前言:
这里只是模拟了spring的一些核心部分的功能,并且不是特别的完整,还有许多的需要完善的地方。
这里是基于注解的方法的,整体的脉络和解析xml文件是差不多的,但是如果细扣里面的细节还是有很多的不一样的,目的只是为了更好的理解spring框架的,学习其思想。
涉及到的前置知识:
- 自定义注解
- 反射
- File的读取
- 类加载
源码地址:
https://gitee.com/heshancai/hsc-spring.git
简单模拟实现的功能:
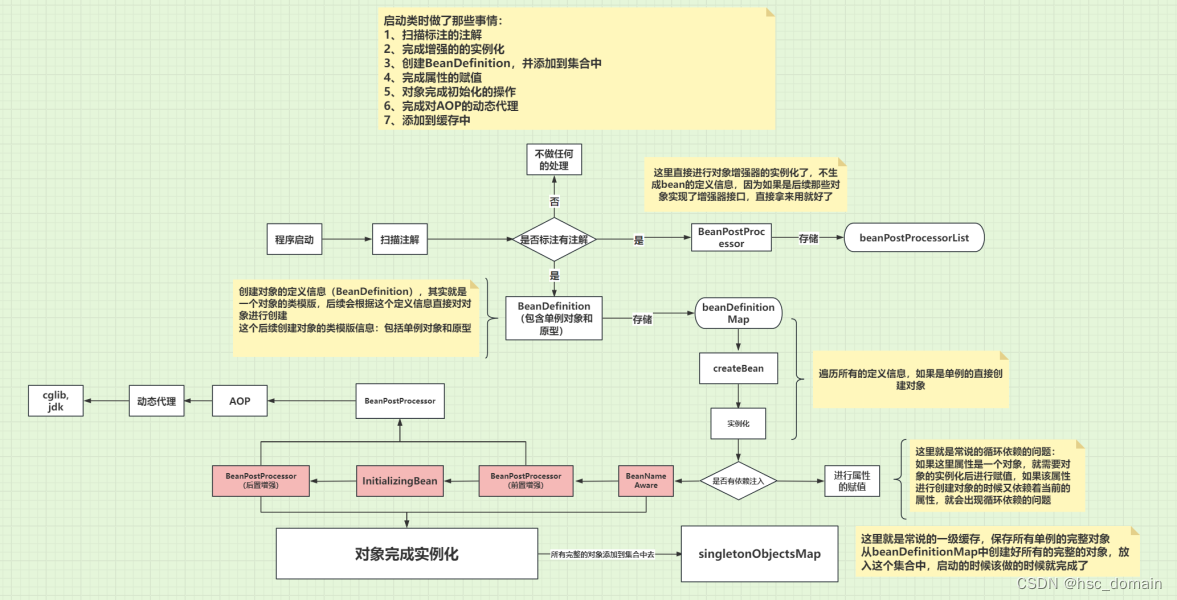
1、ioc控制反转,依赖自动,Aop代理对象,进行注入,通过注解的方式进注解的扫描
2、BeanPostProcessor增强器功能,BeanNameAware功能,InitializingBean功能
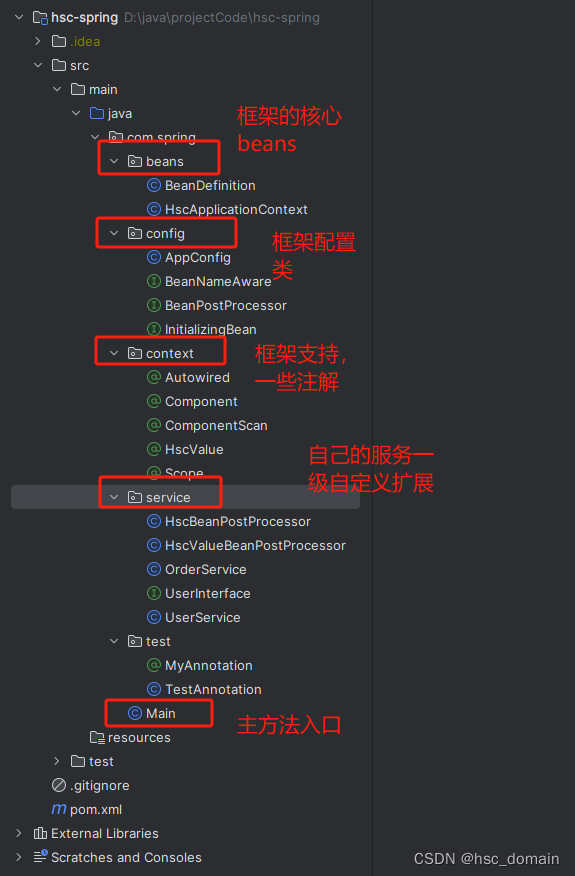
框架的核心对象
BeanDefinition:bean的定义信息
package com.spring.beans;
/**
* 类:bean的定义信息,bean的描述信息
*/
public class BeanDefinition {
//当前的bean的定义信息的类型
private Class type;
//当前的对象的作用域:单例或者原型
private String scope;
//是否懒加载
private boolean isLazy;
public Class getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(Class type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getScope() {
return scope;
}
public void setScope(String scope) {
this.scope = scope;
}
public boolean isLazy() {
return isLazy;
}
public void setLazy(boolean lazy) {
isLazy = lazy;
}
}
HscApplicationContext:启动进行扫描
package com.spring.beans;
import com.spring.config.BeanNameAware;
import com.spring.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import com.spring.config.InitializingBean;
import com.spring.context.*;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.io.File;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class HscApplicationContext {
//成员属性,闯入Class类型参数
private Class configClass;
//创建一个Map集合存放对象的定义信息,其实就是类的描述信息,用于后续创建对象
private Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new HashMap<>();
//存放完整的对象,创建完成的,类似spring的一级缓存
private Map<String, Object> singletonObjectsMap = new HashMap<>();
//存饭增强器对象的集合
private List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessorList = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 在创建对象时就直接将bean创建出来
*
* @param configClass
*/
public HscApplicationContext(Class configClass) {
//给当前的成员属性configClass赋值
this.configClass = configClass;
//1、传入需要spring管理的配置来创建对象
//2、扫描配置类上注解的要扫描的包,看那些类要创建对象
scan(configClass);
//3、扫描完所有要创建对象的类,开始遍历创建对象,根据BeanDefinition创建对象
for (Map.Entry<String, BeanDefinition> entry : beanDefinitionMap.entrySet()) {
//获取对象的名称
String beanName = entry.getKey();
//获取对应的BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = entry.getValue();
//判断当前的beanDefinition是否时单例
if (beanDefinition.getScope().equals("singleton")) {
//单例对象直接创建对象
Object bean = createBean(beanName, beanDefinition);
//将对象放入缓存中,也就是spring常说的一级缓存,获取对象的时候可以直接进行获取到
singletonObjectsMap.put(beanName, bean);
}
}
}
/**
* 创建对象方法
*
* @param beanName
* @param beanDefinition
* @return
*/
private Object createBean(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
//获取当前的class对象
Class definitionType = beanDefinition.getType();
Object instance = null;
try {
// 【实例化对象】:根据Class获取对应的构造器,实例化,创建对象
instance = definitionType.getConstructor().newInstance();
//完成属性的赋值操作:获取所有的属性值
for (Field field : definitionType.getDeclaredFields()) {
//如果有自动注入的话,给属性赋值
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)) {
//强力破解私有属性
field.setAccessible(true);
//给当前的对象instance属性进行赋值 注意这里当一个对象里面依赖着另外的对象,可能这个属性并没进行创建,这里就很像spring说的循环依赖的问题
field.set(instance, getBean(field.getName()));
}
}
//在初始化之前对象对实现了Aware接口的对象做名称的赋值
if (instance instanceof BeanNameAware) {
//如果该对象实现了BeanNameAware接口
((BeanNameAware) instance).setBeanName(beanName);
}
//看当前的对象是否要做前置增强,如果需要做一些增强处理
//获取所有的增强器对象
//前置增强,在初始化之前,我们可以对bean做一些操作,在这里对自定义的注解实现名字的实现
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessorList) {
beanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(instance, beanName);
}
//【初始化bean】调用实现了InitializingBean接口的方法
if (instance instanceof InitializingBean) {
//如果当前的对象实现了InitializingBean接口,调用方法
((InitializingBean) instance).afterPropertiesSet();
}
//初始化后的后置增强,这里做aop的功能,生成代理对象
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessorList) {
//接受代理对象的返回,这里一定要记得接收返回值(代理的对象)
instance = beanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(instance, beanName);
}
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return instance;
}
/**
* 扫描包下所有的注解
*
* @param configClass
*/
private void scan(Class configClass) {
//1、根据ComponetScan类型获取当前的配置的类上的注解信息
ComponentScan configClassAnnotation = (ComponentScan) configClass.getAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
//2、获取注解上value值 为一组数组:com.spring.service com.spring.context
String[] paths = configClassAnnotation.value();
//创建一个集合来装替换后得路径
List<String> listPaths = new ArrayList<>();
//3、将值中的.替换为 / com.spring.service转为com/spring/service 变成文件夹路径
for (String path : paths) {
path=path.replace(".", "/");
listPaths.add(path);
}
//获取类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = HscApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
//扫描这两个包下面的类
listPaths.stream().forEach(path -> {
//根据类加载器获取对应的URL信息
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(path);
//5、读取文件夹路径com/spring/service 转为File对象
File file = new File(resource.getFile());
//检查是否是否是一个目录(文件夹)
if (file.isDirectory()) {
//获取指定包下target下所有的class文件
for (File f : file.listFiles()) {
//获取的当前文件的绝对路径: D:\java\projectCode\hsc-spring\target\classes\com\spring\service\OrderService.class
String absolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath();
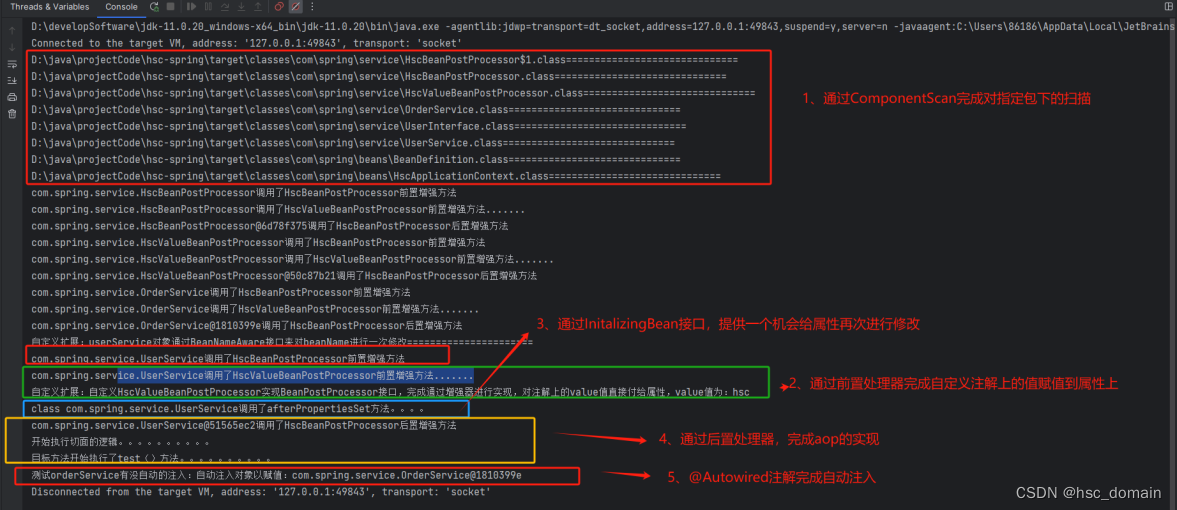
System.out.println(absolutePath + "==============================");
//路径截取 D:\java\projectCode\hsc-spring\target\classes\com\spring\service\UserService.class 截取为:com\spring\service\UserService
absolutePath = absolutePath.substring(absolutePath.indexOf("com"), absolutePath.indexOf(".class"));
// com\spring\service\UserService转为--->com.spring.service.UserService ,
// \符号替代为 . 转义字符:"\\" 表示一个字面上的反斜杠字符 \,则需要写成 \\
absolutePath = absolutePath.replace("\\", ".");
try {
//根据类文件的相对路径加载class文件
Class<?> clazz = classLoader.loadClass(absolutePath);
//过滤所有的类,看那个类上面放有@Component注解
//判断当前类是否是包存在@Component注解
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
//【处理增强器】判断当前的类型有没有实现BeanPostProcessor这个增强的接口
if (BeanPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
//注意这里用的是clazz对象进行判断, 并不是用对象来进行判断是否实现BeanPostProcessor接口
//如果实现了该接口,说明当前对象是一个增强器
//将当前的对象强转为BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor instance = (BeanPostProcessor) clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();
//将当前的增强对象添加到集合中
beanPostProcessorList.add(instance);
}
//获取当前类上的注解对象
Component componentAnnotation = clazz.getAnnotation(Component.class);
//获取创建对象的名称
String beanName = componentAnnotation.value();
//获取该注解中的value值,如果注解value不设置默认为""
if ("".equals(beanName)) {
//如果value值为"",说明没有设置对象的名称
// 如果为"" ,根据类名生成对象名称(beanName)
beanName = Introspector.decapitalize(clazz.getSimpleName());
}
//创建bean的定义信息对象
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
//设置对象的类型属性
beanDefinition.setType(clazz);
//判断当前的类对象,是否设置有@Scope注解
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Scope.class)) {
//如果当前的类标注有@Scope注解
//判断设置的值是单例还是原型
//获取注解对象信息
Scope scopeAnnotation = clazz.getAnnotation(Scope.class);
String scopeValue = scopeAnnotation.value();
//设置当前对象的定义信息
beanDefinition.setScope(scopeValue);
} else {
//如果当前的类上面没有标注有注解,默认是单例的对象,直接进行设置
beanDefinition.setScope("singleton");
}
//完成对当前的类定义信息,放入集合中,为后续的创建对象做准备
beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
});
}
/**
* 根据beanName的名称获取
*
* @param beanName
*/
public Object getBean(String beanName) {
//判断beanDefinition是否存在要创建的bean
if (!this.beanDefinitionMap.containsKey(beanName)) {
//如果不存在直接抛出异常,说明该对象并不是由我们进行管理的
throw new NullPointerException();
}
//判断传入要获取的bean是否是单例的bean,获取BeanDefinition中的定义信息
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
//判断是否是单例的
if (beanDefinition.getScope().equals("singleton")) {
//直接从集合中取 ,因为单例的bean启动的时候已经创建好了
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjectsMap.get(beanName);
//这里注意一个问题,当一个对象创建时依赖着一个属性对象时,这个属性并没有创建,一个执行顺序的问题,这里singletonObject获取到的对象可能是为空的
if (singletonObject == null) {
//如果为空创建对象
singletonObject = createBean(beanName, beanDefinition);
//单例对象放到缓存中
singletonObjectsMap.put(beanName, singletonObject);
}
return singletonObject;
} else {
//原型的bean,重新进行对象的创建
Object prototypeBean = createBean(beanName, beanDefinition);
return prototypeBean;
}
}
}
框架自己的配置类
AppConfig
package com.spring.config;
import com.spring.support.ComponetScan;
/**
* 创建一个配置类,扫描指定的包
*/
@ComponetScan(value = {"com.spring.service","com.spring.support"}) //模拟spring中的注解:自定义注解:扫描com.spring.service包上所有的类
public class AppConfig {
}
BeanNameAware
package com.spring.config;
/**
* 模拟spring给对象提供一个对象名称设置的接口
*/
public interface BeanNameAware {
/**
* 提示一个扩展用来设置对象的名称,比如说我们想获取到我们给spring管理的对象生命的对象名称是什么?
* 如果是我们自己的有设置的名称我们会知道对象的名称就是我们自己设置的,但是如果说是spring自己的用的名称生成策略生成的呢,此时这里就可以拿到对应的名称做相应的操作了
* 只要对象实现了该接口,并且对象该方法做一个实现
* @param name
*/
void setBeanName(String name);
}
BeanPostProcessor
package com.spring.config;
/**
* 模拟spring对bean对象前置增强和后置增强
*/
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* bean对象完成初始化之前的前置增强
* @param bean
* @param beanName
* @return
*/
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
return bean;
}
/**
* bean对象初始化完成后后置增强
* @param bean
* @param beanName
* @return
*/
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName){
return bean;
}
}
InitializingBean
package com.spring.config;
/**
* 模拟spring中InitializingBean接口的
*/
public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
框架的支持,注解信息
@Autowired注解
package com.spring.context;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* 自定义注解
* 创建一个自动注入的注解
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//当前的自定义的注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在
@Target(ElementType.FIELD) //可以应用于字段或属性声明
public @interface Autowired {
}
@Component注解
package com.spring.context;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* 模拟spring中Component注解
* 如果标准了该注解上的,则spring进行管理
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//当前的自定义的注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) //当前的自定义注解应用于类、接口(包括枚举)或注解类型
public @interface Component {
String value() default "";
}
@ComponentScan注解
package com.spring.context;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* 创建一个自定义的注解:
* 1、作用于类、接口(包括枚举)或注解类型
* 2、注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //当前的自定义的注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) //当前的自定义注解应用于类、接口(包括枚举)或注解类型
public @interface ComponentScan {
//定义属性value返回的类型为数组,如果不传的话,默认指为数组
String[] value() default {};
}
@HscValue注解
package com.spring.context;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* 创建一个自定义的注解,使用前置的增强对对象的属性进行赋值
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//当前的自定义的注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在
@Target(ElementType.FIELD) //可以应用于字段或属性声明
public @interface HscValue {
String value() default "";
}
package com.spring.context;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* 设置对象的作用域:单例或者原型
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//当前的自定义的注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) //当前的自定义注解应用于类、接口(包括枚举)或注解类型
public @interface Scope {
//如果传入的注解的没有值,则为""
String value() default "";
}
自己的服务,自定义的扩展
HscBeanPostProcessor
package com.spring.service;
import com.spring.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import com.spring.context.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* 创建自己的增强器实现
*/
//添加自定义的注解,我们自己的容器创建对象进行管理
@Component
public class HscBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
//这里所有的bean都经过,如果要单独对某个bean做处理,写对应的逻辑
System.out.println(bean.getClass().getName() + "调用了HscBeanPostProcessor前置增强方法");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
System.out.println(bean+ "调用了HscBeanPostProcessor后置增强方法");
//在这里可以是实现切面(Aop)的功能,生成一个代理对象
//对userService做代理对象
if (beanName.equals("userService")) {
//创建一个代理对象,创建当前的类加载器,当前对象代理接口
Object proxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(HscBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader(), bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("开始执行切面的逻辑。。。。。。。。。。");
//调用目标对象的方法
return method.invoke(bean, args);
}
});
//返回代理对象
return proxyInstance;
}
return bean;
}
}
HscValueBeanPostProcessor
package com.spring.service;
import com.spring.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import com.spring.context.Component;
import com.spring.context.HscValue;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
/**
* 做一个增强器,用作给对象的属性做赋值操作
*/
@Component //交给容器进行管理
public class HscValueBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
System.out.println(bean.getClass().getName() + "调用了HscValueBeanPostProcessor前置增强方法.......");
//获取当前的类所有的数下
for (Field field : bean.getClass().getDeclaredFields()) {
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(HscValue.class)) {
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
field.set(bean,field.getAnnotation(HscValue.class).value());
System.out.println("自定义扩展:自定义HscValueBeanPostProcessor实现BeanPostProcessor接口,完成通过增强器进行实现,对注解上的value值直接付给属性,value值为:"+field.getAnnotation(HscValue.class).value());
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
return bean;
}
}
OrderService
package com.spring.service;
import com.spring.context.Component;
@Component
public class OrderService {
}
UserInterface
package com.spring.service;
/**
* 创建一个接口做代理对象
*/
public interface UserInterface {
public void test();
}
UserService
package com.spring.service;
import com.spring.config.BeanNameAware;
import com.spring.config.InitializingBean;
import com.spring.context.*;
@Component("userService")
@Scope("singleton")
public class UserService implements UserInterface,BeanNameAware,InitializingBean {
//自动注入orderService
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
//通过增强器进行实现,对注解上的value值直接付给属性
@HscValue("hsc")
private String testName;
private String beanName;
/**
* 对象的名称做修改
*
* @param name
*/
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
//测试通过Aware接口的方式对当前对象的属性值进行赋值操作
System.out.println("自定义扩展:"+name+"对象通过BeanNameAware接口来对beanName进行一次修改======================");
this.beanName = name;
}
/**
* 属性完成成赋值有再提供一个机会来修改属性的行
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println(this.getClass() + "调用了afterPropertiesSet方法。。。。");
}
@Override
public void test() {
//测试orderService有没自动的注入
System.out.println("目标方法开始执行了test()方法。。。。。。。。。。");
System.out.println("测试orderService有没自动的注入:自动注入对象以赋值:" + orderService);
}
public String getTestName() {
return testName;
}
}
程序的入口
Main方法
package com.spring;
import com.spring.config.AppConfig;
import com.spring.service.UserInterface;
import com.spring.service.UserService;
import com.spring.beans.HscApplicationContext;
/**
* 简单模拟spring底层原理
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HscApplicationContext hscApplicationContext = new HscApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
//根据beanName,获取对应的对象
UserInterface userService = (UserInterface) hscApplicationContext.getBean("userService");
userService.test();
}
}