epoll是什么
epoll是Linux内核为处理大批量文件描述符而作了改进的poll,是Linux下多路复用IO接口select/poll的增强版本,它能显著提高程序在大量并发连接中只有少量活跃的情况下的系统CPU利用率。另一点原因就是获取事件的时候,它无须遍历整个被侦听的描述符集,只要遍历那些被内核IO事件异步唤醒而加入Ready队列的描述符集合就行了。epoll除了提供select/poll那种IO事件的水平触发(Level Triggered)外,还提供了边缘触发(Edge Triggered),这就使得用户空间程序有可能缓存IO状态,减少epoll_wait/epoll_pwait的调用,提高应用程序效率。
epoll怎么用
系统提供了三个epoll相关的函数,分别是:
int epoll_create(int size); epoll_create() creates an epoll(7) instance. Since Linux 2.6.8, the size argument is ignored, but must be greater than zero; see NOTES below.
epoll_create() returns a file descriptor referring to the new epoll instance. This file descriptor is used for all the subsequent calls to the epoll interface. When no longer required, the
file descriptor returned by epoll_create() should be closed by using close(2). When all file descriptors referring to an epoll instance have been closed, the kernel destroys the instance and
releases the associated resources for reuse.
epoll_create系统调用会创建一个epoll的实例, 从Linux 2.6.8之后,size参数就被忽略了但是必须要大于0
epoll_create返回一个指向一个新的epoll实例的文件描述符,这个文件描述符被用于随后对于epoll接口的调用。当不再被使用时
epoll_create返回的文件描述符应该用close关闭掉。当指向epoll实例的文件描述符被关闭,内核会释放掉该实例相关的资源
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event);
epfd: epoll_create返回的文件描述符
op: EPOLL_CTL_ADD 把fd注册到epfd的关联 EPOLL_CTL_MOD 用event的属性修改已关联的fd EPOLL_CTL_DEL 把fd从epfd关联中移除,event可以为NULL
fd: 要操作的文件描述符
event:event的events是由以下(常用)标志组成的位掩码
EPOLLIN fd读事件
EPOLLOUT fd写事件
EPOLLET 给关联的fd设置边缘触发行为,默认是水平触发
EPOLLPRI 可读紧急数据
EPOLLERR 关联的fd出现了错误,epoll_wait总是关注此事件,不需要设置
EPOLLHUP fd断开连接事件,epoll_wait总是关注此事件,不需要设置
...
水平触发(Level Triggered):当被监控的文件描述符有读写事件发生时,epoll会通知应用程序去处理,如果一次没有处理完所有的数据,下次调用epoll_wait,内核还会通知应用程序去处理,如果一直不去处理,内核就会一直通知
边缘触发(Edge Triggered):当被监控的文件描述符有读写事件发生时,epoll会通知应用程序去处理,如果没有处理,下次调用epoll_wait,内核不会通知应用程序去处理,直到该文件描述符出现第二次读写事件事,才会通知。
这种模式比水平触发效率高,系统不会充斥大量你不关心的就绪文件描述符。
LT-test: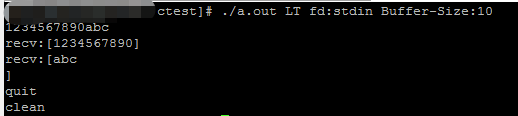
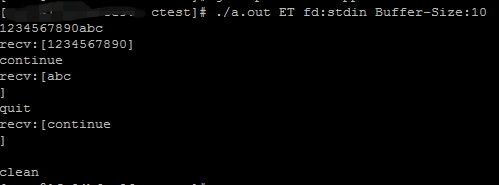
ET-test:
验证了LT模式下没处理完的数据epoll_wait会一直通知,ET模式下不会,直到等到出现下一次事件的触发才会通知
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int maxevents, int timeout);
The epoll_wait() system call waits for events on the epoll(7) instance referred to by the file descriptor epfd. The memory area pointed to by events will contain the events that will be avail‐able for the caller. Up to maxevents are returned by epoll_wait().
The maxevents argument must be greater than zero.
The timeout argument specifies the number of milliseconds that epoll_wait() will block. The call will block until either:
* a file descriptor delivers an event;
* the call is interrupted by a signal handler; or
* the timeout expires.
epoll_wait系统调用会等待epfd上的事件,events指向的内存空间将包含可用的事件。epoll_wait返回最多maxevents个事件,
maxevents参数必须大于0
timeout参数指定epoll_wait阻塞时间(单位是毫秒),阻塞直至:
其中一个文件描述符有事件发生
调用被信号中断
达到了timeout设置的时间 -1为无限等待
返回值:
> 0 发生事件的文件描述符,详细信息放在events数组
= 0 超时
< 0 epoll_wait调用发生了错误
errno: EBADF epfd不是有效的文件描述符
EFAULT events指向的内存空间不可写入
EINTR 当事件发生和超时之前,被信号中断返回该错误
EINVAL epfd不是一个epoll文件描述符或者maxevents 小于等于0
需注意的点:
*注册事件的文件描述符最好设置成非阻塞,因为accept/read/write 当缓冲区没有数据时, 如果文件描述符是阻塞的话会导致线程被阻塞
*设置文件描述符属性 fcntl
简单验证一下epoll LE&ET的区别:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int ep_fd = epoll_create(10);
bool quit = false;
if (-1 == ep_fd){
perror("epoll_create");
return -1;
}
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;
ev.data.fd = 0;
if(-1 == fcntl(ev.data.fd, F_SETFL, fcntl(ev.data.fd, F_GETFL, 0) | O_NONBLOCK)){
perror("fcntl error");
goto END;
}
if (-1 == epoll_ctl(ep_fd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, ev.data.fd, &ev)){
perror("epoll_ctl");
goto END;
}
while(!quit){
struct epoll_event evs[100];
int n = epoll_wait(ep_fd, evs, 100, -1);
if (-1 == n){
perror("epoll_wait");
goto END;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
char data[1025] = "";
int offset = 0, cn = 0;
do{
cn = read(evs[i].data.fd, data+offset, 1024-offset);
if (-1 == cn){
if (errno == EAGAIN || errno == EWOULDBLOCK){
printf("EAGAIN\n");
continue;
}
epoll_ctl(ep_fd, evs[i].data.fd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, evs+i);
}
else if (cn == 0){
epoll_ctl(ep_fd, evs[i].data.fd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, evs+i);
}
else{
if(0 == strcmp(data, "quit\n")){
quit = true;
printf("clean\n");
break;
}
else{
printf("recv:[%s]\n", data);
}
}
}while(cn > 0);
}
}
END:
close(ep_fd);
return 0;
}一个基于epoll的echo程序:
服务端(IPV6):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <signal.h>
#define LISTEN_MAX 100
bool set_socket_noblock(int sockfd)
{
if(-1 == fcntl(sockfd, F_SETFL, fcntl(sockfd, F_GETFL, 0) | O_NONBLOCK))
{
perror("fcntl error");
return false;
}
return true;
}
int new_server_socket(const std::string& ip, unsigned short port, bool no_block)
{
int svr_fd = socket(AF_INET6, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if(-1 == svr_fd)
{
perror("socket error");
return svr_fd;
}
if (no_block && !set_socket_noblock(svr_fd))
{
close(svr_fd);
return -1;
}
struct sockaddr_in6 addr = {AF_INET6, htons(port), 0};
if(1 != inet_pton(AF_INET6, ip.c_str(), &addr.sin6_addr))
{
perror("inet_pton error");
close(svr_fd);
return -1;
}
if(0 != bind(svr_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&addr, sizeof(addr)))
{
perror("bind error");
close(svr_fd);
return -1;
}
if(0 != listen(svr_fd, LISTEN_MAX))
{
perror("listen error");
close(svr_fd);
return -1;
}
return svr_fd;
}
int create_epollfd(int max){
int epfd = epoll_create(max);
if (-1 == epfd)
{
perror("epoll_create");
}
return epfd;
}
int epoll_ctl_op(int epfd, int op, int fd, int events)
{
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = events;
ev.data.fd = fd;
if (-1 == epoll_ctl(epfd, op, fd, &ev))
{
perror("epoll_ctl");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
bool init_epfd_svrfd(const std::string& ip, unsigned short port, int& epfd, int& svrfd)
{
epfd = create_epollfd(10);
if (-1 != epfd)
{
svrfd = new_server_socket(ip, port, true);
if (-1 == svrfd)
{
close(epfd);
}
}
return epfd != -1 && svrfd != -1;
}
void do_accept(const int& epfd, const int& svrfd)
{
do
{
struct sockaddr_in6 addr;
unsigned int len = 0;
int cltfd = accept(svrfd, (struct sockaddr*)&addr, &len);
if (-1 == cltfd)
{
if (EAGAIN != errno && EWOULDBLOCK != errno)
{
perror("accept errno");
}
return ;
}
if (!set_socket_noblock(cltfd) || 0 != epoll_ctl_op(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, cltfd, EPOLLIN|EPOLLET))
{
close(cltfd);
continue;
}
printf("connect success\n");
//you can make session and setcallback function eg.. in here
}while(1);
}
void do_recv(const int& epfd, const int& cltfd)
{
char buf[1025] = "";
int cn = 0, offset = 0, total = 0;
do{
cn = recv(cltfd, buf+offset, 1024-offset, 0);
if (-1 == cn)
{
if (errno != EAGAIN && errno != EWOULDBLOCK)
{
//read发生错误 你可以删除掉clt session
perror("recv error");
close(cltfd);
epoll_ctl(epfd, cltfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, NULL);
return;
}
//echo
cn = send(cltfd, buf, total, 0);
if (-1 == cn)
{
perror("send error");
close(cltfd);
epoll_ctl(epfd, cltfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, NULL);
}
return;
}
else if (cn == 0)
{
perror("recv close");
close(cltfd);
epoll_ctl(epfd, cltfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, NULL);
//对端关闭连接 你可以删除掉clt session
return;
}
total += cn;
}while(cn > 0);
}
bool quit = false;
void signal_handler(int sig)
{
quit = true;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
signal(SIGINT, signal_handler);
int ep_fd, svr_fd;
if (!init_epfd_svrfd("::", 9091, ep_fd, svr_fd))
{
return -1;
}
if (-1 == epoll_ctl_op(ep_fd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, svr_fd, EPOLLIN | EPOLLET))
{
return -1;
}
while(!quit)
{
struct epoll_event evs[100];
int n = epoll_wait(ep_fd, evs, 100, -1);
if (-1 == n)
{
perror("epoll_wait");
quit = true
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
if (evs[i].data.fd == svr_fd)
{
do_accept(ep_fd, svr_fd);
}
else
{
do_recv(ep_fd, evs[i].data.fd);
}
}
}
close(svr_fd);
close(ep_fd);
return 0;
}客户端(IPV6):
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
const char* get_random_str(){
static char *msg[] = {
"test123",
"天气不错哟",
"搜狗输入法真好用",
"!!~~~~!!hello",
"1+2=3",
"call man.print"
};
return msg[random()%6];
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int clt_fd = socket(AF_INET6, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (-1 == clt_fd)
{
perror("socket error");
return -1;
}
int port = 9091;
struct sockaddr_in6 addr = {AF_INET6, htons(port), 0};
if(1 != inet_pton(AF_INET6, "::1", &addr.sin6_addr))
{
perror("inet_pton error");
close(clt_fd);
return -1;
}
if (0 != connect(clt_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&addr, sizeof(addr)))
{
perror("connect error");
close(clt_fd);
return -1;
}
printf("connect success\n");
int cnt = 0, len = 0;
time_t begin = time(NULL);
char data[1025];
while(cnt++ < 200000){
const char* msg = get_random_str();
if(-1 == send(clt_fd, msg, strlen(msg), 0)){
perror("send error");
close(clt_fd);
return -1;
}
len = recv(clt_fd, data, 1024, 0);
if (-1 == len)
{
perror("recv error");
close(clt_fd);
return -1;
}
}
time_t end = time(NULL);
printf("send %f tps\n", cnt*1.0/(int)(end-begin));
close(clt_fd);
return 0;
}阿里云服务器配置:
跑客户端的python脚本:
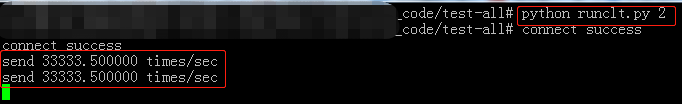
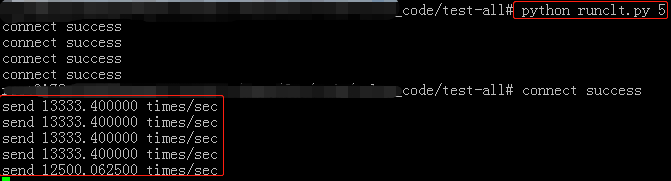
分别1个、2个、5个客户端运行20W次echo的结果:
单核单线程下epoll最大tps大概是6W5左右 测试数据长度为5-16BYTE随机