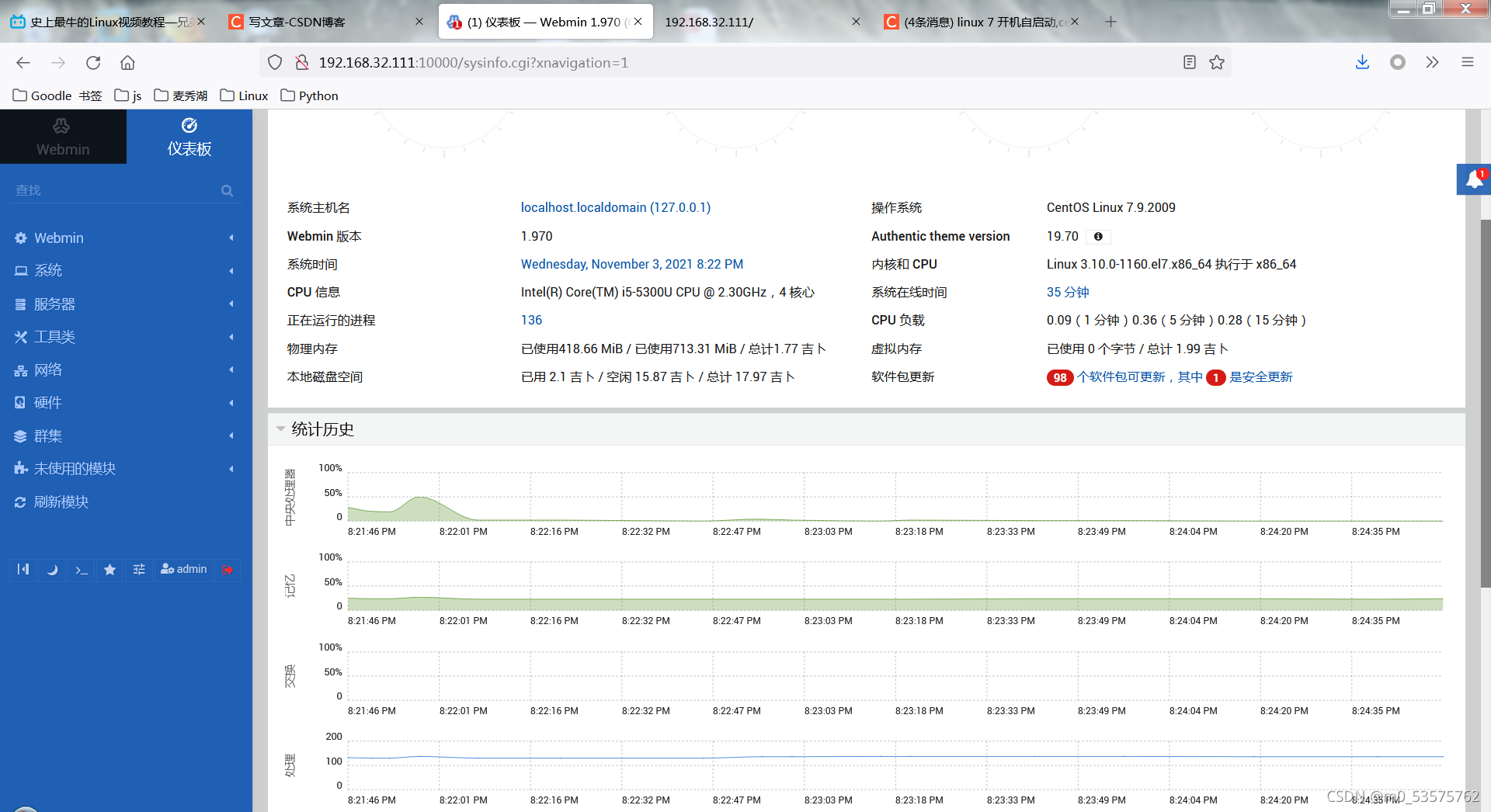
安装webmin了,在网址中输入192.168.32.111:10000,账号密码是:admin;123 就能看见如下界面:
用户配置文件
| /etc/passwd | 用户信息文件 |
1、用户信息文件 目录在/etc/passwd
格式: [ 用户名]:[密码(x代表有密码,但不是存放在这)]:[用户ID: 0->超级用户;1-499->系统用户];[500-65535->普通用户]:[GID(用户初始组ID)]:[备注说明(有无均可)]:[家目录]:[登陆之后的shell]
用户名是root的不一定是超级用户,但是ID号为0d的一定是超级用户。可以把普通用户变为超级用户,只需要把普通用户的ID改为0.
系统用户1-499,不能随便删除,删除灰系统崩溃!
家目录: 普通用户-> /home /用户名 ; 超级用户->/root/
shell:指的是linux的命令解释器
[root@localhost etc]# vim passwd
1 root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
2 bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
3 daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
4 adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
5 lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
6 sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
7 shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
8 halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
9 mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
10 operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
11 games:x:12:100:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin
12 ftp:x:14:50:FTP User:/var/ftp:/sbin/nologin
13 nobody:x:99:99:Nobody:/:/sbin/nologin
14 systemd-network:x:192:192:systemd Network Management:/:/sbin/nologin
15 dbus:x:81:81:System message bus:/:/sbin/nologin
16 polkitd:x:999:998:User for polkitd:/:/sbin/nologin
17 sshd:x:74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin
18 postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin
19 chrony:x:998:996::/var/lib/chrony:/sbin/nologin
20 mxh2:x:1000:1000::/home/mxh2:/bin/bash
21 yangmi:x:1001:1002::/home/yangmi:/bin/bash
22 apache:x:48:48:Apache:/usr/share/httpd:/sbin/nologin
~
注意:普通用户和超级用户最后一个字段都是/bin/bash;如果要暂时禁用某个普通用户,就要把最后一个字段改为/sbin/nologin
影子文件/etc/shadow
/etc/shadow/ 下存储着所有用户的密码,这个文件的权限都没有,只用超级用户能看,普通户用权限不足
[root@localhost etc]# ls -il /etc/shadow
17200643 ----------. 1 root root 852 11月 1 20:39 /etc/shadow
[root@localhost etc]# ls -il /etc/passwd
17200642 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 981 11月 1 20:39 /etc/passwd
普通用户查看shadow:
~
"shadow" [权限不足] 超级用户查看shadow:
[root@localhost etc]# vim shadow
1 root:$6$pJu/JmSt$Y4Imdphqgwk6Cts1E0jTKHxan6Gb/VrU7mKasP4TpIve4HSZkwbeKdmtciFlE2x1Nau/U JjweH77caLfYwz.h1:18925:0:99999:7:::
2 bin:*:18353:0:99999:7:::
3 daemon:*:18353:0:99999:7:::
4 adm:*:18353:0:99999:7:::
5 lp:*:18353:0:99999:7:::
6 sync:*:18353:0:99999:7:::
7 shutdown:*:18353:0:99999:7:::
8 halt:*:18353:0:99999:7:::
9 mail:*:18353:0:99999:7:::
10 operator:*:18353:0:99999:7:::
11 games:*:18353:0:99999:7:::
12 ftp:*:18353:0:99999:7:::
13 nobody:*:18353:0:99999:7:::
14 systemd-network:!!:18922::::::
15 dbus:!!:18922::::::
16 polkitd:!!:18922::::::
17 sshd:!!:18922::::::
18 postfix:!!:18922::::::
19 chrony:!!:18922::::::
20 mxh2:$6$/S7SMaOA$7JqOnHIbDwqAfkvVobm/sWobB4ip8iZZl3utAWl45raW/AGGq8WvA/aAJwusRMt5U4Mhf rfBKz8tWryTTq/Re0:18926:0:99999:7:::
21 yangmi:$6$jjUaVYe2$yHJdbbeC.6X.UPqAZnHXIV1hbYMGjpWG87OfPkUrQqUiNESk2MD97Fe5oFUCMvfobQe WptnOxU.N48cf4cdWp/:18927:0:99999:7:::
"shadow" [只读] 22L, 852C 一共9个字段:
【用户名】:【经过加密的密文】:【最后一次修改密码时间】:【两次密码修改的时间间隔】:【密码有效时间】:【密码有效性到期的警告时间】:【密码过期后宽限天数】:【账号失效时间】:【】
经过加密的密文:如果是!或*就表示没有密码,不能登录;
最后一次修改密码时间:18925指在1970年1月1日后的第18925天;
两次密码修改的时间间隔:默认为0,指随时可以改密码,如果设置为10,表示10天后才能改密码,-1表示密码永远不会失效;
密码过期后宽限天数:不写或者0指时间到期密码立即失效;
账号失效时间:不管你密码是失效还是未失效,账号有效期一道就封号,用时间戳来表示,就是1970.1.1开始后的天数来表示;
计算时间戳的方法:
知道时间戳换算成日期:
[root@localhost etc]# date -d "1970-01-01 18925 days" #这个是root用户最后一次更改密码的时间
2021年 10月 25日 星期一 00:00:00 CST
知道日期换算成时间戳:
[root@localhost ~]# echo $(($(date --date="2021/11/03" +%s)/86400+1))
18934
组信息文件/etc/group
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/group
1 root:x:0:
2 bin:x:1:
3 daemon:x:2:
4 sys:x:3:
5 adm:x:4:
6 tty:x:5:
7 disk:x:6:
8 lp:x:7:
9 mem:x:8:
10 kmem:x:9:
11 wheel:x:10:
12 cdrom:x:11:
13 mail:x:12:postfix
14 man:x:15:
15 dialout:x:18:
16 floppy:x:19:
17 games:x:20:
18 tape:x:33:
19 video:x:39:
20 ftp:x:50:
21 lock:x:54:
22 audio:x:63:
23 nobody:x:99:
24 users:x:100:
"/etc/group" 41L, 519C 4个字段:
【组名】:【组密码位】:【组ID】:【组中附加用户】
组名:默认组名和用户名相同;
组ID:用户ID: 0-》超级用户;1-499-》系统用户];[500-65535-》普通用户
用户的家目录
[root@localhost ~]# ls -il /home/ #普通用户家目录
总用量 0
51042340 drwx------. 2 mxh2 mxh2 115 11月 3 21:28 mxh2
17208613 drwx------. 2 yangmi yangmi 83 10月 25 22:00 yangmi
[root@localhost ~]# ls -ld /root #超级用户家目录
dr-xr-x---. 5 root root 4096 11月 3 22:22 /root
用户的邮箱
目录在 /var/spool/mail
[root@localhost ~]# ls -l /var/spool/mail
总用量 0
-rw-rw----. 1 mxh2 mail 0 10月 24 13:08 mxh2
-rw-rw----. 1 yangmi mail 0 10月 25 21:39 yangmi
用户模板
目录在:/etc/skel
意思就是在/etc/skel/的文件,在每创建以个新用户的时候,用户的家目录就会自动添加/etc/skel/的文件。
[root@localhost ~]# ls -a /etc/skel
. .. .bash_logout .bash_profile .bashrc
[root@localhost ~]# ls -a /home/mxh2
. .. .bash_history .bash_logout .bash_profile .bashrc .lesshst .viminfo
用户管理命令
| useradd | 创建新用户 useradd 用户名 |
| passwd | passwd 用户名 :给用户进行设置密码 passwd :直接为自己修改密码 passwd -l 用户名 锁住用户账号 passwd -u 用户名 解锁用户账号 |
| chage -d 0 用户名 | 这个命令其实是把用户修改密码日期归0(第三个字段)=1970.1.1,系统就会让用户登录一次之后立马修改密码的作用。 |
1、passwd -u 用户名 解锁用户账号;passwd -l 用户名 锁住用户账号
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/shadow
1 root:$6$pJu/JmSt$Y4Imdphqgwk6Cts1E0jTKHxan6Gb/VrU7mKasP4TpIve4HSZkwbeKdmtciFlE2x1Nau/UJ jweH77caLfYwz.h1:18925:0:99999:7:::
20 mxh2:!!$6$/S7SMaOA$7JqOnHIbDwqAfkvVobm/sWobB4ip8iZZl3utAWl45raW/AGGq8WvA/aAJwusRMt5U4Mh frfBKz8tWryTTq/Re0:18926:0:99999:7:::
21 yangmi:$6$jjUaVYe2$yHJdbbeC.6X.UPqAZnHXIV1hbYMGjpWG87OfPkUrQqUiNESk2MD97Fe5oFUCMvfobQeW ptnOxU.N48cf4cdWp/:18927:0:99999:7:::
#发现锁住的用户mxh2和没锁住的用户yangmi对比,密码前面多了两个!!,换句话说,可以手动通过在密码前面加入!!来暂时锁住用户账号。删掉!!即可解锁用户
2、chage -d 0 用户名。这个命令其实是把用户修改密码日期归0(第三个字段)=1970.1.1,系统就会让用户登录一次之后立马修改密码的作用。
[root@localhost ~]# chage -d 0 mxh2
You are required to change your password immediately (root enforced)
Last login: Thu Nov 4 04:12:17 2021 from 192.168.32.3
WARNING: Your password has expired.
You must change your password now and login again!
更改用户 mxh2 的密码 。
为 mxh2 更改 STRESS 密码。
(当前)UNIX 密码:
新的 密码:
| userdel -r 用户名 | 删除用户,-r:表示删除/home/用户名 下的根目 |
| whoami | 查看当前用户是谁 |
| su - 用户名 | 切换用户,-表示连带环境变量一起切换过去, env命令可以查看当前环境变量, exit退出登录 |
1、userdel -r 用户名,删除用户,-r:表示删除/home/用户名 下的根目
[root@localhost ~]# userdel -r yangmi
2、whoami,查看当前用户是谁
[root@localhost ~]# whoami
root
3、su - 用户名,切换用户,-表示连带环境变量一起切换过去,env命令可以查看当前环境变量,exit退出登录
[yangmi@localhost ~]$ su - root
密码:
上一次登录:四 11月 4 04:37:20 CST 2021pts/2 上
[root@localhost ~]# env
XDG_SESSION_ID=62
HOSTNAME=localhost.localdomain
SHELL=/bin/bash
TERM=xterm
HISTSIZE=1000
USER=root
LS_COLORS=rs=0:di=01;34:ln=01;36:mh=00:pi=40;33:so=01;35:do=01;35:bd=40;33;01:cd=40;33;01:or=40;31;01:mi=01;05;37;41:su=37;41:sg=30;43:ca=30;41:tw=30;42:ow=34;42:st=37;44:ex=01;32:*.tar=01;31:*.tgz=01;31:*.arc=01;31:*.arj=01;31:*.taz=01;31:*.lha=01;31:*.lz4=01;31:*.lzh=01;31:*.lzma=01;31:*.tlz=01;31:*.txz=01;31:*.tzo=01;31:*.t7z=01;31:*.zip=01;31:*.z=01;31:*.Z=01;31:*.dz=01;31:*.gz=01;31:*.lrz=01;31:*.lz=01;31:*.lzo=01;31:*.xz=01;31:*.bz2=01;31:*.bz=01;31:*.tbz=01;31:*.tbz2=01;31:*.tz=01;31:*.deb=01;31:*.rpm=01;31:*.jar=01;31:*.war=01;31:*.ear=01;31:*.sar=01;31:*.rar=01;31:*.alz=01;31:*.ace=01;31:*.zoo=01;31:*.cpio=01;31:*.7z=01;31:*.rz=01;31:*.cab=01;31:*.jpg=01;35:*.jpeg=01;35:*.gif=01;35:*.bmp=01;35:*.pbm=01;35:*.pgm=01;35:*.ppm=01;35:*.tga=01;35:*.xbm=01;35:*.xpm=01;35:*.tif=01;35:*.tiff=01;35:*.png=01;35:*.svg=01;35:*.svgz=01;35:*.mng=01;35:*.pcx=01;35:*.mov=01;35:*.mpg=01;35:*.mpeg=01;35:*.m2v=01;35:*.mkv=01;35:*.webm=01;35:*.ogm=01;35:*.mp4=01;35:*.m4v=01;35:*.mp4v=01;35:*.vob=01;35:*.qt=01;35:*.nuv=01;35:*.wmv=01;35:*.asf=01;35:*.rm=01;35:*.rmvb=01;35:*.flc=01;35:*.avi=01;35:*.fli=01;35:*.flv=01;35:*.gl=01;35:*.dl=01;35:*.xcf=01;35:*.xwd=01;35:*.yuv=01;35:*.cgm=01;35:*.emf=01;35:*.axv=01;35:*.anx=01;35:*.ogv=01;35:*.ogx=01;35:*.aac=01;36:*.au=01;36:*.flac=01;36:*.mid=01;36:*.midi=01;36:*.mka=01;36:*.mp3=01;36:*.mpc=01;36:*.ogg=01;36:*.ra=01;36:*.wav=01;36:*.axa=01;36:*.oga=01;36:*.spx=01;36:*.xspf=01;36:
MAIL=/var/spool/mail/root #当前是root用户
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
PWD=/root
LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8
HISTCONTROL=ignoredups
SHLVL=1
HOME=/root
LOGNAME=root
LESSOPEN=||/usr/bin/lesspipe.sh %s
_=/bin/env
[root@localhost ~]# exit
登出
| SetUID | 就是当所有者、所属组、其他人执行这个带有SUID权限的文件时,执行过程中就会把你的权限升级到root的权限来执行,不要给一些命令来增加SUID权限,很危险,比如vim,这样普通用户也能修改/etc/shadow下的权限,增加s权限:chmod 4755 ;去除s权限:chmod 755 (前面多出一个4) |
SUID权限针对二进制文件和可执行程序
[root@localhost ~]# ls -il /etc/passwd
17526171 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1048 11月 8 10:29 /etc/passwd
[root@localhost ~]# ls -il /etc/shadow
17526172 ----------. 1 root root 873 11月 8 10:29 /etc/shadow
[root@localhost ~]# ls -il /usr/bin/passwd
51120392 -rwsr-xr-x. 1 root root 27856 4月 1 2020 /usr/bin/passwd #rws中的s就是SUID权限
增加s权限:chmod 4644 文件名
[root@localhost mxh]# ll
总用量 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 36 10月 28 22:34 1
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 10月 24 10:07 mxhtest.soft -> mxhtest
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 25 10月 23 21:51 test1
drwx-wx-wx. 5 root root 133 11月 4 01:15 xxx
[root@localhost mxh]# chmod 4644 1
[root@localhost mxh]# ll
总用量 4
-rwSr--r--. 1 root root 36 10月 28 22:34 1
去除s权限:chmod 644 文件名
[root@localhost mxh]# chmod 644 1
[root@localhost mxh]# ll
总用量 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 36 10月 28 22:34 1
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 10月 24 10:07 mxhtest.soft -> mxhtest
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 25 10月 23 21:51 test1
drwx-wx-wx. 5 root root 133 11月 4 01:15 xxx
| chattr -或+i | ◆选项 >i:如果对文件设置i属性)那么不允许对文件进行删除、改名,也不能添加和修改数据;如果对目录设置i属性,那么只能修改目录下文件的数据,但不允许建立和删除文件。(好处是连root用户都能限制) |
| chattr -或+a | >a:如果对件设置a属性,那么只能在文件中增加数据,但是不能删除也不能修改数据;如果对目录设置a属性,那么只允许在目录中建立和修改文件,但是不允许删除(好处是连root用户都能限制) |
| lsattr | 查看文件或目录是否有 i属性 |
1、对文件设置i 属性 无法对文件进行修改,改名,删除(好处是连root用户都能限制)
[root@localhost mxh]# mkdir qq
[root@localhost mxh]# touch /qq/ww
touch: 无法创建"/qq/ww": 没有那个文件或目录
[root@localhost mxh]# cd qq
[root@localhost qq]# touch ww
[root@localhost qq]# chattr +i ww
[root@localhost qq]# lsattr ww
----i----------- ww
[root@localhost qq]# rm -rf ww
rm: 无法删除"ww": 不允许的操作
[root@localhost qq]# mv ww ee
mv: 无法将"ww" 移动至"ee": 不允许的操作
[root@localhost qq]# cat ww
[root@localhost qq]# vim ww #会发现可以编辑但是无法保存
2、对目录设置i属性 (好处是连root用户都能限制)
[root@localhost mxh]# lsattr qq
---------------- qq/ww
[root@localhost mxh]# cd qq
[root@localhost qq]# touch 123
touch: 无法创建"123": 权限不够 不能创建和删除目录里的文件
[root@localhost qq]# vim ww #可修改qq目录里的ww文件
[root@localhost qq]# ls
ww
Shell脚本
| echo | 输出命令 |
| 文件名.sh | 表示写shell脚本 |
| #!/bin/Bash | 在脚本第一行写表示这个是脚本 |
| bash 文件名.sh | 运行脚本 |
执行代码:
[root@localhost mxh]# bash 1.sh
mxh is a hansome boy
history | 查看历史命令 |
| history -c | 表示清除历史命令 |
| !序号n | 表示执行序号n的命令 |
| ctrl+U | 剪切或删除当前光标左侧的字符 |
| ctrl+Y | 粘贴以剪切的命令 |
| ctrl+D | 退出·终端 |
输出重定向:意思就是把输出的结果保存到一个文件中
| 命令 &> 文件名 | 把结果输入到这个文件名当中去(会覆盖原始数据)不管输出的是正确的还是错误的都可以写进文件 |
| 命令 &>> 文件名 | 把结果输入到这个文件名当中去(不会覆盖原始数据)不管输出的是正确的还是错误的都可以写进文件 |
| 命令 >>文件1 2>> 文件2 | 把正确的输出追加到文件1,把错误的输出到文件2 (2表示输出错误的结果) |
1、命令 &> 文件名:把结果输入到这个文件名当中去(重复操作,会全部覆盖原始数据)
[root@localhost mxh]# date
2021年 11月 17日 星期三 20:22:44 CST
[root@localhost mxh]# date &> 33 把日期写到33这个文件中
[root@localhost mxh]# cat 33
2021年 11月 17日 星期三 20:23:00 CST
[root@localhost mxh]# ll
总用量 8
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 43 11月 17 20:23 33 #文件
2、命令 &>> 文件名,把结果输入到这个文件名当中去(不会覆盖原始数据)
[root@localhost mxh]# date &>> 33
[root@localhost mxh]# cat 33
2021年 11月 17日 星期三 20:23:00 CST
2021年 11月 17日 星期三 20:26:33 CST #追加内容,不会覆盖原始数据
3、命令 >>文件1 2>> 文件2:把正确的输出追加到文件1,把错误的输出到文件2 (2表示输出错误的结果)
[root@localhost mxh]# date >>33 2>>44
[root@localhost mxh]# cat 33
2021年 11月 17日 星期三 20:53:26 CST
[root@localhost mxh]# cat 44
[root@localhost mxh]# dater >>33 2>>44 #输入错误的命令
[root@localhost mxh]# cat 33
2021年 11月 17日 星期三 20:53:26 CST
[root@localhost mxh]# cat 44
-bash: dater: 未找到命令
| 命令1;命令2 | 先执行命令1,再执行命令2,不管命令1有没有执行成功 |
| 命令1&&命令2 | 先执行命令1,再执行命令2。如果命令1有没有执行成功,则命令2不能执行 |
| 命令1||命令2 | 先执行命令1,如果命令1执行失败,才会执行命令2 |
1、命令1;命令2
[root@localhost mxh]# ls;date
1.sh 33 44 mxhtest.soft qq test1
2021年 11月 17日 星期三 21:02:09 CST
2、命令1&&命令2
[root@localhost mxh]# ls1&&date
-bash: ls1: 未找到命令
[root@localhost mxh]# ls&&date
1.sh 33 44 mxhtest.soft qq test1
2021年 11月 17日 星期三 21:03:06 CST
3、命令1||命令2
[root@localhost mxh]# ls||date
1.sh 33 44 mxhtest.soft qq test1
[root@localhost mxh]# ls1||date
-bash: ls1: 未找到命令
2021年 11月 17日 星期三 21:05:15 CST
Bash通配符
| ? | 匹配任意一个字符 |
| * | 匹配0个或任意多个字符 |
| [ ] | 匹配括号里任意一个字符 |
| [-] | 如[a-z],匹配a-z里其中一个字符 |
| [^-] | 如[^a-z],匹配不是a-z里面的字符 |
Bash其他符号
| ‘ ’ | 单引号,在单引号中的特殊符号,如”$“,“·”(反引号)都没有特殊含义 |
| “ ” | 在双引号中特殊字符都没有特殊含义,除了“$”用有调用函数变量值,“·”拥有引用命令,“\”拥有转义字符这三个拥有特殊含义之外 |
| $() | 如$(date),先执行date命令,再把结果复制给其他变量 |
| # | 在shell脚本中表示注释 |
| $ | 表示引用变量的值 |
| \ | 表示使后面的特殊符号失去作用 |
1、‘ ’、“ ”的区别
[root@localhost mxh]# mxh=sa
[root@localhost mxh]# echo mxh
mxh
[root@localhost mxh]# echo $mxh
sa
[root@localhost mxh]# echo "$mxh"
sa
[root@localhost mxh]# echo '$mxh'
$mxh
2、$():如$(date),先执行date命令,再把结果复制给其他变量
[root@localhost mxh]# echo $(date)
2021年 11月 18日 星期四 20:42:01 CST
[root@localhost mxh]# mxh=$(date)
[root@localhost mxh]# echo $mxh
2021年 11月 18日 星期四 20:44:51 CST
[root@localhost mxh]# echo "$mxh"
2021年 11月 18日 星期四 20:44:51 CST
3、\:表示使后面的特殊符号失去作用
[root@localhost mxh]# mxh=1234
[root@localhost mxh]# echo $mxh
1234
[root@localhost mxh]# echo \$mxh
$mxh
Bash变量
用户自定义变量:
环境变量尽量写大写,便于区分。
| 1 | 变量名称可以由字母、数字和下划线组成,但是不能以数字开头。如果变量名是“2name”则是错误的。但是可以name2 |
| 2 | 在Bash中,变量的默认类型都是字符串型,如果要进行数值运算,则必修指定变量类型为数值型。 |
| 3 | 变量用等号连接值,等号左右两侧不能有空格。变量的值如果有空格,需要使用单引号或双引号包括。 |
| 4 | 在变量的值中,可以使用“\”转义符。◆如果需要增加变量的值,那么可以进行变量值的叠加。不过变量需要用双引号包含“S变量名”或用S{变量名}包含 |
1、变量名称可以由字母、数字和下划线组成,但是不能以数字开头。如果变量名是“2name”则是错误的。
[root@localhost ~]# 2mxh=3
-bash: 2mxh=3: 未找到命令
[root@localhost ~]# mxh=3
[root@localhost ~]# echo $mxh
3
2、变量用等号连接值,等号左右两侧不能有空格。变量的值如果有空格,需要使用单引号或双引号包括。
root@localhost ~]# 2mxh=3
-bash: 2mxh=3: 未找到命令
[root@localhost ~]# mxh=3
[root@localhost ~]# echo $mxh
3
[root@localhost ~]# mxh=shen chao
-bash: chao: 未找到命令
[root@localhost ~]# mxh="shen chao"
[root@localhost ~]# echo $mxh
shen chao
[root@localhost ~]# echo "$mxh"
shen chao
[root@localhost ~]# mxh1='li ming'
[root@localhost ~]# echo mxh1
mxh1
4、在变量的值中,可以使用“\”转义符。如果需要增加变量的值,那么可以进行变量值的叠加。不过变量需要用双引号包含“S变量名”或用S{变量名}包含。
[root@localhost ~]# aa=123
[root@localhost ~]# echo $aa
123
[root@localhost ~]# aa="$aa"456
[root@localhost ~]# echo $aa
123456
[root@localhost ~]# aa=${aa}789
[root@localhost ~]# echo $aa
123456789
变量的分类
| 1 | 用户自定义变量 |
| 2 | 环境变量;这种变量中主要保存的是和系统操作环境相关的数据。 (允许自定义新的环境变量) |
| 3 | 位置参数变量:这种变量主要是用来向脚本当中传递参数或数据的,变量名不能自定义,变量作用是固定的。(只能更改变量的值,不能新建新的变量) |
| 4 | 预定义变量:是Bash中已经定义好的变量,变量名不能自定义,变量作用也是固定的。(只能改变量的值) |
| 5 | set命令查看所有变量的值 |
| 6 | 删除变量:unset 变量名 |
1、set命令查看所有变量的值
[root@localhost ~]# set
BASH=/bin/bash
BASHOPTS=checkwinsize:cmdhist:expand_aliases:extquote:force_fignore:histappend:hostcomplete:interactive_comments:login_shell:progcomp:promptvars:sourcepath
BASH_ALIASES=()
BASH_ARGC=()
BASH_ARGV=()
BASH_CMDS=()
BASH_LINENO=()
BASH_SOURCE=()
BASH_VERSINFO=([0]="4" [1]="2" [2]="46" [3]="2" [4]="release" [5]="x86_64-redhat-linux-
ID=0
IFS=$' \t\n'
LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8
LESSOPEN='||/usr/bin/lesspipe.sh %s'
LINES=25
LOGNAME=root
MACHTYPE=x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu
MAIL=/var/spool/mail/root
MAILCHECK=60
OPTERR=1
OPTIND=1
OSTYPE=linux-gnu
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
PIPESTATUS=([0]="0")
PPID=9662
PROMPT_COMMAND='printf "\033]0;%s@%s:%s\007" "${USER}" "${HOSTNAME%%.*}" "${PWD/#$HOME/~}"'
PS1='[\u@\h \W]\$ '
PS2='> '
PS4='+ '
PWD=/root
SELINUX_LEVEL_REQUESTED=
SELINUX_ROLE_REQUESTED=
SELINUX_USE_CURRENT_RANGE=
SHELL=/bin/bash
SHELLOPTS=braceexpand:emacs:hashall:histexpand:history:interactive-comments:monitor
SHLVL=1
SSH_CLIENT='192.168.32.3 4407 22'
SSH_CONNECTION='192.168.32.3 4407 192.168.32.111 22'
SSH_TTY=/dev/pts/0
TERM=xterm
UID=0
USER=root
XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/run/user/0
XDG_SESSION_ID=13
_=123456789
aa=123456789
colors=/root/.dircolors
mxh='shen chao'
mxh1='li ming'
查找aa的值
[root@localhost ~]# set | grep aa
aa=123456789
2、删除变量:unset 变量
[root@localhost ~]# unset mxh1 删除后在set里查找不到mxh1
环境变量(有一部分是系统自带的,有一部分是用户自定义的)
用户自定义变量只在当前的Shell中生效,而环境变量会在当前Shell和这个Shell的所有子Shell当中生效。如果把环境变量写入相应的配置文件,那么这个环境变量就会在所有的Shell中生效
| 定义环境变量 : | export 环境变量=变量值(一般大写) |
| 查看环境变量 | env 环境变量名 |
| 删除环境变量 | unset 环境变量名 |
1、◆PATH:系统查找命令的路径
[root@localhost ~]#echo SPATH
/usr/lib/qt-3.3/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
[root@localhost ~]# echo $PATH
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
[root@localhost ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg a.out test.c webmin-1.970 webmin-1.970.tar.gz
[root@localhost ~]# knssn
-bash: knssn: 未找到命令
这些路径都是用于存放命令的位置:比如说执行ls命令的时候,系统就会去/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bi 这些路径下需找命令,如果输入错误,或者没有这个命令,系统就会报错,说没有这个命令
2、PATH="SPATH":/root/sh (现在只是临时性的,要写进配置文件才会永久生效)
#PATH变量叠加 (把shell脚本的目录添加到命令的路径中去,就可以直接在根目录下执行脚本,不需要什么绝对路径、相对路径)
[root@localhost mxh]# bash 1.sh
mxh is a hansome boy
[root@localhost mxh]# vim 1.sh
[root@localhost mxh]# pwd
/tmp/mxh
[root@localhost mxh]# PATH="$PATH":/tmp/mxh
[root@localhost mxh]# echo $PATH
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin:/tmp/mxh
[root@localhost mxh]# 1.sh
mxh is a hansome boy
位置参数变量(相当于形参和实参传递)
| $n | n为数字,$0代表命令本身,$1-$9代表第一到第九个参数,十以上的参数需要用大括号包含,如${10}. |
| $* | 这个变量代表命令行中所有的参数,*把所有的参数看成一个整体 |
| $@ | 这个变量也代表命令行中所有的参数,不过$@把每个参数区分对待 |
| $# | 这个变量代表命令行中所有参数的个数 |
1、$n的shell脚本
1 #!/bin/bash
2 echo $0 # $0就是代表命令本身
3 echo $1 # $1代表变量1
4 echo $2 # $2代表变量2
5 echo $3 # $3代表变量3
输出结果
[root@localhost mxh.shell]# bash 1.sh 1 2 3 4
1.sh #对应$0 第一个位置接收命令
1 #对应$1 第二个位置接收1
2 #对应$2 第三个位置接收2
3 #对应$3 第四个位置接收3
因为里面只设置了4个变量,但是输入的有4个变量加上命令本身,所以就溢出,没有打印最有一个数值4
2、两个数字加法运算
[root@localhost mxh.shell]# cat 2.sh
#!/bin/bash
#写一个两个数加法shell
num1=$1
num2=$2
echo sum=$(($num1+$num2))
echo sum=$(($1+$2))
[root@localhost mxh.shell]# bash 2.sh 2 3
sum=5
sum=5
3、$@\$*\$#的区别
#!/bin/bash echo"A total of S#parameters"
#使用S#代表所有参数的个数
echo"The parameters is:S*"
#使用8*代表所有的参数
echo"The parameters is:s@"
#使用8@也代表所有参数(1)$#
[root@localhost mxh.shell]# cat 3.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo $#
[root@localhost mxh.shell]# bash 3.sh 1 2 3 4 5
5
#代表有输入有5个参数(2)$@和$*
[root@localhost mxh.shell]# cat 4.sh
#!/bin/bash
for i in "$@" #$@是区别对待每个参数,加双引号是为了让它是一个整体
do
echo $i
done
for y in "$*" #$* 是把参数看做一个整体
do
echo $y
done
[root@localhost mxh.shell]# bash 4.sh 1 2 3 4 5
1
2
3
4
5
1 2 3 4 5