目录导航
前言
前面的章节我们讲了 Spring Cloud 服务熔断
本节,继续微服务专题的内容分享,共计16小节,分别是:
- 微服务专题01-Spring Application
- 微服务专题02-Spring Web MVC 视图技术
- 微服务专题03-REST
- 微服务专题04-Spring WebFlux 原理
- 微服务专题05-Spring WebFlux 运用
- 微服务专题06-云原生应用(Cloud Native Applications)
- 微服务专题07-Spring Cloud 配置管理
- 微服务专题08-Spring Cloud 服务发现
- 微服务专题09-Spring Cloud 负载均衡
- 微服务专题10-Spring Cloud 服务熔断
- 微服务专题11-Spring Cloud 服务调用
- 微服务专题12-Spring Cloud Gateway
- 微服务专题13-Spring Cloud Stream (上)
- 微服务专题14-Spring Cloud Bus
- 微服务专题15-Spring Cloud Stream 实现
- 微服务专题16-Spring Cloud 整体回顾
本节内容重点为:
- Spring Cloud Feign :介绍声明式客户端REST实现 Spring Cloud Feign的使用方式(如
@EnableFeignClients、@FeignClient),结合 Eureka 构建分布式服务应用 - 整合支持:Spring Cloud Feign 整合 Hystrix 以及 Ribbon
REST 服务端框架纵向比较
Spring Cloud Feign 是 OpenFeign 扩展,并且使用 Spring MVC 注解来做 URI 映射,比如 @RequestMapping 或 @GetMapping 之类
OpenFeign:灵感来自于 JAX-RS(Java REST 标准),重复发明轮子。
JAX-RS:Java REST 标准,可移植性高,Jersey(Servlet 容器)、Weblogic
JSR 参考链接:https://github.com/mercyblitz/jsr
| 技术栈 | HTTP 方法 | 变量路径 | 请求参数 | 自描述消息 | 内容协商 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JAX-RS | @GET | @PathParam | @FormParam | @Produces(“application/widgets+xml”) | |
| Spring Web MVC | @GetMapping | @PathVariable | @RequestParam | @RequestMapping(produces="application/widgets+xml") | |
| OpenFeign | @RequestLine(“GET…”) | @Param | @Param | ||
| Spring Cloud Feign | @GetMapping | @PathVariable | @RequestParam |
REST 核心概念(Java 技术描述)
现在我们回顾一下 REST 核心概念,它将贯穿整个SpringCloud的环节。
- 请求映射
@RequestMapping
- 请求参数处理
@RequestParam
- 请求主题处理
@RequestBody
- 响应处理
@ResponseBody
@ResponseStatus
@ResponseBody + @ResponseStatus <= ResponseEntity
ResponseBody+ ResponseStatus 没有头处理
- 自描述消息
@RequestMapping(produces="application/widgets+xml")
- 内容协商
ContentNegotiationManager
理论知识:https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Content_negotiation
RestTemplate 服务调用
我们首先分析一下服务调用引入背景,在前面的章节我们就提到了通过使用注解 @LoadBalanced 来使用 RestTemplate 作为服务调用。RestTemplate 不依赖于服务接口,耦合性更低,这样对比于dubbo会更加轻量级,它仅关注 REST 响应内容。但是我们也应该清楚RestTemplate 的局限性:
- 面向 URL 组件,必须依赖于 主机+端口 + URI。
- 并非接口编程(Spring Cloud中,需要理解应用名称+ 服务 URI)。
举例:
@RestController
public class ClientController {
@Autowired
@LoadBalanced // 依赖注入 Ribbon RestTemplate Bean
private RestTemplate lbRestTemplate;
@GetMapping("/lb/invoke/{serviceName}/say") // -> /say
public String lbInvokeSay(@PathVariable String serviceName,
@RequestParam String message) {
// Ribbon RestTemplate 发送请求到服务器
// 输出响应
return lbRestTemplate.getForObject("http://" + serviceName + "/say?message=" + message, String.class);
}
}
这里的url我们注意下,类似于网关的zuul ,关于zuul我们下节会介绍,这里只是做一个抽象的总结:即,网关zull的访问地址可以概括为:IP:port/ $ {service_name}/${uri}
Spring Cloud Feign 服务调用
本节我们主要讲 Spring Cloud Feign 实现的服务调用过程。
Feign 的基本用法
- 服务(应用)定位
Spring Cloud Feign 客户端加入注解 @FeignClient。
@FeignClient("${service.name}") // 服务提供方的应用名称
- 服务 URI 定位
整合 Spring Cloud Feign
- 增加 Spring Cloud Feign 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 整合
@EnableFeignClients
@SpringBootApplication // 标准 Spring Boot 应用
@EnableDiscoveryClient // 激活服务发现客户端
@EnableScheduling
@EnableFeignClients
public class SpringCloudClientApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SpringApplicationBuilder(SpringCloudClientApplication.class)
.web(WebApplicationType.SERVLET)
.run(args);
}
}
- 整合
@FeignClient
之前实现
@GetMapping("/lb/invoke/{serviceName}/say") // -> /say
public String lbInvokeSay(@PathVariable String serviceName,
@RequestParam String message) {
// Ribbon RestTemplate 发送请求到服务器
// 输出响应
return lbRestTemplate.getForObject("http://" + serviceName + "/say?message=" + message, String.class);
}
整合 @FeignClient 实现
@FeignClient(name = "spring-cloud-server-application")
public interface SayingService {
@GetMapping("/say")
String say(@RequestParam("message") String message);
}
- 注入
SayingService
@Autowired
private SayingService sayingService;
SayingService
@GetMapping("/feign/say")
public String feignSay(@RequestParam String message) {
return sayingService.say(message);
}
- 启动 ZK 服务器
- 启动客户端与服务器
启动 spring-cloud-server-application、 启动 spring-cloud-client-application
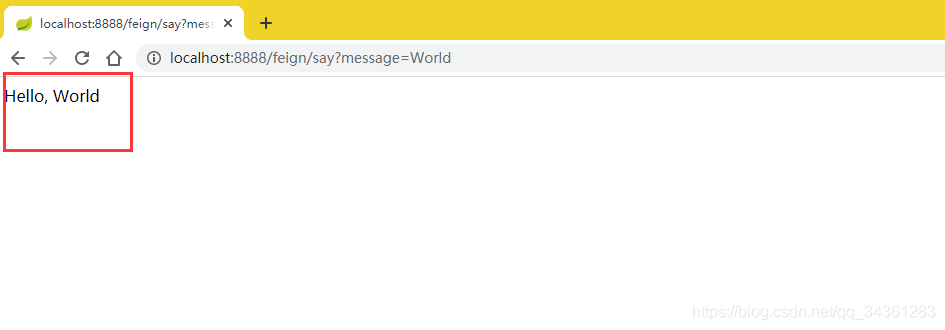
- 观察实验结果
访问地址;http://localhost:8888/feign/say?message=World
Spring Cloud Feign 编程模型特征
上面的一个简单demo我们总结出,feign的特性有:
@Enable模块驱动@*Client绑定客户端接口,指定应用名称- 客户端接口指定请求映射
@RequetMapping - 客户端接口指定请求参数
@RequetParam- 必须指定
@RequestParam#value()
- 必须指定
@Autowired客户端接口是一个代理
实现自定义 RestClient(模拟 @FeignClient)
接下来,我们根据上面的使用的feign 的演示案例,我们模拟feign自己手写一个 RestClient。
- 实现
@RestClient
/**
* Rest Client 注解
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RestClient {
/**
* REST 服务应用名称
* @return
*/
String name();
}
- 实现
@RestClient服务接口
@RestClient(name = "spring-cloud-server-application")
public interface SayingRestService {
@GetMapping("/say")
String say(@RequestParam("message") String message);
}
- 实现
@Enable模块
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(RestClientsRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableRestClient {
/**
* 指定 @RestClient 接口
* @return
*/
Class<?>[] clients() default {};
}
- 实现
RestClientsRegistrar
简单地概括一下整理实现逻辑:
- 指定
@RestClient服务接口- 识别
@RestClient - 过滤所有
@RequestMapping方法
- 识别
- 将
@RestClient服务接口注册 Bean@RestClient服务接口形成代理实现say方法执行 REST 请求
public class RestClientsRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar,
BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware {
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
private Environment environment;
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
ClassLoader classLoader = metadata.getClass().getClassLoader();
Map<String, Object> attributes =
metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableRestClient.class.getName());
// attributes -> { clients : SayingRestService}
Class<?>[] clientClasses = (Class<?>[]) attributes.get("clients");
// 接口类对象数组
// 筛选所有接口
Stream.of(clientClasses)
.filter(Class::isInterface) // 仅选择接口
.filter(interfaceClass ->
findAnnotation(interfaceClass, RestClient.class) != null) // 仅选择标注 @RestClient
.forEach(restClientClass -> {
// 获取 @RestClient 元信息
RestClient restClient = findAnnotation(restClientClass, RestClient.class);
// 获取 应用名称(处理占位符)
String serviceName = environment.resolvePlaceholders(restClient.name());
// RestTemplate -> serviceName/uri?param=...
// @RestClient 接口编程 JDK 动态代理
Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, new Class[]{restClientClass},
new RequestMappingMethodInvocationHandler(serviceName, beanFactory));
// 将 @RestClient 接口代理实现注册为 Bean(@Autowired)
// BeanDefinitionRegistry registry
String beanName = "RestClient." + serviceName;
// 实现方略二:SingletonBeanRegistry
if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) {
SingletonBeanRegistry singletonBeanRegistry = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry;
singletonBeanRegistry.registerSingleton(beanName, proxy);
}
// registerBeanByFactoryBean(serviceName,proxy,restClientClass,registry);
});
}
private static class RestClientClassFactoryBean implements FactoryBean {
private final Object proxy;
private final Class<?> restClientClass;
private RestClientClassFactoryBean(Object proxy, Class<?> restClientClass) {
this.proxy = proxy;
this.restClientClass = restClientClass;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return proxy;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return restClientClass;
}
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
}
}
- 实现 InvocationHandler,过滤 @RequestMapping 方法。
public class RequestMappingMethodInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private final ParameterNameDiscoverer parameterNameDiscoverer
= new DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer();
private final String serviceName;
private final BeanFactory beanFactory;
public RequestMappingMethodInvocationHandler(String serviceName,
BeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.serviceName = serviceName;
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 过滤 @RequestMapping 方法
GetMapping getMapping = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, GetMapping.class);
if (getMapping != null) {
// 得到 URI
String[] uri = getMapping.value();
// http://${serviceName}/${uri}
StringBuilder urlBuilder = new StringBuilder("http://").append(serviceName).append("/").append(uri[0]);
// 获取方法参数数量
int count = method.getParameterCount();
// 方法参数是有顺序
// FIXME
// String[] paramNames = parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(method);
// 方法参数类型集合
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
Annotation[][] annotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
StringBuilder queryStringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Annotation[] paramAnnotations = annotations[i];
Class<?> paramType = paramTypes[i];
RequestParam requestParam = (RequestParam) paramAnnotations[0];
if (requestParam != null) {
String paramName = "";
// paramNames[i];
// HTTP 请求参数
String requestParamName = StringUtils.hasText(requestParam.value()) ? requestParam.value() :
paramName;
String requestParamValue = String.class.equals(paramType)
? (String) args[i] : String.valueOf(args[i]);
// uri?name=value&n2=v2&n3=v3
queryStringBuilder.append("&")
.append(requestParamName).append("=").append(requestParamValue);
}
}
String queryString = queryStringBuilder.toString();
if (StringUtils.hasText(queryString)) {
urlBuilder.append("?").append(queryString);
}
// http://${serviceName}/${uri}?${queryString}
String url = urlBuilder.toString();
// 获取 RestTemplate , Bean 名称为“loadBalancedRestTemplate”
// 获得 BeanFactory
RestTemplate restTemplate = beanFactory.getBean("loadBalancedRestTemplate", RestTemplate.class);
return restTemplate.getForObject(url, method.getReturnType());
}
return null;
}
}
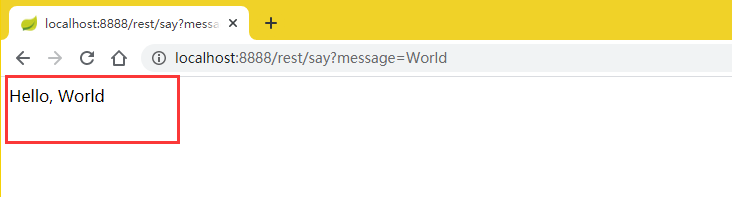
- 自定义rest client 测试
访问地址:http://localhost:8888/rest/say?message=World
得到结果:
Feign 常见问题总结
-
能跟dubbo一样,消费端像调用本地接口方法一样调用服务端提供的服务么?还有就是远程调用方法参数对象不用实现序列化接口么?
答: FeignClient 类似 Dubbo,不过需要增加以下 @Annotation,和调用本地接口类似
-
Feign通过注释驱动弱化了调用Service细节,但是Feign的Api设定会暴露service地址,那还有实际使用价值么?
答:实际价值是存在的,Feign API 暴露 URI,比如:"/person/save"
-
整合ribbon不是一定要关闭注册中心吧?
答: Ribbon 对于 Eureka 是不强依赖,不过也不排除
-
生产环境上也都是feign的?
答: 不少的公司在用,需要 Spring Cloud 更多整合:
Feign 作为客户端,Ribbon 作为负载均衡,Eureka 作为注册中心,Zuul 作为网关,Security 作为安全 OAuth 2 认证。 -
Ribbon直接配置在启动类上是作用所有的controller,那如果想作用在某个呢?
答:Ribbon 是控制全局的负载均衡,主要作用于客户端 Feign,Controller是调用 Feign 接口,可能让人感觉直接作用了 Controller。
-
其实eureka也有ribbon中简单的负载均衡吧?
答:Eureka 也要 Ribbon 的实现,可以参考
com.netflix.ribbon:ribbon-eureka -
如果服务提供方,没有接口,我客户端一般咋处理?要根据服务信息,自建feign接口?
答:当然可以,可是 Feign 的接口定义就是要求强制实现
-
无法连接注册中心的老服务,如何调用cloud服务?
答:可以通过域名的配置 Ribbon 服务白名单
-
eureka 有时监控不到宕机的服务 正确的启动方式是什么?
答:这可以调整的心跳检测的频率
后记
本节代码地址:Feign
更多架构知识,欢迎关注本套Java系列文章:Java架构师成长之路