一、前置条件
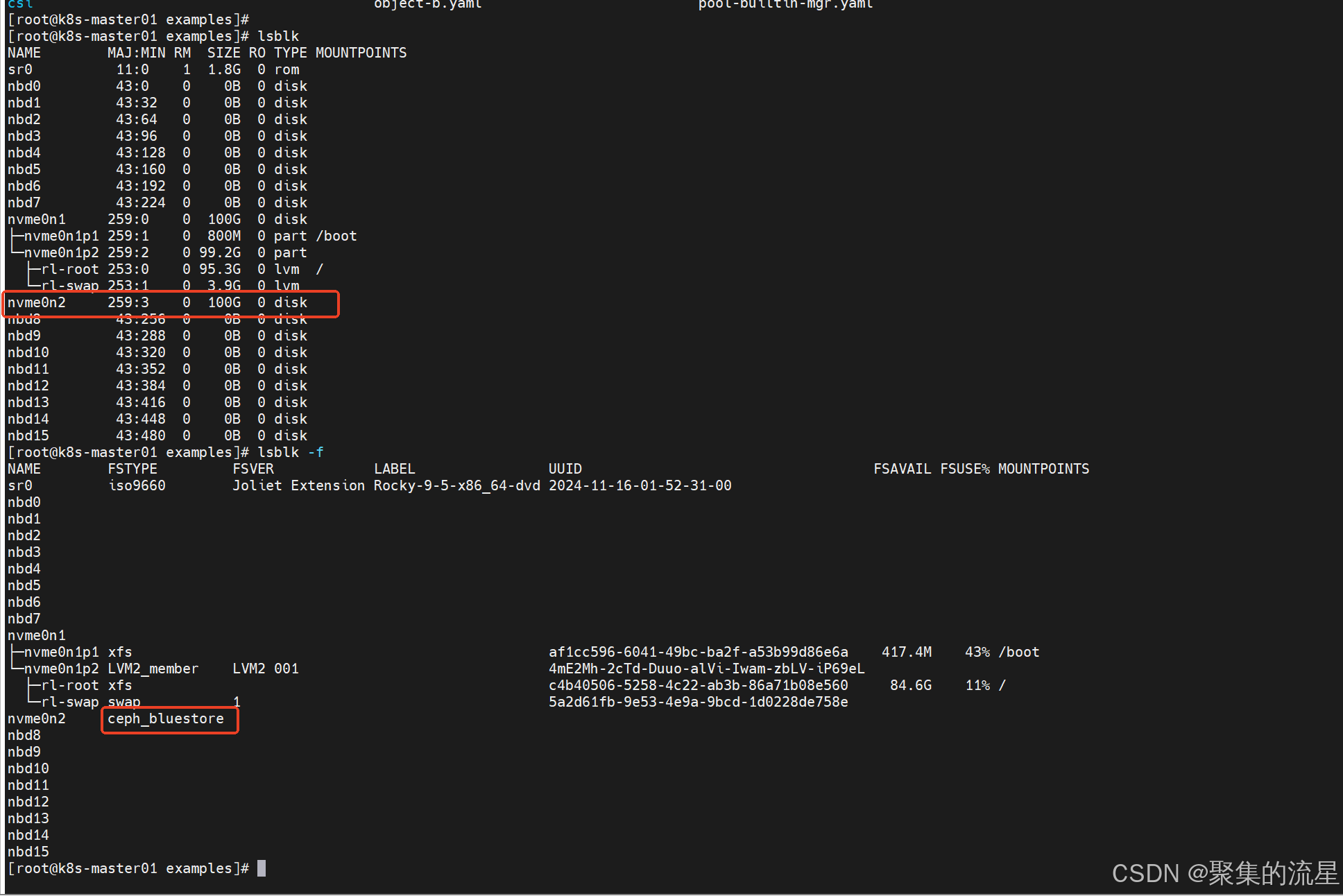
需要在机器上准备空闲的硬盘,如果是虚拟机的话,每台虚拟机添加100g硬盘,rook能自动检测空闲的硬盘
可以看到我这里空闲硬盘已经被rook所使用
二、部署rook-ceph
参考官网文档https://github.com/rook/rook/tree/master
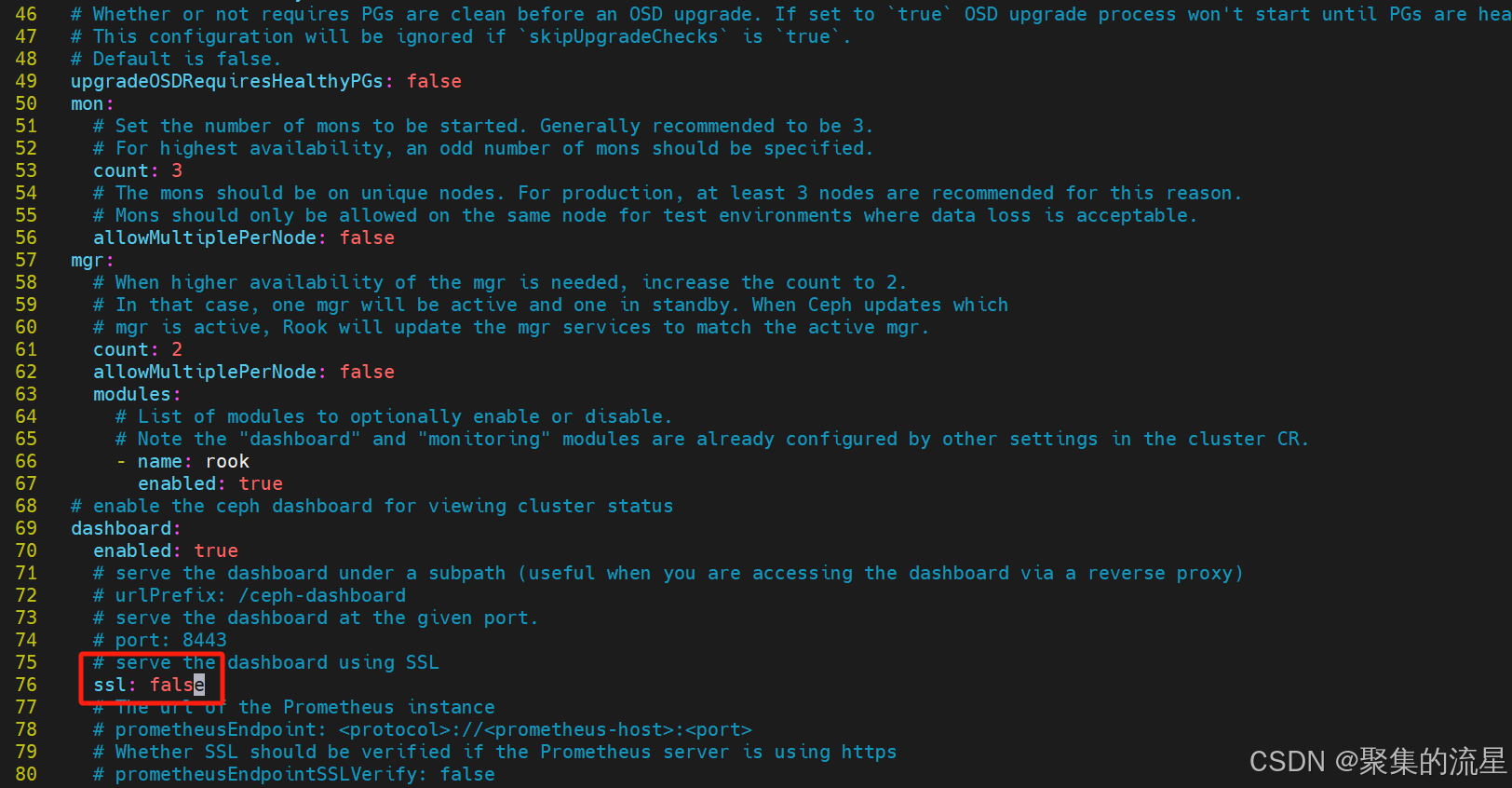
在创建集群之前,修改cluster.yaml
需要将其中dashboard的ssl关闭,不然登录ceph的dashboard会提升tls证书认证失败
cd rook/deploy/examplesvim cluster.yaml$ git clone --single-branch --branch master https://github.com/rook/rook.git
cd rook/deploy/examples
kubectl create -f crds.yaml -f common.yaml -f operator.yaml
kubectl create -f cluster.yaml部署NodePort的dashboard服务
kubectl create -f dashboard-external-http.yaml
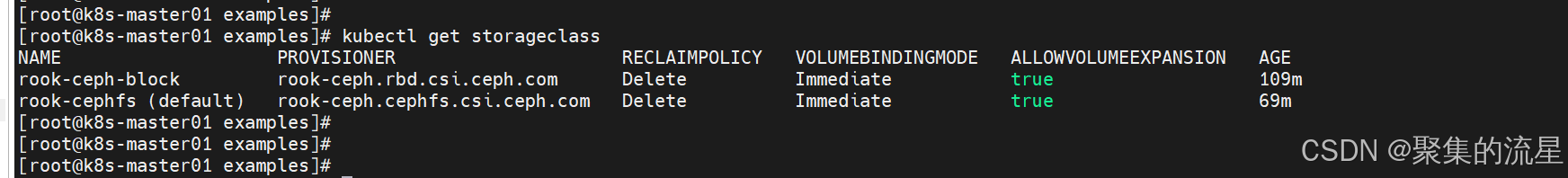
三、创建storeclass
创建块存储
cd /deploy/examples/csi/rbd/
kubectl create -f storageclass.yaml创建cephfs系统,并设置默认类
vi rook-cephfs.yamlapiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephFilesystem
metadata:
name: myfs
namespace: rook-ceph # namespace:cluster
spec:
# The metadata pool spec. Must use replication.
metadataPool:
replicated:
size: 3
requireSafeReplicaSize: true
parameters:
# Inline compression mode for the data pool
# Further reference: https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/rados/configuration/bluestore-config-ref/#inline-compression
compression_mode:
none
# gives a hint (%) to Ceph in terms of expected consumption of the total cluster capacity of a given pool
# for more info: https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/rados/operations/placement-groups/#specifying-expected-pool-size
#target_size_ratio: ".5"
# The list of data pool specs. Can use replication or erasure coding.
dataPools:
- name: replicated
failureDomain: host
replicated:
size: 3
# Disallow setting pool with replica 1, this could lead to data loss without recovery.
# Make sure you're *ABSOLUTELY CERTAIN* that is what you want
requireSafeReplicaSize: true
parameters:
# Inline compression mode for the data pool
# Further reference: https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/rados/configuration/bluestore-config-ref/#inline-compression
compression_mode:
none
# gives a hint (%) to Ceph in terms of expected consumption of the total cluster capacity of a given pool
# for more info: https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/rados/operations/placement-groups/#specifying-expected-pool-size
#target_size_ratio: ".5"
# Whether to preserve filesystem after CephFilesystem CRD deletion
preserveFilesystemOnDelete: true
# The metadata service (mds) configuration
metadataServer:
# The number of active MDS instances
activeCount: 1
# Whether each active MDS instance will have an active standby with a warm metadata cache for faster failover.
# If false, standbys will be available, but will not have a warm cache.
activeStandby: true
# The affinity rules to apply to the mds deployment
placement:
# nodeAffinity:
# requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
# nodeSelectorTerms:
# - matchExpressions:
# - key: role
# operator: In
# values:
# - mds-node
# topologySpreadConstraints:
# tolerations:
# - key: mds-node
# operator: Exists
# podAffinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app
operator: In
values:
- rook-ceph-mds
# topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname will place MDS across different hosts
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- weight: 100
podAffinityTerm:
labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app
operator: In
values:
- rook-ceph-mds
# topologyKey: */zone can be used to spread MDS across different AZ
# Use <topologyKey: failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/zone> in k8s cluster if your cluster is v1.16 or lower
# Use <topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone> in k8s cluster is v1.17 or upper
topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone
# A key/value list of annotations
# annotations:
# key: value
# A key/value list of labels
# labels:
# key: value
# resources:
# The requests and limits set here, allow the filesystem MDS Pod(s) to use half of one CPU core and 1 gigabyte of memory
# limits:
# cpu: "500m"
# memory: "1024Mi"
# requests:
# cpu: "500m"
# memory: "1024Mi"
priorityClassName: system-cluster-critical
livenessProbe:
disabled: false
startupProbe:
disabled: false
# Filesystem mirroring settings
# mirroring:
# enabled: true
# list of Kubernetes Secrets containing the peer token
# for more details see: https://docs.ceph.com/en/latest/dev/cephfs-mirroring/#bootstrap-peers
# peers:
#secretNames:
#- secondary-cluster-peer
# specify the schedule(s) on which snapshots should be taken
# see the official syntax here https://docs.ceph.com/en/latest/cephfs/snap-schedule/#add-and-remove-schedules
# snapshotSchedules:
# - path: /
# interval: 24h # daily snapshots
# startTime: 11:55
# manage retention policies
# see syntax duration here https://docs.ceph.com/en/latest/cephfs/snap-schedule/#add-and-remove-retention-policies
# snapshotRetention:
# - path: /
# duration: "h 24"
---
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: rook-cephfs
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
# Change "rook-ceph" provisioner prefix to match the operator namespace if needed
provisioner: rook-ceph.cephfs.csi.ceph.com # driver:namespace:operator
parameters:
# clusterID is the namespace where the rook cluster is running
# If you change this namespace, also change the namespace below where the secret namespaces are defined
clusterID: rook-ceph # namespace:cluster
# CephFS filesystem name into which the volume shall be created
fsName: myfs
# Ceph pool into which the volume shall be created
# Required for provisionVolume: "true"
pool: myfs-replicated
# The secrets contain Ceph admin credentials. These are generated automatically by the operator
# in the same namespace as the cluster.
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-name: rook-csi-cephfs-provisioner
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-namespace: rook-ceph # namespace:cluster
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-name: rook-csi-cephfs-provisioner
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-namespace: rook-ceph # namespace:cluster
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-name: rook-csi-cephfs-node
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-namespace: rook-ceph # namespace:cluster
# (optional) The driver can use either ceph-fuse (fuse) or ceph kernel client (kernel)
# If omitted, default volume mounter will be used - this is determined by probing for ceph-fuse
# or by setting the default mounter explicitly via --volumemounter command-line argument.
# mounter: kernel
reclaimPolicy: Delete
allowVolumeExpansion: true
mountOptions:
# uncomment the following line for debugging
#- debugkubectl apply -f rook-cephfs.yaml