关注程序员的AI工具,解答更多专业问题
1、概述
约束布局ConstraintLayout 是一个ViewGroup,可以在Api9以上的Android系统使用它,它的出现主要是为了解决布局嵌套过多的问题,以灵活的方式定位和调整小部件。
2、作用
为什么要用ConstraintLayout?
在开发过程中经常能遇到一些复杂的UI,可能会出现布局嵌套过多的问题,嵌套得越多,设备绘制视图所需的时间和计算功耗也就越多。
ConstraintLayout使用起来比RelativeLayout更灵活,性能更出色。
ConstraintLayout可以按照比例约束控件位置和尺寸,能够更好地适配屏幕大小不同的机型。
- 减少嵌套、性能更好;
- 能更好适配多屏幕尺寸;
3、使用ConstraintLayout
使用约束布局的关键点:
- 约束布局采用相对定位原理,即控件相对于另一个控件的约束
- 一个控件至少三个方向的约束
3.1 添加依赖
在app/build.gradle文件中添加ConstraintLayout的依赖
implementation 'com.android.support.constraint:constraint-layout:xxx'3.2 相对定位
相对定位是在ConstraintLayout中创建布局的基本构建块之一。这些约束允许您将给定的小部件相对于另一个小部件定位。您可以在水平和垂直轴上约束小部件:
- 水平轴:左,右,起点和终点
- 垂直轴:顶部,底部和文本基线
一般概念是将窗口小部件的给定一侧限制为任何其他窗口小部件的另一侧。
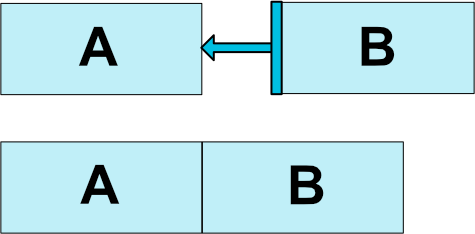
例如,为了将按钮B定位在按钮A的右侧(图1):
<Button android:id="@+id/buttonA" ... />
<Button android:id="@+id/buttonB" ...
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@+id/buttonA" />这告诉系统我们希望将按钮B的左侧限制在按钮A的右侧。这种位置限制意味着系统将尝试使两侧共享相同的位置。
可用约束的列表(图2):
layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOflayout_constraintLeft_toRightOflayout_constraintRight_toLeftOflayout_constraintRight_toRightOflayout_constraintTop_toTopOflayout_constraintTop_toBottomOflayout_constraintBottom_toTopOflayout_constraintBottom_toBottomOflayout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOflayout_constraintStart_toEndOflayout_constraintStart_toStartOflayout_constraintEnd_toStartOflayout_constraintEnd_toEndOf
它们都引用另一个小部件或parent(将引用父容器,即ConstraintLayout):
<Button android:id="@+id/buttonB" ...
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent" />3.3 Margin用法
如果设置了边距,则会将它们应用于相应的约束(如果存在)(图3),从而将边距强制为目标端与源端之间的空间。可以使用通常的布局边距属性来达到此效果:
android:layout_marginStartandroid:layout_marginEndandroid:layout_marginLeftandroid:layout_marginTopandroid:layout_marginRightandroid:layout_marginBottom
请注意,边距只能为正数或等于零,并且采用Dimension。
连接到View.GONE小部件时的边距
当位置限制目标的可见性为View.GONE,设置的边距值才生效,否则不生效
layout_goneMarginStartlayout_goneMarginEndlayout_goneMarginLeftlayout_goneMarginToplayout_goneMarginRightlayout_goneMarginBottom
例如,假设TextView2的左边约束在TextView1的右边,并给TextView2设一个app:layout_goneMarginLeft="10dp",代码如下:
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout ...>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/TextView1"
.../>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/TextView2"
...
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@+id/TextView1"
app:layout_goneMarginLeft="10dp"
/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>效果如下,TextView2在TextView1的右边,且没有边距。
把TextView1的可见性设为gone,效果如下:
TextView1消失后,TextView2有一个距离左边10dp的边距。
3.4 居中定位
相对父控件(也可以是其它控件)水平居中
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button android:id="@+id/button" ...
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>相对父控件(也可以是其它控件)垂直居中
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button android:id="@+id/button" ...
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>水平垂直居中
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button android:id="@+id/button" ...
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>3.5 偏移定位
可以使用bias属性调整位置,使一侧偏向另一侧,可以设计出更好地适应屏幕尺寸变化的用户界面。
layout_constraintHorizontal_bias 水平方向偏移layout_constraintVertical_bias 垂直方向偏移
例如,以下将使左侧具有30%的偏差,而不是默认值50%,这样左侧将更短,而小部件则更偏向左侧:
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout ...>
<Button android:id="@+id/button" ...
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.3"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>3.6 圆形定位
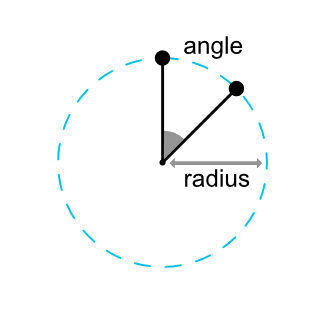
可以以一定角度和距离相对于另一个窗口小部件中心限制窗口小部件中心。这使小部件放置在圆上。
使用以下属性:
layout_constraintCircle:引用另一个小部件IDlayout_constraintCircleRadius:到另一个小部件中心的距离layout_constraintCircleAngle:小部件应处于哪个角度(以度为单位,范围从0到360)
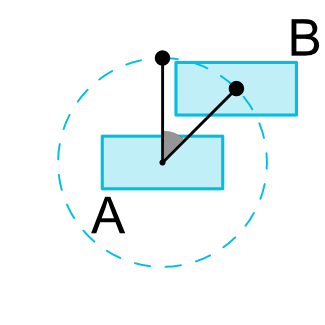
<Button android:id="@+id/buttonA" ... />
<Button android:id="@+id/buttonB" ...
app:layout_constraintCircle="@+id/buttonA"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="45" />3.7 尺寸限制
为ConstraintLayout设置最小和最大尺寸
android:minWidth设置布局的最小宽度android:minHeight设置布局的最小高度android:maxWidth设置布局的最大宽度android:maxHeight设置布局的最大高度
这些最小和最大尺寸将在ConstraintLayout尺寸设置为时使用WRAP_CONTENT。
其它控件尺寸约束
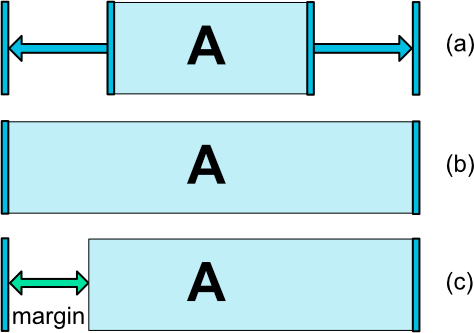
可以通过3种不同的方式设置android:layout_width和 android:layout_height属性来指定小部件的尺寸:
- 用特定的尺寸(文字值
123dp或Dimension参考) - 使用
WRAP_CONTENT,这将要求小部件计算自己的大小 - 使用
0dp,等同于“MATCH_CONSTRAINT”
(a)是wrap_content
(b)是0dp
(c)是0dp,并设置了margin
重要提示: MATCH_PARENT不建议用于中包含的小部件ConstraintLayout。如果要达到MATCH_CONSTRAINT效果,可以将相应的左/右或上/下约束设置"parent"。
3.8 尺寸百分比
要使用百分比,您需要设置以下内容:
- 尺寸应设置为
MATCH_CONSTRAINT(0dp) - 默认值应设置为百分比
app:layout_constraintWidth_default="percent"或app:layout_constraintHeight_default="percent" - 然后将
layout_constraintWidth_percentorlayout_constraintHeight_percent属性设置为介于0和1之间的值
3.9 Ratio比率用法
可以将小部件的一个尺寸定义为另一尺寸的比例。为此,需要至少将一个约束维度设置为0dp(即MATCH_CONSTRAINT),并将属性layout_constraintDimensionRatio设置为给定的比率。例如:
<Button android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="0dp"
app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="1:1" />该比率可以表示为:
如果两个尺寸都设置为MATCH_CONSTRAINT(0dp),也可以使用比率。在这种情况下,系统将设置满足所有约束并保持指定的宽高比的最大尺寸。要基于另一侧的尺寸来约束一个特定的侧面,可以预先附加W,“”或H,分别约束宽度或高度。例如,如果一个尺寸受两个目标约束(例如,宽度为0dp并以父对象为中心),则可以指定通过 在比率的前面添加字母W(用于约束宽度)或H(用于约束高度)来约束哪一侧,并用逗号分隔:
- 浮点值,表示宽度和高度之间的比率
- 形式为“宽度:高度”的比率
<Button android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="H,16:9"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"/>将按照16:9的比例设置按钮的高度,而按钮的宽度将使约束与父项匹配。
3.10 Chains链式用法
链在单个轴上(水平或垂直)提供类似组的行为。另一个轴可以独立约束。
建立一条链
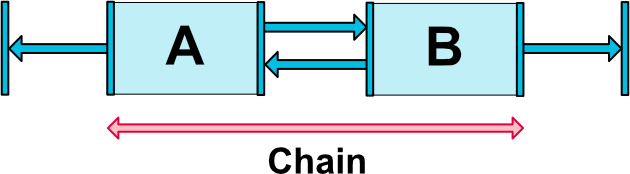
如果一组小部件通过双向连接链接在一起,则它们被视为一条链(请参见下图,其中显示了带有两个小部件的最小链)。
链头
链由在链的第一个元素(链的“头”)上设置的属性控制:
头部是水平链的最左侧小部件,垂直链的最顶部小部件。
例子:
<TextView
android:id="@+id/TextView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf="@+id/TextView2" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/TextView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@+id/TextView1"
app:layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf="@+id/TextView3"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/TextView3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@+id/TextView2"
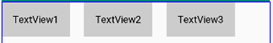
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent" />3个TextView相互约束,两端两个TextView分别与parent约束,成为一条链,效果如下:
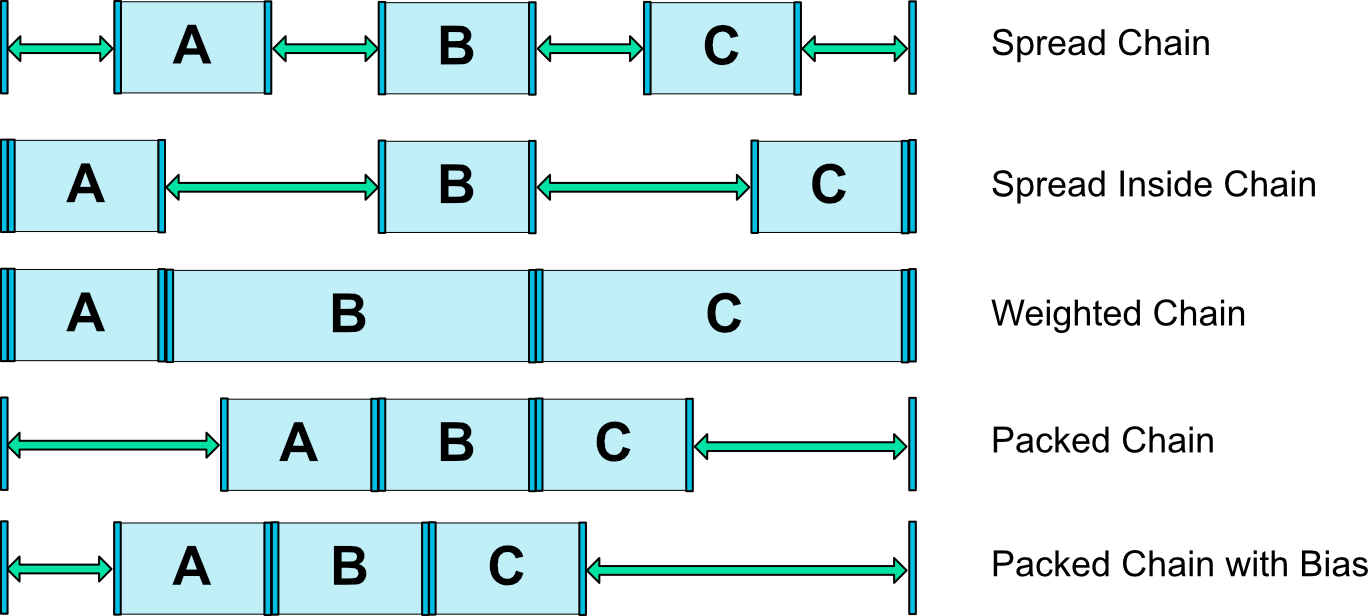
我们可以在链头中设置设置layout_constraintHorizontal_chainStyle或layout_constraintVertical_chainStyle在链的第一个元素上时,链的行为将根据指定的样式而改变(默认为CHAIN_SPREAD)。
CHAIN_SPREAD-元素将散布(默认样式)- Weighted chain(加权链)-在
CHAIN_SPREAD模式下,如果将某些小部件设置为MATCH_CONSTRAINT,它们将分割可用空间 CHAIN_SPREAD_INSIDE-展开元素,但链的两端贴近parent;CHAIN_PACKED-链中的元素将被打包在一起。子项的水平或垂直偏差属性将影响打包元素的位置
在链中的元素上使用边距时,这些边距是可加的。(1.1版本后加入的特性)
例如,在水平链上,如果一个元素定义的右边距为10dp,下一个元素定义的左边距为5dp,则这两个元素之间的结果边距为15dp。
计算链用于定位项目的剩余空间时,将项目及其边距一起考虑。剩余空间不包含边距。
3.11 虚拟帮助对象
除了前面详细介绍的内在功能之外,您还可以使用特殊的辅助对象ConstraintLayout来帮助您进行布局。当前,该Guideline对象允许您创建相对于ConstraintLayout容器定位的水平和垂直参考线。然后可以通过将小部件约束到此类准则来对其进行定位。
3.12 Guideline参考线(虚拟帮助对象)
android:orientation 垂直vertical,水平horizontal
layout_constraintGuide_begin 开始位置
layout_constraintGuide_end 结束位置
layout_constraintGuide_percent 距离顶部的百分比(orientation = horizontal时则为距离左边)
水平参考线Guideline
<!--Guideline辅助线不会显示,垂直辅助线,开始位置为屏幕宽的0.5-->
<android.support.constraint.Guideline
android:id="@+id/gl_vertical"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
app:layout_constraintGuide_percent="0.5"/>垂直参考线Guideline
<!--Guideline辅助线不会显示,垂直辅助线,开始位置为屏幕宽的0.5-->
<android.support.constraint.Guideline
android:id="@+id/gl_vertical"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
app:layout_constraintGuide_percent="0.5"/>3.13 Barrier屏障
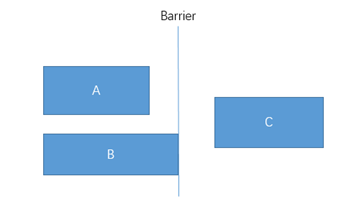
假设有3个控件ABC,C在AB的右边,但是AB的宽是不固定的,这个时候C无论约束在A的右边或者B的右边都不对。当出现这种情况可以用Barrier来解决。Barrier可以在多个控件的一侧建立一个屏障,如下所示:
<TextView
android:id="@+id/TextView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/TextView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/TextView1" />
<android.support.constraint.Barrier
android:id="@+id/barrier"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:barrierDirection="right"
app:constraint_referenced_ids="TextView1,TextView2" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/TextView3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@+id/barrier" />- app:barrierDirection为屏障所在的位置,可设置的值有:bottom、end、left、right、start、top
- app:constraint_referenced_ids为屏障引用的控件,可设置多个(用“,”隔开)
3.14 Group组
Group可以把多个控件归为一组,方便隐藏或显示一组控件,举个例子:
<TextView
android:id="@+id/TextView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/TextView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@+id/TextView1" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/TextView3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@id/TextView2" /> <android.support.constraint.Group
android:id="@+id/group"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:visibility="invisible"
app:constraint_referenced_ids="TextView1,TextView3" />3.15 Placeholder占位符
Placeholder指的是占位符。在Placeholder中可使用setContent()设置另一个控件的id,使这个控件移动到占位符的位置。举个例子:
<android.support.constraint.Placeholder
android:id="@+id/placeholder"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:content="@+id/textview"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#cccccc"
android:padding="16dp"
android:text="TextView"
android:textColor="#000000"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />新建一个Placeholder约束在屏幕的左上角,新建一个TextView约束在屏幕的右上角,在Placeholder中设置 app:content="@+id/textview",这时TextView会跑到屏幕的左上角。效果如下:
3.16 Optimizer优化器
在1.1中,公开了约束优化器。可以通过将标签app:layout_optimizationLevel添加到ConstraintLayout元素来决定应用哪些优化。
- none 无:不应用任何优化
- standard 标准:默认。仅优化直接约束和障碍约束
- direct 直接:优化直接约束
- barrier 障碍:优化障碍约束
- chain 链:优化链约束(实验)
- dimensions 尺寸:优化尺寸度量(实验性),减少匹配约束元素的度量数量
该属性是一个掩码,因此您可以通过列出所需的优化来决定打开或关闭特定的优化。例如:app:layout_optimizationLevel ="direct | barrier | chain"