Lottie是什么
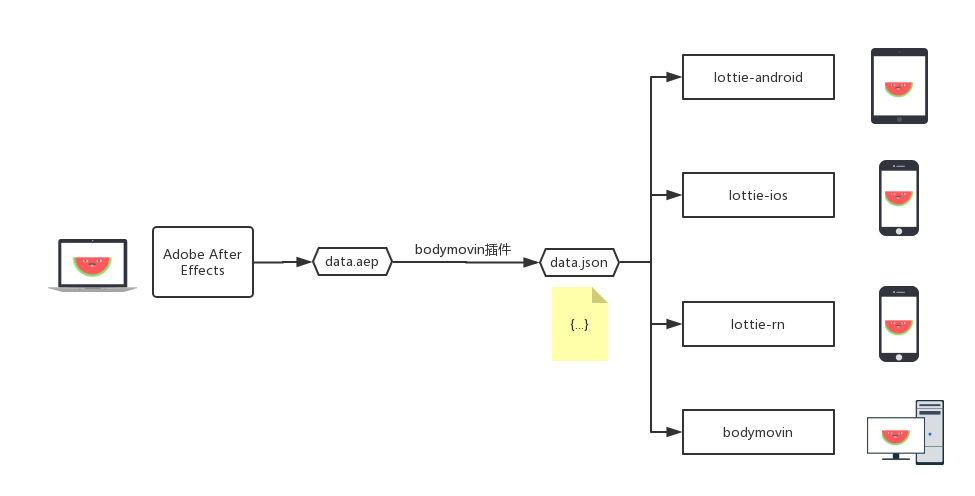
Lottie是Airbnb开源的一套跨平台的、完整的动画效果解决方案,适用于 Android、iOS、Web 和 Windows 平台,它解析使用 Bodymovin 导出为 json 的 Adobe After Effects 动画,并在移动设备和 Web 上本地呈现它们!如下图:
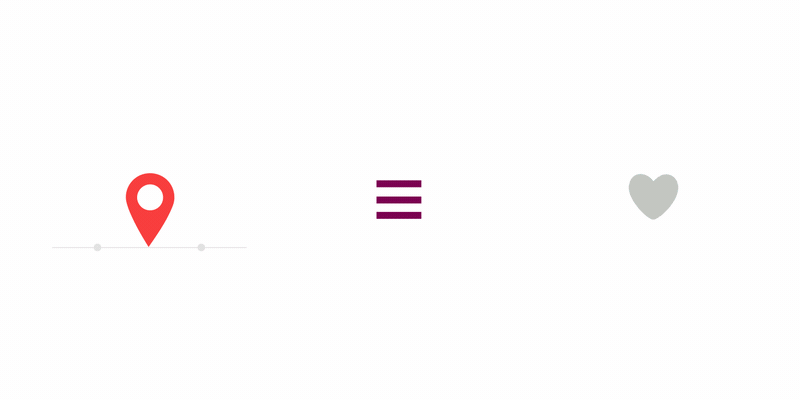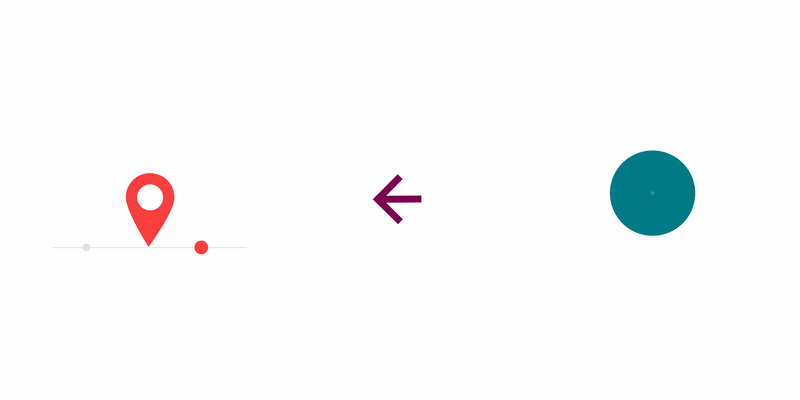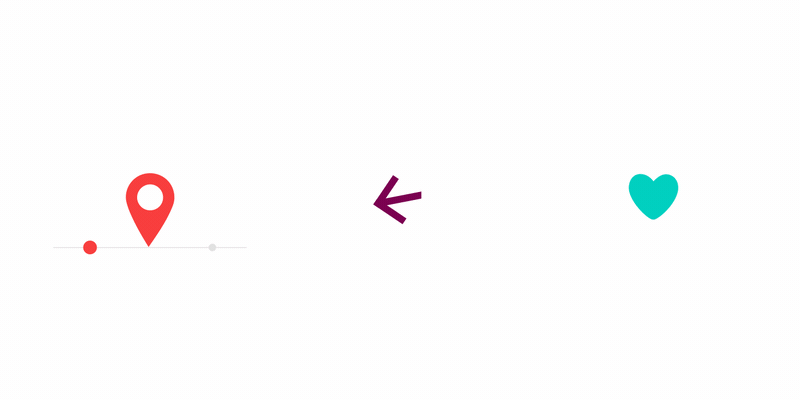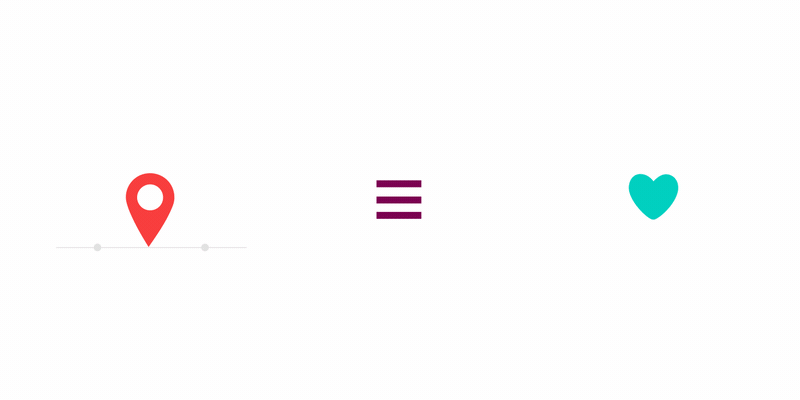
以下是Lottie官网给出的一些动画效果
Airbnb为什么要做Lottie
1、为什么要使用LOTTIE?
先看看在没有Lottie之前我们实现复杂动画的方式:
- 使用GIF,占用空间大,有些动画显示效果不佳,需要适配分辨率,Android原生不支持GIF动画的显示。
- 使用帧动画,占用空间大,依然会遇到不同分辨率适配的问题。
- 组合式动画,通过大量代码实现复杂的动画效果。
2、使用Lottie可以解决的问题:
- 开发无需编写动画,只需加载
- Android, iOS, 和React Native多平台支持
- 可手动设置进度,绑定手势,事件等
- 可网络加载,动态控制播放速度等
- 降低动画设计和开发成本
- 解决设计提供动画效果与实现不一致问题
- 占用空间更小
- 不同的手机分辨率不需要适配
3、LOTTIE适用于哪些场景?
- 启动(splash)动画:典型场景是APP logo动画的播放
- 上下拉刷新(refresh)动画:所有APP都必备的功能,利用 Lottie可以做的更加简单酷炫了
- 加载(loading)动画:典型场景是网络请求的loading动画
- 提示(tips)动画:典型场景是空白页的提示
- 按钮(button)动画:典型场景如switch按钮、编辑按钮、播放按钮等按钮的
- 礼物(gift)动画:典型场景是直播类APP的高级动画播放
4、我们想要使用LOTTIE替代哪些动画?
- 首先并不是在APP中所有的动画都要用Lottie来替换
- 一些可以通过属性动画来实现的简单动画就不需要用Lottie来实现了
- 替代一些通过代码不好实现的动画效果
- 替代GIF动画和帧动画
可以参考Airbnb的官网
为什么叫Lottie
Lottie 以德国电影导演和剪影动画最重要的先驱 Lotte Reineger(洛特.雷尼格)的名字命名。她最著名的电影是《艾哈迈德王子历险记》(1926 年)——现存最古老的长篇动画电影,比沃尔特·迪斯尼的长篇白雪公主和七个小矮人(1937 年)早了十多年 Lotte Reineger 的艺术。她导演了世界上首批动画故事片之一:《阿基米德王子历险记》(改编自《一千零一夜》) 
环境安装
(1)AE下载
这里使用的AE版本是Adobe After Effects CC 2017版,注意此版本只适用于WIN 64位系统,网盘下载 https://pan.baidu.com/s/1boYKfld,安装过程中按照内置说明安装即可.
(2)安装bodymovin插件
下载插件
这里使用的BodyMovin插件版本是5.4.4,下载链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1wEhX7jR74jkQLyPm0u_KdQ密码:34k3。
想了解此插件可以在GitHub上搜索airbnb,bodymovin.zxp插件位于airbnb/lottie-web/tree/master/build/extension目录下
安装插件
安装插件的步骤如下所示。
- 先关闭AE
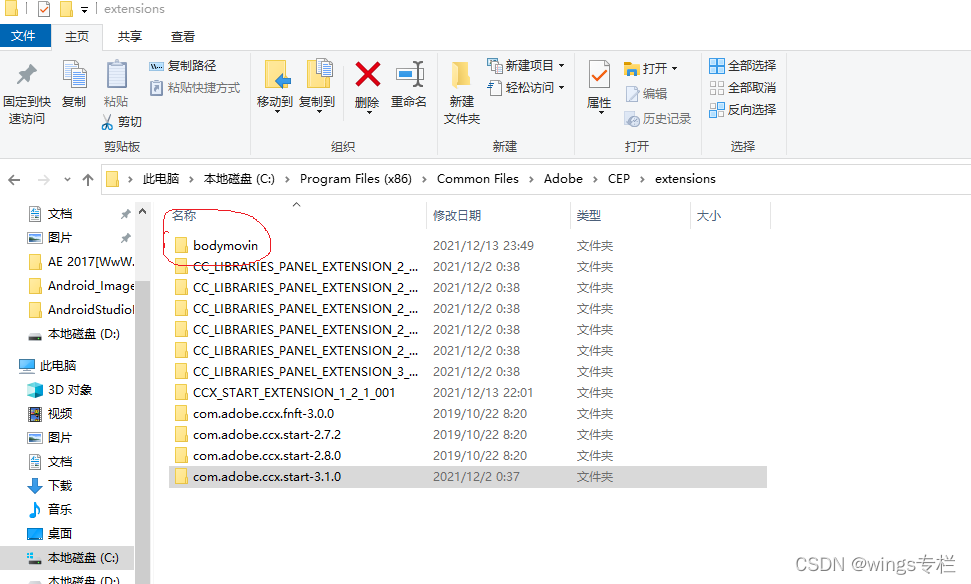
- 将bodymovin.zxp的后缀改为rar,然后使用WinRAR解压,(其他解压软件也可以,比如7zip,也可以直接解压,5.4.4版本的bodymovin.zxp本身就是一个压缩包,高版本的bodymovin插件需要使用ZXP installer安装器来安装,具体可看https://github.com/airbnb/lottie-web),并将解压后的文件夹直接复制到C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\Adobe\CEP\extensions或者是C:\AppData\Roaming\Adobe\CEP\extensions下,对于MAC机器路径是 /Library/Application/Support/Adob/CE/extensions/bodymovin
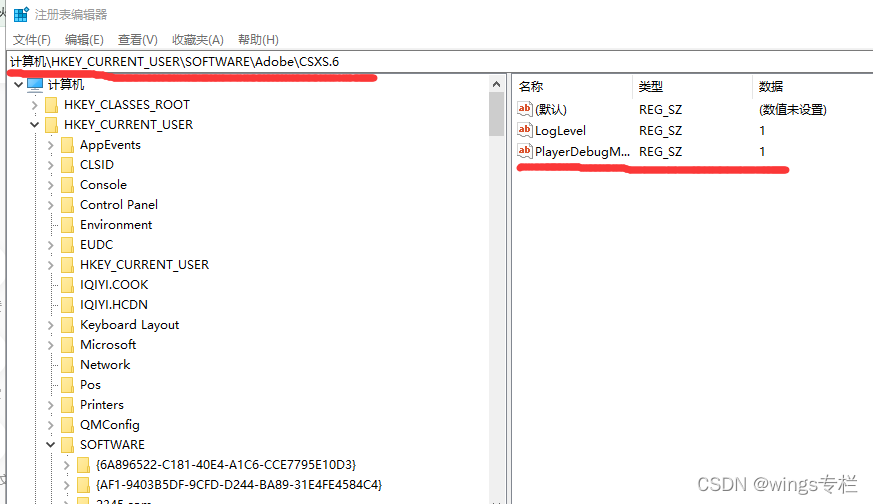
- 修改注册表.对于Windows,打开注册表修改器,找到HKEY_CURRENT_USER/Software/Adobe/CSXS.6,并在此路径下添加一个名为PlayerDebugMode的KEY,并赋值为1;对于MAC,打开文件~/Library/Preferences/com.adobe.CSXS.6.plist并在末尾添加一行,键为PlayerDebugMode,值为1.
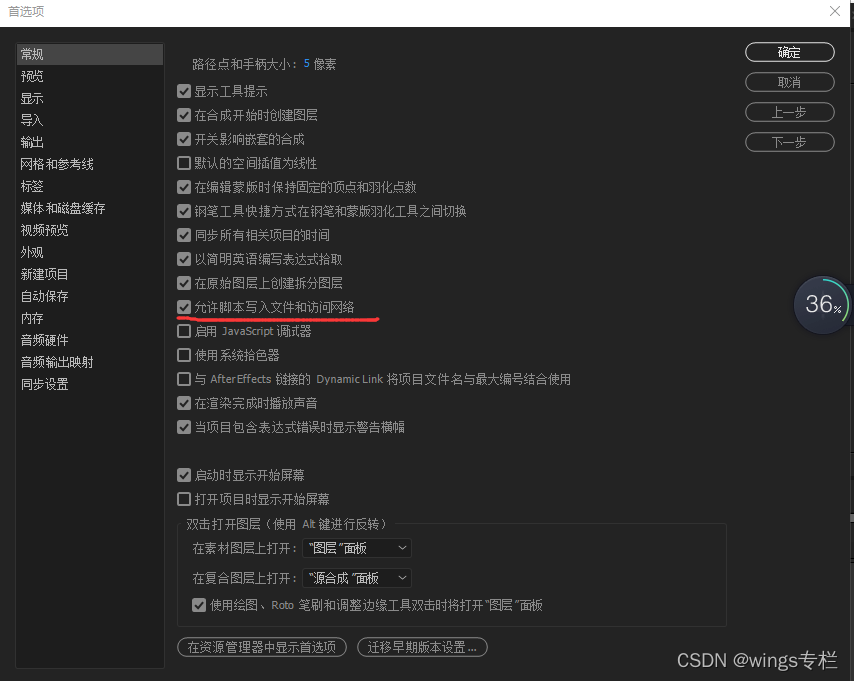
- 设置AE 无论以何种方式安装bodymovin插件,都需要在AE的编辑->首选项->常规中勾选允许脚本写入文件和访问网络(默认不开启)
Lottie的完整使用流程
- 导出JSON文件
打开一个AE动画文件(.aep结尾的文件),按下空格键,就可以播放动画。这里使用Lottie官方提供的一个EmptyState.aep文件,打开如下图:
通过“窗口->扩展->Bodymovin”即可打开Bodymovin插件窗口,如下图
打开的Bodymovin插件如下
选择导出json文件的目录,点击Render即可渲染导出data.json文件,然后使用Android的lottie库加载即可。
Lottie JSON文件的属性含义
以下将详细讲解json文件的结构
- 最外层结构
{
"v": "5.4.4",
"fr": 15,
"ip": 0,
"op": 75,
"w": 500,
"h": 500,
"ddd": 0,
"assets":[],
"layers":[],
"markers":[]
}
- 属性的含义:
| 属性 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| v | bodymovin的版本 |
| fr | 帧率 |
| ip | 起始关键帧 |
| op | 结束关键帧 |
| w | 动画宽度 px(这里的px值仅是一个单位标识,并不是在Android屏幕上显示时所占的px数,这个数值会根据屏幕分辨率进行缩放) |
| h | 动画高度 px |
| nm | 文件名,该复合图层的名称 |
| ddd | 无用标识,源码未作解析 |
| assets | 动画图片资源信息 |
| layers | 动画图层信息 |
| markers | 标记,AE设计师给你自己看的注释 |
从这里可以获取 设计的动画的宽高,帧相关的信息,动画所需要的图片资源的信息以及图层信息。
- Markers
标记就是注释,是AE设计师给自己看的,我们一般用不到,如果对图层使用了标记功能,那么所有的标记将显示AI这个字段对应的列表中。
以下是Markers的结构:
"Markers":[
{
"tm":7,
"cm":"标记1",
"dr":0
}
]
每个字段都有tm、cm、dr字段,意义如下:
- tm:表示开始时间
- cm:表示注释内容,对应合成标记页面中的注释部分
- dr:表示持续帧数,不是持续时间,是帧数
- layers标记
"layers":[
{
"ddd": 0, // 无用标识
"ind": 0, // layer id 图层 id
"ty": 2, // 当前图层类型
"nm": "btnSlice.png", // 图层名称
"cl": "png",
"refId": "image_0",// 引用的资源 id,如果是ImageLayer 那么就是图片的id
"ks": {....}, // 图层的变换操作组,图层动画的关键帧信息
"ao": 0, // 无用标识
"shapes':[] // 没有添加任何动画操作时渲染出的效果
"ip": 0, // 该图层起始关键帧索引
"op": 90.0000036657751, //该图层结束关键帧索引
"st": 0, // startFrame 开始
"bm": 0, // 无用标识
"sr": 1// 时间伸缩,控制动画的播放速度
}
]
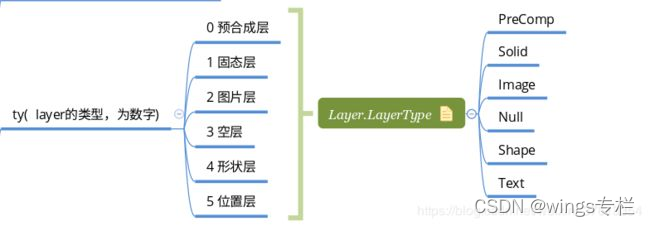
其中ty字段表示当前图层的类型。Lottie支持AE中的所有图层类型,并会为每种图层枚举一个值——合成图层(0)、固态图层(1)、图片图层(2)、空对象(3)、形状图层(4)、文本图层(5)、未知图层(6),其中未知图层是兜底策略,以防有新的图层样式,Bodymovin识别不了。
- layers->ks标记
ks标记是保存该图层动画关键帧信息的,支持我们常见的动画操作
"ks":{
"o":{...},// 不透明度
"r":{...},// 旋转
"p":{...},// 位置
"a":{...},// 锚点
"s":{...} // 缩放
}
- assets
图片资源信息
"assets": [
{
"id": "image_0",//图片ID
"w": 500, //图片宽度
"h": 500, // 图片高度
"u": "images/", // 所在文件夹
"p": "voice_thinking_image_0.png", // 图片名称
"e":0 // 无用标识
}
]
当涉及到外部资源时,就会在assets标识中显示所涉及资源的列表,这里有一张图片资源,所以assets列表中只有一组内容。当我们导出json文件时,还有一个images文件夹,其中的内容就是我们的图片,图片的命名是Bodymovin自动生成的,命名规则是img_x,其中x表示在导出时的图片顺序索引,从0开始。
Lottie的使用方法
1、基本使用
- 添加依赖
dependencies {
...
implementation "com.airbnb.android:lottie:4.2.2"
...
}
- 使用LottieAnimationView
把用到的JSON文件放在assets文件夹下,如果导出时有images文件夹,则一并放入
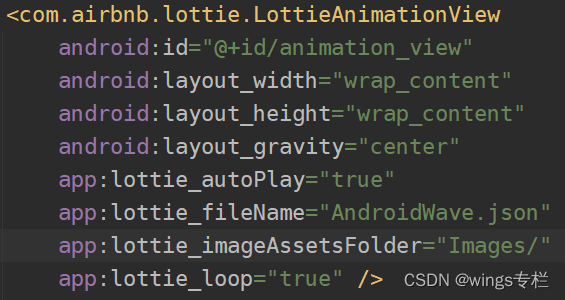
在布局文件中使用
- lottie_imageAssetsFolder是指如果Lottie中有图片,取assets目录下的哪个文件中去找。这里指定的路径是Images/,程序就会去assets/Images/下查找。
- lottie_autoPlay是指是否自动播放,true就自动播放,反之不是,不指定默认false
- lottie_loop是否循环播放,默认fasle,只播放一次
- lottie_fileName该属性用于在本地加载时指定JSON文件名,默认从assets文件夹中查找JSON文件。如果在aasets文件夹下找不到对应的JSON文件,就会抛出异常。文件除了可以使用.json格式以外,还可以使用.zip格式的压缩文件
2、LottieAnimationView其他自定义属性
- lottie_rawRes:进行本地加载时也可以放在raw文件夹下,该属性用于指定在raw文件夹下的JSON文件名
使用方法如下:
JSON文件名前需要使用"@raw/"引入,且文件名不带.json后缀
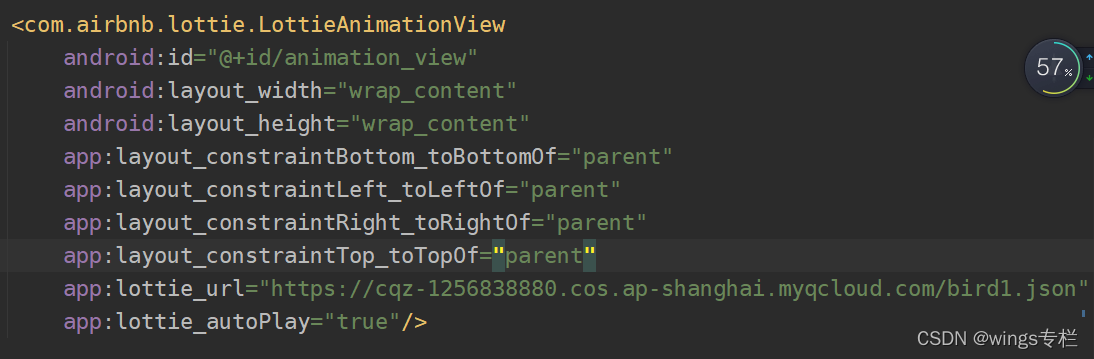
- lottie_url:当需要在xml中加载在线资源时,便可以使用lottie_url这个属性来加载,使用方法如下:
-
lottie_repeatMode:指定循环播放的循序,取值为repeat或reverse,repeat表示正常顺序播放,reverse表示倒序播放。
-
lottie_repeatCount :指定循环次数,取值为整数类型
-
lottie_progress:用于指定动画初次显示时的进度,类型为float,取值范围为0~1。用法如下:
因为没有设置自动播放和循环播放,所以动画就会固定在进度为80%的位置。如果设置了自动播放和循环播放,则会看不到初始化设置的进度效果。
-
lottie_scale:用于设置画布的缩放大小,注意这里是画布大小,不是其中图片大小。在lottie的json文件开头,w表示画布的宽度,h表示画布的高度。当设置了lottie_scale = 2之后,画布的大小就变成了(w2,h2)
LottieAnimationView可以设置的属性如下:
<declare-styleable name="LottieAnimationView"> //切记这个名字不能随便改,这个是官方命名
<attr name="lottie_fileName" format="string" /> //值得一提的是:lottie_fileName和lottie_rawRes不能同时设置,不然会报错。
<attr name="lottie_rawRes" format="reference" />
<attr name="lottie_url" format="string" />
<attr name="lottie_autoPlay" format="boolean" />
<attr name="lottie_loop" format="boolean" />
<attr name="lottie_repeatMode" format="enum">
<enum name="restart" value="1" />
<enum name="reverse" value="2" />
</attr>
<attr name="lottie_repeatCount" format="integer" />
<attr name="lottie_imageAssetsFolder" format="string" />
<attr name="lottie_progress" format="float" />
<attr name="lottie_enableMergePathsForKitKatAndAbove" format="boolean" />
<attr name="lottie_colorFilter" format="color" />// 修改颜色,这种修改方式,只能使用在背景透明的动画上,如果lottie动画本身就自带了背景色,那这种方式并不适用。因为addColorFilter的实现原理是为每一层都加上了colorfilter,会连背景色也被替换。导致看不出动画效果。 // addColorFilter,另外参考 addColorFilterToLayer addColorFilterToContent
<attr name="lottie_scale" format="float" />
</declare-styleable>
LottieAnimationView对象进行动画操作:
LottieAnimationView animationView = (LottieAnimationView)findViewById(R.id.animation_view);
// 布局中不指定文件可以在此设置,路径设置同布局文件
animationView.setAnimation("hello-world.json");
// 是否循环播放
animationView.loop(true);
// 设置播放速率,例如:2代表播放速率是不设置时的二倍
animationView.setSpeed(2f);
// 开始播放
animationView.playAnimation();
// 暂停播放
animationView.pauseAnimation();
// 取消播放
animationVIew.cancelAnimation();
// 设置播放进度
animationView.setProgress(0.5f);
// 判断是否正在播放
animationView.isAnimating();
setAnimation()有六种方法,可以直接设置动画的Json对象,或者设置Json文件相对路径名:
setAnimation(@RawRes final int rawRes)
setAnimation(final String assetName)
setAnimationFromJson(String jsonString) //不建议使用
setAnimationFromJson(String jsonString, @Nullable String cacheKey)
setAnimation(JsonReader reader, @Nullable String cacheKey)
setAnimationFromUrl(String url)
playAnimation()有一种方法:
public void playAnimation()
3、其他非常用功能
- 替换文本:JSON文件都是以key-value形式出现的,在代码中找到对应的key,改变他的value即可。使用LottieAnimationView的TextDelegate即可实现
LottieAnimationView lottieAnimationView = findViewById(R.id.lottie_view);
TextDelegate textDelegate = new TextDelegate(lottieAnimationView);
textDelegate.setText("我是原内容","我是替换内容");
lottieAnimationView.setTextDelegate(textDelegate);
- 替换图片资源:找到JSON文件中assets数据中对应图片的id,使用LottieAnimationView的updateBitmap即可实现图片替换
LottieAnimationView lottieAnimationView = findViewById(R.id.lottie_view);
findViewById(R.id.ghost_view).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
lottieAnimationView.updateBitmap("image_0",bitmap);
}
});
- 更改动画属性:使用LottieAnimationView的addValueCallback函数可实现改变lottie支持的各种属性(具体参考LottieProperty类)
- 改变填充颜色:使用LottieAnimationView的addValueCallback函数可实现
Lottie的适配原理
通过阅读源码发现 Lottie在 Android 平台已经做了适配工作,解析时,读取宽高之后会再乘以手机的密度。再在使用的时候判断适配后的宽高是否超过屏幕的宽高,如果超过则再进行缩放。以此保障 Lottie 在 Android 平台的显示效果。
lottie4.2.2版本的核心代码如下:
// Utils
public static float dpScale() {
if (dpScale == -1) {
dpScale = Resources.getSystem().getDisplayMetrics().density;
}
return dpScale;
}
//LottieCompositionMoshiParser
public static LottieComposition parse(JsonReader reader) throws IOException {
float scale = Utils.dpScale();
......
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
......
int scaledWidth = (int) (width * scale);
int scaledHeight = (int) (height * scale);
Rect bounds = new Rect(0, 0, scaledWidth, scaledHeight);
Rect bounds = new Rect(0, 0, scaledWidth, scaledHeight);
composition.init(bounds, startFrame, endFrame, frameRate, layers, layerMap, precomps,
images, characters, fonts, markers);
return composition;
}
//LottieDrawable
private float getMaxScale(@NonNull Canvas canvas, LottieComposition composition) {
float maxScaleX = canvas.getWidth() / (float) composition.getBounds().width();
float maxScaleY = canvas.getHeight() / (float) composition.getBounds().height();
return Math.min(maxScaleX, maxScaleY);
}
private void drawWithNewAspectRatio(Canvas canvas) {
......
LottieComposition composition = this.composition;
......
Rect bounds = getBounds();
// In fitXY mode, the scale doesn't take effect.
float scaleX = bounds.width() / (float) composition.getBounds().width();
float scaleY = bounds.height() / (float) composition.getBounds().height();
if (isExtraScaleEnabled) {
float maxScale = Math.min(scaleX, scaleY);
float extraScale = 1f;
if (maxScale < 1f) {
extraScale = extraScale / maxScale;
scaleX = scaleX / extraScale;
scaleY = scaleY / extraScale;
}
if (extraScale > 1) {
saveCount = canvas.save();
float halfWidth = bounds.width() / 2f;
float halfHeight = bounds.height() / 2f;
float scaledHalfWidth = halfWidth * maxScale;
float scaledHalfHeight = halfHeight * maxScale;
canvas.translate(
halfWidth - scaledHalfWidth,
halfHeight - scaledHalfHeight);
canvas.scale(extraScale, extraScale, scaledHalfWidth, scaledHalfHeight);
}
}
matrix.reset();
matrix.preScale(scaleX, scaleY);
compositionLayer.draw(canvas, matrix, alpha);
if (saveCount > 0) {
canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount);
}
}
private void drawWithOriginalAspectRatio(Canvas canvas) {
CompositionLayer compositionLayer = this.compositionLayer;
LottieComposition composition = this.composition;
if (compositionLayer == null || composition == null) {
return;
}
float scale = this.scale;
float extraScale = 1f;
float maxScale = getMaxScale(canvas, composition);
if (scale > maxScale) {
scale = maxScale;
extraScale = this.scale / scale;
}
int saveCount = -1;
if (extraScale > 1) {
saveCount = canvas.save();
float halfWidth = composition.getBounds().width() / 2f;
float halfHeight = composition.getBounds().height() / 2f;
float scaledHalfWidth = halfWidth * scale;
float scaledHalfHeight = halfHeight * scale;
canvas.translate(
getScale() * halfWidth - scaledHalfWidth,
getScale() * halfHeight - scaledHalfHeight);
canvas.scale(extraScale, extraScale, scaledHalfWidth, scaledHalfHeight);
}
matrix.reset();
matrix.preScale(scale, scale);
compositionLayer.draw(canvas, matrix, alpha);
if (saveCount > 0) {
canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount);
}
}
@Override
public int getIntrinsicWidth() {
return composition == null ? -1 : (int) (composition.getBounds().width() * getScale());
}
@Override
public int getIntrinsicHeight() {
return composition == null ? -1 : (int) (composition.getBounds().height() * getScale());
}
Lottie的绘制原理
1、从Json到动画显示的实现思路
设计师把一个复杂的动画使用多个图层来表示,每个图层展示一部分内容,图层中的内容也可以拆分为多个元素。拆分元素之后,根据动画需求,可以单独对图层或者图层中的元素做平移、旋转、收缩等动画(主要是通过Canvas绘制以及对Matrix进行操作)
2、如何加载JSON数据并显示图像的
animationView.setAnimation(“data.json”);
通过setAnimation()来看看,上面json数据到显示图像的过程
- LottieAnimationView初始化的时候会首先创建LottieDrawable对象,init()函数中进行初始化的时候,解析xml设置的属性。创建LottieDrawable对象代码段:
@SuppressWarnings({"unused", "WeakerAccess"})
public class LottieAnimationView extends AppCompatImageView {
private final LottieListener<LottieComposition> loadedListener = new LottieListener<LottieComposition>() {
@Override public void onResult(LottieComposition composition) {
setComposition(composition);
}
};
private final LottieListener<Throwable> failureListener = new LottieListener<Throwable>() {
@Override public void onResult(Throwable throwable) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to parse composition", throwable);
}
};
private final LottieDrawable lottieDrawable = new LottieDrawable();
......
init()函数的代码段:
private void init(@Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
TypedArray ta = getContext().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.LottieAnimationView);
boolean hasRawRes = ta.hasValue(R.styleable.LottieAnimationView_lottie_rawRes);
boolean hasFileName = ta.hasValue(R.styleable.LottieAnimationView_lottie_fileName);
boolean hasUrl = ta.hasValue(R.styleable.LottieAnimationView_lottie_url);
if (hasRawRes && hasFileName) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("lottie_rawRes and lottie_fileName cannot be used at " +
"the same time. Please use only one at once.");
} else if (hasRawRes) {
int rawResId = ta.getResourceId(R.styleable.LottieAnimationView_lottie_rawRes, 0);
if (rawResId != 0) {
setAnimation(rawResId);
}
} else if (hasFileName) {
String fileName = ta.getString(R.styleable.LottieAnimationView_lottie_fileName);
if (fileName != null) {
setAnimation(fileName);
}
} else if (hasUrl) {
String url = ta.getString(R.styleable.LottieAnimationView_lottie_url);
if (url != null) {
setAnimationFromUrl(url);
}
}
....
}
- setAnimation(String assetName),加载JSON文件。主要是通过LottieCompositionFactory这个类加载。
其中setAnimation()函数代码:
public void setAnimation(final String assetName) {
this.animationName = assetName;
animationResId = 0;
setCompositionTask(fromAssets(assetName));
}
private LottieTask<LottieComposition> fromAssets(final String assetName) {
if (isInEditMode()) {
return new LottieTask<>(new Callable<LottieResult<LottieComposition>>() {
@Override public LottieResult<LottieComposition> call() {
return cacheComposition ?
LottieCompositionFactory.fromAssetSync(getContext(), assetName) : LottieCompositionFactory.fromAssetSync(getContext(), assetName, null);
}
}, true);
} else {
return cacheComposition ?
LottieCompositionFactory.fromAsset(getContext(), assetName) : LottieCompositionFactory.fromAsset(getContext(), assetName, null);
}
}
setCompositionTask函数代码段:
private void setCompositionTask(LottieTask<LottieComposition> compositionTask) {
clearComposition();
cancelLoaderTask();
this.compositionTask = compositionTask
.addListener(loadedListener)
.addFailureListener(wrappedFailureListener);
}
- 通过异步加载,最终会调用到fromJsonSync()对Json文件进行解析。LottieCompositionFactory.fromAsset()函数代码:
public static LottieTask<LottieComposition> fromAsset(Context context, final String fileName) {
// Prevent accidentally leaking an Activity.
final Context appContext = context.getApplicationContext();
return cache(fileName, new Callable<LottieResult<LottieComposition>>() { //在这里它会先从缓存中去找,如果找不到才会去加载资源
@Override public LottieResult<LottieComposition> call() {
return fromAssetSync(appContext, fileName);
}
});
}
- 解析结果通过LottieListener->onResult回调到主线程,然后会将Json数据转换成LottieComposition对象。LottieTask类中回调代码段:
private void notifyListeners() {
// Listeners should be called on the main thread.
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
if (result == null || task.isCancelled()) {
return;
}
// Local reference in case it gets set on a background thread.
LottieResult<T> result = LottieTask.this.result;
if (result.getValue() != null) {
notifySuccessListeners(result.getValue());
} else {
notifyFailureListeners(result.getException());
}
}
});
}
LottieListener->onResult()代码段:
public class LottieAnimationView extends AppCompatImageView {
private final LottieListener<LottieComposition> loadedListener = new LottieListener<LottieComposition>() {
@Override public void onResult(LottieComposition composition) {
setComposition(composition);
}
};
private final LottieListener<Throwable> wrappedFailureListener = new LottieListener<Throwable>() {
@Override
public void onResult(Throwable result) {
if (fallbackResource != 0) {
setImageResource(fallbackResource);
}
LottieListener<Throwable> l = failureListener == null ? DEFAULT_FAILURE_LISTENER : failureListener;
l.onResult(result);
}
};
...
- lottieDrawable.setComposition(),将LottieComposition对象设置给LottieDrawable。
// LottieAnimationView
public void setComposition(@NonNull LottieComposition composition) {
if (L.DBG) {
Log.v(TAG, "Set Composition \n" + composition);
}
lottieDrawable.setCallback(this);
this.composition = composition;
boolean isNewComposition = lottieDrawable.setComposition(composition);
enableOrDisableHardwareLayer();
if (getDrawable() == lottieDrawable && !isNewComposition) {
// We can avoid re-setting the drawable, and invalidating the view, since the composition
// hasn't changed.
return;
}
// If you set a different composition on the view, the bounds will not update unless
// the drawable is different than the original.
setImageDrawable(null);
setImageDrawable(lottieDrawable);
requestLayout();
for (LottieOnCompositionLoadedListener lottieOnCompositionLoadedListener : lottieOnCompositionLoadedListeners) {
lottieOnCompositionLoadedListener.onCompositionLoaded(composition);
}
}
- 通过LottieDrawable生成CompositionLayer对象,并初始化基本的属性
// LottieDrawable
public boolean setComposition(LottieComposition composition) {
if (this.composition == composition) {
return false;
}
clearComposition();
this.composition = composition;
buildCompositionLayer();
animator.setComposition(composition);
setProgress(animator.getAnimatedFraction());
setScale(scale);
updateBounds();
...
}
private void buildCompositionLayer() {
compositionLayer = new CompositionLayer(
this, LayerParser.parse(composition), composition.getLayers(), composition);
if (outlineMasksAndMattes) {
compositionLayer.setOutlineMasksAndMattes(true);
}
}
- CompositionLayer会根据层的类型不同而生成不同的层,这个是对所有层进行管理的一个类,这个类也是继承自BaseLayer(BaseLayer是所有层的父类)。
public CompositionLayer(LottieDrawable lottieDrawable, Layer layerModel, List<Layer> layerModels,
LottieComposition composition) {
...
BaseLayer mattedLayer = null;
for (int i = layerModels.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
Layer lm = layerModels.get(i);
BaseLayer layer = BaseLayer.forModel(lm, lottieDrawable, composition);
if (layer == null) {
continue;
}
layerMap.put(layer.getLayerModel().getId(), layer);
if (mattedLayer != null) {
mattedLayer.setMatteLayer(layer);
mattedLayer = null;
} else {
layers.add(0, layer);
switch (lm.getMatteType()) {
case Add:
case Invert:
mattedLayer = layer;
break;
}
}
}
...
}
根据不同的LayerType绘制不同的图层
// BaseLayer.java
@Nullable
static BaseLayer forModel(
CompositionLayer compositionLayer, Layer layerModel, LottieDrawable drawable, LottieComposition composition) {
switch (layerModel.getLayerType()) {
case SHAPE:
return new ShapeLayer(drawable, layerModel, compositionLayer);
case PRE_COMP:
return new CompositionLayer(drawable, layerModel,
composition.getPrecomps(layerModel.getRefId()), composition);
case SOLID:
return new SolidLayer(drawable, layerModel);
case IMAGE:
return new ImageLayer(drawable, layerModel);
case NULL:
return new NullLayer(drawable, layerModel);
case TEXT:
return new TextLayer(drawable, layerModel);
case UNKNOWN:
default:
// Do nothing
Logger.warning("Unknown layer type " + layerModel.getLayerType());
return null;
}
}
- 通过setImageDrawable(lottieDrawable)将图像显示出来,显示第一帧动画。
// LottieDrawable
public boolean setComposition(LottieComposition composition) {
if (this.composition == composition) {
return false;
}
isDirty = false;
clearComposition();
this.composition = composition;
buildCompositionLayer();
animator.setComposition(composition);
setProgress(animator.getAnimatedFraction());
setScale(scale);
// We copy the tasks to a new ArrayList so that if this method is called from multiple threads,
// then there won't be two iterators iterating and removing at the same time.
Iterator<LazyCompositionTask> it = new ArrayList<>(lazyCompositionTasks).iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
LazyCompositionTask t = it.next();
// The task should never be null but it appears to happen in rare cases. Maybe it's an oem-specific or ART bug.
// https://github.com/airbnb/lottie-android/issues/1702
if (t != null) {
t.run(composition);
}
it.remove();
}
lazyCompositionTasks.clear();
composition.setPerformanceTrackingEnabled(performanceTrackingEnabled);
// Ensure that ImageView updates the drawable width/height so it can
// properly calculate its drawable matrix.
Callback callback = getCallback();
if (callback instanceof ImageView) {
((ImageView) callback).setImageDrawable(null);
((ImageView) callback).setImageDrawable(this);
}
return true;
}
3、如何加载JSON数据并显示图像的
animationView.playAnimation();
- 利用属性动画计算进度
在初始化LottieDrawable的同时也会创建LottieValueAnimator,LottieValueAnimator继承至ValueAnimator,Lottie的动画是用到了属性动画来产生一个0~1的插值,根据不同的插值来设置当前动画进度。
初始化代码:
public class LottieDrawable extends Drawable implements Drawable.Callback, Animatable {
private interface LazyCompositionTask {
void run(LottieComposition composition);
}
private final Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
private LottieComposition composition;
private final LottieValueAnimator animator = new LottieValueAnimator();
...
在LottieDrawable构造函数中注册监听进度回调:
private final ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener progressUpdateListener = new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
if (compositionLayer != null) {
compositionLayer.setProgress(animator.getAnimatedValueAbsolute());
}
}
};
public LottieDrawable() {
animator.addUpdateListener(progressUpdateListener);
}
当执行LottieDrawable.playAnimation方法时,也是调用animator.playAnimation()
@MainThread
public void playAnimation() {
if (compositionLayer == null) {
lazyCompositionTasks.add(c -> playAnimation());
return;
}
if (animationsEnabled() || getRepeatCount() == 0) {
animator.playAnimation();
}
if (!animationsEnabled()) {
setFrame((int) (getSpeed() < 0 ? getMinFrame() : getMaxFrame()));
animator.endAnimation();
}
}
- 通过CompositionLayer将setProgress实现的显示具体进度动画
代码如下:
@Override public void setProgress(@FloatRange(from = 0f, to = 1f) float progress) {
super.setProgress(progress);
if (timeRemapping != null) {
// The duration has 0.01 frame offset to show end of animation properly.
// https://github.com/airbnb/lottie-android/pull/766
// Ignore this offset for calculating time-remapping because time-remapping value is based on original duration.
float durationFrames = lottieDrawable.getComposition().getDurationFrames() + 0.01f;
float compositionDelayFrames = layerModel.getComposition().getStartFrame();
float remappedFrames = timeRemapping.getValue() * layerModel.getComposition().getFrameRate() - compositionDelayFrames;
progress = remappedFrames / durationFrames;
}
if (timeRemapping == null) {
progress -= layerModel.getStartProgress();
}
//Time stretch needs to be divided if is not "__container"
if (layerModel.getTimeStretch() != 0 && !"__container".equals(layerModel.getName())) {
progress /= layerModel.getTimeStretch();
}
for (int i = layers.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
layers.get(i).setProgress(progress);
}
}
- 通知进度改变
// BaseKeyframeAnimation
public void setProgress(@FloatRange(from = 0f, to = 1f) float progress) {
if (progress < getStartDelayProgress()) {
progress = getStartDelayProgress();
} else if (progress > getEndProgress()) {
progress = getEndProgress();
}
if (progress == this.progress) {
return;
}
this.progress = progress;
notifyListeners();
}
其中notifyListeners中代码:
public void notifyListeners() {
for (int i = 0; i < listeners.size(); i++) {
listeners.get(i).onValueChanged();
}
}
- 最终回调到LottieAnimationView的invalidateDrawable
@Override public void invalidateDrawable(@NonNull Drawable dr) {
if (getDrawable() == lottieDrawable) {
// We always want to invalidate the root drawable so it redraws the whole drawable.
// Eventually it would be great to be able to invalidate just the changed region.
super.invalidateDrawable(lottieDrawable);
} else {
// Otherwise work as regular ImageView
super.invalidateDrawable(dr);
}
}
- 最后触发LottieDrawable重绘
@Override public void draw(@NonNull Canvas canvas) {
L.beginSection("Drawable#draw");
if (compositionLayer == null) {
return;
}
...
matrix.reset();
matrix.preScale(scale, scale);
compositionLayer.draw(canvas, matrix, alpha);
L.endSection("Drawable#draw");
...
}
其中CompositionLayer.draw函数:
@Override void drawLayer(Canvas canvas, Matrix parentMatrix, int parentAlpha) {
L.beginSection("CompositionLayer#draw");
canvas.save();
newClipRect.set(0, 0, layerModel.getPreCompWidth(), layerModel.getPreCompHeight());
parentMatrix.mapRect(newClipRect);
for (int i = layers.size() - 1; i >= 0 ; i--) {
boolean nonEmptyClip = true;
if (!newClipRect.isEmpty()) {
nonEmptyClip = canvas.clipRect(newClipRect);
}
if (nonEmptyClip) {
BaseLayer layer = layers.get(i);
layer.draw(canvas, parentMatrix, parentAlpha);
}
}
canvas.restore();
L.endSection("CompositionLayer#draw");
}
4、原理总结:
- 首先会通过LottieCompositionFactory的对应类型设置json资源文件
- 然后再fromJsonSync方法里面会把json文件解析出图层的大小并且绘制相应的图片资源文件和图层
- 资源加载完后,会在回调里面设置LottieAnimationView的Composition,从而调用LottieDrawable的setComposition()方法
- 在setComposition方法里面会通过buildCompositionLayer()方法去创建一个CompositionLayer图层
- 其中CompositionLayer继承BaseLayer,通过BaseLayer的forModel()静态方法获取不同的图层类型
- 然后LottieDrawable的setComposition()方法里面会开始执行一个ValueAnimation动画
- 这个动画会驱使BaseLayer的draw()方法不断执行,通过Matrix的矩阵形式不断的绘制各个图层从而形成动画
- 而这些图层的矩阵变换的数据来源于BaseKeyframeAnimation里面有一个Keyframe对象会去Json里面获取相应得数据。
参考
Lottie开源动画库介绍与使用示例
AE插件bodymovin如何安装
Lottie 实现炫酷动画背后的原理
Lottie的使用和源码详解
Lottie官网