Lambda表达式的介绍
Lambda表达式是 Java8 中最重要的新功能之一。使用 Lambda 表达式可以替代只有一个抽象函数的接口实现,告别匿名内部类,代码看起来更简洁易懂。Lambda表达式同时还提升了对集合、框架的迭代、遍历、过滤数据的操作。
Lambda表达式的特点
1:函数式编程
2:参数类型自动推断
3:代码量少,简洁
public class LambdaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
// @Override
// public void run() {
// System.out.println("running1!");
// }
// };
// runnable.run();
//
// Runnable runnable2 = ()-> System.out.println("running2!");
// Runnable runnable3 = ()-> {
// System.out.println("running3!");
// };
// runnable2.run();
// runnable3.run();
//
// Callable<String> callable = new Callable<String>() {
// @Override
// public String call() throws Exception {
// return "jason1";
// }
// };
// System.out.println(callable.call());
//
// Callable<String> callable1 = ()-> {return "jason2";};
// Callable<String> callable2 = ()->"jason3";
// System.out.println(callable1.call());
// System.out.println(callable2.call());
// StudentDao dao = new StudentDao() {
// @Override
// public void insert(Student student) {
// System.out.println("插入一个学生信息" + student);
// }
// };
// dao.insert(new Student());
//
// StudentDao dao1 = (student)-> System.out.println("插入:" + student);
// StudentDao dao2 = (Student student)-> System.out.println("插入:" + student);
// StudentDao dao3 = (student)->{
// System.out.println("插入:" + student);
// };
// StudentDao dao4 = (Student student)->{
// System.out.println("插入:" + student);
// };
// StudentDao dao5 = student -> System.out.println("插入:" + student);
// StudentDao dao6 = student -> {
// System.out.println("插入:" + student);
// };
//
// dao1.insert(new Student());
// dao2.insert(new Student());
// dao3.insert(new Student());
// dao4.insert(new Student());
// dao5.insert(new Student());
// dao6.insert(new Student());
// TeacherDao teacherDao = new TeacherDao() {
// @Override
// public int get(Teacher teacher) {
// return 1;
// }
// };
// System.out.println(teacherDao.get(new Teacher()));
//
// TeacherDao teacherDao1 = (teacher)->{return 2;};
// TeacherDao teacherDao2 = (teacher)->3;
// TeacherDao teacherDao3 = teacher->{return 4; };
// TeacherDao teacherDao4 = teacher->5;
// System.out.println(teacherDao1.get(new Teacher()));
// System.out.println(teacherDao2.get(new Teacher()));
// System.out.println(teacherDao3.get(new Teacher()));
// System.out.println(teacherDao4.get(new Teacher()));
/*
在JDK中,提供了一些代表输入和输出的接口,他们本身是没有什么意义的,只是为了
方便的使用lambda表达式来编写代码,从而获取对应的执行结果。
*/
// Supplier<Integer> supplier = new Supplier<Integer>() {
// @Override
// public Integer get() {
// return 1;
// }
// };
// Supplier<Integer> supplier1 = ()->1;
// System.out.println(supplier.get());
// Consumer<String> consumer = new Consumer<String>() {
// @Override
// public void accept(String s) {
// System.out.println(s);
// }
// };
// Consumer<String> consumer1 = (s)-> System.out.println(s);
// consumer.accept("jason1");
// consumer1.accept("jason2");
//
// Function<Integer,String> function = (i)->i+"jason3";
// Function<Integer,String> function1 = (Integer i)->{return i + "jason4";};
// System.out.println(function.apply(200));
// function1.apply(300);
// BiFunction<String,String,Integer> bf = (a,b)-> a.length() + b.length();
// System.out.println(bf.apply("老于", "很帅"));
//
// Runnable runnable1 = ()-> System.out.println(get());
// Runnable runnable2 = ()->{
// String str = find();
// System.out.println(str);
// };
// Runnable runnable3 = ()->exec();
// Runnable runnable4 = ()-> 1;
// Runnable runnable5 = ()-> "ok";
// Runnable runnable6 = ()-> get();
// Runnable runnable7 = ()-> true?1:2;
// runnable1.run();
// runnable2.run();
// runnable3.run();
// LambdaInterface li1 = new LambdaInterface() {
// @Override
// public int get(int num) {
// return num;
// }
// };
// System.out.println(li1.get(200));
// LambdaInterface li1 = (num)-> get(num);
// LambdaInterface li2 = (num)-> System.out.println(num);
// LambdaInterface li3 = (num)->{return get(num);};
LambdaInterface li4 = (num)->{return num;};
LambdaInterface li5 = (num)->num;
LambdaInterface li6 = num->num;
LambdaInterface li7 = num->{return num;};
System.out.println(li4.get(300));
Function<Integer,Integer> function = (num)->num;
System.out.println(function.apply(100));
Consumer<Integer> consumer1 = (num)-> System.out.println(num);
consumer1.accept(1000);
Consumer<Integer> consumer2 = (num)->getNum(num);
consumer2.accept(2000);
Function<String,String> f1 = (str)->str.toUpperCase();
Function<String,String> f2 = (str)->toUpperCase(str);
System.out.println(f1.apply("abcdefg"));
System.out.println(f2.apply("abcdefgefg"));
BiFunction<String,String,Integer> bf = (a,b)->a.length()+b.length();
System.out.println(bf.apply("老于", "很帅"));
BiFunction<String,String,Integer> bf1 = (a,b)->getStrLength(a,b);
System.out.println(bf1.apply("老于", "很帅"));
}
public static void getNum(int num){
System.out.println(num);
}
public static String toUpperCase(String str){
return str.toUpperCase();
}
public static Integer getStrLength(String str1,String str2){
return str1.length()+str2.length();
}
// public static int get(){
// return 1;
// }
//
// public static String find(){
// return "find";
// }
//
// public static void exec() {
// find();
// }
}@FunctionalInterface
public interface StudentDao {
public void insert(Student student);
}public class Student {
}
public class Teacher {
}@FunctionalInterface
public interface TeacherDao {
public int get (Teacher teacher);
}Lambda表达式应用场景:任何有函数式接口的地方
函数式接口:只有一个抽象方法(Object类中的方法除外)的接口是函数式接口
函数式接口
Supplier 代表一个输出
Consumer 代表一个输入
BiConsumer 代表两个输入
Function 代表一个输入,一个输出(一般输入和输出是不同类型的)
UnaryOperator 代表一个输入,一个输出(输入和输出是相同类型的)
BiFunction 代表两个输入,一个输出(一般输入和输出是不同类型的)
BinaryOperator 代表两个输入,一个输出(输入和输出是相同类型的)
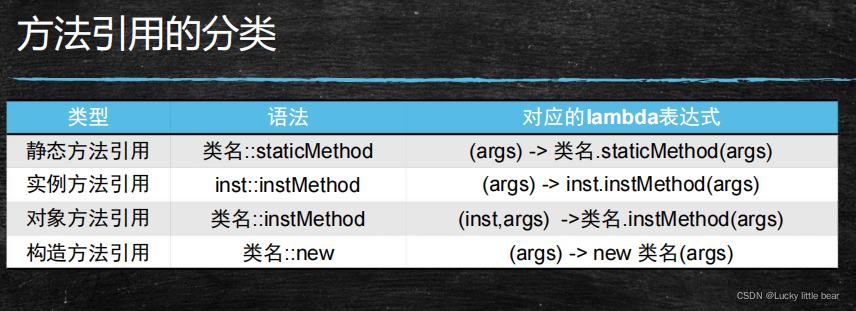
方法的引用:方法引用是用来直接访问类或者实例的已经存在的方法或者构造方法,方法引用提供了一种引用而不执行方法的方式,如果抽象方法的实现恰好可以使用调用另外一个方法来实现,就有可能可以使用方法引用。
静态方法引用:如果函数式接口的实现恰好可以通过调用一个静态方法来实现,那么就可以使用静态方法引用
实例方法引用:如果函数式接口的实现恰好可以通过调用一个实例的实例方法来实现,那么就可以使用实例方法引用
对象方法引用:抽象方法的第一个参数类型刚好是实例方法的类型,抽象方法剩余的参数恰好可以当做实例方法的参数。如果函数式接口的实现能由上面说的实例方法调用来实现的话,那么就可以使用对象方法引用
构造方法引用:如果函数式接口的实现恰好可以通过调用一个类的构造方法来实现,那么就可以使用构造方法引用
why1:
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private int score;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, int score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Student("zhangfei",18,69));
list.add(new Student("guanyu",20,70));
list.add(new Student("zhaoyun",26,75));
list.add(new Student("liubei",30,85));
list.add(new Student("huangzhong",23,90));
//查询年龄大于25岁的学生信息
getByAge(list);
//查询分数大于80分的学生信息
System.out.println("***********************************");
getByScore(list);
}
public static void getByAge(ArrayList<Student> students){
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (Student student : students){
if(student.getAge()>25){
list.add(student);
}
}
for(Student student : list){
System.out.println(student);
}
}
public static void getByScore(ArrayList<Student> students){
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(Student student : students){
if(student.getScore()>80){
list.add(student);
}
}
for(Student student : list){
System.out.println(student);
}
}
}
why2:
public class AgeFilter implements StudentFilter {
@Override
public boolean compare(Student student) {
return student.getAge()>25;
}
}public class ScoreFilter implements StudentFilter {
@Override
public boolean compare(Student student) {
return student.getScore()>80;
}
}public interface StudentFilter {
public boolean compare(Student student);
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Student("zhangfei",18,69));
list.add(new Student("gunayu",20,70));
list.add(new Student("zhaoyun",26,75));
list.add(new Student("liubei",30,85));
list.add(new Student("huangzhong",23,90));
//查询年龄大于25岁的学生信息
getByFilter(list,new AgeFilter());
//查询年龄大于80分的学生信息
System.out.println("***********************************");
getByFilter(list,new ScoreFilter());
}
public static void getByFilter(ArrayList<Student> students,StudentFilter studentFilter){
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(Student student : students) {
if (studentFilter.compare(student)) {
list.add(student);
}
}
for (Student student : list){
System.out.println(student);
}
}
}
why3:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Student("zhangfei",18,69));
list.add(new Student("guanyu",20,70));
list.add(new Student("zhaoyun",26,75));
list.add(new Student("liubei",30,85));
list.add(new Student("huangzhong",23,90));
//查询年龄大于25岁的学生信息
getByFilter(list, new StudentFilter() {
@Override
public boolean compare(Student student) {
return student.getAge() > 25;
}
});
//查询大于80分的学生信息
System.out.println("**********************************");
getByFilter(list, new StudentFilter() {
@Override
public boolean compare(Student student) {
return student.getScore()>80;
}
});
//查询名字长度大于6的学生信息
System.out.println("**********************************");
getByFilter(list, new StudentFilter() {
@Override
public boolean compare(Student student) {
return student.getName().length() > 6;
}
});
}
public static void getByFilter(ArrayList<Student> students, StudentFilter filter){
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (Student student : students){
if(filter.compare(student)){
list.add(student);
}
}
printStudent(list);
}
public static void printStudent(ArrayList<Student> students){
for (Student student : students){
System.out.println(student);
}
}
}
why4:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Student("zhangfei",18,69));
list.add(new Student("guanyu",20,70));
list.add(new Student("zhaoyun",26,75));
list.add(new Student("liubei",30,85));
list.add(new Student("huangzhong",23,90));
//查询年龄大于25岁的学生信息
getByFilter(list,(student) -> student.getAge() >25);
//查询大于80分的学生信息
System.out.println("*********************");
getByFilter(list,(student)->student.getScore() > 80);
//查询姓名长度大于6的学生信息
System.out.println("******************************");
getByFilter(list,(student -> student.getName().length() >6));
}
public static void getByFilter(ArrayList<Student> students, StudentFilter filter){
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (Student student : students){
if(filter.compare(student)){
list.add(student);
}
}
printStudent(list);
}
public static void printStudent(ArrayList<Student> students){
for (Student student1 : students){
System.out.println(student1);
}
}
}