C++深度解析教程笔记11
本文学习自狄泰软件学院 唐佐林老师的 C++深度解析教程,图片全部来源于课程PPT,仅用于个人学习记录
第37课 - 智能指针分析
实验-内存未释放并优化
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int i;
public:
Test(int i)//带参数的构造函数
{
this->i = i;
cout<<"Test();"<<endl;
}
int value()
{
return i;
}
~Test()//析构函数
{
cout<<"~Test();"<<endl;
}
};
//优化,定义一个指针类,成员变量类型为Test*
class pointer
{
Test * mp;
public:
pointer(Test* p=NULL)//构造函数默认值为NULL
{
mp=p;
}
Test * operator ->()
{
return mp;
}
Test operator *()
{
return *mp;
}
~pointer()
{
delete mp;
}
};
int main()
{
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
//Test* p = new Test(i);
//优化
pointer p = new Test(i);
cout << p->value() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
实验-指针作为类
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int i;
public:
Test(int i)
{
cout << "Test(int i)" << endl;
this->i = i;
}
int value()
{
return i;
}
~Test()
{
cout << "~Test()" << endl;
}
};
class Pointer
{
Test* mp;
public:
Pointer(Test* p = NULL)
{
mp = p;
}
Pointer(const Pointer& obj)
{
mp = obj.mp;
const_cast<Pointer&>(obj).mp = NULL;
}
Pointer& operator = (const Pointer& obj)
{
if( this != &obj )
{
delete mp;
mp = obj.mp;
const_cast<Pointer&>(obj).mp = NULL;
}
return *this;
}
Test* operator -> ()
{
return mp;
}
Test& operator * ()
{
return *mp;
}
bool isNull()
{
return (mp == NULL);
}
~Pointer()
{
delete mp;
}
};
int main()
{
Pointer p1 = new Test(0);
cout << p1->value() << endl;
Pointer p2 = p1;
cout << p1.isNull() << endl;
cout << p2->value() << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
Test(int i)
0
1
0
~Test()
*/
智能指针的使用军规
只能用来指向堆空间中的对象或者变量
小结
指针特征操作符(->和*)可以被重载重载
指针特征符能够使用对象代替指针
智能指针只能用于指向堆空间中的内存
智能指针的意义在于最大程度的避免内存问题
第38课 - 逻辑操作符的陷阱
逻辑运算符的原生语义
一操作数只有两种值(true和false)
一逻辑表达式不用完全计算就能确定最终值一最终结果只能是true或者false
实验-逻辑与或
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int func(int i)
{
cout << "int func(int i) : i = " << i << endl;
return i;
}
int main()
{
if( func(0) && func(1) )
{
cout << "Result is true!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Result is false!" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
if( func(0) || func(1) )
{
cout << "Result is true!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Result is false!" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
/*
int func(int i) : i = 0
Result is false!
int func(int i) : i = 0
int func(int i) : i = 1
Result is true!
*/
逻辑操作符可以重载吗?重载逻辑操作符有什么意义?
实验-重载与或
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int mValue;
public:
Test(int v)
{
mValue = v;
}
int value() const
{
return mValue;
}
};
bool operator && (const Test& l, const Test& r)
{
return l.value() && r.value();
}
bool operator || (const Test& l, const Test& r)
{
return l.value() || r.value();
}
Test func(Test i)
{
cout << "Test func(Test i) : i.value() = " << i.value() << endl;
return i;
}
int main()
{
Test t0(0);
Test t1(1);
if( operator && (func(t0) , func(t1)))
{
cout << "Result is true!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Result is false!" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
if( func(t0) && func(t1) )
{
cout << "Result is true!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Result is false!" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
if( operator ||(func(t0), func(t1) ))
{
cout << "Result is true!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Result is false!" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
if( func(1) || func(0) )
{
cout << "Result is true!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Result is false!" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
/*
Test func(Test i) : i.value() = 1
Test func(Test i) : i.value() = 0
Result is false!
Test func(Test i) : i.value() = 1
Test func(Test i) : i.value() = 0
Result is false!
Test func(Test i) : i.value() = 1
Test func(Test i) : i.value() = 0
Result is true!
Test func(Test i) : i.value() = 0
Test func(Test i) : i.value() = 1
Result is true!
*/
■一些有用的建议
一实际工程开发中避免重载逻辑操作符
一通过重载比较操作符代替逻辑操作符重载
一直接使用成员函数代替逻辑操作符重载
一使用全局函数对逻辑操作符进行重载
逻辑操作符重载后无法完全实现原生的语义
问题的本质分析
1.C++通过函数调用扩展操作符的功能
2.进入函数体前必须完成所有参数的计算
3.函数参数的计算次序是不定的
4.短路法则完全失效
小结
C++从语法上支持逻辑操作符重载
重载后的逻辑操作符不满足短路法则
工程开发中不要重载逻辑操作符
通过重载比较操作符替换逻辑操作符重载
通过专用成员函数替换逻辑操作符重载
第39课 - 逗号操作符的分析
逗号操符(,)构成逗号表达式
一逗号表达式用于将多个子表达式接为一人表达式一逗号表达式的值为最后一个子表达式的值
一逗号表达式中的前N-1人子表达式可以没有返回值
一逗号表达式按照从左向右的顺序计算每个子表达式的值 expl, exp2, exp3, … , expN
实验-逗号表达式
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void func(int i)
{
cout << "func() : i = " << i << endl;
}
int main()
{
int a[3][3] = {
(0, 1, 2),
(3, 4, 5),
(6, 7, 8)
};
/*int a[3][3] = {
{0, 1, 2},
{3, 4, 5},
{6, 7, 8}
};*/
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while( i < 5 )
func(i),
i++;
for(i=0; i<3; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<3; j++)
{
cout << a[i][j] << endl;
}
}
(i, j) = 6;//j=6
cout << "i = " << i << endl;
cout << "j = " << j << endl;
return 0;
}
/*
func() : i = 0
func() : i = 1
func() : i = 2
func() : i = 3
func() : i = 4
2
5
8
0
0
0
0
0
0
i = 3
j = 6
*/
实验-重载逗号操作符的问题
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int mValue;
public:
Test(int i)
{
mValue = i;
}
int value()
{
return mValue;
}
};
/* case2:
Test& operator , (const Test& a, const Test& b)
{
return const_cast<Test&>(b);
}
*/
Test func(Test& i)
{
cout << "func() : i = " << i.value() << endl;
return i;
}
int main()
{
Test t0(0);
Test t1(1);
//Test tt=(t0,t1);
// Test tt = (func(t0), func(t1)); case1 调用默认逗号
//Test tt = (func(t0), func(t1)); //case2 (operator , (func(t0), func(t1)) ) 等价于 (func(t0), func(t1))
Test tt = func(t1);//case3
cout << tt.value() << endl; // 1
return 0;
}
/*
case1:未手动重载逗号
func() : i = 0
func() : i = 1
1
case2:手动重载逗号
func() : i = 1
func() : i = 0
1
func() : i = 1
1
*/
小结
第40课 - 前置操作符和后置操作符
i++; ++i;
的值作为返回值,i自增自增 1,i 的值作为返回值
//i
下面的代码有没有区别?为什么?
实验-vs2010反汇编
int i = 0;
000C139E mov dword ptr [i],0
i++;
000C13A5 mov eax,dword ptr [i]
000C13A8 add eax,1
000C13AB mov dword ptr [i],eax
++i;
000C13AE mov eax,dword ptr [i]
000C13B1 add eax,1
000C13B4 mov dword ptr [i],eax
实验-重载自增操作符
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int mValue;
public:
Test(int i)
{
mValue = i;
}
int value()
{
return mValue;
}
Test& operator ++ ()//前置++
{
++mValue;
return *this;
}
//无后置重载 报错error: no 'operator++(int)' declared for postfix '++' [-fpermissive]
/*
void operator++(int)//编译通过了
{
}*/
Test operator++(int)//优化
{
Test res=*this;//Test res(mValue);//先取值
mValue++; //再加一
return res;
}
/*
Test operator ++ (int)//后置++
{
Test ret(mValue);
mValue++;
return ret;
}*/
};
int main()
{
Test t(0);
cout<<"t="<<t.value()<<endl;
Test tt= t.operator++(); //Test tt=++t;
cout<<"tt="<<tt.value()<<endl;
cout<<"t="<<t.value()<<endl;
//前置++ ok
/*
t=0
tt=1
t=1
*/
// t++;// error: no 'operator++(int)' declared for postfix '++' [-fpermissive]t++;
// t.operator ++ ();
Test h(0);
cout<<"h="<<h.value()<<endl;
//Test hh=h.operator++(2); //Test hh=h++;
Test hh=h.operator++(0); //占位参数
cout<<"hh="<<hh.value()<<endl;
cout<<"h="<<h.value()<<endl;
return 0;
}
完善复数类:自增重载
Complex& operator++()
{
a++;
b++;
return *this;
}
Complex operator++(int)
{
Complex ret=*this;//Complex ret(a, b);
a++;
b++;
return ret;
}
小结
第41课 - 类型转换函数(上)
实验-隐式类型转换
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
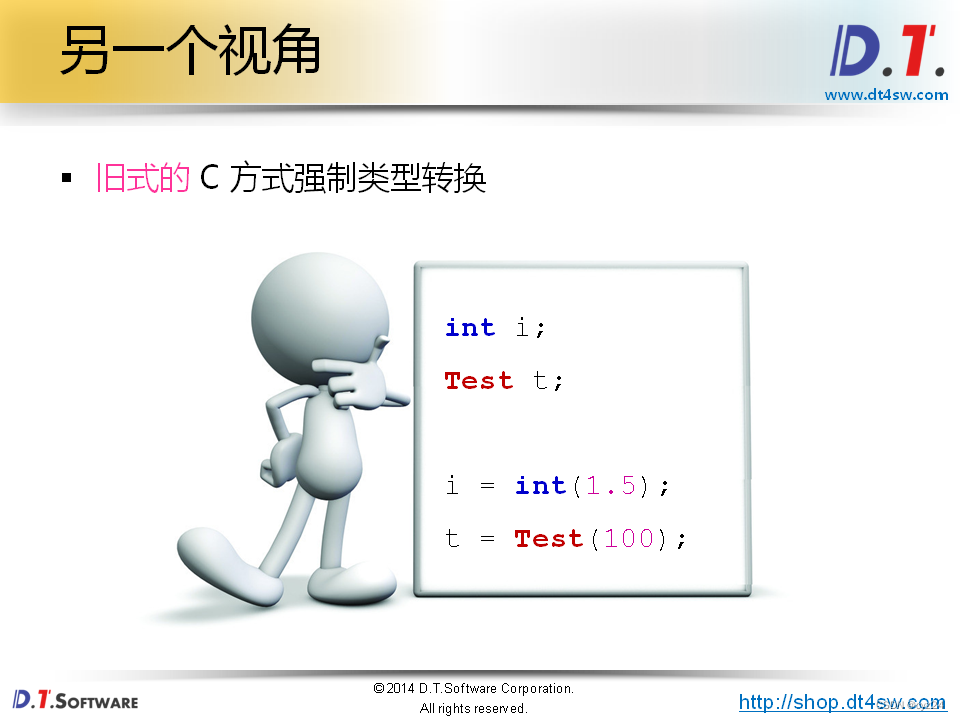
short s = 'a';
unsigned int ui = 1000;
int i = -2000;
double d = i;
cout << "d = " << d << endl;
cout << "ui = " << ui << endl;
cout << "ui + i = " << ui + i << endl;
if( (ui + i) > 0 )
{
cout << "Positive" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Negative" << endl;
}
cout << "sizeof(s + 'b') = " << sizeof(s + 'b') << endl;//编译器并没有隐式转为short
return 0;
}
/*
d = -2000
ui = 1000
ui + i = 4294966296
Positive
sizeof(s + 'b') = 4 */
实验-类类型与int相互转换
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int mValue;
public:
Test()
{
mValue = 0;
}
/*
explicit Test(int i)
{
mValue = i;
}*/
Test(int i)
{
mValue = i;
}
Test operator + (const Test& p)
{
Test ret(mValue + p.mValue);
return ret;
}/**/
int value()
{
return mValue;
}
};
int main()
{
Test t;
//类类型转换为int
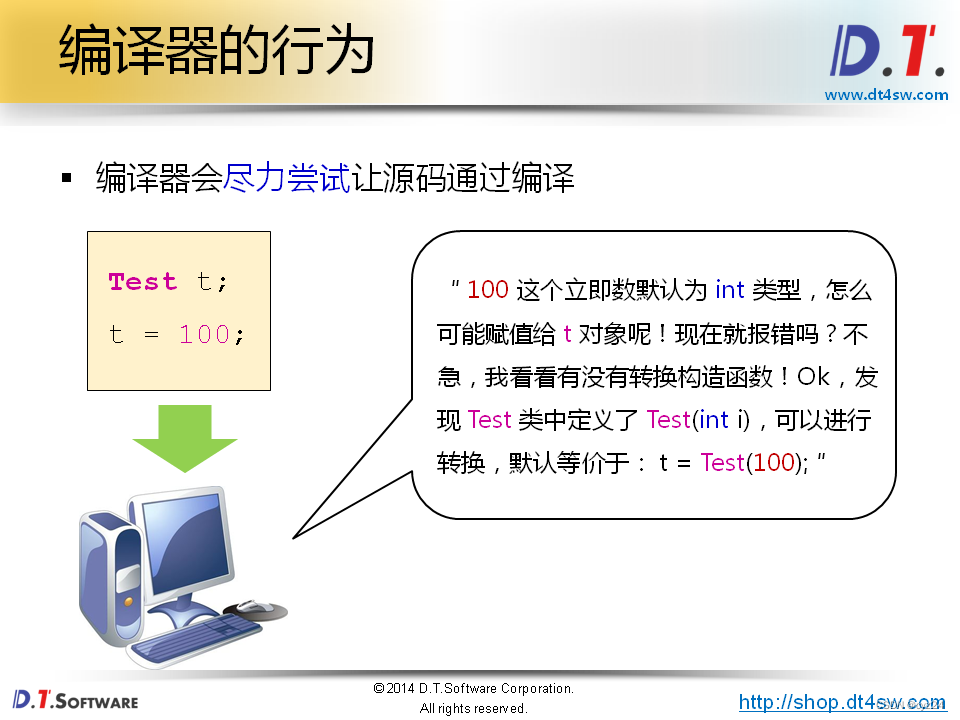
t = static_cast<Test>(5); // t = Test(5);
Test r;
r = t + 10;//未explicit 构造函数,调用重载,自动隐式转换,r.value()=15,要避免
// r = t + static_cast<Test>(10);
//r = t + Test(10);
cout << r.value() << endl;
return 0;
}
小结
第42课 - 类型转换函数(下)
实验-类型转换函数operator
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int mValue;
public:
Test(int i = 0)
{
mValue = i;
}
int value()
{
return mValue;
}
operator int ()//类型转换函数
{
return mValue;
}
};
int main()
{
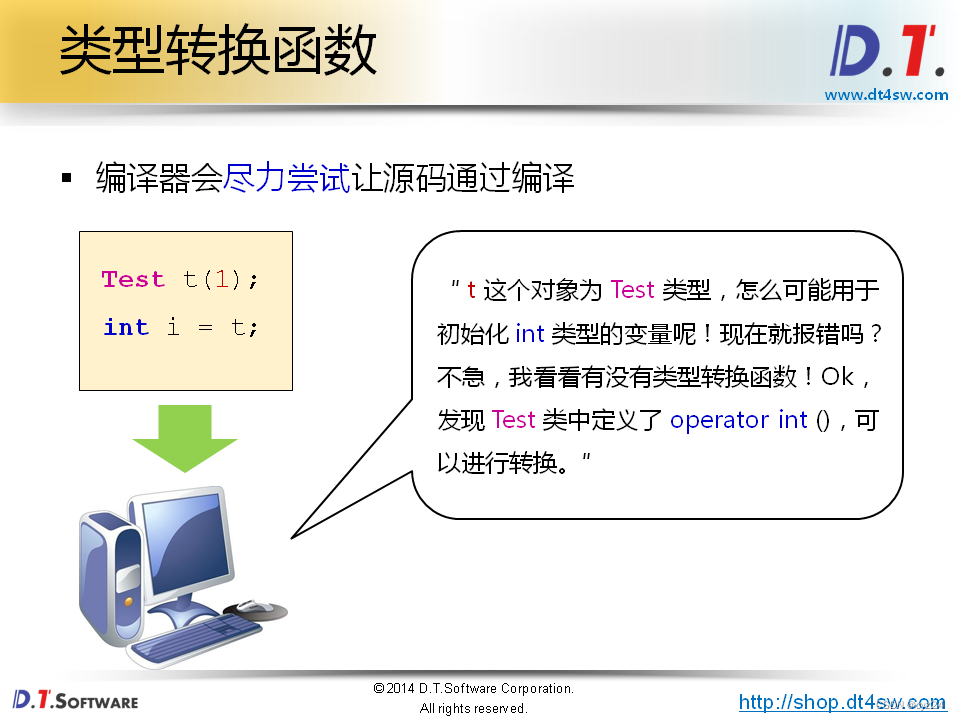
Test t(100);
int i = t;
cout << "t.value() = " << t.value() << endl; //t.value() = 100
cout << "i = " << i << endl; //i = 100
return 0;
}
实验-类型转换成员函数
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test;
class Value
{
public:
Value()
{
}
explicit Value(Test& t)//
{
}
};
class Test
{
int mValue;
public:
Test(int i = 0)
{
mValue = i;
}
int value()
{
return mValue;
}
operator Value()//Value ToValue()
{
Value ret;
cout << "operator Value()" << endl;
return ret;
}
};
int main()
{
Test t(100);
Value v = t;//Value v = t.ToValue();
return 0;
}
//operator Value()