之前写过一篇关于retrofit的笼统介绍,但是碍于当时对于retrofit了解不多,很多东西都是一带而过,
没有讲明白,在接下来的文章中将陆续介绍转换器、注解、拦截器、Call与Observable的区别
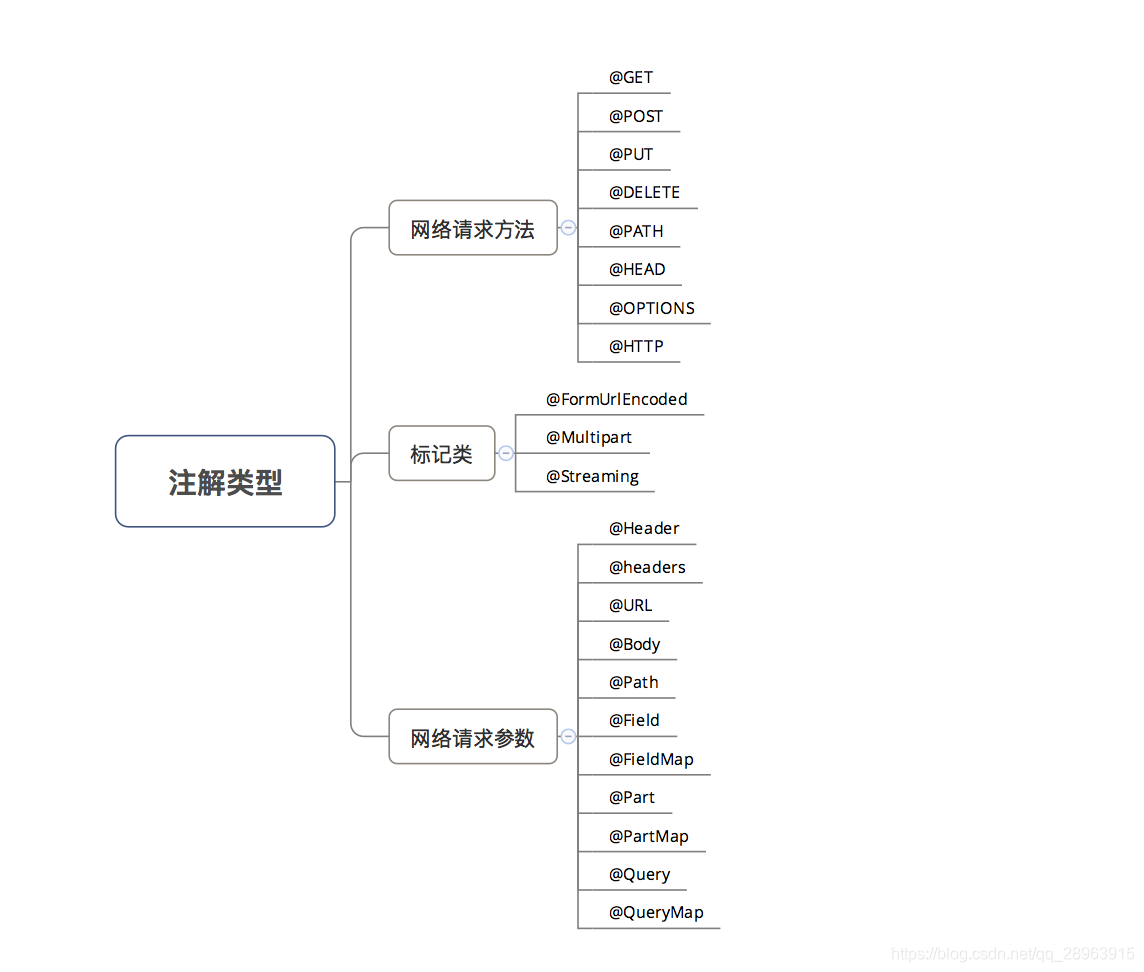
本篇首先介绍注解,我们先来给注解分一下类:
示例:
@GET(“article/list/{page}/json”)
Observable<BaseResponse
b. @HTTP
作用:替换@GET、@POST、@PUT、@DELETE、@HEAD注解的作用 及 更多功能拓展
具体使用:通过属性method、path、hasBody进行设置:
method:网络请求的方法(区分大小写)
path:网络请求地址路径
hasBody:是否有请求体
@HTTP(method = “GET”, path = “blog/{id}”, hasBody = false)
Call getCall(@Path(“id”) int id);
{id} 表示是一个变量
method 的值 retrofit 不会做处理,所以要自行保证准确
c. @FormUrlEncoded
表示请求体是一个Form表单,发送form-encoded的数据
通常跟@Field & @FieldMap和@Query和@QueryMap注解配合使用,只不过前者用于Post请求 后者用于Get请求
表明是一个表单格式的请求(Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded):
@POST("/form")
@FormUrlEncoded
Call testFormUrlEncoded1(@Field(“username”) String name, @Field(“age”) int age);
d. @Multipart
作用:表示请求体是一个Form表单,发送form-encoded的数据(适用于有文件上传的场景)
通常跟@Part & @PartMap注解配合使用
Part 后面支持三种类型:RequestBody、okhttp3.MultipartBody.Part} 、任意类型
除 okhttp3.MultipartBody.Part 以外,其它类型都必须带上表单字段okhttp3.MultipartBody.Part中已经包含了表单字段的信息
@POST("/form")
@Multipart
Call testFileUpload1(@Part(“name”) RequestBody name, @Part(“age”) RequestBody age, @Part MultipartBody.Part file);
// 具体使用
//@Multipart
MediaType textType = MediaType.parse(“text/plain”);
RequestBody name = RequestBody.create(textType, “Carson”);
RequestBody age = RequestBody.create(textType, “24”);
RequestBody file = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse(“application/octet-stream”), “这里是模拟文件的内容”);
MultipartBody.Part filePart = MultipartBody.Part.createFormData(“file”, “test.txt”, file);
Call call3 = service.testFileUpload1(name, age, filePart);
e. @Header & @Headers作用:添加请求头 &添加不固定的请求头
@GET(“user”)
Call getUser(@Header(“Authorization”) String authorization)
多个请求头
@Multipart
@POST(“member/avatar”)
Observable uploadImage(@HeaderMap Map<String, String> headers, @Part MultipartBody.Part file);
@Headers(“Authorization: authorization”)
@GET(“user”)
Call getUser()
// 以上的效果是一致的。
// 区别在于使用场景和使用方式
// 1. 使用场景:@Header用于添加不固定的请求头,@Headers用于添加固定的请求头
// 2. 使用方式:@Header作用于方法的参数;@Headers作用于方法
f. @Body作用:以 Post方式 传递 自定义数据类型 给服务器
1.可以跟FormBody(表单)、RequestBody(请求体)、对象(自动将请求体转成json)配合使用,
2.特别注意:如果提交的是一个Map,那么作用相当于 @Field,不过Map要经过 FormBody.Builder 类处理成为符合 Okhttp 格式的表单详情见ParamsSet
3.@Body不能跟@Multipart或者@FormUrlEncoded一块用,否则会报错
//如果参数是请求体 可以通过@Body注解 传入一个对象或者map 然后将其转成json
//RequestBody body = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8"), "json字符串");//可能不支持
//RequestBody body = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("application/json;charset=utf-8"), bodyStr);
//RequestBody body = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("application/text;charset=utf-8"), "加密串");
public class ParamsSet {
//通过body表单提交参数 相当于Field 这个没有验证过是否可以使用
public RequestBody getRequestBody(HashMap<String, String> hashMap) {
StringBuffer data = new StringBuffer();
if (hashMap != null && hashMap.size() > 0) {
Iterator iter = hashMap.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) iter.next();
Object key = entry.getKey();
Object val = entry.getValue();
data.append(key).append("=").append(val).append("&");
}
}
String jso = data.substring(0, data.length() - 1);
RequestBody requestBody = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8"), jso);
return requestBody;
}
public FormBody getFormBody(HashMap<String, String> hashMap) {
FormBody.Builder builder = new FormBody.Builder();
if (hashMap != null && hashMap.size() > 0) {
Iterator iter = hashMap.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) iter.next();
String key = (String) entry.getKey();
String val = (String) entry.getValue();
builder.add(key,val);
}
}
return builder.build();
}
//通过body提交请求体json请求体
public RequestBody getRequestBody2(HashMap<String, String> hashMap) {
RequestBody requestBody = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("application/json;charset=utf-8"),new Gson().toJson(hashMap));
return requestBody;
}
//通过body提交请求体文本请求体
public RequestBody getRequestBody3(HashMap<String, String> hashMap) {
String json = new Gson().toJson(hashMap);
//将json转成某种加密文本
RequestBody requestBody = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("application/text;charset=utf-8"),json);
return requestBody;
}
}
g. @Path 作用:URL地址的缺省值
h.@Url 作用:直接传入一个请求的 URL变量 用于URL设置
当有URL注解时,@GET传入的URL就可以省略
当GET、POST…HTTP等方法中没有设置Url时,则必须使用 Url 提供
i.@Streaming 表示返回的数据以流的形式返回,适用于返回数据较大的场景,
如果没有使用该注解,默认把数据全部载入内存,之后获取数据也是从内存中获取的,文件过大会造成内存溢出
https://blog.csdn.net/impure/article/details/79658098
Query、Field和Part这三者都支持数组和实现了Iterable接口的类型,如List,Set等,方便向后台传递数组。
retrofit介绍:
https://www.cnblogs.com/baiqiantao/p/7494850.html