昇思25天学习打卡营第24天 | Pix2Pix实现图像转换
Pix2Pix模型
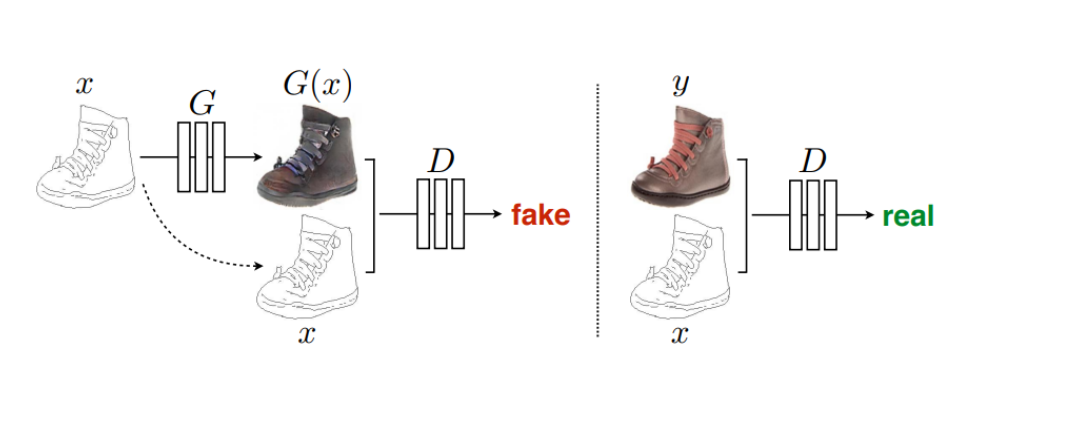
Pix2Pix是基于条件生成对抗网络(cGAN, Condition Generative Adversarial Networks)的一种图像转换模型,可以用于图像到图像的翻译。
cGAN
cGAN的生成器将输入图片作为指导信息,由输入图片不断生成“假”图像,完成从像素到像素的映射,而传统的GAN则是由随机噪声生成“假”图像。
CGAN的损失函数
cGAN的损失函数为:
L
c
G
A
N
(
G
,
D
)
=
E
(
x
,
y
)
[
log
(
D
(
x
,
y
)
)
]
+
E
(
x
,
z
)
[
log
(
1
−
D
(
x
,
G
(
x
,
z
)
)
)
)
]
L_{cGAN}(G,D)=E_{(x,y)}[\log(D(x,y))]+E_{(x,z)}[\log(1-D(x,G(x,z))))]
LcGAN(G,D)=E(x,y)[log(D(x,y))]+E(x,z)[log(1−D(x,G(x,z))))]
- 判别器 D D D需要尽可能区分真实图像和假图像,即使 log ( D ( x , y ) ) \log(D(x,y)) log(D(x,y))最大化;
- 生成器 G G G需要生成最真实的“假”图像 y y y以欺骗 D D D,即使 log ( 1 − D ( G ( x , z ) ) ) \log(1-D(G(x,z))) log(1−D(G(x,z)))最小化。
则cGAN的目标可以简化为:
arg
min
G
max
D
L
c
G
A
N
(
G
,
D
)
\arg\min_G\max_D L_{cGAN}(G,D)
argGminDmaxLcGAN(G,D)
数据
实验使用处理过的外墙(facades)数据
from download import download
url = "https://mindspore-website.obs.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/notebook/models/application/dataset_pix2pix.tar"
download(url, "./dataset", kind="tar", replace=True)
from mindspore import dataset as ds
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
dataset = ds.MindDataset("./dataset/dataset_pix2pix/train.mindrecord", columns_list=["input_images", "target_images"], shuffle=True)
data_iter = next(dataset.create_dict_iterator(output_numpy=True))
# 可视化部分训练数据
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 3), dpi=140)
for i, image in enumerate(data_iter['input_images'][:10], 1):
plt.subplot(3, 10, i)
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow((image.transpose(1, 2, 0) + 1) / 2)
plt.show()
网络构建
生成器
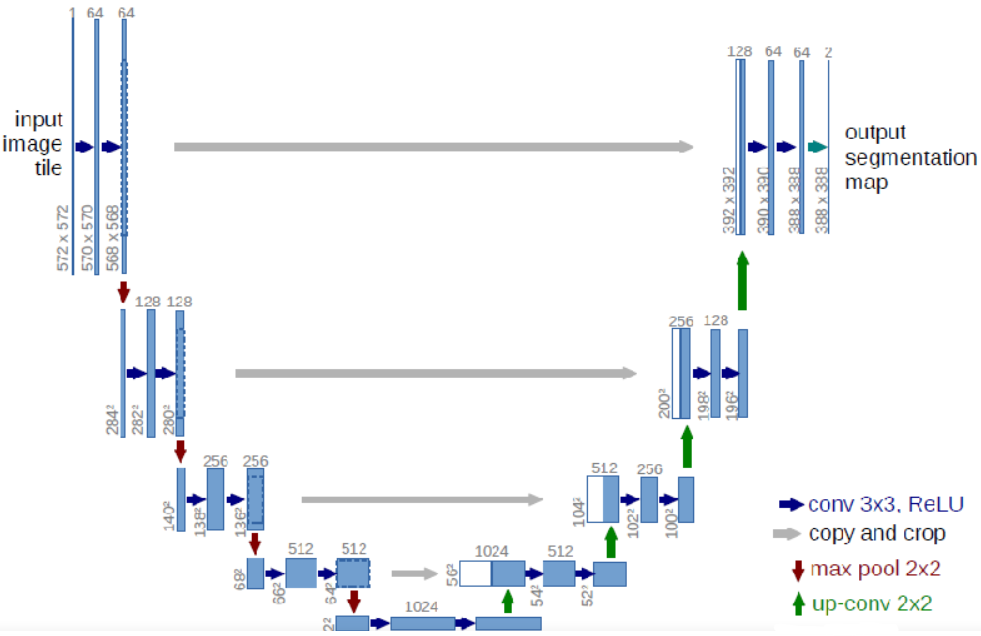
生成器 G G G采用U-Net结构,由两个部分组成:
- 压缩路径:由卷积和降采样组成;
- 扩张路径:由卷积和上采样组成。
import mindspore
import mindspore.nn as nn
import mindspore.ops as ops
class UNetSkipConnectionBlock(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self, outer_nc, inner_nc, in_planes=None, dropout=False,
submodule=None, outermost=False, innermost=False, alpha=0.2, norm_mode='batch'):
super(UNetSkipConnectionBlock, self).__init__()
down_norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(inner_nc)
up_norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(outer_nc)
use_bias = False
if norm_mode == 'instance':
down_norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(inner_nc, affine=False)
up_norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(outer_nc, affine=False)
use_bias = True
if in_planes is None:
in_planes = outer_nc
down_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, inner_nc, kernel_size=4,
stride=2, padding=1, has_bias=use_bias, pad_mode='pad')
down_relu = nn.LeakyReLU(alpha)
up_relu = nn.ReLU()
if outermost:
up_conv = nn.Conv2dTranspose(inner_nc * 2, outer_nc,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=1, pad_mode='pad')
down = [down_conv]
up = [up_relu, up_conv, nn.Tanh()]
model = down + [submodule] + up
elif innermost:
up_conv = nn.Conv2dTranspose(inner_nc, outer_nc,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=1, has_bias=use_bias, pad_mode='pad')
down = [down_relu, down_conv]
up = [up_relu, up_conv, up_norm]
model = down + up
else:
up_conv = nn.Conv2dTranspose(inner_nc * 2, outer_nc,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=1, has_bias=use_bias, pad_mode='pad')
down = [down_relu, down_conv, down_norm]
up = [up_relu, up_conv, up_norm]
model = down + [submodule] + up
if dropout:
model.append(nn.Dropout(p=0.5))
self.model = nn.SequentialCell(model)
self.skip_connections = not outermost
def construct(self, x):
out = self.model(x)
if self.skip_connections:
out = ops.concat((out, x), axis=1)
return out
class UNetGenerator(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, ngf=64, n_layers=8, norm_mode='bn', dropout=False):
super(UNetGenerator, self).__init__()
unet_block = UNetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 8, ngf * 8, in_planes=None, submodule=None,
norm_mode=norm_mode, innermost=True)
for _ in range(n_layers - 5):
unet_block = UNetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 8, ngf * 8, in_planes=None, submodule=unet_block,
norm_mode=norm_mode, dropout=dropout)
unet_block = UNetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 4, ngf * 8, in_planes=None, submodule=unet_block,
norm_mode=norm_mode)
unet_block = UNetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf * 2, ngf * 4, in_planes=None, submodule=unet_block,
norm_mode=norm_mode)
unet_block = UNetSkipConnectionBlock(ngf, ngf * 2, in_planes=None, submodule=unet_block,
norm_mode=norm_mode)
self.model = UNetSkipConnectionBlock(out_planes, ngf, in_planes=in_planes, submodule=unet_block,
outermost=True, norm_mode=norm_mode)
def construct(self, x):
return self.model(x)
判别器
判别器使用PatchGAN结构。
import mindspore.nn as nn
class ConvNormRelu(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self,
in_planes,
out_planes,
kernel_size=4,
stride=2,
alpha=0.2,
norm_mode='batch',
pad_mode='CONSTANT',
use_relu=True,
padding=None):
super(ConvNormRelu, self).__init__()
norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_planes)
if norm_mode == 'instance':
norm = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_planes, affine=False)
has_bias = (norm_mode == 'instance')
if not padding:
padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2
if pad_mode == 'CONSTANT':
conv = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride, pad_mode='pad',
has_bias=has_bias, padding=padding)
layers = [conv, norm]
else:
paddings = ((0, 0), (0, 0), (padding, padding), (padding, padding))
pad = nn.Pad(paddings=paddings, mode=pad_mode)
conv = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride, pad_mode='pad', has_bias=has_bias)
layers = [pad, conv, norm]
if use_relu:
relu = nn.ReLU()
if alpha > 0:
relu = nn.LeakyReLU(alpha)
layers.append(relu)
self.features = nn.SequentialCell(layers)
def construct(self, x):
output = self.features(x)
return output
class Discriminator(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self, in_planes=3, ndf=64, n_layers=3, alpha=0.2, norm_mode='batch'):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
kernel_size = 4
layers = [
nn.Conv2d(in_planes, ndf, kernel_size, 2, pad_mode='pad', padding=1),
nn.LeakyReLU(alpha)
]
nf_mult = ndf
for i in range(1, n_layers):
nf_mult_prev = nf_mult
nf_mult = min(2 ** i, 8) * ndf
layers.append(ConvNormRelu(nf_mult_prev, nf_mult, kernel_size, 2, alpha, norm_mode, padding=1))
nf_mult_prev = nf_mult
nf_mult = min(2 ** n_layers, 8) * ndf
layers.append(ConvNormRelu(nf_mult_prev, nf_mult, kernel_size, 1, alpha, norm_mode, padding=1))
layers.append(nn.Conv2d(nf_mult, 1, kernel_size, 1, pad_mode='pad', padding=1))
self.features = nn.SequentialCell(layers)
def construct(self, x, y):
x_y = ops.concat((x, y), axis=1)
output = self.features(x_y)
return output
Pix2Pix网络
import mindspore.nn as nn
from mindspore.common import initializer as init
g_in_planes = 3
g_out_planes = 3
g_ngf = 64
g_layers = 8
d_in_planes = 6
d_ndf = 64
d_layers = 3
alpha = 0.2
init_gain = 0.02
init_type = 'normal'
net_generator = UNetGenerator(in_planes=g_in_planes, out_planes=g_out_planes,
ngf=g_ngf, n_layers=g_layers)
for _, cell in net_generator.cells_and_names():
if isinstance(cell, (nn.Conv2d, nn.Conv2dTranspose)):
if init_type == 'normal':
cell.weight.set_data(init.initializer(init.Normal(init_gain), cell.weight.shape))
elif init_type == 'xavier':
cell.weight.set_data(init.initializer(init.XavierUniform(init_gain), cell.weight.shape))
elif init_type == 'constant':
cell.weight.set_data(init.initializer(0.001, cell.weight.shape))
else:
raise NotImplementedError('initialization method [%s] is not implemented' % init_type)
elif isinstance(cell, nn.BatchNorm2d):
cell.gamma.set_data(init.initializer('ones', cell.gamma.shape))
cell.beta.set_data(init.initializer('zeros', cell.beta.shape))
net_discriminator = Discriminator(in_planes=d_in_planes, ndf=d_ndf,
alpha=alpha, n_layers=d_layers)
for _, cell in net_discriminator.cells_and_names():
if isinstance(cell, (nn.Conv2d, nn.Conv2dTranspose)):
if init_type == 'normal':
cell.weight.set_data(init.initializer(init.Normal(init_gain), cell.weight.shape))
elif init_type == 'xavier':
cell.weight.set_data(init.initializer(init.XavierUniform(init_gain), cell.weight.shape))
elif init_type == 'constant':
cell.weight.set_data(init.initializer(0.001, cell.weight.shape))
else:
raise NotImplementedError('initialization method [%s] is not implemented' % init_type)
elif isinstance(cell, nn.BatchNorm2d):
cell.gamma.set_data(init.initializer('ones', cell.gamma.shape))
cell.beta.set_data(init.initializer('zeros', cell.beta.shape))
class Pix2Pix(nn.Cell):
"""Pix2Pix模型网络"""
def __init__(self, discriminator, generator):
super(Pix2Pix, self).__init__(auto_prefix=True)
self.net_discriminator = discriminator
self.net_generator = generator
def construct(self, reala):
fakeb = self.net_generator(reala)
return fakeb
总结
这一节介绍了Pix2Pix网络,该网络使用cGAN模型实现了图像到图像的映射。相对于传统GAN使用随机噪声来生成图像,cGAN直接使用输入图像来生成新图像。在Pix2Pix的实现中,使用了U-Net结构来保留不同分辨率下的细节信息。