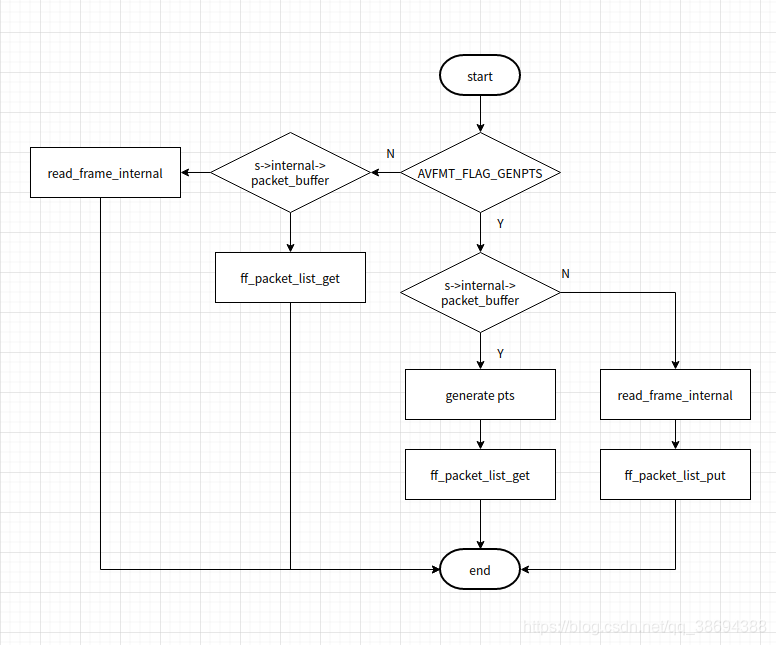
av_read_frame的作用是读取一帧视频数据或者读取多帧音频数据,读取的数据都是待解码的数据,该函数的流程如下所示:
函数的源码如下所示:
int av_read_frame(AVFormatContext *s, AVPacket *pkt)
{
const int genpts = s->flags & AVFMT_FLAG_GENPTS;
int eof = 0;
int ret;
AVStream *st;
//不自动生成时间戳,走此flow,好像一般不走这里
if (!genpts) {
// ffmpeg内部读取的时候其实是将解析出来的一帧帧数据放入一个队列中,所以此处先检查解析包队列中是否有数据,
// 如果有,直接读取,否则调用真正的读取函数。
// 此处为何要使用缓存队列而不是直接读取,因为在解析的时候有可能一次解析N个帧,
// 如mpegts 一个PES中可能包含2帧,所以解析出来的帧直接放入队列中。
ret = s->internal->packet_buffer
? ff_packet_list_get(&s->internal->packet_buffer,
&s->internal->packet_buffer_end, pkt)
: read_frame_internal(s, pkt);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
goto return_packet;
}
for (;;) {
AVPacketList *pktl = s->internal->packet_buffer;
if (pktl) {
AVPacket *next_pkt = &pktl->pkt;
if (next_pkt->dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
int wrap_bits = s->streams[next_pkt->stream_index]->pts_wrap_bits;
// last dts seen for this stream. if any of packets following
// current one had no dts, we will set this to AV_NOPTS_VALUE.
int64_t last_dts = next_pkt->dts;
av_assert2(wrap_bits <= 64);
while (pktl && next_pkt->pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
if (pktl->pkt.stream_index == next_pkt->stream_index &&
av_compare_mod(next_pkt->dts, pktl->pkt.dts, 2ULL << (wrap_bits - 1)) < 0) {
if (av_compare_mod(pktl->pkt.pts, pktl->pkt.dts, 2ULL << (wrap_bits - 1))) {
// not B-frame
next_pkt->pts = pktl->pkt.dts;
}
if (last_dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
// Once last dts was set to AV_NOPTS_VALUE, we don't change it.
last_dts = pktl->pkt.dts;
}
}
pktl = pktl->next;
}
if (eof && next_pkt->pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE && last_dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
// Fixing the last reference frame had none pts issue (For MXF etc).
// We only do this when
// 1. eof.
// 2. we are not able to resolve a pts value for current packet.
// 3. the packets for this stream at the end of the files had valid dts.
next_pkt->pts = last_dts + next_pkt->duration;
}
pktl = s->internal->packet_buffer;
}
/* read packet from packet buffer, if there is data */
st = s->streams[next_pkt->stream_index];
if (!(next_pkt->pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE && st->discard < AVDISCARD_ALL &&
next_pkt->dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE && !eof)) {
ret = ff_packet_list_get(&s->internal->packet_buffer,
&s->internal->packet_buffer_end, pkt);
goto return_packet;
}
}
ret = read_frame_internal(s, pkt);
if (ret < 0) {
if (pktl && ret != AVERROR(EAGAIN)) {
eof = 1;
continue;
} else
return ret;
}
ret = ff_packet_list_put(&s->internal->packet_buffer,
&s->internal->packet_buffer_end,
pkt, 0);
if (ret < 0) {
av_packet_unref(pkt);
return ret;
}
}
return_packet:
st = s->streams[pkt->stream_index];
if ((s->iformat->flags & AVFMT_GENERIC_INDEX) && pkt->flags & AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY) {
ff_reduce_index(s, st->index);
av_add_index_entry(st, pkt->pos, pkt->dts, 0, 0, AVINDEX_KEYFRAME);
}
if (is_relative(pkt->dts))
pkt->dts -= RELATIVE_TS_BASE;
if (is_relative(pkt->pts))
pkt->pts -= RELATIVE_TS_BASE;
return ret;
}
该函数中主要调用了两个函数,如果paketList中有数据,则调用ff_packet_list_get直接从list中读取一帧数据,如果没有则调用read_frame_internal重新读取一帧数据放到list中。
ff_packet_list_get函数比较简单,直接把buf的指针置为pktl->next,其源码如下所示:
int ff_packet_list_get(AVPacketList **pkt_buffer,
AVPacketList **pkt_buffer_end,
AVPacket *pkt)
{
AVPacketList *pktl;
av_assert0(*pkt_buffer);
pktl = *pkt_buffer;
*pkt = pktl->pkt;
*pkt_buffer = pktl->next;
if (!pktl->next)
*pkt_buffer_end = NULL;
av_freep(&pktl);
return 0;
}
read_frame_internal 在ffmpeg中实现了将format格式的packet,最终转换成一帧帧的es流packet,并解析填充了packet的pts,dts等信息,为最终解码提供了重要的数据,read_frame_internal,调用ff_read_packet,该函数最终调用s->iformat->read_packet指针函数,也就是说不同的farmat的read_packet函数也不相同,具体实现可以到libavformat目录下对应的源文件查看。
这次分析暂时到这里,分析ffmpeg源码感觉像无限套娃,看来要好好提高代码阅读能力啊。
参考博客
https://blog.csdn.net/fallenink/article/details/8307104
https://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020/article/details/12678577
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39683826/article/details/115767168
https://blog.csdn.net/yihuanyihuan/article/details/88528439