目录
Spring Boot与缓存
什么是cache
cache 是一个高性能的分布式内存对象缓存系统,用于动态Web应用以减轻数据库负载。它通过在内存中缓存数据和对象来减少读取数据库的次数,从而提供动态、数据库驱动网站的速度。
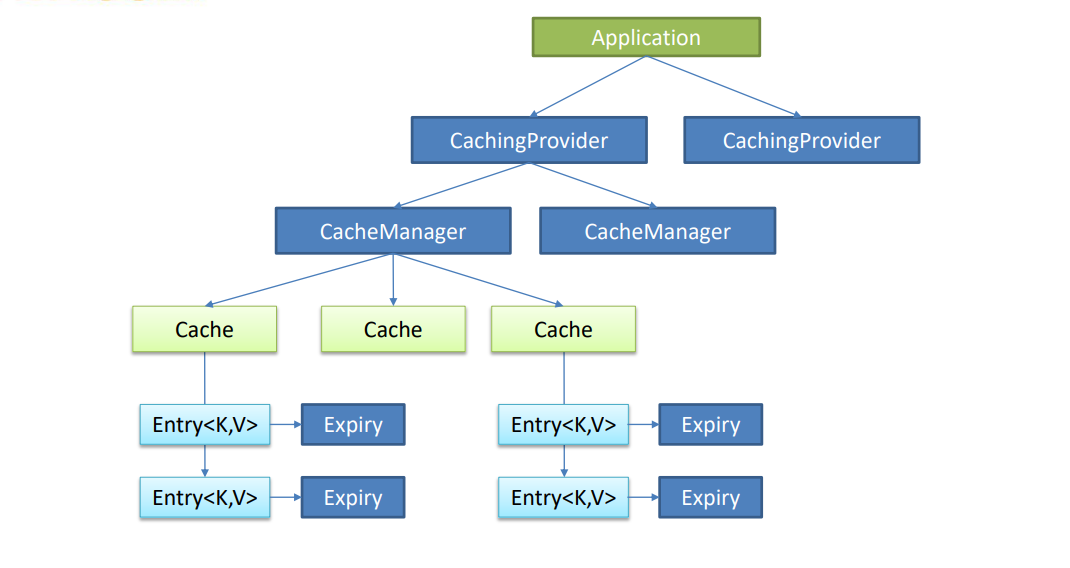
java cache:JSR107
Java Caching定义了5个核心接口,分别是CachingProvider, CacheManager, Cache, Entry 和 Expiry。
- CachingProvider:定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager。一个应用可以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。
- CacheManager:定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,这些Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅被一个CachingProvider所拥有。
- Cache:是一个类似Map的数据结构并临时存储以Key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个CacheManager所拥有。
- Entry:是一个存储在Cache中的key-value对。
- Expiry:每一个存储在Cache中的条目有一个定义的有效期,即Expiry Duration。一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。
Spring缓存抽象
Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache 和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术; 并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们开发;
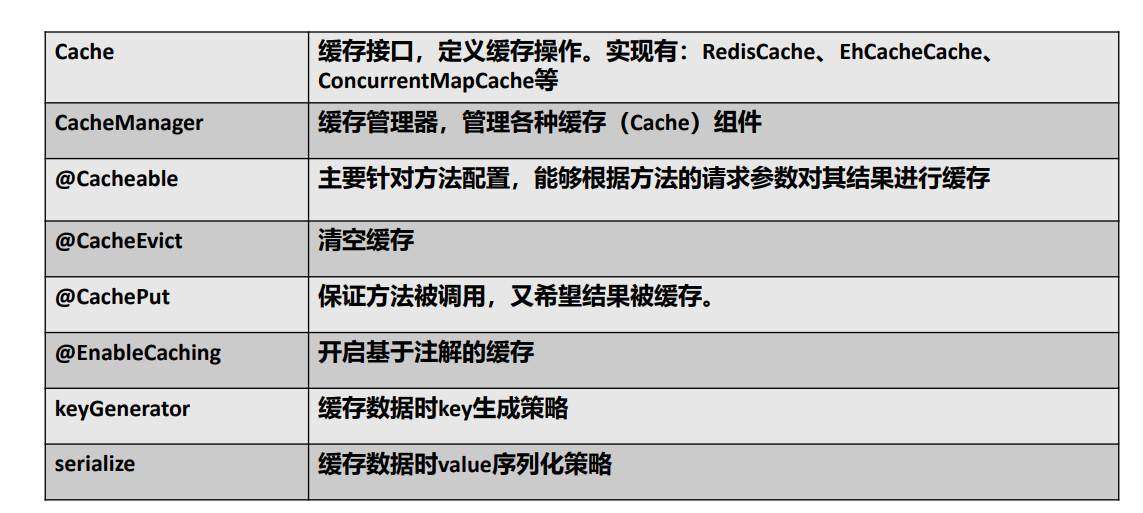
1. 几个重要概念&缓存注解
2. 在上面常用的三个注解:@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict中,主要有以下的参数可以将要缓存的数据进行过滤和配置。主要参数如下:
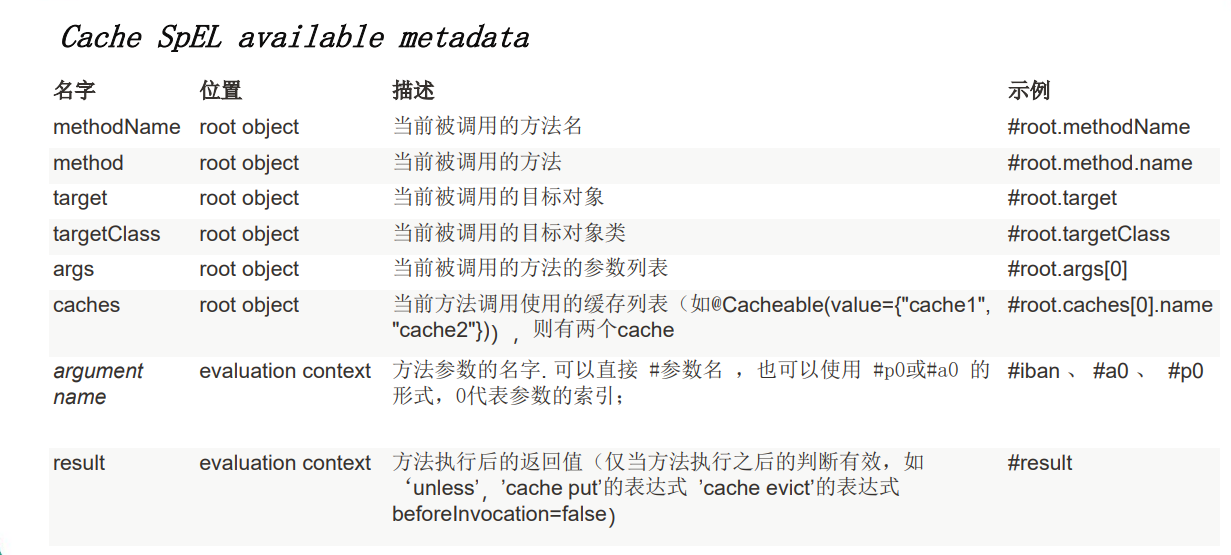
3. 在以上的参数:key、condition、unless中,除了可以使用字符串进行配置,也可以使用SpEL表达式进行动态的配置。主要SpEL表达式介绍如下:
redis和cache的使用场景和区别
- 存储方式:cache 把数据全部存在内存之中,断电后会挂掉,数据不能超过内存大小 ;redis有部分存在硬盘上,这样能保证数据的持久性,支持数据的持久化。cache挂掉后,数据不可恢复; redis数据丢失后可以通过aof恢复 。
- 数据支持类型:Redis和cache都是将数据存放在内存中,cache只支持<key,value>型数据,不过cache还可用于缓存其他东西,例如图片、视频等等;Redis不仅仅支持简单的k/v类型的数据,同时还提供list,set,hash等数据结构的存储。
- 可靠性上:Cache不支持数据持久化,断电或重启后数据消失,但其稳定性是有保证的。Redis支持数据持久化和数据恢复,允许单点故障,但是同时也会付出性能的代价。
- 应用场景: Cache:动态系统中减轻数据库负载,提升性能;做缓存,适合多读少写,大数据量的情况(如人人网大量查询用户信息、好友信息、文章信息等)。Redis:适用于对读写效率要求都很高,数据处理业务复杂和对安全性要求较高的系统(如新浪微博的计数和微博发布部分系统,对数据安全性、读写要求都很高)。
SpringBoot缓存的使用
在真实的开发中,cache缓存的使用一般也会整合Redis一起使用;当然也可以不整合Redis,直接使用Cache,两者操作的区别是:只引入’spring-boot-starter-cache’模块,不要引入’spring-boot-starter-data-redis’模块。然后使用@EnableCaching开启缓存,直接使用使用缓存注解就可以实现缓存了,其缓存的value是该注解下方法的返回结果,key如果不进行配置的话默认是方法名。
下面就来实现SpringBoot 整合redis实现缓存:
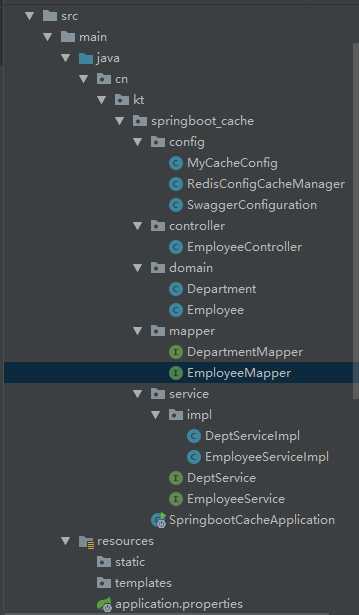
目录结构如下:
0. 开启缓存的注解:@EnableCaching
在项目启动类中:
package cn.kt.springboot_cache;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
@MapperScan("cn.kt.springboot_cache.mapper")
@EnableCaching
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootCacheApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootCacheApplication.class, args);
}
}
1. 导入数据库文件
本次使用的数据库是:springboot_cache
创建了两个表:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `department`;
CREATE TABLE `department` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`departmentName` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 4 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
INSERT INTO `department` VALUES (1, '软件部');
INSERT INTO `department` VALUES (2, '产品部');
INSERT INTO `department` VALUES (3, '测试部门');
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `employee`;
CREATE TABLE `employee` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`lastName` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`email` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`gender` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`d_id` int(11) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 5 CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES (1, 'Nick', '[email protected]', '男', 1);
INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES (2, '路飞', '[email protected]', '男', 1);
INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES (4, 'lufei', NULL, NULL, NULL);
2. 导入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3. 编写配置文件
# 数据库驱动:
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# 数据库连接地址
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot_cache?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
# 数据库用户名&密码:
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
# mybatis需要开启驼峰命名匹配规则
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
logging.level.cn.kt.springboot_cache.mapper=debug
# Redis数据库索引(默认为0)
spring.redis.database=0
# Redis服务器地址
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
# Redis服务器连接端口
spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
spring.redis.password=
# 连接超时时间(毫秒)
spring.redis.timeout=5000ms
4. 创建javaBean封装类
Department.java
public class Department implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String departmentName;
/* 省略get、set、构造方法 */
}
Employee.java
public class Employee implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private String gender; //性别 1男 0女
private Integer dId;
/* 省略get、set、构造方法 */
5. 编写dao层
本次实践是使用了mybatis,采用简单的注解做持久层
EmployeeMapper.java
package cn.kt.springboot_cache.mapper;
import cn.kt.springboot_cache.domain.Employee;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
/**
* @author tao
* @date 2021-09-01 7:48
* 概要:
*/
@Mapper
public interface EmployeeMapper {
@Select("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE id = #{id}")
public Employee getEmpById(Integer id);
@Update("UPDATE employee SET lastName=#{lastName},email=#{email},gender=#{gender},d_id=#{dId} WHERE id=#{id}")
public void updateEmp(Employee employee);
@Delete("DELETE FROM employee WHERE id=#{id}")
public void deleteEmpById(Integer id);
@Insert("INSERT INTO employee(lastName,email,gender,d_id) VALUES(#{lastName},#{email},#{gender},#{dId})")
public void insertEmployee(Employee employee);
@Select("SELECT * FROM employee WHERE lastName = #{lastName}")
Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName);
}
6. 编写service层
Service接口
EmployeeService.java
package cn.kt.springboot_cache.service;
import cn.kt.springboot_cache.domain.Employee;
/**
* @author tao
* @date 2021-09-20 10:08
* 概要:
*/
public interface EmployeeService {
Employee getEmp(Integer id);
Employee updateEmp(Employee employee);
void deleteEmp(Integer id);
Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName);
}
Service实现类
EmployeeServiceImpl.java
package cn.kt.springboot_cache.service.impl;
import cn.kt.springboot_cache.domain.Employee;
import cn.kt.springboot_cache.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import cn.kt.springboot_cache.service.EmployeeService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Caching;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author tao
* @date 2021-09-20 10:23
* 概要:
*/
@Service
public class EmployeeServiceImpl implements EmployeeService {
@Autowired
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
/**
* 将方法的运行结果进行缓存;以后再要相同的数据,直接从缓存中获取,不用调用方法;
* CacheManager管理多个Cache组件的,对缓存的真正CRUD操作在Cache组件中,每一个缓存组件有自己唯一一个名字;
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
//key = "#id+#root.methodName+#root.caches[0].name",
//@Cacheable(cacheNames = {"emp"}, keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator", condition = "#a0>1")
@Cacheable(cacheNames = {"emp"}, key = "#id", condition = "#a0>1")
public Employee getEmp(Integer id) {
System.out.println("查询" + id + "号员工");
Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);
return emp;
}
//更新的key和缓存中的key要相同
@CachePut(cacheNames = {"emp"}, key = "#result.id")
public Employee updateEmp(Employee employee) {
System.out.println("updateEmp:" + employee);
employeeMapper.updateEmp(employee);
return employee;
}
@CacheEvict(value = "emp", key = "#id"/*beforeInvocation = true*/)
public void deleteEmp(Integer id) {
System.out.println("deleteEmp:" + id);
employeeMapper.deleteEmpById(id);
//int i = 10/0;
}
// @Caching 定义复杂的缓存规则
@Caching(
// 定义了三个缓存规则,进行缓存了三次:分别根据lastName、返回结果id、返回结果email为key进行缓存
cacheable = {
@Cacheable(value = "emp", key = "#lastName")
},
put = {
@CachePut(value = "emp", key = "#result.id"),
@CachePut(value = "emp", key = "#result.email")
}
)
public Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName) {
return employeeMapper.getEmpByLastName(lastName);
}
}
7. 编写控制层
EmployeeController.java
package cn.kt.springboot_cache.controller;
import cn.kt.springboot_cache.domain.Employee;
import cn.kt.springboot_cache.service.EmployeeService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author tao
* @date 2021-09-20 10:26
* 概要:
*/
@RestController
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@GetMapping("/emp/{id}")
public Employee getEmployee(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
Employee emp = employeeService.getEmp(id);
return emp;
}
@GetMapping("/emp")
public Employee update(Employee employee) {
Employee emp = employeeService.updateEmp(employee);
return emp;
}
@GetMapping("/delemp")
public String deleteEmp(Integer id) {
employeeService.deleteEmp(id);
return "success";
}
@GetMapping("/emp/lastname/{lastName}")
public Employee getEmpByLastName(@PathVariable("lastName") String lastName) {
return employeeService.getEmpByLastName(lastName);
}
}
8. 编写MyCacheConfig配置类(可选)
在该配置类中。主要对Cache进行一些配置,如配置keyGenerator,当然这个可以使用key进行代替。
@Configuration
public class MyCacheConfig {
@Bean("myKeyGenerator")
public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() {
return new KeyGenerator() {
@Override
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
return method.getName() + "[" + Arrays.asList(params).toString() + "]";
}
};
}
}
测试结果
在上面的demo中,定义了简单的CRUD,并且使用了Cache的常用注解,可以通过get请求直接进行测试。
-
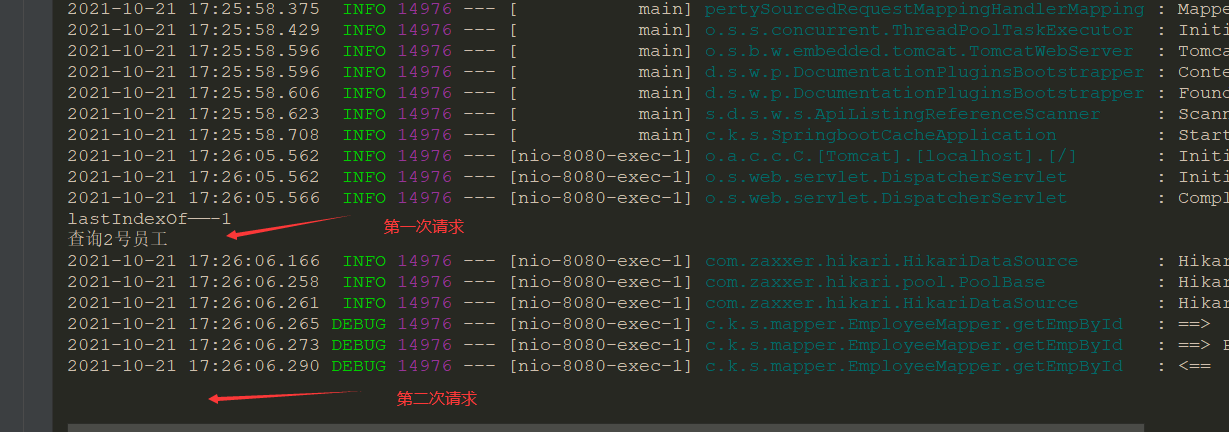
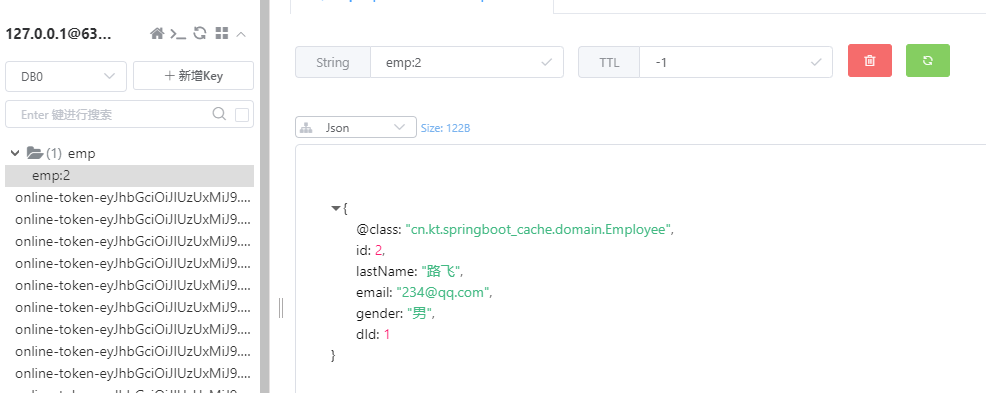
请求两次:http://localhost:8080/emp/2
发现第二次请求并没有执行dao层的方法体,但数据仍然查出来了
原因是先查询了缓存 -
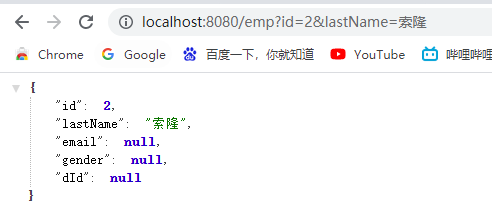
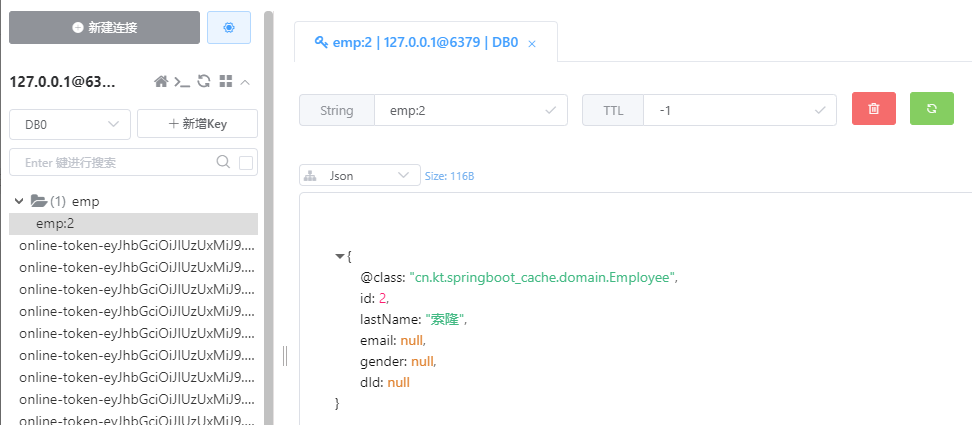
执行CacheEvict的更新请求:http://localhost:8080/emp?id=2&lastName=索隆
@CachePut:既调用方法,又更新缓存数据;同步更新缓存
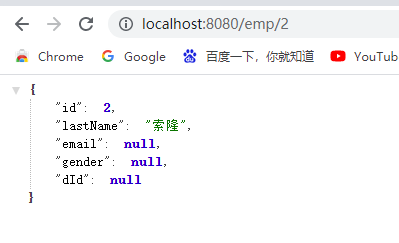
再执行:http://localhost:8080/emp/2
发现修改了数据库,和更新了缓存,再次查询并不会执行查询的dao层的方法体 -
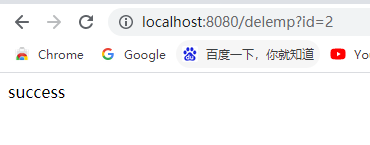
执行删除操作:http://localhost:8080/delemp?id=2
@CacheEvict:缓存清除
发现缓存数据已经清除 -
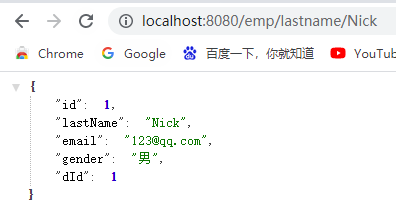
测试@Caching 定义复杂的缓存规则:http://localhost:8080/emp/lastname/Nick
由于再实现类中定义了三个缓存规则,进行缓存了三次:分别根据lastName、返回结果id、返回结果email为key进行缓存
Cache根据配置的规则缓存了三次
整合redis注解缓存并设置时间
查阅了相关资料,Cache注解中并没有提供想Redis一样设置缓存过期时间的方法,但这个功能再开发中又相对的很重要,因此整理出了下面的一种方法:通过全部配置RedisCacheManager,再查询时进行过滤判断,在缓存存入Redis时进行过期时间的配置。
这种形式使用是将 cacheName后加#可以区分时间
操作方法如下:
- 新建配置类RedisConfigCacheManager.java
package cn.kt.springboot_cache.config;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.*;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Created by tao.
* Date: 2021/10/21 15:21
* 描述:
*/
public class RedisConfigCacheManager extends RedisCacheManager {
public RedisConfigCacheManager(RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter, RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration) {
super(cacheWriter, defaultCacheConfiguration);
}
public RedisConfigCacheManager(RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter, RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration, String... initialCacheNames) {
super(cacheWriter, defaultCacheConfiguration, initialCacheNames);
}
public RedisConfigCacheManager(RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter, RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration, boolean allowInFlightCacheCreation, String... initialCacheNames) {
super(cacheWriter, defaultCacheConfiguration, allowInFlightCacheCreation, initialCacheNames);
}
public RedisConfigCacheManager(RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter, RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration, Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> initialCacheConfigurations) {
super(cacheWriter, defaultCacheConfiguration, initialCacheConfigurations);
}
public RedisConfigCacheManager(RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter, RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration, Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> initialCacheConfigurations, boolean allowInFlightCacheCreation) {
super(cacheWriter, defaultCacheConfiguration, initialCacheConfigurations, allowInFlightCacheCreation);
}
private static final RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair<Object> DEFAULT_PAIR = RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
private static final CacheKeyPrefix DEFAULT_CACHE_KEY_PREFIX = cacheName -> cacheName + ":";
@Override
protected RedisCache createRedisCache(String name, RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfig) {
final int lastIndexOf = StringUtils.lastIndexOf(name, '#');
System.out.println("lastIndexOf——" + lastIndexOf);
if (lastIndexOf > -1) {
final String ttl = StringUtils.substring(name, lastIndexOf + 1);
final Duration duration = Duration.ofSeconds(Long.parseLong(ttl));
cacheConfig = cacheConfig.entryTtl(duration);
//修改缓存key和value值的序列化方式
cacheConfig = cacheConfig.computePrefixWith(DEFAULT_CACHE_KEY_PREFIX)
.serializeValuesWith(DEFAULT_PAIR);
final String cacheName = StringUtils.substring(name, 0, lastIndexOf);
return super.createRedisCache(cacheName, cacheConfig);
} else {
final Duration duration = Duration.ofSeconds(-1);
cacheConfig = cacheConfig.entryTtl(duration);
//修改缓存key和value值的序列化方式
cacheConfig = cacheConfig.computePrefixWith(DEFAULT_CACHE_KEY_PREFIX)
.serializeValuesWith(DEFAULT_PAIR);
final String cacheName = StringUtils.substring(name, 0);
return super.createRedisCache(cacheName, cacheConfig);
}
}
}
- 在上述可选的MyCacheConfig配置类中加入以下方法
/*redis配置类*/
@Bean
@Primary
public RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(
Object.class);
// 解决查询缓存转换异常的问题
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// 配置序列化(解决乱码的问题)
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofMillis(-1))
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisSerializer))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer))
.disableCachingNullValues();
RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter = RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(factory);
/*return RedisConfigCacheManager.builder(factory)
// .withInitialCacheConfigurations()
.transactionAware()
.build();*/
return new RedisConfigCacheManager(cacheWriter, config);
}
参考文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/mrsans/articles/14113591.html
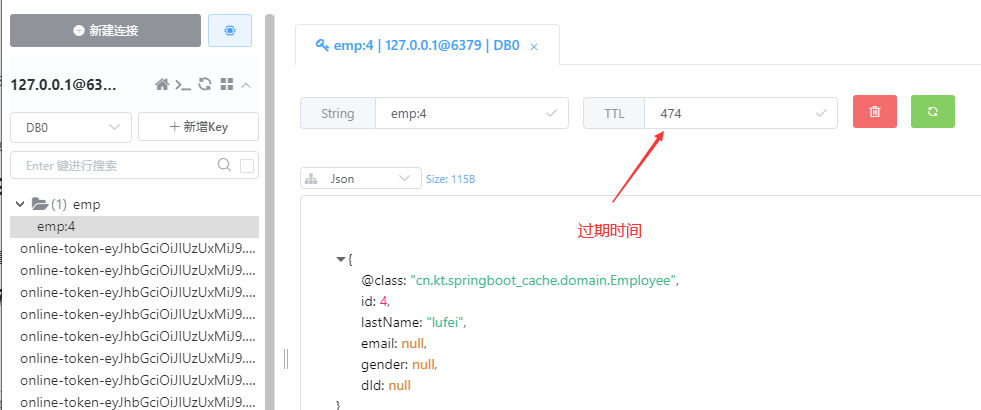
通过以上配置,即可以自定义的配置缓存的过期时间,单位秒
如何配置过期时间呢?
在cacheNames 缓存名后面加上 ”#过期时间“
@Cacheable(cacheNames = {“emp#500”}, key = “#id”, condition = “#a0>1”)
结果如下: