柏林噪声
Perlin Noise是Ken Perlin在1983年开发的一种梯度噪音,这是一种用于在计算机生成的表面上产生自然出现纹理的技术,使用Perlin噪声合成的纹理通常用于CGI,通过模仿自然界中纹理的受控随机外观,使计算机生成的视觉元素(如物体表面,火焰,烟雾或云)看起来更自然。 − − W i k i --Wiki −−Wiki
理论知识链接
噪音 - Perlin
一篇文章搞懂柏林噪声算法,附代码讲解
http://libnoise.sourceforge.net/index.html
不只是噪声,更是数学美 —浅谈Perlin Noise(理论知识完美)
不只是噪音–知乎(写的超棒!!)
代码实现(Python)
由Ken Perlin 2002年原始JAVA代码改编而来
#-*- coding:utf8 -*-
# PYTHON REFERENCE IMPLEMENTATION OF IMPROVED NOISE - COPYRIGHT 2002 KEN PERLIN.
import math
import numpy as np
def PerlinNoise(x,y,z, octaves=6, persistence=0.5):
# Sum of Noise Function = Perlin Noise
# Each successive noise function you add is known as an octave
total = 0
p = persistence # reference value: 1/4, 1/2 ,3/4
for i in range(octaves):
frequency=2**i
amplitude=p**i
octave=ImprovedNoise(x * frequency, y * frequency, z * frequency) * amplitude
total+=octave
return total
def ImprovedNoise(x, y, z):
# frequency=1/wavelength
# It returns floating point numbers between -1.0 and 1.0
# FIND UNIT CUBE THAT CONTAINS POINT.
X = int(math.floor(x)) & 255
Y = int(math.floor(y)) & 255
Z = int(math.floor(z)) & 255
# FIND RELATIVE X,Y,Z OF POINT IN CUBE.
x -= math.floor(x)
y -= math.floor(y)
z -= math.floor(z)
# COMPUTE FADE CURVES FOR EACH OF X,Y,Z.
u,v,w = fade(x),fade(y),fade(z)
# HASH COORDINATES OF THE 8 CUBE CORNERS
# AND ADD BLENDED RESULTS FROM 8 CORNERS OF CUBE
A = p[X ]+Y; AA = p[A]+Z; AB = p[A+1]+Z;
B = p[X+1]+Y; BA = p[B]+Z; BB = p[B+1]+Z;
return lerp(w, lerp(v, lerp(u, grad(p[AA ], x , y , z ),
grad(p[BA ], x-1, y , z )),
lerp(u, grad(p[AB ], x , y-1, z ),
grad(p[BB ], x-1, y-1, z ))),
lerp(v, lerp(u, grad(p[AA+1], x , y , z-1 ),
grad(p[BA+1], x-1, y , z-1 )),
lerp(u, grad(p[AB+1], x , y-1, z-1 ),
grad(p[BB+1], x-1, y-1, z-1 ))))
def fade(t):
return t * t * t * (t * (t * 6 - 15) + 10)
def lerp(t, a, b):
return a + t * (b - a)
def grad(hash, x, y, z):
# CONVERT LO 4 BITS OF HASH CODE INTO 12 GRADIENT DIRECTIONS.
h = hash & 15
u = x if h < 8 else y
v = y if h < 4 else x if h==12 or h==14 else z
return (u if (h&1)==0 else -u)+(v if (h&2)==0 else -v)
permutation = [ 151,160,137,91,90,15,
131,13,201,95,96,53,194,233,7,225,140,36,103,30,69,142,8,99,37,240,21,10,23,
190, 6,148,247,120,234,75,0,26,197,62,94,252,219,203,117,35,11,32,57,177,33,
88,237,149,56,87,174,20,125,136,171,168, 68,175,74,165,71,134,139,48,27,166,
77,146,158,231,83,111,229,122,60,211,133,230,220,105,92,41,55,46,245,40,244,
102,143,54, 65,25,63,161, 1,216,80,73,209,76,132,187,208, 89,18,169,200,196,
135,130,116,188,159,86,164,100,109,198,173,186, 3,64,52,217,226,250,124,123,
5,202,38,147,118,126,255,82,85,212,207,206,59,227,47,16,58,17,182,189,28,42,
223,183,170,213,119,248,152, 2,44,154,163, 70,221,153,101,155,167, 43,172,9,
129,22,39,253, 19,98,108,110,79,113,224,232,178,185, 112,104,218,246,97,228,
251,34,242,193,238,210,144,12,191,179,162,241, 81,51,145,235,249,14,239,107,
49,192,214, 31,181,199,106,157,184, 84,204,176,115,121,50,45,127, 4,150,254,
138,236,205,93,222,114,67,29,24,72,243,141,128,195,78,66,215,61,156,180
]
p=permutation*2
Perlin noise library for Python
该包旨在为您提供简单易用的快速函数,用于
在Python程序中生成Perlin噪声。
安装
安装前先下载微软开发环境
https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/downloads/
找到 Other Tools and Frameworks 点开,
下载 Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable for Visual Studio 2017安装即可。
pip安装
pip indtsll noise
本地安装
GitHub下载源文件,然后运行
python setup.py install
安装错误: Failed building wheel for noise
https://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/#noise
下载对应版本,安装解析环境,cp后面是Python的版本号
noise-1.2.2-cp36-cp36m-win32.whl
noise-1.2.2-cp36-cp36m-win_amd64.whl
noise-1.2.2-cp37-cp37m-win32.whl
noise-1.2.2-cp37-cp37m-win_amd64.whl
pip install C:\Users\Admin\Anaconda3\Scripts\noise-1.2.2-cp36-cp36m-win_amd64.whl
示例代码
#-*- coding:utf8 -*-
from noise import pnoise2,pnoise3
import numpy as np
from numpy import sin,cos,arccos,arcsin,sqrt
import pandas as pd
import random
def timer(func):
import datetime
from functools import wraps
@wraps(func)
def decorated(*args, **kwargs):
starttime = datetime.datetime.now()
res=func(*args, **kwargs)
endtime = datetime.datetime.now()
print('time used {} sec'.format((endtime - starttime).seconds))
return res
return decorated
class Sphere:
def __init__(self,radius):
self.radius=radius
def coord_trans(self,longitude,latitude,radius=None):
'''
coordinate transformation
Cartesian coordinates
'''
lat,lon=latitude,longitude
if radius is None:
r=self.radius
else:
r=radius
x = r * cos(lat) * cos(lon)
y = r * cos(lat) * sin(lon)
z = r * sin(lat)
return x,y,z
def distance(self,lon,lat,angle='degrees',radius=None):
if angle=='degrees':
lon,lat=np.radians([lon,lat])
a1,a2=lat
b1,b2=lon
if radius is None:
r1=r2 =self.radius
elif isinstance(radius,(int,float)):
r1=r2 = radius
else:
r1,r2,*_=radius
'Cartesian distance'
tmp = cos(a1) * cos(a2) * cos(b1 - b2) + sin(a1) * sin(a2)
L = sqrt(r1 ** 2 + r2 ** 2 - 2 * r1 * r2 * tmp)
if r1==r2:
'spherical distance'
S = r1 * arccos(tmp)
return L,S
else:
return L,None
@timer
def create_sphere(self,unit=0.1,multiplier=1.0,stretch=1.0,
seed=None,*args,**kwargs):
'''
Spherical coordinate system (lon,lat,r)
0 <= r < math.inf
0 <= lon <= PI * 2
-PI / 2 <= lat <= PI / 2
'''
lon=np.arange(-180,180,unit)
lat=np.arange(-90,90+unit,unit)
'coordinate transformation'
# coord = pd.MultiIndex.from_product([lon, lat], names=['lon', 'lat'])
# coord = pd.DataFrame(index=coord).reset_index()
lon1,lat1=np.meshgrid(lon,lat)
x, y, z = self.coord_trans(np.radians(lon1), np.radians(lat1), radius=stretch)
'default arguments'
if seed is None:
seed=random.randint(0,256)
else:
seed=int(seed)
'Define numpy ufunc(universal function)'
ufunc_pnoise3=lambda x,y,z:pnoise3(x, y, z,base=seed,*args,**kwargs)
self.ufunc_pnoise3=np.frompyfunc(ufunc_pnoise3, 3, 1)
h = self.ufunc_pnoise3(x,y,z)
# h=pd.pivot(coord.lat, coord.lon, h)
print('seed={}'.format(seed))
return lon,lat,h
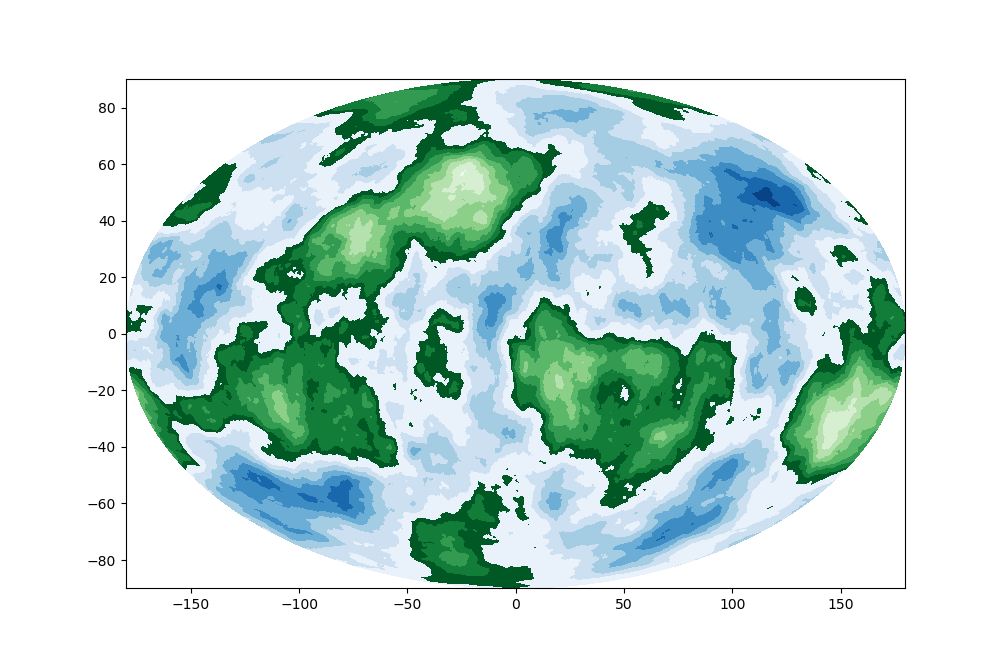
def draw_sphere(self,lon,lat,h,map='ellipse'):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
h1=h.copy()
h2=h.copy()
h1[h<0]=None
h2[h>0]=None
fig=plt.figure()
if map=='ellipse':
lon,lat=np.meshgrid(lon,lat)
lon=sqrt(1-(lat/90)**2)*lon
plt.contourf(lon, lat, h1, cmap='Greens_r')
plt.contourf(lon, lat, h2, cmap='Blues_r')
elif map=='cosine':
lon,lat=np.meshgrid(lon,lat)
lon=cos(np.radians(lat))*lon
plt.contourf(lon, lat, h1, cmap='Greens_r')
plt.contourf(lon, lat, h2, cmap='Blues_r')
else:
plt.contourf(lon, lat, h1, cmap='Greens_r')
plt.contourf(lon, lat, h2, cmap='Blues_r')
plt.show()
earth=Sphere(radius=2)
lon,lat,h=earth.create_sphere(octaves=10, persistence=0.5,multiplier=2,seed=57)
earth.draw_sphere(lon,lat,h,map='ellipse')