yolov5_obb旋转框检测的优化版本,算法直接预测旋转框的角度,并替换box loss为kld或probloss。训练后的模型可直接进行稀疏训练、剪枝和微调,剪枝后的通道为8的倍数,以供工程加速。跟踪部分参考了yolov7_obb的跟踪版本。github地址:
https://github.com/yzqxy/yolov5_obb_prune_tracking
如果对你有帮助记得点个星星,鼓励一下博主!
一、旋转框标注和数据格式转换
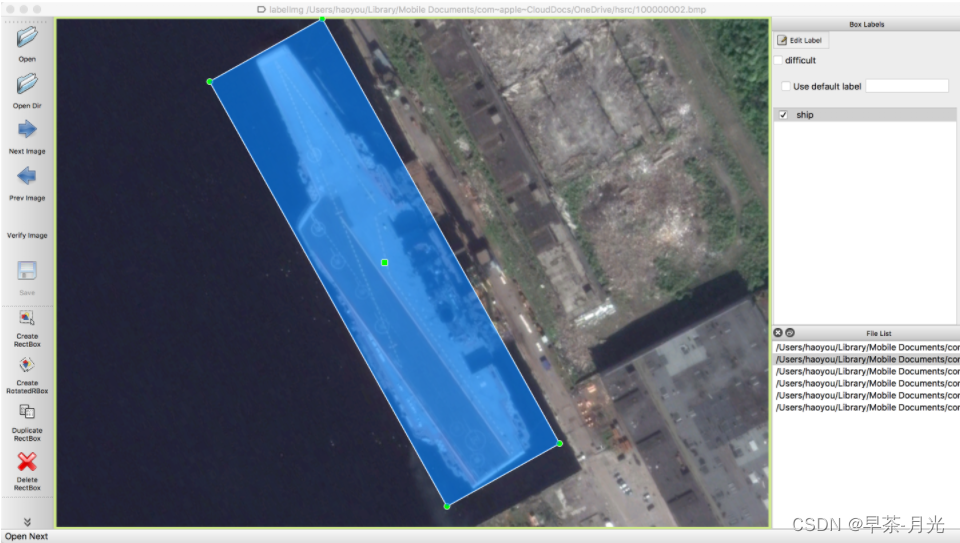
1、标注软件:roLabelImg
图片来源(https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38346042/article/details/129314975)
软件快捷键如下:
1) w: 创建水平矩形目标框
2) e: 创建旋转矩形目标框
3) zxcv: 旋转目标框,键z和建x是逆时针旋转,键c和键v是顺时针旋转
2、数据格式转换
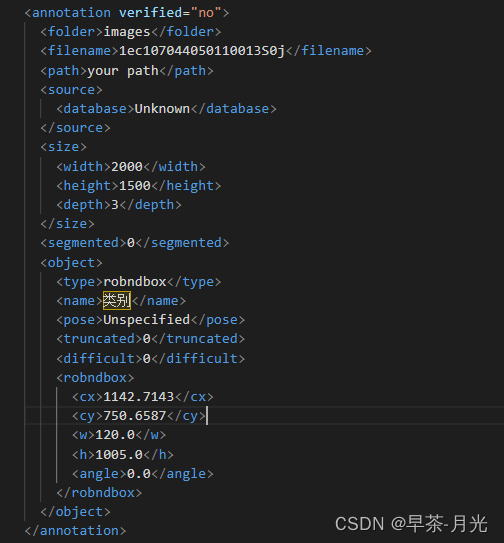
标注存储xml文件
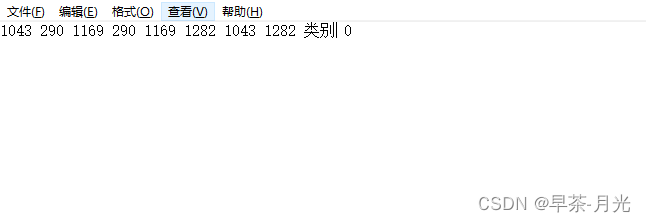
将xml转成yolov5_obb可训练的txt格式------将旋转框的中心点,宽高和角度的存储形式转换成四个角点坐标表现形式
# 文件名称 :roxml_to_dota.py
# 功能描述 :把rolabelimg标注的xml文件转换成dota能识别的xml文件,
# 再转换成dota格式的txt文件
# 把旋转框 cx,cy,w,h,angle,或者矩形框cx,cy,w,h,转换成四点坐标x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4
import os
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import math
cls_list=['你的类别']
def edit_xml(xml_file, dotaxml_file):
"""
修改xml文件
:param xml_file:xml文件的路径
:return:
"""
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
objs = tree.findall('object')
for ix, obj in enumerate(objs):
x0 = ET.Element("x0") # 创建节点
y0 = ET.Element("y0")
x1 = ET.Element("x1")
y1 = ET.Element("y1")
x2 = ET.Element("x2")
y2 = ET.Element("y2")
x3 = ET.Element("x3")
y3 = ET.Element("y3")
# obj_type = obj.find('bndbox')
# type = obj_type.text
# print(xml_file)
if (obj.find('robndbox') == None):
obj_bnd = obj.find('bndbox')
obj_xmin = obj_bnd.find('xmin')
obj_ymin = obj_bnd.find('ymin')
obj_xmax = obj_bnd.find('xmax')
obj_ymax = obj_bnd.find('ymax')
#以防有负值坐标
xmin = max(float(obj_xmin.text),0)
ymin = max(float(obj_ymin.text),0)
xmax = max(float(obj_xmax.text),0)
ymax = max(float(obj_ymax.text),0)
obj_bnd.remove(obj_xmin) # 删除节点
obj_bnd.remove(obj_ymin)
obj_bnd.remove(obj_xmax)
obj_bnd.remove(obj_ymax)
x0.text = str(xmin)
y0.text = str(ymax)
x1.text = str(xmax)
y1.text = str(ymax)
x2.text = str(xmax)
y2.text = str(ymin)
x3.text = str(xmin)
y3.text = str(ymin)
else:
obj_bnd = obj.find('robndbox')
obj_bnd.tag = 'bndbox' # 修改节点名
obj_cx = obj_bnd.find('cx')
obj_cy = obj_bnd.find('cy')
obj_w = obj_bnd.find('w')
obj_h = obj_bnd.find('h')
obj_angle = obj_bnd.find('angle')
cx = float(obj_cx.text)
cy = float(obj_cy.text)
w = float(obj_w.text)
h = float(obj_h.text)
angle = float(obj_angle.text)
obj_bnd.remove(obj_cx) # 删除节点
obj_bnd.remove(obj_cy)
obj_bnd.remove(obj_w)
obj_bnd.remove(obj_h)
obj_bnd.remove(obj_angle)
x0.text, y0.text = rotatePoint(cx, cy, cx - w / 2, cy - h / 2, -angle)
x1.text, y1.text = rotatePoint(cx, cy, cx + w / 2, cy - h / 2, -angle)
x2.text, y2.text = rotatePoint(cx, cy, cx + w / 2, cy + h / 2, -angle)
x3.text, y3.text = rotatePoint(cx, cy, cx - w / 2, cy + h / 2, -angle)
# obj.remove(obj_type) # 删除节点
obj_bnd.append(x0) # 新增节点
obj_bnd.append(y0)
obj_bnd.append(x1)
obj_bnd.append(y1)
obj_bnd.append(x2)
obj_bnd.append(y2)
obj_bnd.append(x3)
obj_bnd.append(y3)
tree.write(dotaxml_file, method='xml', encoding='utf-8') # 更新xml文件
# 转换成四点坐标
def rotatePoint(xc, yc, xp, yp, theta):
xoff = xp - xc;
yoff = yp - yc;
cosTheta = math.cos(theta)
sinTheta = math.sin(theta)
pResx = cosTheta * xoff + sinTheta * yoff
pResy = - sinTheta * xoff + cosTheta * yoff
return str(int(xc + pResx)), str(int(yc + pResy))
def totxt(xml_path, out_path):
# 想要生成的txt文件保存的路径,这里可以自己修改
files = os.listdir(xml_path)
i=0
for file in files:
tree = ET.parse(xml_path + os.sep + file)
root = tree.getroot()
name = file.split('.')[0]
output = out_path +'\\'+name + '.txt'
file = open(output, 'w')
i=i+1
objs = tree.findall('object')
for obj in objs:
cls = obj.find('name').text
box = obj.find('bndbox')
x0 = int(float(box.find('x0').text))
y0 = int(float(box.find('y0').text))
x1 = int(float(box.find('x1').text))
y1 = int(float(box.find('y1').text))
x2 = int(float(box.find('x2').text))
y2 = int(float(box.find('y2').text))
x3 = int(float(box.find('x3').text))
y3 = int(float(box.find('y3').text))
if x0<0:
x0=0
if x1<0:
x1=0
if x2<0:
x2=0
if x3<0:
x3=0
if y0<0:
y0=0
if y1<0:
y1=0
if y2<0:
y2=0
if y3<0:
y3=0
for cls_index,cls_name in enumerate(cls_list):
if cls==cls_name:
file.write("{} {} {} {} {} {} {} {} {} {}\n".format(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, cls,cls_index))
file.close()
# print(output)
print(i)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# -----**** 第一步:把xml文件统一转换成旋转框的xml文件 ****-----
roxml_path = r" 已标注并需要转换的xml文件"
dotaxml_path = r'存储dota格式的xml文件的输出路径' #
out_path = r'存储data格式yolov5_obb可训练的txt文件的路径'
filelist = os.listdir(roxml_path)
for file in filelist:
edit_xml(os.path.join(roxml_path, file), os.path.join(dotaxml_path, file))
# -----**** 第二步:把旋转框xml文件转换成txt格式 ****-----
totxt(dotaxml_path, out_path)
二、v5_obb检测(旋转框)
整理好即将上传GitHub。
1、环境安装
环境安装跟着原版的yolov5_obb来
https://github.com/hukaixuan19970627/yolov5_obb/blob/master/docs/install.md
除此之外需要安装mmcv,需要调用它编译好的旋转框iou计算函数。以下是博主的环境,python版本为3.7.15。
2、数据配置与读取
数据集配置部分,用的是yolov5obb_demo.yaml。
path: dataset/你的路径/ # dataset root dir
train: train.txt #images # train images (relative to 'path')
val: val.txt #images # val images (relative to 'path')
test: val.txt #images # test images (optional)
nc: 1 # number of classes
names: ['你的类别',]
顺带一提,如果跑公开数据集DOTA,由于DOTA数据集中照片分辨率过大,需要用到DOTA_devkit文件夹里的imgsplit.py对图像进行切分后进行训练,这块好久没弄了,各位读者自行研究一下。
数据读取dataset部分,需要注意两点:
1、verify_image_label函数,确保你的gt读取无误,原版979行有些许问题,改成如下:
for label in labels:
if isinstance(cls_name_list,dict):
cls_id=list(cls_name_list.values()).index(label[8])
elif isinstance(cls_name_list,list):
cls_id=cls_name_list.index(label[8])
else:
raise TypeError(f'type of cls_name_list is {type(cls_name_list) },while dict or list is expected')
2、gt旋转框的数据格式是4个角点的表现形式,网络改预测框的x,y,w,h和θ,并直接预测θ,不需要像原版把角度映射成一个180维度的高斯分布,原版效果一般且不利于工程部署。因此需要修改poly2rbox函数,将use_gaussian置为False,use_pi置为TRUE。
rboxes = poly2rbox(polys=labels[:, 1:],
num_cls_thata=hyp['cls_theta'] if hyp else 180,
radius=hyp['csl_radius'] if hyp else 6.0,
use_pi=True, use_gaussian=False)
得到的robxes格式为[x, y, w, h, theta] 并将角度限制在 [-pi/2, pi/2)区间内。
3、输出头修改
既然直接预测角度而不是预测角度的高斯分量,则原版用180维度输出预测角度改成1即可。
# self.no = nc + 5 + 180 # number of outputs per anchor
self.no = nc + 5 + 1 # number of outputs per anchor
4、loss计算(重点)
kld loss参考的v7_obb大佬的代码分享,后续的跟踪也是,respect。
https://github.com/Egrt/yolov7-obb
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/603765606
GWD loss到KLD loss的理解可以阅读以下文章
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/372357305?utm_id=0
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/380016283
class KLDloss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, taf=1.0, fun="sqrt"):
super(KLDloss, self).__init__()
self.fun = fun
self.taf = taf
self.pi = 3.141592
def forward(self, pred, target): # pred [[x,y,w,h,angle], ...]
#assert pred.shape[0] == target.shape[0]
pred = pred.view(-1, 5)
target = target.view(-1, 5)
delta_x = pred[:, 0] - target[:, 0]
delta_y = pred[:, 1] - target[:, 1]
pre_angle_radian = pred[:, 4]
targrt_angle_radian = target[:, 4]
# pre_angle_radian = self.pi *(((pred[:, 4] * 180 / self.pi ) + 90)/180)
# targrt_angle_radian = self.pi *(((target[:, 4] * 180 / self.pi ) + 90)/180)
delta_angle_radian = pre_angle_radian - targrt_angle_radian
kld = 0.5 * (
4 * torch.pow( ( delta_x.mul(torch.cos(targrt_angle_radian)) + delta_y.mul(torch.sin(targrt_angle_radian)) ), 2) / torch.pow(target[:, 2], 2)
+ 4 * torch.pow( ( delta_y.mul(torch.cos(targrt_angle_radian)) - delta_x.mul(torch.sin(targrt_angle_radian)) ), 2) / torch.pow(target[:, 3], 2)
)\
+ 0.5 * (
torch.pow(pred[:, 3], 2) / torch.pow(target[:, 2], 2) * torch.pow(torch.sin(delta_angle_radian), 2)
+ torch.pow(pred[:, 2], 2) / torch.pow(target[:, 3], 2) * torch.pow(torch.sin(delta_angle_radian), 2)
+ torch.pow(pred[:, 3], 2) / torch.pow(target[:, 3], 2) * torch.pow(torch.cos(delta_angle_radian), 2)
+ torch.pow(pred[:, 2], 2) / torch.pow(target[:, 2], 2) * torch.pow(torch.cos(delta_angle_radian), 2)
)\
+ 0.5 * (
torch.log(torch.pow(target[:, 3], 2) / torch.pow(pred[:, 3], 2))
+ torch.log(torch.pow(target[:, 2], 2) / torch.pow(pred[:, 2], 2))
)\
- 1.0
if self.fun == "sqrt":
kld = kld.clamp(1e-7).sqrt()
elif self.fun == "log1p":
kld = torch.log1p(kld.clamp(1e-7))
else:
pass
kld_loss = 1 - 1 / (self.taf + kld)
return kld_loss
在kld loss上进一步优化使用了probiou_loss ,可以提不少点,代码参考的是百度的PP-YOLO-E-R(吐槽一下,百度的环境真的很难配,会出现奇奇怪怪的版本问题,不过技术还是牛逼的),博主后续会更新anchor_free方法yolov8_obb,也参考了一些PP-YOLO-E-R方法。
def gbb_form(boxes):
xy, wh, angle = torch.split(boxes, [2, 2, 1], dim=-1)
return torch.concat([xy, wh.pow(2) / 12., angle], dim=-1)
def rotated_form(a_, b_, angles):
cos_a = torch.cos(angles)
sin_a = torch.sin(angles)
a = a_ * torch.pow(cos_a, 2) + b_ * torch.pow(sin_a, 2)
b = a_ * torch.pow(sin_a, 2) + b_ * torch.pow(cos_a, 2)
c = (a_ - b_) * cos_a * sin_a
return a, b, c
def probiou_loss(pred, target, eps=1e-3, mode='l1'):
"""
pred -> a matrix [N,5](x,y,w,h,angle - in radians) containing ours predicted box ;in case of HBB angle == 0
target -> a matrix [N,5](x,y,w,h,angle - in radians) containing ours target box ;in case of HBB angle == 0
eps -> threshold to avoid infinite values
mode -> ('l1' in [0,1] or 'l2' in [0,inf]) metrics according our paper
"""
gbboxes1 = gbb_form(pred)
gbboxes2 = gbb_form(target)
x1, y1, a1_, b1_, c1_ = gbboxes1[:,
0], gbboxes1[:,
1], gbboxes1[:,
2], gbboxes1[:,
3], gbboxes1[:,
4]
x2, y2, a2_, b2_, c2_ = gbboxes2[:,
0], gbboxes2[:,
1], gbboxes2[:,
2], gbboxes2[:,
3], gbboxes2[:,
4]
a1, b1, c1 = rotated_form(a1_, b1_, c1_)
a2, b2, c2 = rotated_form(a2_, b2_, c2_)
t1 = 0.25 * ((a1 + a2) * (torch.pow(y1 - y2, 2)) + (b1 + b2) * (torch.pow(x1 - x2, 2))) + \
0.5 * ((c1+c2)*(x2-x1)*(y1-y2))
t2 = (a1 + a2) * (b1 + b2) - torch.pow(c1 + c2, 2)
t3_ = (a1 * b1 - c1 * c1) * (a2 * b2 - c2 * c2)
t3 = 0.5 * torch.log(t2 / (4 * torch.sqrt(F.relu(t3_)) + eps))
B_d = (t1 / t2) + t3
# B_d = t1 + t2 + t3
B_d = torch.clip(B_d, min=eps, max=100.0)
l1 = torch.sqrt(1.0 - torch.exp(-B_d) + eps)
l_i = torch.pow(l1, 2.0)
l2 = -torch.log(1.0 - l_i + eps)
if mode == 'l1':
probiou = l1
if mode == 'l2':
probiou = l2
return probiou
loss 计算部分
device = targets.device
lcls = torch.zeros(1, device=device)
lobj = torch.zeros(1, device=device)
box_loss = torch.zeros(1, device=device)
tcls, tbox, indices, anchors = self.build_targets(p, targets) # targets
# Losses # 依次遍历三个feature map的预测输出pi
for i, pi in enumerate(p): # layer index, layer predictions
b, a, gj, gi = indices[i] # image, anchor, gridy, gridx
tobj = torch.zeros_like(pi[...,0], dtype=pi.dtype,device=device) # target obj
n = b.shape[0] # number of targets
if n:
prediction_pos = pi[b, a, gj, gi] # prediction subset corresponding to targets, (n_targets, self.no)
xy = prediction_pos[:, :2].sigmoid() * 2. - 0.5
wh = (prediction_pos[:, 2:4].sigmoid() * 2) ** 2 * anchors[i]
angle = (prediction_pos[:, 4:5].sigmoid() - 0.5) * math.pi
pbox = torch.cat((xy, wh, angle), 1)
#方法一 KLDloss
# kldloss = self.kld_loss_n(pbox,tbox[i])
# box_loss +=kldloss.mean()
# # Objectness
# tobj[b, a, gj, gi] = (1.0 - self.gr) + self.gr * (1 - kldloss).detach().clamp(0).type(tobj.dtype) # iou ratio
# 方法二 probloss
probloss = probiou_loss(pbox,tbox[i])
box_loss +=probloss.mean()
# Objectness
tobj[b, a, gj, gi] = (1.0 - self.gr) + self.gr * (1 - probloss).detach().clamp(0).type(tobj.dtype) # iou ratio
4、评估
1、非极大值抑制部分,需要对模型预测的角度进行后处理再输出
theta_pred=x[:, 4]
# theta_pred = (theta_pred - 90) / 180 * pi # [n_conf_thres, 1] θ ∈ [-pi/2, pi/2)
# theta_pred=torch.sigmoid(theta_pred)
theta_pred = (theta_pred-0.5)*math.pi # [n_conf_thres, 1] θ ∈ [-pi/2, pi/2)
2、原版评估模块先将预测框转成4个角点的poly格式,然后利用poly2hbb函数获取旋转框的最大外接矩形框,最后xywh2xyxy函数再将xywh坐标转成xyxy格式,预测框和gt框都处理完之后在经过process_batch进行匹配
poly = rbox2poly(pred[:, :5]) # (n, 8)
pred_poly = torch.cat((poly, pred[:, -2:]), dim=1) # (n, [poly, conf, cls])
hbbox = xywh2xyxy(poly2hbb(pred_poly[:, :8])) # (n, [x1 y1 x2 y2])
pred_hbb = torch.cat((hbbox, pred_poly[:, -2:]), dim=1) # (n, [xyxy, conf, cls])
pred_polyn = pred_poly.clone() # predn (tensor): (n, [poly, conf, cls])
scale_polys(im[si].shape[1:], pred_polyn[:, :8], shape, shapes[si][1]) # native-space pred
hbboxn = xywh2xyxy(poly2hbb(pred_polyn[:, :8])) # (n, [x1 y1 x2 y2])
pred_hbbn = torch.cat((hbboxn, pred_polyn[:, -2:]), dim=1) # (n, [xyxy, conf, cls]) native-space pred
# Evaluate
if nl:
# tbox = xywh2xyxy(labels[:, 1:5]) # target boxes
tpoly = rbox2poly(labels[:, 1:6]) # target poly
tbox = xywh2xyxy(poly2hbb(tpoly)) # target hbb boxes [xyxy]
scale_coords(im[si].shape[1:], tbox, shape, shapes[si][1]) # native-space labels
labels_hbbn = torch.cat((labels[:, 0:1], tbox), 1) # native-space labels (n, [cls xyxy])
correct = process_batch(pred_hbbn, labels_hbbn, iouv)
if plots:
confusion_matrix.process_batch(pred_hbbn, labels_hbbn)
else:
correct = torch.zeros(pred.shape[0], niou, dtype=torch.bool)
可以将其替换成直接计算旋转框iou的方式来评估,比最大外接矩形框的评估方式更加精确。
三、v5_obb模型剪枝(旋转框)
剪枝部分参考了:
https://blog.csdn.net/IEEE_FELLOW/article/details/117236025
https://github.com/midasklr/yolov5prune/tree/v6.0
需要注意的是prune.py中obtain_bn_mask函数,为了满足剪枝后的通道数为8的倍数,做了额外的处理,你也可舍弃这个操作。
#获取bn_mask并处理为8的整数倍
mask = obtain_bn_mask(bn_module, thre)
四、v5_obb使用mmrotate评估(旋转框)
更改以下路径以后,直接运行eval_rotate_PR.py即可,该脚本搬的mmrotate的评估方法。
weights='your model path'
img_path='your data path'
label_path='your label path'
cls_name_list=['your cls']
五、v5_obb跟踪(旋转框)
跟踪参考v7_obb大佬的代码分享。
https://github.com/Egrt/yolov7-obb
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/603765606
直接运行track_predict.py即可实现跟踪效果。可修改测试视频以及输出路径。博主提供了一个可供测试的视频和车辆旋转框检测模型,不过模型是用原版的yolov5_obb训练的,读者可自己替换为最新的模型,并替换YoloDeepSort文件夹中的yolov5结构。
video_path = "test_video/test12.avi"
video_save_path = "test_video/output.mp4"
video_fps = 10
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
half='False'
weights='runs/car/weights/last.pt'
model = DetectMultiBackend(weights, device=device, dnn=False)
model.model.half() if half else model.model.float()
六、v8_obb
yolov8_obb旋转框检测
yolov8_obb模型剪枝
yolov8_obb旋转框跟踪
七、结语
希望此项目和博文对您的工作和学业有所帮助,祝大家生活愉快,身体健康!