------紧接上篇博客,我们继续来实现登录后的功能代码-------:
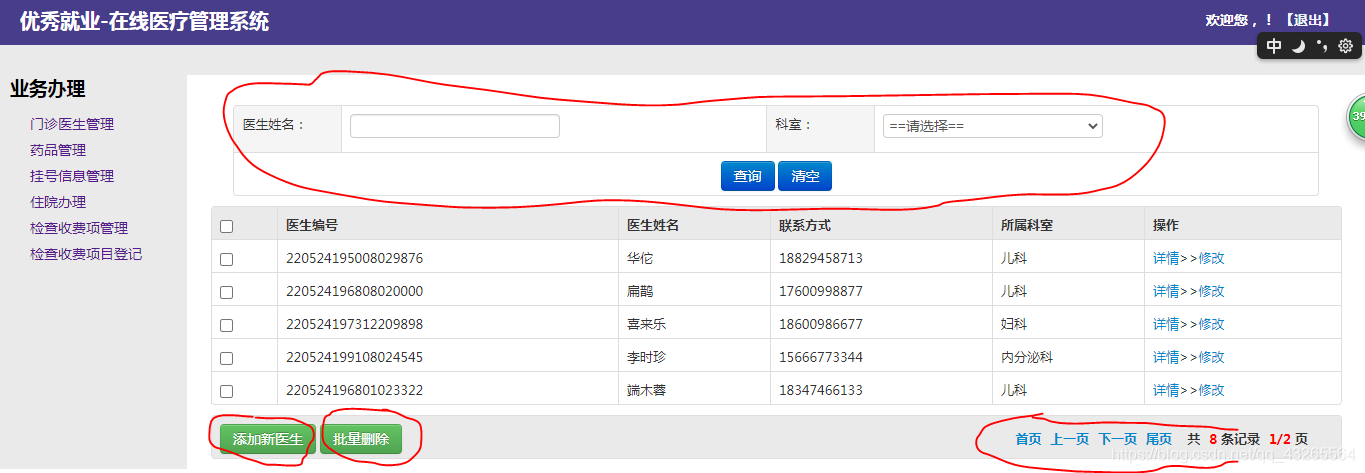
1.首先有一个医生管理模块,先将主界面展示一下,方便理解具体的功能:
- 在门诊医生管理里面有三块小的功能:根据医生姓名的模糊查询----根据查询的结果实现分页展示----和添加删除功能.
- 对于医生的增加和展示就不细说了,因为这个和管理员的注册一样,都是从界面获取数据执行sql语句.我们这篇文章主要说一下分页查询和模糊查询.
2.分页查询的工具类分析:
- 首先分析分页查询需要哪些数据:
| 数据 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| totalCount | 总数据量(这个就是显示当前总共查询了多少条数据) |
| currentPage | 当前的页码,比如这一页是第一页还是第二页 |
| pageCount | 总页数 |
| lastPage | 上一页的页码 |
| nextPage | 下一页的页码 |
| pageSize | 每一页的数据量(就是一页展示多少条数据) |
| startIndex | 起始下标(这个数据是sql查询的关键) |
- OK,上面这些就是我们需要获取的数据,但当有三个数据获取时,其他都可以知道了,分别是:totalCount,currentPage,pageSize,totalCount是可以通过数据库查询获取,currentPage可以从界面获取,pageSize是我们自定义的,OK,到这里我们就可以开始写工具类了.
public class PageTool {
private int totalCount;//总数据量
private int currentPage;//当前页面
private int pageCount;//总页数
private int lastPage;//上一页页数
private int nextPage;//下一页页数
private int pageSize;//每一页数据量
private int startIndex;//起始下标
public int getTotalCount() {
return totalCount;
}
public void setTotalCount(int totalCount) {
this.totalCount = totalCount;
}
public int getCurrentPage() {
return currentPage;
}
public void setCurrentPage(int currentPage) {
this.currentPage = currentPage;
}
public int getPageCount() {
return pageCount;
}
public void setPageCount(int pageCount) {
this.pageCount = pageCount;
}
public int getLastPage() {
return lastPage;
}
public void setLastPage(int lastPage) {
this.lastPage = lastPage;
}
public int getNextPage() {
return nextPage;
}
public void setNextPage(int nextPage) {
this.nextPage = nextPage;
}
public int getPageSize() {
return pageSize;
}
public void setPageSize(int pageSize) {
this.pageSize = pageSize;
}
public int getStartIndex() {
return startIndex;
}
public void setStartIndex(int startIndex) {
this.startIndex = startIndex;
}
public PageTool() {
}
/*
为什么只传递总数据量及当前页码呢?
每页数据量给定为死值,不需要传
我们只需要再知道当前页码及总数据量,其他的值都可以推算出来!
所以只传递当前页码及总数据量
*/
public PageTool(int totalCount, String currentPage) {
super();
this.totalCount = totalCount;
//将每页数据量给定为死值
pageSize = 5;
initialCurrentPage(currentPage);
initialPageCount();
initialLastPage();
initialNextPage();
initialStartIndex();
}
//初始化当前页码
private void initialStartIndex() {
startIndex = (currentPage - 1) * pageSize;
}
//初始化下一页页码
private void initialNextPage() {
if (currentPage == pageCount) {
nextPage = pageCount;
} else {
nextPage = currentPage + 1;
}
}
//初始化上一页页码
private void initialLastPage() {
if (currentPage == 1) {
lastPage = 1;
} else {
lastPage = currentPage - 1;
}
}
//初始化总页数的方法
private void initialPageCount() {
pageCount = totalCount / pageSize + (totalCount % pageSize == 0 ? 0 : 1);
}
//初始化当前页码的方法
private void initialCurrentPage(String currentPage) {
/*
从页面获取到的当前页码有两种情况:
1、当前页码为null,代表第一次进行分页展示页面,那么当前页码就是第一页
2、当前页码不为null,就代表点击了首页、尾页、上一页、下一页的按钮,传递的值
*/
if (currentPage == null) {
this.currentPage = 1;
} else {
this.currentPage = Integer.valueOf(currentPage);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PageTool [totalCount=" + totalCount + ", currentPage=" + currentPage + ", pageCount=" + pageCount
+ ", lastPage=" + lastPage + ", nextPage=" + nextPage + ", pageSize=" + pageSize + ", startIndex="
+ startIndex + "]";
}
}
- 当我们获取总数据量和页码时,就可以构建这个工具类对象来实现查询数据了
这里我们来聊一下有关查询结果都实现分页的思想:
- 我们无论是通过条件来查询,还是点击下一页来查询数据,其实就是多增加了一些sql语句中的条件判断,所以我们这里需要使用到两个思想:
- 1---->查询功能的方法里面需要构造一个包含医生姓名和科室的对象,用来处理用户通过姓名查询和科室查询 2—>sql语句的拼接,查询数据的不同就是因为不同的where条件,所以我们通过拼接来动态实现不同的查询需求
- OK,有了这两点思想,我们来开始写代码:首先是servlet中关于查询数据的功能方法:
public void findAllDoctor(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1.无论查询数据的方式是什么,先构造一个包含医生姓名和科室的对象
//1-1获取姓名和科室,不用管是否为空
String dname=request.getParameter("dname");
String department=request.getParameter("department");
//1-2构建模糊查询对象
Doctor doctor=null;
if (department!=null) {//1-3这里是用户进行按照科室查询,姓名无所谓
doctor=new Doctor(dname,Integer.valueOf(department));
}else {//1-4如果这里用户没有选择科室查询而是其他,把科室默认设置为0,表中科室0为无意义
doctor=new Doctor(dname, 0);
}
//2.获取总量,将构建的对象传入,因为我们考虑所有情况
int totalCount=doctorService.selectDoctorCount(doctor);
//2.获取的当前页码,这个是从页面获取的
String currentPage = request.getParameter("currentPage");
PageTool pageTool=new PageTool(totalCount, currentPage);
//1.获取医生对象集合,也是要把对象传入来查询
List<Doctor> doctors=doctorService.findAllDoctor(pageTool,doctor);
//2.存储到域对象中
request.setAttribute("doctors", doctors);
//将分页信息存储
request.setAttribute("pageTool", pageTool);
//将模糊查询的结构存储起来
request.setAttribute("doctor", doctor);
//3.通过请求转发
request.getRequestDispatcher("doctor/index.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
- 然后最为关键的就是Dao中我们怎么根据传递的一个包含姓名和科室的对象来按情况查询,首先是获取数据总量
//获取数据总量
public int selectDoctorCount(Doctor doctor) {
//1.定义一个可变的字符串对象来拼接条件
//1-1.where 1=1这个属于防止我们姓名和科室都为空出现sql语句错误
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder("select count(*) from doctor where 1=1 ");
//1.当姓名不为null,并且去掉空格也不为null
if (doctor.getDname()!=null&& !doctor.getDname().trim().equals("")) {
sb.append(" and dname like '%"+doctor.getDname()+"%' ");
}
//2.当选择的科室不为0
if (doctor.getDepartment()!=0) {
sb.append(" and department ="+doctor.getDepartment());
}
int row=0;
long a=0;
try {
a=qRunner.query(sb.toString(),new ScalarHandler<Long>());
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
row=(int)a;
return row;
}
- 然后再看查询结果的Dao中的代码:
//查询医生返回集合
public List<Doctor> findAllDoctor(PageTool pageTool, Doctor doctor) {
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder("select * from doctor where 1=1 ");
//1.当姓名不为null,并且去掉空格也不为null
if (doctor.getDname()!=null&& !doctor.getDname().trim().equals("")) {
sb.append(" and dname like '%"+doctor.getDname()+"%' ");
}
//2.当选择的科室不为0
if (doctor.getDepartment()!=0) {
sb.append(" and department = "+doctor.getDepartment());
}
sb.append(" limit ?,? ");
List<Doctor> doctors=null;
try {
doctors=qRunner.query(sb.toString(),new BeanListHandler<Doctor>(Doctor.class),pageTool.getStartIndex(),pageTool.getPageSize());
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return doctors;
}
- 到这一步,分页和模糊查询的核心就解决了,我们来看看界面展示的代码:
<table class="table table-bordered table-hover definewidth m10" >
<tr>
<th colspan="5"> <div class="inline pull-right page">
<a href='${path }doctor?func=findAllDoctor¤tPage=1' >首页</a>
<a href='${path }doctor?func=findAllDoctor¤tPage=${pageTool.lastPage}&dname=${doctor.dname }&department=${doctor.department}'>上一页</a>
<a href='${path }doctor?func=findAllDoctor¤tPage=${pageTool.nextPage}&dname=${doctor.dname }&department=${doctor.department}'>下一页</a>
<a href='${path }doctor?func=findAllDoctor¤tPage=${pageTool.pageCount}&dname=${doctor.dname }&department=${doctor.department}'>尾页</a>
共<span class='current'> ${pageTool.totalCount } </span>条记录
<span class='current'> ${pageTool.currentPage }/${pageTool.pageCount } </span>页
</div>
<div>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-success" id="newNav">添加新医生</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-success" id="delAll">批量删除</button>
</div>
</th>
</tr>
</table>
- 使用el表达式将获取的数据填入就可以,这里是分页按钮的数据填充.
---------到这里分页查询展示和模糊查询的功能就实现了-----
3.批量删除的操作:
- 通过checkbox来获取所有被选择的信息id:
$("#delAll").click(function(){
var ids="";
$(".one:checked").each(function(){
ids= ids+","+$(this).val()
})
if(ids==""){
alert("请选择要删除的医生")
return;
}
ids=ids.substring(1);
if(confirm("确定要删除吗?")){
window.location="${path}doctor?func=deleteDoctor&ids="+ids;
}
})
- 最终我们获取的是 1,2,4这样一个字符串
- Dao中执行的代码:
//删除
public int deleteDoctor(String ids) {
int row=0;
try {
row=qRunner.update("delete from doctor where did in ("+ids+")");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return row;
}
- 注意,这里的id为数字类型字符串,如果不为数字怎么办,这里使用循环执行删除:
public int deleteMedicine(String ids) {
int row=0;
try {
String[] split = ids.split(",");
for (String string : split) {
row=qRunner.update("delete from medicine where mid in ('"+string+"')");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return row;
}
- 不过一般我们不执行delete语句,我们使用update来修改数据中的伪删除字段为true;