一,消息传递
在OC中,传递消息就是在对象上调用方法。
相对于C语言的方法就“静态绑定”的函数,在编译器就决定了运行时所要调用的函数。在OC中,如果向某对象传递消息,就会使用动态绑定机制来决定需要调用那个方法。调用那个方法完全取决于运行期决定,甚至可以在程序运行时改变。编译时并不能确定方法有没有对应的实现,没有写方法的具体实现也不会报错。
给对象发送消息可以这样来写:
id returnValue = [someObject messageName:parameter];
本例中,someObject叫做“接收者”(receiver),messageName叫做“选择子”(selector)。选择子与参数合起来称作“消息”(message)。编译器将其转换为C语言函数调用objc_msgSend
id returnValue = objc_msgSend(someObject, @selector(messageName:), parameter);
这个函数将消息接受者,选择子和参数作为主要参数,其原型如下:
objc_msgSend(receiver, selector) // 不带参数
objc_msgSend(receiver, selector, arg1, arg2,...) // 带参数
消息传递的关键在于objc_class结构体有两个关键的字段:
- isa 指向父类的指针
- methodLists 类的方法分发表(dispatch table)
其中对象的isa指针让对象可以访问类和类的继承链。
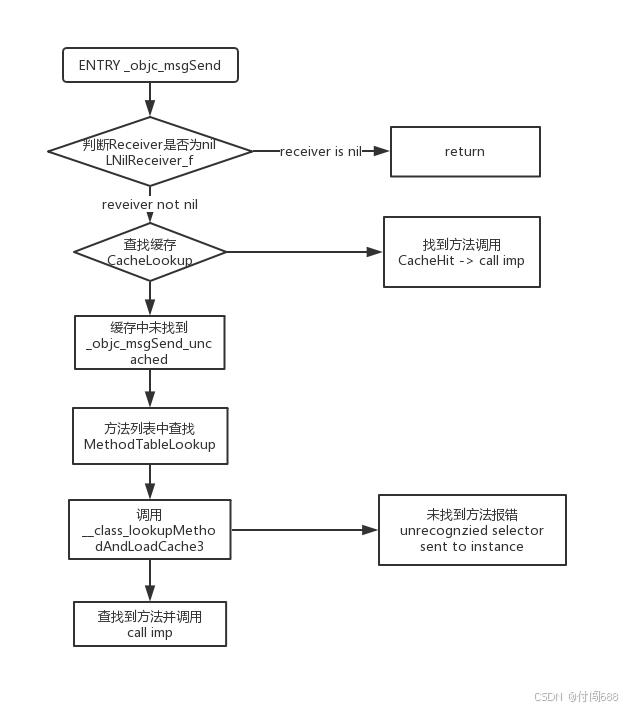
消息传递的过程:
- 当消息传递给一个对象时,首先从运行时系统缓存
objc_cache中进行查找。如果找到则执行,否则执行下面的步骤 objc_msgSend通过isa指针获取类的结构体,然后通过选择子作为“键”在方法分发表methodLists查找应该执行的方法,实际上查找的就是相应方法的IMP函数指针,Dispatch table是一张SEL和IMP的对应表。也就是说方法编号SEL最后还要通过Dispatch table表找到对应的IMP,IMP是一个函数指针,然后去执行这个方法- 如果未找到,通过
isa找到父类并在父类的分发表中查找,一直沿着类的继承链找到NSObject类,一旦找到则传入相应的参数来执行方法的具体实现,并将该方法加入到本类的方法缓存objc_cache。如果一直未找到方法的实现那么消息发送阶段结束,进入动态解析阶段,解析到就结束。如果未解析到,则会进入消息转发流程。
消息传递分为三个阶段:
- 消息发送阶段
- 动态解析阶段
- 消息转发阶段
方法查找的核心函数就是 _class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3 函数,接下来重点分析 _class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3 函数内的源码。
IMP _class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3(id obj, SEL sel, Class cls)
{
return lookUpImpOrForward(cls, sel, obj,
YES/*initialize*/, NO/*cache*/, YES/*resolver*/);
}
lookUpImpOrForward 函数
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver)
{
// initialize = YES , cache = NO , resolver = YES
IMP imp = nil;
bool triedResolver = NO;
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
// 缓存查找, 因为cache传入的为NO, 这里不会进行缓存查找, 因为在汇编语言中CacheLookup已经查找过
// Optimistic cache lookup
if (cache) {
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) return imp;
}
// runtimeLock is held during isRealized and isInitialized checking
// to prevent races against concurrent realization.
// runtimeLock is held during method search to make
// method-lookup + cache-fill atomic with respect to method addition.
// Otherwise, a category could be added but ignored indefinitely because
// the cache was re-filled with the old value after the cache flush on
// behalf of the category.
runtimeLock.lock();
checkIsKnownClass(cls);
if (!cls->isRealized()) {
realizeClass(cls);
}
if (initialize && !cls->isInitialized()) {
runtimeLock.unlock();
_class_initialize (_class_getNonMetaClass(cls, inst));
runtimeLock.lock();
// If sel == initialize, _class_initialize will send +initialize and
// then the messenger will send +initialize again after this
// procedure finishes. Of course, if this is not being called
// from the messenger then it won't happen. 2778172
}
retry:
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
// Try this class's cache.
// 防止动态添加方法,缓存会变化,再次查找缓存。
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
// 如果查找到imp, 直接调用done, 返回方法地址
if (imp) goto done;
// 查找方法列表, 传入类对象和方法名
// Try this class's method lists.
{
// 根据sel去类对象里面查找方法
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(cls, sel);
if (meth) {
// 如果方法存在,则缓存方法
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, cls);
// 方法缓存之后, 取出imp, 调用done返回imp
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
// 如果类方法列表中没有找到, 则去父类的缓存中或方法列表中查找方法
// Try superclass caches and method lists.
{
unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();
for (Class curClass = cls->superclass;
curClass != nil;
curClass = curClass->superclass)
{
// Halt if there is a cycle in the superclass chain.
if (--attempts == 0) {
_objc_fatal("Memory corruption in class list.");
}
// 查找父类的缓存
// Superclass cache.
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);
if (imp) {
if (imp != (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) {
// 在父类中找到方法, 在本类中缓存方法, 注意这里传入的是cls, 将方法缓存在本类缓存列表中, 而非父类中
// Found the method in a superclass. Cache it in this class.
log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);
goto done;
}
else {
// Found a forward:: entry in a superclass.
// Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method
// resolver for this class first.
break;
}
}
// 查找父类的方法列表
// Superclass method list.
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
// 同样拿到方法, 在本类进行缓存
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, curClass);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
}
// ---------------- 消息发送阶段完成 ---------------------
// ---------------- 进入动态解析阶段 ---------------------
// 上述列表中都没有找到方法实现, 则尝试解析方法
// No implementation found. Try method resolver once.
if (resolver && !triedResolver) {
runtimeLock.unlock();
_class_resolveMethod(cls, sel, inst);
runtimeLock.lock();
// Don't cache the result; we don't hold the lock so it may have
// changed already. Re-do the search from scratch instead.
triedResolver = YES;
goto retry;
}
// ---------------- 动态解析阶段完成 ---------------------
// ---------------- 进入消息转发阶段 ---------------------
// No implementation found, and method resolver didn't help.
// Use forwarding.
imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
cache_fill(cls, sel, imp, inst);
done:
runtimeLock.unlock();
return imp;
}
方法缓存
在进行查找时,OC会运行时会利用缓存机制来提高查找的速度,在方法查找中,他会将最近使用过的方法实现存储在缓存中下次调用相同的方法就可以直接在缓存中获取实现,避免了反复查找的过程。
类缓存(objc_cache)
struct objc_cache {
unsigned int mask /* total = mask + 1 */ OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
unsigned int occupied OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
Method _Nullable buckets[1] OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
};
-
mask: 指定分配的缓存 bucket 的总数。,所以缓存的 size(total)是 mask+1。
-
occupied: 指定实际占用的缓存bucket的总数。
-
buckets: 指向 Method 数据结构指针的数组。
为了加速消息分发, 系统会对方法和对应的地址进行缓存,就放在 objc_cache 中,所以在实际运行中,大部分常用的方法都是会被缓存起来的。
SEL和IMP
IMP是OC方法实现代码块的地址,可以通过它像C语言函数一样直接调用方法实现。
typedef id (&IMP)(id,SEL,...);
IMP是一个函数指针,这个被指向的函数包含一个接搜消息的对象id(self指针),调用方法的选择子SEL(方法名),以及不定个数的方法参数,并返回一个id.
SEL是OC中表示方法名的数据类型,在运行时有编译器生成的唯一标识符用于在对象查找并调用相应的方法。
/// An opaque type that represents a method selector.
typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;
OC编译时会根据方法的名字包括参数序列,生成区分这个方法的唯一ID,不管是子类还是父类,只要方法的名字包括参数序列相同,它们的ID就相同。
二,消息转发
当一个对象能够接收一个消息时,会走完正常的消息传递过程。弱无法接受会发生什么呢?
- 默认情况下,如果以[object message] 的形式调用方法,如果object无法响应message消息时,编译器会报错
- 如果是以performselector 的形式调用方法,则需要等到运行时才能确定object是否能接受message消息,则程序崩溃
当不确定一个对象是否能接受某个消息时,可以调用respondsToSelector:来进行判断
if ([self respondsToSelector:@selector(method)]) {
[self performSelector:@selector(method)];
}
当一个对象无法接受莫哥消息时,就会启动“消息转发”机制。通过学习转发机制可以告诉对象如何处理未知的消息。
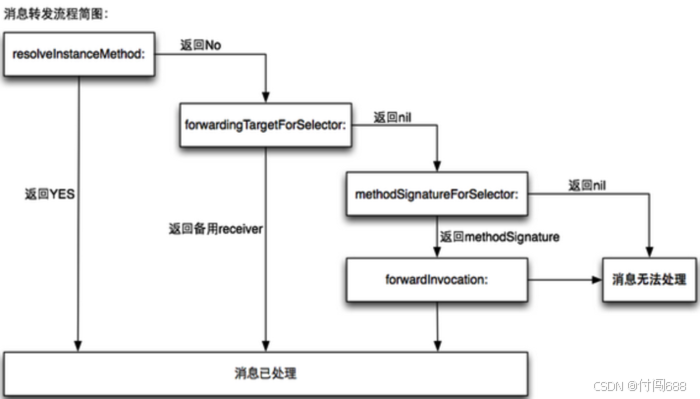
消息转发机制分为三个阶段:
- 动态方法解析
- 备用接受者
- 完整消息转发
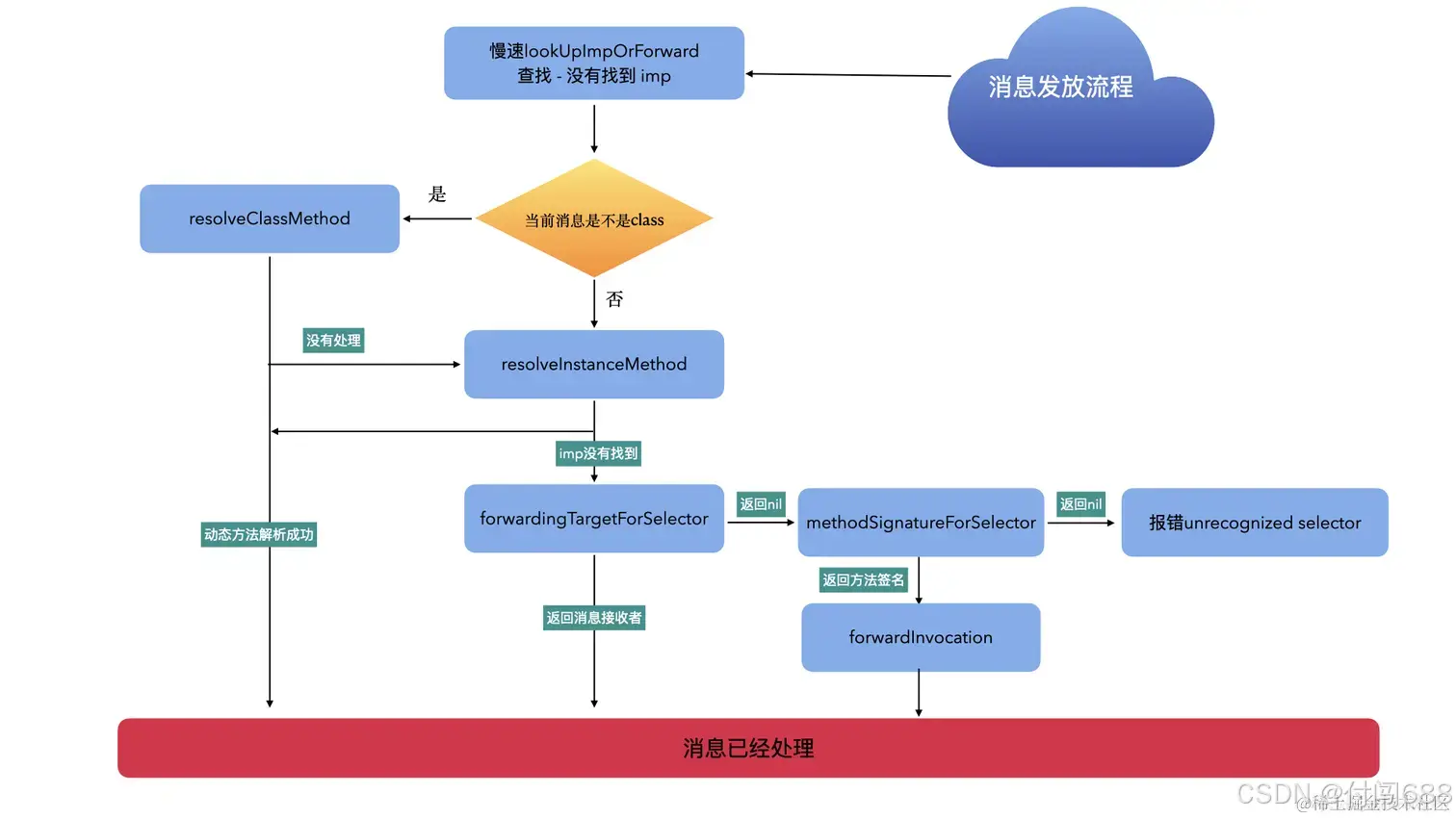
1,动态方法解析
// No implementation found. Try method resolver once.
//未找到实现。尝试一次方法解析器
if (slowpath(behavior & LOOKUP_RESOLVER)) {
behavior ^= LOOKUP_RESOLVER;
return resolveMethod_locked(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}
如果没找到方法则尝试调用resolveMethod_locked动态解析,只会执行一次:
/***********************************************************************
* resolveMethod_locked
* Call +resolveClassMethod or +resolveInstanceMethod.
*
* Called with the runtimeLock held to avoid pressure in the caller
* Tail calls into lookUpImpOrForward, also to avoid pressure in the callerb
**********************************************************************/
static NEVER_INLINE IMP
resolveMethod_locked(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
{
lockdebug::assert_locked(&runtimeLock);
ASSERT(cls->isRealized());
runtimeLock.unlock();
//判断是不是元类
if (! cls->isMetaClass()) {
// try [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
resolveInstanceMethod(inst, sel, cls);
}
else {
// try [nonMetaClass resolveClassMethod:sel]
// and [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
resolveClassMethod(inst, sel, cls);
if (!lookUpImpOrNilTryCache(inst, sel, cls)) {
resolveInstanceMethod(inst, sel, cls);
}
}
// chances are that calling the resolver have populated the cache
// so attempt using it
return lookUpImpOrForwardTryCache(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}
主要用的的方法如下
// 类方法未找到时调起,可以在此添加方法实现
+ (BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel;
// 对象方法未找到时调起,可以在此添加方法实现
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel;
//其中参数sel为未处理的方法
上述代码的大致流程:
- 先检查进行解析的是否是元类
- 如果不是元类,则调用resolveInstanceMethod:进行对象方法动态调用
- 如果是元类,则调用resolveClassMethod:进行类方法动态解析,完成类方法动态解析后,再次查询cls中的imp,如果没有找到,则进行一次对象方法动态解析
两个方法resolveInstanceMethod和resolveClassMethod则称为方法的动态决议。
执行完上述代码后返回lookUpImpOrForwardTryCache:
IMP lookUpImpOrForwardTryCache(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
{
return _lookUpImpTryCache(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}
这个方法调用的是_lookUpImpTryCache方法:
ALWAYS_INLINE
static IMP _lookUpImpTryCache(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
{
lockdebug::assert_unlocked(&runtimeLock);
if (slowpath(!cls->isInitialized())) {
// see comment in lookUpImpOrForward
return lookUpImpOrForward(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}
IMP imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp != NULL) goto done;
#if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES
if (fastpath(cls->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache(/* strict */true))) {
imp = cache_getImp(cls->cache.preoptFallbackClass(), sel);
}
#endif
if (slowpath(imp == NULL)) {
return lookUpImpOrForward(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}
done:
if ((behavior & LOOKUP_NIL) && imp == (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) {
return nil;
}
return imp;
}
可以看到这里有cache_getImp;也就是说在进行一次动态决议之后,还会通过cache_getImp从cache里找一遍方法的sel。
#endif
if (slowpath(imp == NULL)) {
return lookUpImpOrForward(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}
如果还是没找到(imp == NULL),也就是无法通过动态添加方法的话,还会执行一次lookUpImpOrForward,这时候进lookUpImpOrForward方法,这里behavior传的值会发生变化。
第二次进入lookUpImpOrForward方法后,执行到if (slowpath(behavior & LOOKUP_RESOLVER))这个判断时
// 这里就是消息转发机制第一层的入口
if (slowpath(behavior & LOOKUP_RESOLVER)) {
behavior ^= LOOKUP_RESOLVER;
return resolveMethod_locked(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}
根据变化后的behavior值和LOOKUP_RESOLVER值之间的关系导致该if语句内部只能进入第一次。解释了为什么开头说的该动态解析resolveMethod_locked为什么只执行一次次
具体实现
+(BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel {
if ([NSStringFromSelector(sel) isEqualToString:@"instanceMethodTest:"]) {
Method method = class_getInstanceMethod([self class], @selector(addDynamicInstanceMethod:));
IMP methodIMP = method_getImplementation(method);
const char * types = method_getTypeEncoding(method);
class_addMethod([self class], sel, methodIMP, types);
return YES;
}
return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel];
}
+(BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel {
if ([NSStringFromSelector(sel) isEqualToString:@"classMethodTest:"]) {
// 类方法都是存在元类中,所以添加方法需要往元类上添加
Class metaClass = object_getClass([self class]);
Method method = class_getClassMethod([self class], @selector(addDynamicClassMethod:));
IMP methodIMP = method_getImplementation(method);
const char * types = method_getTypeEncoding(method);
class_addMethod(metaClass, sel, methodIMP, types);
return YES;
}
return [super resolveClassMethod:sel];
}
-(void)addDynamicInstanceMethod:(NSString *)value {
NSLog(@"addDynamicInstanceMethod value = %@",value);
}
+(void)addDynamicClassMethod:(NSString *)value {
NSLog(@"addDynamicClassMethod value = %@",value);
}
2,备用接受者(快速转发)
当cache中没有找到imp,猎类的继承链里的方法列表都没有找到imp,并且resolve InstanceMethod / resolveClassMethod返回NO就进入快速消息转发。也就是本类没有能力去处理这个消息,那么就交给其他类去处理。
done:
if ((behavior & LOOKUP_NIL) && imp == (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) {
return nil;
}
return imp;
从imp == (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache进入消息转发机制。
查看一下这个方法:
竟然是汇编实现的这就又印证了汇编速度更快的结论
STATIC_ENTRY __objc_msgForward_impcache
// No stret specialization.
b __objc_msgForward
END_ENTRY __objc_msgForward_impcache
ENTRY __objc_msgForward
adrp x17, __objc_forward_handler@PAGE
ldr p17, [x17, __objc_forward_handler@PAGEOFF]
TailCallFunctionPointer x17
END_ENTRY __objc_msgForward
具体实现
-(id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
if ([NSStringFromSelector(aSelector) isEqualToString:@"instanceMethodTestFastForwarding:"]) {
SubFromView * subFromView = [[SubFromView alloc]init];
if ([subFromView respondsToSelector:aSelector]) {
return subFromView;
}
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
+(id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
if ([NSStringFromSelector(aSelector) isEqualToString:@"classMethodTestFastForwarding:"]) {
if ([SubFromView respondsToSelector:aSelector]) {
return [SubFromView class];
}
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
我们在新建的SubFromView完成相应方法的实现,然后就将消息最终转发给了su bFromview实现。
3,完整消息转发(慢速转发)
//封装方法
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
NSString *method = NSStringFromSelector(aSelector);
if ([method isEqualToString:@"sendMessage:"]) {
//把这个方法存起来
return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v@:@"];
}
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation {
//获得方法编号
SEL sel = [anInvocation selector];
//还来找备胎
SpareWheel *sp = [SpareWheel new];
//判断能否响应方法
if ([sp respondsToSelector:sel]) {
anInvocation.target = sp;
}else {
[super forwardInvocation:anInvocation];
}
}
慢速转发需要同时实现methodSignatureForSelector和forwardInvocation两个函数,相当于是重新给该消息进行签名,然后调用forwardInvocation转发。[NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:“v@😡”];,这里的"v@😡"是苹果官方的类型定义,
快速转发和慢速转发都会将消息转发给别的对象,它们的区别是什么?
- 慢速转发可以转发给多个对象,而快速转发最多只能转发一个
- 快速转发需要实现
forwardingTargetForSelector这个方法,但是慢速必须同时实现methodSignatureForSelector和forwardInvocation方法。 - 块速转发必须指定转发对象或者进行快速转发,而慢速转发作为最终步骤,可以不指定转发对象,也可以控制是否调用doesNotRecognizeSelector来控制抛异常。所以慢速转发可以避免闪退,如果最终没有可转发的对象,可以进行错误提示,提高用户体验。
总结:
-
动态方法解析不处理,会进入消息转发流程
-
消息转发流程有快速转发和慢速转发
-
如果消息转发阶段,快速转发和慢速转发不处理,就进入doesNotRecognizeSelector默认抛出异常信息