什么是websocket?
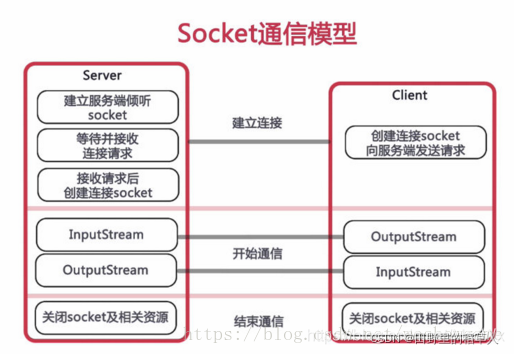
- WebSocket 协议是基于 TCP 的一种新的网络协议。
- 它实现了客户端与服务器之间的全双工通信,既然是全双工,就说明了服务器可以主动发送信息给客户端。
为什么不使用 HTTP 协议呢?
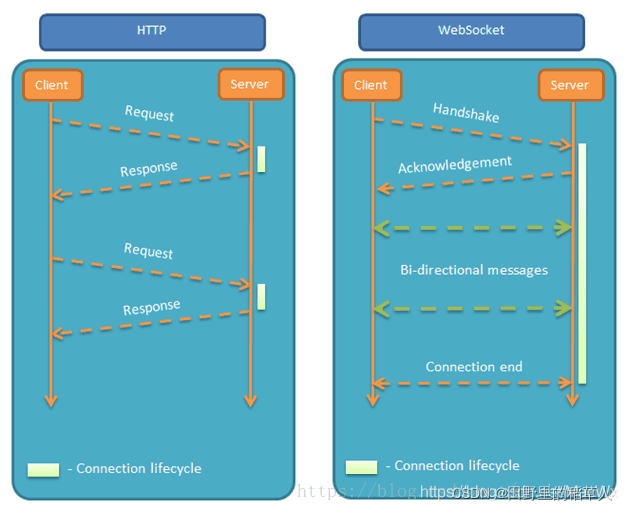
这是因为HTTP是单工通信,通信只能由客户端发起,客户端请求一下,服务器处理一下,于是 websocket 应运而生。
WebSocket 相比普通的 Socket 来说,仅仅是借助 HTTP 协议完成握手,创建连接。后续的所有通信,都和 HTTP 协议无关。
HTTP与WebSocket的关系
结论:
- WebSocket和HTTP都是基于TCP协议的两个不同的协议
- WebSocket依赖于HTTP连接
问题:
- WebSocket依赖于HTTP连接,那么它如何从连接的HTTP协议转化为WebSocket协议?
- WebSocket为什么要依赖于HTTP协议的连接?
每个WebSocket连接都始于一个HTTP请求。
具体来说,WebSocket协议在第一次握手连接时,通过HTTP协议在传送WebSocket支持的版本号,协议的字版本号,原始地址,主机地址等等一些列字段给服务器端:
GET /chat HTTP/1.1
Host: server.example.com
Upgrade: websocket
Connection: Upgrade
Sec-WebSocket-Key:dGhlIHNhbXBsZSBub25jZQ==
Origin: http://example.com
Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13
注意,关键的地方是,这里面有个Upgrade首部,用来把当前的HTTP请求升级到WebSocket协议,这是HTTP协议本身的内容,是为了扩展支持其他的通讯协议。
如果服务器支持新的协议,则必须返回101:
HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols
Upgrade: websocket
Connection: Upgrade
Sec-WebSocket-Accept:s3pPLMBiTxaQ9kYGzzhZRbK+xOo=
至此,HTTP请求物尽其用,如果成功触发onopen事件,否则触发onerror事件,后面的传输则不再依赖HTTP协议。
快速入门
1、 在 pom.xml 文件中,引入相关依赖。
<dependencies>
<!-- 实现对 WebSocket 相关依赖的引入,方便~ -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocket</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入 Fastjson ,实现对 JSON 的序列化,因为后续我们会使用它解析消息 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.62</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2、 创建 WebsocketServerEndpoint 类,定义 Websocket 服务的端点(EndPoint)。
@Controller
@ServerEndpoint("/")
public class WebsocketServerEndpoint {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session, EndpointConfig config) {
logger.info("[onOpen][session({}) 接入]", session);
}
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(Session session, String message) {
logger.info("[onOpen][session({}) 接收到一条消息({})]", session, message); // 生产环境下,请设置成 debug 级别
}
@OnClose
public void onClose(Session session, CloseReason closeReason) {
logger.info("[onClose][session({}) 连接关闭。关闭原因是({})}]", session, closeReason);
}
@OnError
public void onError(Session session, Throwable throwable) {
logger.info("[onClose][session({}) 发生异常]", session, throwable);
}
}
- 在类上,添加
@Controller注解,保证创建一个WebsocketServerEndpoint Bean。 - 在类上,添加 JSR-356 定义的
@ServerEndpoint注解,标记这是一个WebSocket EndPoint,路径为/。 WebSocket一共有四个事件,分别对应使用 JSR-356 定义的@OnOpen、@OnMessage、@OnClose、@OnError注解。
3、创建 WebsocketServerEndpoint 配置类
@Configuration
// @EnableWebSocket // 无需添加该注解,因为我们并不是使用 Spring WebSocket
public class WebSocketConfiguration {
@Bean
public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter() {
return new ServerEndpointExporter();
}
}
该 Bean 的作用,是扫描添加有 @ServerEndpoint 注解的 Bean 。
4、创建 Application.java 类,配置 @SpringBootApplication 注解即可
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
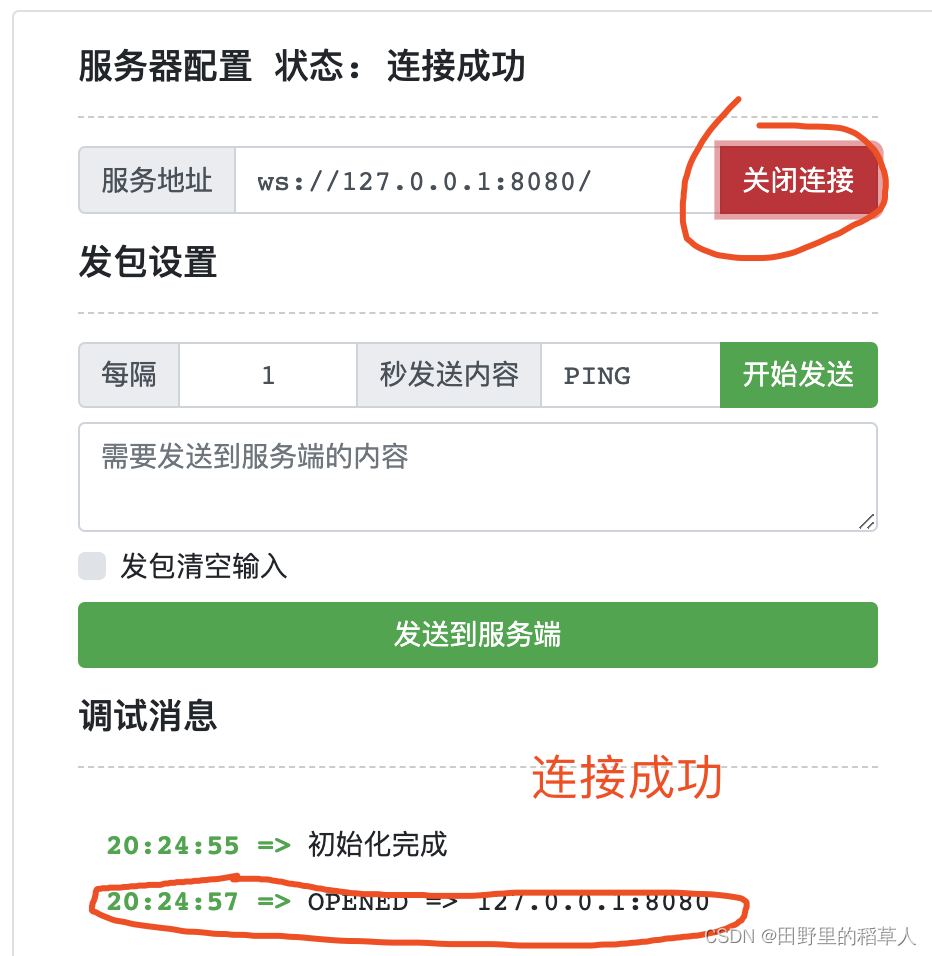
测试 WebSocket 连接,使用 WEBSOCKET 在线测试工具
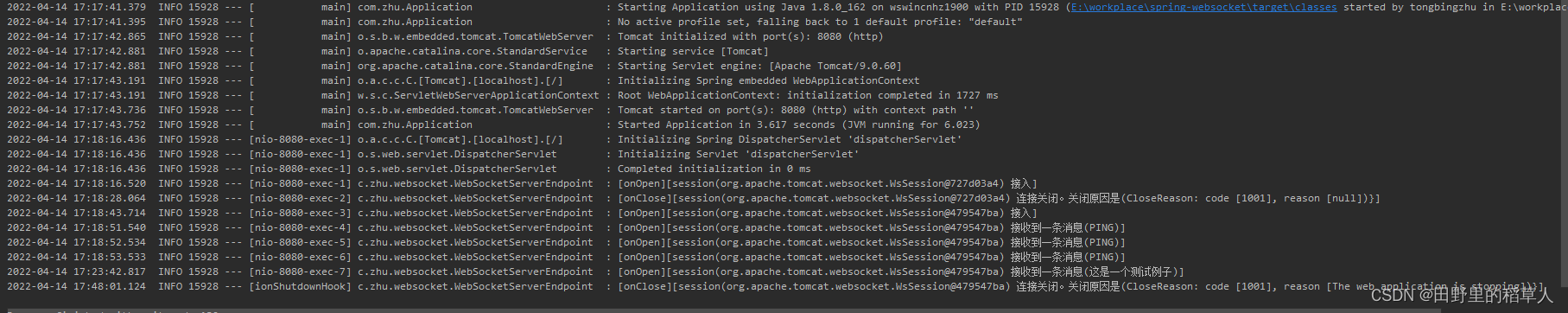
查看一下控制台:
SpringBoot+WebSocket 实时监控异常
首先熟悉下Demo的结构,构建一个spring boot项目:
1、导依赖
<!-- 实现对 WebSocket 相关依赖的引入,方便~ -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocket</artifactId>
<version>2.6.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入 Fastjson ,实现对 JSON 的序列化,因为后续我们会使用它解析消息 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.62</version>
</dependency>
2、WebSocketConfig配置类
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.socket.server.standard.ServerEndpointExporter;
@Configuration
public class WebSocketConfig {
// 启用spring boot 对WebSocket的支持,
// 注入一个ServerEndpointExporter,该Bean会自动注册使用@ServerEndpoint注解申明的websocket endpoint【扫描添加有 @ServerEndpoint 注解的 Bean】
@Bean
public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter(){
return new ServerEndpointExporter();
}
}
@ServerEndpoint。这个注解告诉容器给定的类应该被认为是一个 WebSocket 端点。必需value元素指定
WebSocket 端点的路径@ServerEndpoint 注解这是一个类层次的注解,它的功能主要是将目前的类定义成一个 websocket
服务器端。注解的值将被用于监听用户连接的终端访问 URL 地址,客户端可以通过这个 URL 来连接到 WebSocket 服务器端
3、WebSocketServer类,用来进行服务端和客户端之间的交互
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.websocket.*;
import javax.websocket.server.PathParam;
import javax.websocket.server.ServerEndpoint;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArraySet;
@Component
@Slf4j
@Service
@ServerEndpoint("/api/websocket/{sid}")
public class WebSocketServer {
//当前在线连接数
private static int onlineCount = 0;
//存放每个客户端对应的MyWebSocket对象
private static CopyOnWriteArraySet<WebSocketServer> webSocketSet = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<WebSocketServer>();
private Session session;
//接收sid
private String sid = "";
/**
* 连接建立成功调用的方法
*/
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session, @PathParam("sid") String sid) {
this.session = session;
webSocketSet.add(this); //加入set中
this.sid = sid;
addOnlineCount(); //在线数加1
try {
sendMessage("conn_success");
log.info("有新窗口开始监听:" + sid + ",当前在线人数为:" + getOnlineCount());
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("websocket IO Exception");
}
}
/**
* 连接关闭调用的方法
*/
@OnClose
public void onClose() {
webSocketSet.remove(this); //从set中删除
subOnlineCount(); //在线数减1
log.info("释放的sid为:"+sid);
log.info("有一连接关闭!当前在线人数为" + getOnlineCount());
}
/**
* 收到客户端消息后调用的方法
* @ Param message 客户端发送过来的消息
*/
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(String message, Session session) {
log.info("收到来自窗口" + sid + "的信息:" + message);
//群发消息
for (WebSocketServer item : webSocketSet) {
try {
item.sendMessage(message);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* @ Param session
* @ Param error
*/
@OnError
public void onError(Session session, Throwable error) {
log.error("发生错误");
error.printStackTrace();
}
/**
* 实现服务器主动推送
*/
public void sendMessage(String message) throws IOException {
this.session.getBasicRemote().sendText(message);
}
/**
* 群发自定义消息
*/
public static void sendInfo(String message, @PathParam("sid") String sid) throws IOException {
log.info("推送消息到窗口" + sid + ",推送内容:" + message);
for (WebSocketServer item : webSocketSet) {
try {
//为null则全部推送
if (sid == null) {
// item.sendMessage(message);
} else if (item.sid.equals(sid)) {
item.sendMessage(message);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
continue;
}
}
}
public static synchronized int getOnlineCount() {
return onlineCount;
}
public static synchronized void addOnlineCount() {
WebSocketServer.onlineCount++;
}
public static synchronized void subOnlineCount() {
WebSocketServer.onlineCount--;
}
public static CopyOnWriteArraySet<WebSocketServer> getWebSocketSet() {
return webSocketSet;
}
}
4、WebSocketController类,用于进行接口测试
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Controller("web_Scoket_system")
@RequestMapping("/api/socket")
public class SystemController {
//页面请求
@GetMapping("/index/{userId}")
public ModelAndView socket(@PathVariable String userId) {
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("/socket1");
mav.addObject("userId", userId);
return mav;
}
//推送数据接口
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/socket/push/{cid}")
public Map pushToWeb(@PathVariable String cid, String message) {
Map<String,Object> result = new HashMap<>();
try {
WebSocketServer.sendInfo(message, cid);
result.put("code", cid);
result.put("msg", message);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
}
5、配置application.yml
#端口
server:
port: 18801
#密码,因为接口不需要权限,所以加了个密码做校验
mySocket:
myPwd: jae_123
6、测试
- 打开前端页面,进行WebSocket连接
控制台输出,连接成功 - 因为是模拟数据,所以全部显示正常,没有异常提交时的页面呈现
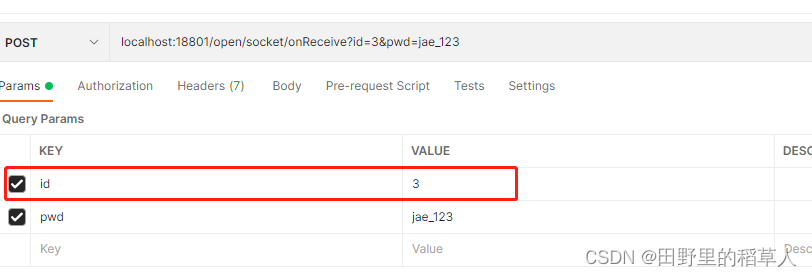
- 接下来,我们用接口测试工具Postman提交一个异常
注意id为3的这个数据的状态变化
消息
在 HTTP 协议中,是基于 Request/Response 请求响应的同步模型,进行交互。在 Websocket协议中,是基于Message 消息的异步模型,进行交互。
因为 WebSocket 协议,不像 HTTP 协议有 URI 可以区分不同的 API 请求操作,所以我们需要在 WebSocket 的 Message 里,增加能够标识消息类型,这里我们采用 type 字段。
{
type: "", // 消息类型
body: {} // 消息体
}
- type 字段,消息类型。通过该字段,我们知道使用哪个 MessageHandler 消息处理器。
- body 字段,消息体。不同的消息类型,会有不同的消息体。
- Message 采用 JSON 格式编码,主要考虑便捷性