本文解决的问题
基本假设:二部图只有邻接矩阵,没有节点特征,并且进行链路预测,有部分链路未知。
如果你有初始节点特征,直接换掉即可
实现思路
这段代码主要是用于构建一个基于图卷积神经网络(GCN)的二分类模型,实现对给定邻接矩阵的节点间关系进行分类。具体实现步骤如下:
加载邻接矩阵数据,并将邻接矩阵转换为张量形式。
根据邻接矩阵生成正负样本的边索引。
自己创建节点特征x, 和结果y。
将数据随机分为训练、验证和测试集。
从正负样本中随机选取相同数量的边,形成平衡的训练集。
创建一个GCN模型,用于学习节点特征和边信息之间的关系。
通过训练得到最优的模型参数,并在测试集上评估模型性能。
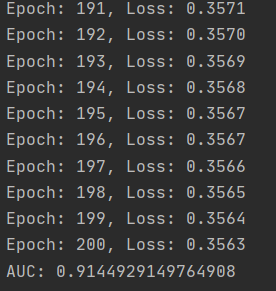
结果
代码全览
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch_geometric.nn import GCNConv
from torch_geometric.utils import to_undirected
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
# 加载邻接矩阵数据
adj_matrix = pd.read_csv('m_d.csv', header=None, index_col=None).values
# 将邻接矩阵转换为张量,这里要将列索引加上总节点数,使得列节点的索引不与行节点重复
num_nodes = adj_matrix.shape[0] + adj_matrix.shape[1]
edge_index_pos = np.column_stack(np.argwhere(adj_matrix != 0))
edge_index_pos[:, 1] += adj_matrix.shape[0]
edge_index_pos = torch.tensor(edge_index_pos, dtype=torch.long)
# 获取不相关连接 为了构建训练数据
edge_index_neg = np.column_stack(np.argwhere(adj_matrix == 0))
edge_index_neg[:, 1] += adj_matrix.shape[0]
edge_index_neg = torch.tensor(edge_index_neg, dtype=torch.long)
# 获取平衡样本
num_pos_edges_number = edge_index_pos.shape[1]
selected_neg_edge_indices = torch.randint(high=edge_index_neg.shape[1], size=(num_pos_edges_number,), dtype=torch.long)
edge_index_neg_selected = edge_index_neg[:, selected_neg_edge_indices]
edg_index_all = torch.cat((edge_index_pos, edge_index_neg_selected), dim=1)
# 创建数据
x = torch.ones((num_nodes, 1)) # 没有节点特征,所以设置为1
y = torch.cat((torch.ones((edge_index_pos.shape[1], 1)),
torch.zeros((edge_index_neg_selected.shape[1], 1))), dim=0) # 将所有y值设置为1,0
# 将邻接矩阵转换为无向图(会将每条边复制成两条相反的边)
edge_index = to_undirected(edge_index_pos)
# 将数据拆分为训练、验证和测试集
idx = np.arange(y.shape[0])
np.random.shuffle(idx)
train_idx = idx[:int(0.8 * len(idx))] # 用前80%的样本作为训练集
test_idx = idx[int(0.8 * len(idx)):] # 用后20%的样本作为测试集
# 创建一个GCN模型
class GCNII(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(GCNII, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = GCNConv(in_channels, 2 * out_channels, cached=True)
self.conv2 = GCNConv(2 * out_channels, out_channels)
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(out_channels*2, 1)
def forward(self, x, edge_index, edge_index_pos, edge_index_neg, edge_weight=None,param={}):
x = F.relu(self.conv1(x, edge_index, edge_weight))
x = F.relu(self.conv2(x, edge_index, edge_weight))
# 按照边的顺序将节点特征向量重新排列
edg_index_all = torch.cat((edge_index_pos, edge_index_neg), dim=1)
Em, Ed = self.pro_data(x, edg_index_all) # 筛选数据 获得源节点特征和目标节点
# 将源节点特征和目标节点特征拼接起来
x = torch.cat((Em, Ed),dim=1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def pro_data(self, x, edg_index):
m_index = edg_index[0]
d_index = edg_index[1]
Em = torch.index_select(x, 0, m_index) # 沿着x1的第0维选出m_index
Ed = torch.index_select(x, 0, d_index)
return Em, Ed
# 模型构建
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model = GCNII(in_channels=x.shape[1], out_channels=16).to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, weight_decay=0.0005)
# 训练模型
model.train()
for epoch in range(1, 201):
optimizer.zero_grad()
out = model(x, edge_index, edge_index_pos=edge_index_pos, edge_index_neg=edge_index_neg_selected,
param={'m_number': adj_matrix.shape[0], 'd_number': adj_matrix.shape[1]})
# 使用train数据进行训练
loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(out[train_idx], y[train_idx].float())
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
loss = loss.item()
print(f'Epoch: {epoch:03d}, Loss: {loss:.4f}')
# 模型验证
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# 获得所有数据
out = model(x, edge_index, edge_index_pos=edge_index_pos, edge_index_neg=edge_index_neg_selected,
param={'m_number':adj_matrix.shape[0],'d_number':adj_matrix.shape[1]})
# 提取验证集数据
out_pred = out[test_idx]
y_pred = y[test_idx]
# 计算AUC
auc = roc_auc_score(y_pred, out_pred)
print('AUC:', auc)
代码详解
以下是更详细的代码解释:
首先,导入需要用到的库:
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch_geometric.nn import GCNConv
from torch_geometric.utils import to_undirected
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
然后,加载邻接矩阵数据并将其转换为张量形式:
adj_matrix = pd.read_csv('m_d.csv', header=None, index_col=None).values
num_nodes = adj_matrix.shape[0] + adj_matrix.shape[1]
edge_index_pos = np.column_stack(np.argwhere(adj_matrix != 0))
edge_index_pos[:, 1] += adj_matrix.shape[0]
edge_index_pos = torch.tensor(edge_index_pos, dtype=torch.long)
edge_index_neg = np.column_stack(np.argwhere(adj_matrix == 0))
edge_index_neg[:, 1] += adj_matrix.shape[0]
edge_index_neg = torch.tensor(edge_index_neg, dtype=torch.long)
这里的 adj_matrix 是一个邻接矩阵,表示节点之间的连接情况。edge_index_pos 表示有边相连的节点对的索引,edge_index_neg 则表示没有边相连的节点对的索引。
接下来,从正负样本中随机选取相同数量的边,形成平衡的训练集:
num_pos_edges_number = edge_index_pos.shape[1]
selected_neg_edge_indices = torch.randint(high=edge_index_neg.shape[1], size=(num_pos_edges_number,), dtype=torch.long)
edge_index_neg_selected = edge_index_neg[:, selected_neg_edge_indices]
edg_index_all = torch.cat((edge_index_pos, edge_index_neg_selected), dim=1)
这里使用 torch.randint 函数从负样本索引中随机抽取与正样本相同数量的索引,以达到正负样本平衡的目的。
然后,创建数据集,并将邻接矩阵转换为无向图(会将每条边复制成两条相反的边):
x = torch.ones((num_nodes, 1))
y = torch.cat((torch.ones((edge_index_pos.shape[1], 1)),
torch.zeros((edge_index_neg_selected.shape[1], 1))), dim=0)
edge_index = to_undirected(edge_index_pos)
x 是节点特征矩阵,这里没有节点特征,所以全部设为 1。y 表示分类标签,其中正样本标签为 1,负样本标签为 0。edge_index 是无向图上的边索引。
接着,将数据随机分为训练、验证和测试集:
这里使用 numpy 库的 random.shuffle 函数将数据索引随机打乱,并按照 8:2 的比例划分为训练集和测试集。
idx = np.arange(y.shape[0])
np.random.shuffle(idx)
train_idx = idx[:int(0.8 * len(idx))]
test_idx = idx[int(0.8 * len(idx)):]
然后,创建一个 GCN 模型:
GCNII 是一个继承自 torch.nn.Module 的类,它包含了两层 GCN 卷积 (self.conv1, self.conv2) 和一个全连接层 (self.fc)。在前向传播函数中,首先对节点特征进行两层 GCN 卷积操作,然后将边索引按照顺序重新排列,接着通过 pro_data 函数筛选出源节点和目标节点的特征向量,并将其拼接在一起,最后通过全连接层得到输出。
class GCNII(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(GCNII, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = GCNConv(in_channels, 2 * out_channels, cached=True)
self.conv2 = GCNConv(2 * out_channels, out_channels)
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(out_channels*2, 1)
def forward(self, x, edge_index, edge_index_pos, edge_index_neg, edge_weight=None,param={}):
"""前向传播函数"""
# 对节点特征进行两层 GCN 卷积操作
x = F.relu(self.conv1(x, edge_index, edge_weight))
x = F.relu(self.conv2(x, edge_index, edge_weight))
# 筛选数据,获取源节点特征和目标节点特征
edg_index_all = torch.cat((edge_index_pos, edge_index_neg), dim=1)
Em, Ed = self.pro_data(x, edg_index_all)
# 将源节点特征和目标节点特征拼接起来,并通过全连接层得到输出
x = torch.cat((Em, Ed),dim=1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def pro_data(self, x, edg_index):
"""筛选数据,获取源节点特征和目标节点特征"""
m_index = edg_index[0]
d_index = edg_index[1]
Em = torch.index_select(x, 0, m_index)
Ed = torch.index_select(x, 0, d_index)
return Em, Ed
接下来,构建模型并开始训练:
这里首先判断是否有可用的 GPU,然后创建一个 GCNII 模型,并使用 Adam 优化器对模型参数进行训练。在训练过程中,计算模型输出和分类标签之间的二元交叉熵损失,并调用 backward 函数计算梯度并更新模型参数。
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model = GCNII(in_channels=x.shape[1], out_channels=16).to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, weight_decay=0.0005)
model.train()
for epoch in range(1, 201):
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 计算输出,使用 train_idx 进行训练
out = model(x, edge_index, edge_index_pos=edge_index_pos, edge_index_neg=edge_index_neg_selected,
param={'m_number': adj_matrix.shape[0], 'd_number': adj_matrix.shape[1]})
loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(out[train_idx], y[train_idx].float())
# 反向传播计算梯度并更新参数
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
loss = loss.item()
print(f'Epoch: {epoch:03d}, Loss: {loss:.4f}')
最后,在测试集上评估模型性能:
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# 计算模型输出
out = model(x, edge_index, edge_index_pos=edge_index_pos, edge_index_neg=edge_index_neg_selected,
param={'m_number':adj_matrix.shape[0],'d_number':adj_matrix.shape[1]})
# 提取验证集数据并计算 AUC
out_pred = out[test_idx]
y_pred = y[test_idx]
auc = roc_auc_score(y_pred, out_pred)
print('AUC:', auc)