接上篇:国密算法 SM9 公钥加密 数字签名 密钥交换 基于身份的密码算法(IBC)完整高效的开源python代码-CSDN博客
接触过国密算法Python库——hggm的朋友可能知道,库中SM2、SM3、SM4、ZUC都区分了慢速版和快速版:慢速版纯Python实现,代码逻辑清晰适合教学;快速版用了外挂(如numba),牺牲代码可读性或部分Python特性以追求更高的效率。上篇SM9代码虽然集成了若干关于效率优化的文献研究成果,但毕竟是纯Python实现的,我还是放在了慢速版(/slow目录下),这显然是给自己挖了坑。没发现合适的外挂,故而继续在数学上做文章,在上篇代码的基础上,主要进行了3项优化:
①固定点乘预计算。SM9的两个椭圆曲线群G1、G2的生成元分别是P1、P2,还有用户签名私钥ds,算法中多次出现与这些固定点的点乘运算(k·P),类似SM2,可提前计算好k的每一个字节位置与P相乘的结果并保存,后续点乘运算则转变为31次点加法。实测有6.~倍的效率提升。
②采用Comb固定基的高次幂运算。算法中多次出现以gs和ge为底的幂运算(gs=e(P1, Ppub_s), ge=e(Ppub_e, P2)),提前计算好gs和ge的预计算表,后续幂运算转变为31次乘法和31次平方计算(见文献:王江涛,樊荣,黄哲. SM9中高次幂运算的快速实现方法[J]. 计算机工程,2023,49(9):118-124,136. DOI:10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0065618)。实测有4倍左右的效率提升。
③固定G2点的双线性对预计算。用户加密私钥de(椭圆曲线群G2上的点)经常参与双线性对计算,可预先计算好双线性对Miller循环中由该点衍生出的所有系数,后续计算双线性对时可简化线函数,并省略点加。不过实测只有10%左右的效率提升。
当然上述优化都是针对特定的计算步骤,签名验签、加解密、密钥交换等算法中也包含了许多不符合上述情况的耗时步骤,因此实际提升幅度没有那么大。虽然依旧是纯Python实现,但上述优化也以牺牲可读性为代价,所以放在了快速版这边。
完整代码如下:
import os
from random import randrange
from math import ceil
from .SM3 import digest as sm3
# SM9总则(GB_T 38635.1-2020) A.1 系统参数
q = 0XB640000002A3A6F1D603AB4FF58EC74521F2934B1A7AEEDBE56F9B27E351457D # 基域特征
N = 0XB640000002A3A6F1D603AB4FF58EC74449F2934B18EA8BEEE56EE19CD69ECF25 # 群的阶
# 群G1的生成元 P1=(x_p1, y_p1)
x_p1 = 0X93DE051D62BF718FF5ED0704487D01D6E1E4086909DC3280E8C4E4817C66DDDD
y_p1 = 0X21FE8DDA4F21E607631065125C395BBC1C1C00CBFA6024350C464CD70A3EA616
# 群G2的生成元 P2=(x_p2, y_p2)
x_p2 = (0X85AEF3D078640C98597B6027B441A01FF1DD2C190F5E93C454806C11D8806141,
0X3722755292130B08D2AAB97FD34EC120EE265948D19C17ABF9B7213BAF82D65B)
y_p2 = (0X17509B092E845C1266BA0D262CBEE6ED0736A96FA347C8BD856DC76B84EBEB96,
0XA7CF28D519BE3DA65F3170153D278FF247EFBA98A71A08116215BBA5C999A7C7)
HASH_SIZE = 32 # sm3输出256位(32字节)
N_SIZE = 32 # 阶的字节数
KEY_LEN = 128 # 默认密钥位数
K2_len = 256 # MAC函数中密钥K2的位数
def to_byte(x, size=None):
if type(x) is int:
return x.to_bytes(size if size else ceil(x.bit_length() / 8), byteorder='big')
elif type(x) in (str, bytes):
x = x.encode() if type(x) is str else x
return x[:size] if size and len(x) > size else x # 超过指定长度,则截取左侧字符
elif type(x) in (tuple, list):
return b''.join(to_byte(c, size) for c in x)
return bytes(x)[:size] if size else bytes(x)
# 将字节转换为int
def to_int(byte):
return int.from_bytes(byte, byteorder='big')
# 广义的欧几里得除法求模逆(耗时约为slow/SM2代码内get_inverse函数的43%)
def mod_inv(a, mod=q):
if a == 0:
return 0
lm, low, hm, high = 1, a % mod, 0, mod
while low > 1:
r = high // low
lm, low, hm, high = hm - lm * r, high - low * r, lm, low
return lm % mod
class FQ:
def __init__(self, n):
self.n = n
def __add__(self, other):
return FQ(self.n + other.n)
def __sub__(self, other):
return FQ(self.n - other.n)
def __mul__(self, other): # 右操作数可为int
return FQ(self.n * (other.n if type(other) is FQ else other) % q)
def __truediv__(self, other): # 右操作数可为int
return FQ(self.n * mod_inv(other.n if type(other) is FQ else other) % q)
def __pow__(self, other): # 操作数应为int
return FQ(pow(self.n, other, q) if other else 1)
def __eq__(self, other): # 右操作数可为int
return self.n % q == (other.n if type(other) is FQ else other) % q
def __neg__(self):
return FQ(-self.n)
def __repr__(self):
return 'FQ(%064X)' % (self.n % q)
def __bytes__(self):
return to_byte(self.n % q, N_SIZE)
def is_zero(self):
return self.n % q == 0
def inv(self):
return FQ(mod_inv(self.n))
def sqr(self):
return FQ(self.n * self.n % q)
@classmethod
def one(cls):
return cls(1)
@classmethod
def zero(cls):
return cls(0)
class FQ2:
def __init__(self, *coeffs): # 国标中的表示是高位在前,而此处coeffs是低位在前
self.coeffs = coeffs
def __add__(self, other):
(a0, a1), (b0, b1) = self.coeffs, other.coeffs
return FQ2(a0 + b0, a1 + b1)
def __sub__(self, other):
(a0, a1), (b0, b1) = self.coeffs, other.coeffs
return FQ2(a0 - b0, a1 - b1)
def sqr(self):
a0, a1 = self.coeffs
return FQ2((a0 * a0 - (a1 * a1 << 1)) % q, (a0 * a1 << 1) % q) # (a0^2 - 2 * a1^2, 2 * a0 * a1)
def sqr_u(self):
a0, a1 = self.coeffs
return FQ2(-(a0 * a1 << 2) % q, (a0 * a0 - (a1 * a1 << 1)) % q) # (-4 * a0 * a1, a0^2 - 2 * a1^2)
def mul_b_u(self, b): # 带参数乘法
(a0, a1), (b0, b1) = self.coeffs, b.coeffs
return FQ2(-(a0 * b1 + a1 * b0 << 1) % q, (a0 * b0 - (a1 * b1 << 1)) % q) # (-2*(a0*b1+a1*b0), a0*b0-2*a1*b1)
def __mul__(self, other):
if type(other) is int:
a0, a1 = self.coeffs
return FQ2(a0 << 1, a1 << 1) if other == 2 else FQ2(a0 * other % q, a1 * other % q)
(a0, a1), (b0, b1) = self.coeffs, other.coeffs
a0b0, a1b1 = a0 * b0, a1 * b1 # Karatsuba 思想方法(节约一次乘法),实测此处约有5%提升,用在其他地方未见性能提升
return FQ2((a0b0 - (a1b1 << 1)) % q, ((a0 + a1) * (b0 + b1) - (a0b0 + a1b1)) % q) # (a0*b0-2*a1*b1,a0*b1+a1*b0)
def __rmul__(self, other):
return self.__mul__(other)
def __truediv__(self, other):
if type(other) is int:
other_inv = mod_inv(other)
return FQ2([c * other_inv % q for c in self.coeffs])
return self * other.inv()
def inv(self):
a0, a1 = self.coeffs
if a0 == 0:
return FQ2(0, -mod_inv(a1 << 1)) # (0, -(2 * a1)^-1)
if a1 == 0:
return FQ2(mod_inv(a0), 0) # (a0^-1, 0)
k = mod_inv(a0 * a0 + (a1 * a1 << 1)) # k = (a0^2 + 2 * a1^2)^-1
return FQ2(a0 * k % q, -a1 * k % q) # (a0 * k, -a1 * k)
def conjugate(self): # 共轭
a0, a1 = self.coeffs
return self.__class__(a0, -a1)
def get_fp_list(self): # 返回所有基域元素(高位在前)
if type(self) is FQ2:
return [i % q for i in self[::-1]]
return [y for x in self[::-1] for y in x.get_fp_list()] if self.coeffs else [0] * 4 # 注意FQ4对象零值的处理
def __repr__(self):
return '%s(%s)' % (self.__class__.__name__, ', '.join('%064X' % i for i in self.get_fp_list()))
def __bytes__(self): # 字节串高位在前
return to_byte(self.get_fp_list(), N_SIZE)
def __eq__(self, other):
return self.get_fp_list() == other.get_fp_list()
def __neg__(self):
return self.__class__(*[-c for c in self.coeffs])
def __getitem__(self, item):
return self.coeffs[item]
def is_zero(self):
return all(c % q == 0 for c in self.coeffs) if type(self) is FQ2 else all(c.is_zero() for c in self.coeffs)
@classmethod
def one(cls):
return FQ2_one if cls is FQ2 else (FQ12_one if cls is FQ12 else FQ4_one)
@classmethod
def zero(cls):
return FQ2_zero if cls is FQ2 else ()
class FQ4(FQ2): # 零元的coeffs为空,可优化FQ12稀疏乘法运算
def __add__(self, other):
if not self.coeffs:
return other
if not other.coeffs:
return self
(a0, a1), (b0, b1) = self.coeffs, other.coeffs
return FQ4(a0 + b0, a1 + b1)
def __sub__(self, other):
if not self.coeffs:
return -other
if not other.coeffs:
return self
(a0, a1), (b0, b1) = self.coeffs, other.coeffs
return FQ4(a0 - b0, a1 - b1)
def sqr(self):
if not self.coeffs:
return FQ4_zero
a0, a1 = self.coeffs
return FQ4(a0.sqr() + a1.sqr_u(), a0 * a1 * 2) # (a0^2 + a1^2 * u, 2 * a0 * a1)
def sqr_v(self):
if not self.coeffs:
return FQ4_zero
a0, a1 = self.coeffs
return FQ4(a0.mul_b_u(a1) * 2, a0.sqr() + a1.sqr_u()) # (2 * a0 * a1 * u, a0^2 + a1^2 * u)
def mul_b_v(self, b): # 带参数乘法
if not self.coeffs or not b.coeffs:
return FQ4_zero
(a0, a1), (b0, b1) = self.coeffs, b.coeffs
return FQ4(a0.mul_b_u(b1) + a1.mul_b_u(b0), a0 * b0 + a1.mul_b_u(b1)) # (a0*b1*u+a1*b0*u, a0*b0+a1*b1*u)
def __mul__(self, other):
if not self.coeffs:
return FQ4_zero
if type(other) is int:
a0, a1 = self.coeffs
return FQ4(a0 * other, a1 * other)
if not other.coeffs:
return FQ4_zero
(a0, a1), (b0, b1) = self.coeffs, other.coeffs
return FQ4(a0 * b0 + a1.mul_b_u(b1), a0 * b1 + a1 * b0) # (a0*b0+a1*b1*u, a0*b1+a1*b0)
def inv(self):
if not self.coeffs:
return FQ4_zero
a0, a1 = self.coeffs
k = (a1.sqr_u() - a0.sqr()).inv()
return FQ4((-a0 * k), a1 * k)
class FQ12(FQ2):
def __add__(self, other):
(a0, a1, a2), (b0, b1, b2) = self.coeffs, other.coeffs
return FQ12(a0 + b0, a1 + b1, a2 + b2)
def __sub__(self, other):
(a0, a1, a2), (b0, b1, b2) = self.coeffs, other.coeffs
return FQ12(a0 - b0, a1 - b1, a2 - b2)
def sqr(self):
a0, a1, a2 = self.coeffs
return FQ12(a0.sqr() + a1.mul_b_v(a2) * 2, a0 * a1 * 2 + a2.sqr_v(), a0 * a2 * 2 + a1.sqr())
def __mul__(self, other):
(a0, a1, a2), (b0, b1, b2) = self.coeffs, other.coeffs
return FQ12(a0 * b0 + a1.mul_b_v(b2) + a2.mul_b_v(b1), a0 * b1 + a1 * b0 + a2.mul_b_v(b2),
a0 * b2 + a1 * b1 + a2 * b0)
def sqr2(self): # 分圆循环子群Gϕ6(Fp2)中的元素平方
a, b, c = self.coeffs
a2, b2, c2v = a.sqr(), b.sqr(), c.sqr_v()
return FQ12(a2 + (a2 - a.conjugate()) * 2, c2v + (c2v + b.conjugate()) * 2, b2 + (b2 - c.conjugate()) * 2)
def __pow__(self, other): # 实际运行此函数的对象都是分圆循环子群Gϕ6(Fp2)中的元素
if other > 10: # 加减法
h, k = bin(3 * other)[2:], bin(other)[2:]
k, t, nf = '0' * (len(h) - len(k)) + k, self, self.frobenius6()
for i in range(1, len(h) - 1):
t = t.sqr2()
if h[i] == '1' and k[i] == '0':
t = t * self
elif h[i] == '0' and k[i] == '1':
t = t * nf
else:
t = self
for ri in bin(other)[3:]:
t = t.sqr2() * self if ri == '1' else t.sqr2()
return t
def inv(self):
a0, a1, a2 = self.coeffs
a0_2, a1_2 = a0.sqr(), a1.sqr()
if a2.is_zero():
k = (a0 * a0_2 + a1.mul_b_v(a1_2)).inv()
return FQ12(a0_2 * k, (-a0 * a1 * k), a1_2 * k)
t0, t1, t2 = a1_2 - a0 * a2, a0 * a1 - a2.sqr_v(), a0_2 - a1.mul_b_v(a2)
t3 = a2 * (t1.sqr() - t0 * t2).inv()
return FQ12(t2 * t3, (-t1 * t3), t0 * t3)
def frobenius(self):
(a0, a1), (b0, b1), (c0, c1) = self.coeffs
a = FQ4(a0.conjugate(), a1.conjugate() * alpha3)
b = FQ4(b0.conjugate() * alpha1, b1.conjugate() * alpha4)
c = FQ4(c0.conjugate() * alpha2, c1.conjugate() * alpha5)
return FQ12(a, b, c)
def frobenius2(self):
a, b, c = self.coeffs
return FQ12(a.conjugate(), b.conjugate() * alpha2, c.conjugate() * alpha4)
def frobenius3(self):
(a0, a1), (b0, b1), (c0, c1) = self.coeffs
a = FQ4(a0.conjugate(), -a1.conjugate() * alpha3)
b = FQ4(b0.conjugate() * alpha3, b1.conjugate())
c = FQ4(-c0.conjugate(), c1.conjugate() * alpha3)
return FQ12(a, b, c)
def frobenius6(self):
a, b, c = self.coeffs
return FQ12(a.conjugate(), -b.conjugate(), c.conjugate())
class ECC_Point:
def __init__(self, *pt): # 采用Jacobian射影坐标计算,输入仿射坐标后会转换为Jacobian射影坐标
self.pt = pt if len(pt) == 3 else (*pt, pt[0].one())
@classmethod
def from_byte(cls, byte): # 输入bytes类型仿射坐标,构建点对象
fp_num = len(byte) // (N_SIZE << 1) # 单个坐标包含的域元素个数
if fp_num in (1, 2) and len(byte) % N_SIZE == 0:
fp_list = [to_int(byte[i:i + N_SIZE]) for i in range(0, len(byte), N_SIZE)] # 将bytes转换为域元素列表
if fp_num == 1:
return cls(FQ(fp_list[0]), FQ(fp_list[1]))
x_list, y_list = fp_list[fp_num - 1::-1], fp_list[:fp_num - 1:-1] # 从bytes到FQ2对象保存的域元素,需翻转高低位顺序
return cls(FQ2(*x_list), FQ2(*y_list))
return False
def is_inf(self):
return self[2].is_zero()
def is_on_curve(self): # 检查点是否满足曲线方程 y^2 == x^3 + b
x, y, z = self.pt
return y ** 2 == x ** 3 + (_b1 if type(x) is FQ else _b2) * z ** 6
def double(self):
x, y, z = self.pt
_3x2, _2y = x.sqr() * 3, y * 2
_4y2 = _2y.sqr()
_4xy2 = x * _4y2
x3 = _3x2.sqr() - _4xy2 * 2
return ECC_Point(x3, _3x2 * (_4xy2 - x3) - _4y2.sqr() * _2_inv, _2y * z)
def zero(self):
cls = self[0].__class__
return ECC_Point(cls.one(), cls.one(), cls.zero())
def __add__(self, p2):
if self.is_inf():
return p2
if p2.is_inf():
return self
(x1, y1, z1), (x2, y2, z2) = self.pt, p2.pt
z1_2, z2_2 = z1.sqr(), z2.sqr()
T1, T2 = x1 * z2_2, x2 * z1_2
T3, T4, T5 = T1 - T2, y1 * z2_2 * z2, y2 * z1_2 * z1
T6, T7, T3_2 = T4 - T5, T1 + T2, T3.sqr()
T8, T9 = T4 + T5, T7 * T3_2
x3 = T6.sqr() - T9
T10 = T9 - x3 * 2
y3 = (T10 * T6 - T8 * T3_2 * T3) * _2_inv
z3 = z1 * z2 * T3
return ECC_Point(x3, y3, z3)
def multiply(self, n): # 算法一:二进制展开法
if n in (0, 1):
return self if n else self.zero()
Q = self
for i in bin(n)[3:]:
Q = Q.double() + self if i == '1' else Q.double()
return Q
def __mul__(self, n): # 算法三:滑动窗法
k = bin(n)[2:]
l, r = len(k), 5 # 滑动窗口为5效果较好
if r >= l: # 如果窗口大于k的二进制位数,则本算法无意义
return self.multiply(n)
P_ = {1: self, 2: self.double()} # 保存P[j]值的字典
for i in range(1, 1 << (r - 1)):
P_[(i << 1) + 1] = P_[(i << 1) - 1] + P_[2]
t = r
while k[t - 1] != '1':
t -= 1
hj = int(k[:t], 2)
Q, j = P_[hj], t
while j < l:
if k[j] == '0':
Q = Q.double()
j += 1
else:
t = min(r, l - j)
while k[j + t - 1] != '1':
t -= 1
hj = int(k[j:j + t], 2)
Q = Q.multiply(1 << t) + P_[hj]
j += t
return Q
def __rmul__(self, n):
return self.__mul__(n)
def __eq__(self, p2):
(x1, y1, z1), (x2, y2, z2) = self.pt, p2.pt
z1_2, z2_2 = z1.sqr(), z2.sqr()
return x1 * z2_2 == x2 * z1_2 and y1 * z2_2 * z2 == y2 * z1_2 * z1
def __neg__(self):
x, y, z = self.pt
return ECC_Point(x, -y, z)
def __getitem__(self, item):
return self.pt[item]
def __repr__(self):
return '%s%s' % (self.__class__.__name__, self.normalize())
def __bytes__(self):
return to_byte(self.normalize(), N_SIZE if type(self[0]) is FQ else None)
def normalize(self):
x, y, z = self.pt
if not hasattr(self, 'normalize_tuple'):
if z != z.one():
z_inv = z.inv()
z_inv_2 = z_inv.sqr()
x, y = x * z_inv_2, y * z_inv_2 * z_inv
self.normalize_tuple = (x.n, y.n) if type(x) is FQ else (x, y)
return self.normalize_tuple
def frobenius(self):
x, y, z = self.pt
return ECC_Point(x.conjugate(), y.conjugate(), z.conjugate() * alpha1)
def frobenius2_neg(self):
x, y, z = self.pt
return ECC_Point(x, -y, z * alpha2)
FQ2_one, FQ2_zero = FQ2(1, 0), FQ2(0, 0) # FQ2单位元、零元
FQ4_one, FQ4_zero = FQ4(FQ2_one, FQ2_zero), FQ4() # FQ4单位元、零元
FQ12_one = FQ12(FQ4_one, FQ4_zero, FQ4_zero) # FQ12单位元
P1 = ECC_Point(FQ(x_p1), FQ(y_p1)) # 群G1的生成元
P2 = ECC_Point(FQ2(*x_p2[::-1]), FQ2(*y_p2[::-1])) # 群G2的生成元
_b1, _b2 = FQ(5), FQ2(0, 5) # b2=βb=(1,0)*5
alpha1 = 0X3F23EA58E5720BDB843C6CFA9C08674947C5C86E0DDD04EDA91D8354377B698B # -2^((q - 1)/12)
alpha2 = 0XF300000002A3A6F2780272354F8B78F4D5FC11967BE65334 # -2^((q - 1)/6)
alpha3 = 0X6C648DE5DC0A3F2CF55ACC93EE0BAF159F9D411806DC5177F5B21FD3DA24D011 # -2^((q - 1)/4)
alpha4 = 0XF300000002A3A6F2780272354F8B78F4D5FC11967BE65333 # -2^((q - 1)/3)
alpha5 = 0X2D40A38CF6983351711E5F99520347CC57D778A9F8FF4C8A4C949C7FA2A96686
_2_inv = 0X5B2000000151D378EB01D5A7FAC763A290F949A58D3D776DF2B7CD93F1A8A2BF # 1/2
_3div2 = 0X5B2000000151D378EB01D5A7FAC763A290F949A58D3D776DF2B7CD93F1A8A2C0 # 3/2
R_ate_a_NAF = '0100000000000000000000000000000000000010001020200020200101000020' # a=6t+2的二进制非相邻表示(2-NAF)(去首10)
hlen = 320 # 8 * ceil(5 * log(N, 2) / 32)
_t, _6t, _6t_3 = 0x600000000058F98A, 0X2400000000215D93C, 0X2400000000215D93F
# 输入系数值和点P,求线函数值
def g_value(a_tuple, P):
(a0, a1, a4), (xP, yP) = a_tuple, P
return FQ12(FQ4(a0, a1 * yP), FQ4_zero, FQ4(a4 * xP, FQ2_zero))
# 获取线函数g T,Q(P)的系数值(分母在最终模幂时值为1,可消去)
def get_g_a_tuple(T, Q):
(xT, yT, zT), (xQ, yQ, zQ) = T, Q
zT_2, zQ_2 = zT.sqr(), zQ.sqr()
zQ_3, t1 = zQ * zQ_2, (xT * zQ_2 - xQ * zT_2) * zT * zQ
a1, t2 = t1 * zQ_3, (yT * zQ_3 - yQ * zT * zT_2) * zQ
a0, a4 = t1 * yQ - t2 * xQ, t2 * zQ_2
return a0, a1, a4
# 线函数g T,Q(P),求过点T和Q的直线在P上的值
def g(T, Q, nP):
return g_value(get_g_a_tuple(T, Q), nP)
# 获取线函数g T,T(P)的系数值(分母在最终模幂时值为1,可消去),利用中间值完成倍点计算
def get_g2_a_tuple(T):
x, y, z = T
_z2, _3x2, _2y = z.sqr(), x.sqr() * 3, y * 2
_4y2, _2yz = _2y.sqr(), _2y * z
a1, a0, a4, _4xy2 = _z2 * _2yz, _4y2 * _2_inv - _3x2 * x, _3x2 * _z2, x * _4y2
x3 = _3x2.sqr() - _4xy2 * 2
y3 = _3x2 * (_4xy2 - x3) - _4y2.sqr() * _2_inv
return (a0, a1, a4), ECC_Point(x3, y3, _2yz)
# 线函数g T,T(P),求过点T的切线在P上的值,利用中间值完成倍点计算
def g2(T, nP):
a_tuple, double_T = get_g2_a_tuple(T)
return g_value(a_tuple, nP), double_T
# BN曲线上R_ate对的计算
def e(P, Q):
nQ, nP_xy = -Q, (-P).normalize()
f, T = g2(Q, nP_xy)
for ai in R_ate_a_NAF:
new_g, T = g2(T, nP_xy)
f = f.sqr() * new_g
if ai == '1':
f, T = f * g(T, Q, nP_xy), T + Q
elif ai == '2': # 用2代替-1
f, T = f * g(T, nQ, nP_xy), T + nQ
Q1, nQ2 = Q.frobenius(), Q.frobenius2_neg()
return final_exp(f * g(T, Q1, nP_xy) * g(T + Q1, nQ2, nP_xy))
# 最终模幂
def final_exp(f):
m = f.frobenius6() * f.inv() # f^(p^6 - 1)
s = m.frobenius2() * m # m^(p^2 + 1)
# 困难部分 s^(p^3 + (6t^2+1)p^2 + (-36t^3-18t^2-12t+1)p + (-36t^3-30t^2-18t-2))
s_6t = s ** _6t
s_6t2 = s_6t ** _t
s_36t3_18t2_12t, a2 = s_6t2 ** _6t_3 * s_6t.sqr2(), s_6t2 * s
a1, a0 = s_36t3_18t2_12t.frobenius6() * s, (s_36t3_18t2_12t * s_6t * a2.sqr2()).frobenius6()
return s.frobenius3() * a2.frobenius2() * a1.frobenius() * a0
# 获取线函数的系数值序列
def get_a_list(Q):
a_tuple, T = get_g2_a_tuple(Q)
a_list, nQ = [a_tuple], -Q
for ai in R_ate_a_NAF:
a_tuple, T = get_g2_a_tuple(T)
a_list.append(a_tuple)
if ai != '0':
a_list.append(get_g_a_tuple(T, nQ if ai == '2' else Q))
T = T + (nQ if ai == '2' else Q)
Q1, nQ2 = Q.frobenius(), Q.frobenius2_neg()
return a_list + [get_g_a_tuple(T, Q1), get_g_a_tuple(T + Q1, nQ2)]
def e_fast(P, a_list):
nP_xy = (-P).normalize()
f, i = g_value(a_list[0], nP_xy), 1
for ai in R_ate_a_NAF:
f, i = f.sqr() * g_value(a_list[i], nP_xy), i + 1
if ai != '0':
f, i = f * g_value(a_list[i], nP_xy), i + 1
return final_exp(f * g_value(a_list[i], nP_xy) * g_value(a_list[-1], nP_xy))
# 获取Comb固定基的预计算表(256个FQ12的列表)
def get_comb_list(n):
comb_list = [FQ12_one, n]
for i in range(7):
tmp = comb_list[2**i]
for _ in range(32):
tmp = tmp.sqr2()
comb_list += [tmp * c for c in comb_list]
return comb_list
# Comb固定基的幂运算
def comb_pow(r, comb_list):
r_bin, res = '0' * (256 - r.bit_length()) + bin(r)[2:], FQ12_one
for i in range(32):
a = int(''.join(r_bin[j] for j in range(i, 256, 32)), 2)
res = comb_list[a] if res is FQ12_one else res.sqr2() * comb_list[a]
return res
# 获取固定点乘的预计算表(32行256列的椭圆曲线点矩阵)
def get_kP_list(P):
one, kP_list = P, []
for i in range(32):
line_list = [0, one] # O, P
for j in range(1, 128):
line_list.append(line_list[j].double()) # 2j·P
line_list.append(line_list[-1] + one) # (2j+1)·P
kP_list.append(line_list)
one = line_list[128].double() if i < 31 else 0
return kP_list
# 使用预计算表的快速点乘
def fast_kG(k, kP_list):
P_list = [kP_list[i][byte] for i, byte in enumerate(k.to_bytes(32, byteorder='little')) if byte]
return sum(P_list[1:], P_list[0])
# SM9算法(GB_T 38635.2-2020) 5.3.6定义的密钥派生函数
# Z为bytes类型,klen表示输出密钥比特长度(8的倍数);输出为bytes类型
def KDF(Z, klen=KEY_LEN):
ksize, K = klen >> 3, bytearray()
for ct in range(1, ceil(ksize / HASH_SIZE) + 1):
K.extend(sm3(Z + to_byte(ct, 4)))
return K[:ksize]
# SM9算法(GB_T 38635.2-2020) 5.3.2.2和5.3.2.3定义的密码函数
def H(i, Z):
Ha = to_int(KDF(to_byte(i, 1) + Z, hlen))
return Ha % (N - 1) + 1
# SM9算法(GB_T 38635.2-2020) 5.3.5定义的消息认证码函数
def MAC(K2, Z):
return sm3(Z + K2)
class SM9: # SM9算法(GB_T 38635.2-2020)
def __init__(self, ID='', ds=None, Ppub_s=None, de=None, Ppub_e=None, hid_s=1, hid_e=3, ks=None, ke=None):
self.ID, self.ID_byte, self.hid_s_byte, self.hid_e_byte = ID, to_byte(ID), to_byte(hid_s, 1), to_byte(hid_e, 1)
if ks: # 作为密钥生成中心,给定签名主私钥(若要随机生成,可指定ks=-1)
self.ks = ks if 0 < ks < N else randrange(1, N)
self.Ppub_s = fast_kG(self.ks, _kP2)
if ke: # 作为密钥生成中心,给定加密主私钥(若要随机生成,可指定ke=-1)
self.ke = ke if 0 < ke < N else randrange(1, N)
self.Ppub_e = fast_kG(self.ke, _kP1)
if ds and Ppub_s: # 作为用户,给定用户签名私钥和签名主公钥
self.k_ds_list, self.Ppub_s, self.gs = get_kP_list(ds), Ppub_s, e(P1, Ppub_s)
self.gs_comb_list = get_comb_list(self.gs)
if de and Ppub_e: # 作为用户,给定用户加密私钥和加密主公钥
self.de_a_list, self.Ppub_e, self.ge = get_a_list(de), Ppub_e, e(Ppub_e, P2)
self.ge_comb_list = get_comb_list(self.ge)
def KGC_gen_user(self, ID):
ID_byte, ds, Ppub_s, de, Ppub_e = to_byte(ID), None, None, None, None
if hasattr(self, 'ks'):
t1 = (H(1, ID_byte + self.hid_s_byte) + self.ks) % N
if t1 == 0: # 需重新产生签名主密钥,并更新所有用户的签名密钥
return False
t2 = self.ks * mod_inv(t1, N) % N
ds, Ppub_s = fast_kG(t2, _kP1), self.Ppub_s # 用户签名私钥和签名主公钥
if hasattr(self, 'ke'):
t1 = (H(1, ID_byte + self.hid_e_byte) + self.ke) % N
if t1 == 0: # 需重新产生加密主密钥,并更新所有用户的加密密钥
return False
t2 = self.ke * mod_inv(t1, N) % N
de, Ppub_e = fast_kG(t2, _kP2), self.Ppub_e # 用户加密私钥和加密主公钥
return SM9(ID, ds, Ppub_s, de, Ppub_e, self.hid_s_byte, self.hid_e_byte)
# 6.2 数字签名生成算法
def sign(self, M, r=None, outbytes=True):
l = 0
while l == 0:
r = r if r else randrange(1, N) # A2
w = bytes(self.gs_pow(r)) # A3
h = H(2, to_byte(M) + w) # A4
l = (r - h) % N # A5
S = fast_kG(l, self.k_ds_list) # A6
return to_byte([h, S]) if outbytes else (h, S)
# 6.4 数字签名验证算法
def verify(self, ID, M_, sig):
h_, S_ = (to_int(sig[:N_SIZE]), ECC_Point.from_byte(sig[N_SIZE:])) if type(sig) is bytes else sig
if not 0 < h_ < N or not S_ or not S_.is_on_curve(): # B1、B2
return False
t = self.gs_pow(h_) # B4
h1 = H(1, to_byte(ID) + self.hid_s_byte) # B5
P = fast_kG(h1, _kP2) + self.Ppub_s # B6
u = e(S_, P) # B7
w_ = bytes(u * t) # B8
h2 = H(2, to_byte(M_) + w_) # B9
return h_ == h2
# A 发起协商(也可用作B生成rB、RB;outbytes=True时输出bytes)
# 7.2 密钥交换协议 A1-A3
def agreement_initiate(self, IDB, r=None, outbytes=True):
QB = fast_kG(H(1, to_byte(IDB) + self.hid_e_byte), _kP1) + self.Ppub_e # A1
rA = r if r else randrange(1, N) # A2
RA = QB * rA # A3
return rA, bytes(RA) if outbytes else RA
# B 响应协商(option=True时计算选项部分)
# 7.2 密钥交换协议 B1-B6
def agreement_response(self, RA, IDA, option=False, rB=None, klen=KEY_LEN, outbytes=True):
RA = ECC_Point.from_byte(RA) if type(RA) is bytes else RA
if not RA or not RA.is_on_curve(): # B4
return False, 'RA不属于椭圆曲线群G1'
rB, RB = self.agreement_initiate(IDA, rB, outbytes) # B1-B3
g1, g2 = self.e_de(RA), bytes(self.ge_pow(rB)) # B4
g1, g3 = bytes(g1), bytes(g1 ** rB) # B4
tmp_byte = to_byte([IDA, self.ID_byte, RA, RB])
SKB = KDF(tmp_byte + g1 + g2 + g3, klen) # B5
if not option:
return True, (RB, SKB)
self.tmp_byte2 = g1 + sm3(g2 + g3 + tmp_byte)
SB = sm3(to_byte(0x82, 1) + self.tmp_byte2) # B6(可选部分)
return True, (RB, SKB, SB)
# A 协商确认
# 7.2 密钥交换协议 A5-A8
def agreement_confirm(self, rA, RA, RB, IDB, SB=None, option=False, klen=KEY_LEN):
RB = ECC_Point.from_byte(RB) if type(RB) is bytes else RB
if not RB or not RB.is_on_curve(): # A5
return False, 'RB不属于椭圆曲线群G1'
g1_, g2_ = bytes(self.ge_pow(rA)), self.e_de(RB) # A5
g2_, g3_ = bytes(g2_), bytes(g2_ ** rA) # A5
tmp_byte = to_byte([self.ID_byte, IDB, RA, RB])
if option and SB: # A6(可选部分)
tmp_byte2 = g1_ + sm3(g2_ + g3_ + tmp_byte)
S1 = sm3(to_byte(0x82, 1) + tmp_byte2)
if S1 != SB:
return False, 'S1 != SB'
SKA = KDF(tmp_byte + g1_ + g2_ + g3_, klen) # A7
if not option or not SB:
return True, SKA
SA = sm3(to_byte(0x83, 1) + tmp_byte2) # A8
return True, (SKA, SA)
# B 协商确认(可选部分)
# 7.2 密钥交换协议 B8
def agreement_confirm2(self, SA):
if not hasattr(self, 'tmp_byte2'):
return False, 'step error'
S2 = sm3(to_byte(0x83, 1) + self.tmp_byte2)
if S2 == SA:
del self.tmp_byte2
return True, ''
return False, 'S2 != SA'
# 8.2 密钥封装算法
def encaps(self, IDB, klen, r=None, outbytes=True):
K = bytes()
while K == bytes(len(K)):
r, C = self.agreement_initiate(IDB, r, outbytes) # A1-A3
w = bytes(self.ge_pow(r)) # A5
K = KDF(to_byte([C, w, IDB]), klen)
return K, C
# 8.4 密钥封装算法
def decaps(self, C, klen):
C = ECC_Point.from_byte(C) if type(C) is bytes else C
if not C or not C.is_on_curve(): # B1
return False, 'C不属于椭圆曲线群G1'
w_ = bytes(self.e_de(C)) # B2
K_ = KDF(to_byte([C, w_, self.ID_byte]), klen) # B3
return (True, K_) if K_ != bytes(len(K_)) else (False, 'K为全0比特串')
# 9.2 加密算法
def encrypt(self, IDB, M, r=None, outbytes=True):
M = to_byte(M)
K, C1 = self.encaps(IDB, (len(M) << 3) + K2_len, r, outbytes) # A1-A6.a.1
K1, K2 = K[:len(M)], K[len(M):] # A6.a.1
C2 = bytes(M[i] ^ K1[i] for i in range(len(M))) # A6.a.2
C3 = MAC(K2, C2) # A7
return to_byte([C1, C3, C2]) if outbytes else (C1, C3, C2)
# 9.4 解密算法
def decrypt(self, C):
C3_start, C3_end = N_SIZE << 1, (N_SIZE << 1) + HASH_SIZE
C1, C3, C2 = (C[:C3_start], C[C3_start:C3_end], C[C3_end:]) if type(C) is bytes else C
res, K_ = self.decaps(C1, (len(C2) << 3) + K2_len) # B1-B3.a.1
if not res:
return False, K_.replace('C', 'C1')
K1_, K2_ = K_[:len(C2)], K_[len(C2):] # B3.a.1
if K1_ == bytes(len(K_)):
return False, 'K1\'为全0比特串'
u = MAC(K2_, C2) # B4
if u != C3:
return False, 'u != C3'
return True, bytes(C2[i] ^ K1_[i] for i in range(len(C2))) # B3.a.2
def e_de(self, P):
return e_fast(P, self.de_a_list)
def gs_pow(self, r):
return comb_pow(r, self.gs_comb_list)
def ge_pow(self, r):
return comb_pow(r, self.ge_comb_list)
_SM9kG_file = 'hggm/SM9_kG.bin' # 预计算数据文件的位置
_kP1, _kP2 = [], [] # P1、P2点的预计算表
if os.path.exists(_SM9kG_file):
with open(_SM9kG_file, 'rb') as f: # 读取预计算数据文件
data = f.read()
G1_size, G2_size = N_SIZE << 1, N_SIZE << 2 # G1点坐标字节数、G2点坐标字节数
P1_line, line = 255 * G1_size, 255 * (G1_size + G2_size) # 一行G1点坐标字节数、一行总字节数
for i in range(0, N_SIZE * line, line):
_kP1.append([0] + [ECC_Point.from_byte(data[j:j + G1_size]) for j in range(i, i + P1_line, G1_size)])
_kP2.append([0] + [ECC_Point.from_byte(data[j:j + G2_size]) for j in range(i + P1_line, i + line, G2_size)])
else: # 预计算数据文件不存在
_kP1, _kP2 = get_kP_list(P1), get_kP_list(P2) # 生成P1、P2点的预计算表
with open(_SM9kG_file, 'wb') as f: # 将预计算表写入二进制文件
f.write(b''.join(map(bytes, [P for x, y in zip(_kP1, _kP2) for P in x[1:] + y[1:]])))
完善了测试代码,创建KGC的代码比上版稍有变动:
IDA, IDB, message = 'Alice', 'Bob', 'Chinese IBS standard'
kgc = SM9(ks=0x130E78459D78545CB54C587E02CF480CE0B66340F319F348A1D5B1F2DC5F4,
ke=0x2E65B0762D042F51F0D23542B13ED8CFA2E9A0E7206361E013A283905E31F)
sm9_A, sm9_B = kgc.KGC_gen_user(IDA), kgc.KGC_gen_user(IDB)
assert bytes(sm9_A.gs).hex().swapcase().endswith('F0F071D7D284FCFB')
print("-----------------test sign and verify---------------")
r = 0x033C8616B06704813203DFD00965022ED15975C662337AED648835DC4B1CBE
signature = sm9_A.sign(message, r)
assert signature.hex().swapcase().endswith('827CC2ACED9BAA05')
assert sm9_B.verify(IDA, message, signature)
print("success")
print("-----------------test key agreement---------------")
rA = 0x5879DD1D51E175946F23B1B41E93BA31C584AE59A426EC1046A4D03B06C8
rA, RA = sm9_A.agreement_initiate(IDB, rA) # A发起协商
# A将RA发送给B
rB = 0x018B98C44BEF9F8537FB7D071B2C928B3BC65BD3D69E1EEE213564905634FE
res, content = sm9_B.agreement_response(RA, IDA, True, rB) # B响应协商
if not res:
print('B报告协商错误:', content)
return
RB, SKB, SB = content
# B将RB、SB发送给A
res, content = sm9_A.agreement_confirm(rA, RA, RB, IDB, SB, True) # A协商确认
if not res:
print('A报告协商错误:', content)
return
SKA, SA = content
assert SKA.hex().swapcase() == '68B20D3077EA6E2B825315836FDBC633'
# A将SA发送给B
res, content = sm9_B.agreement_confirm2(SA) # B协商确认
if not res:
print('B报告协商错误:', content)
return
assert SKA == SKB
print("success")
print("-----------------test encrypt and decrypt---------------")
message = 'Chinese IBE standard'
kgc = SM9(ke=0x01EDEE3778F441F8DEA3D9FA0ACC4E07EE36C93F9A08618AF4AD85CEDE1C22)
sm9_A, sm9_B = kgc.KGC_gen_user(IDA), kgc.KGC_gen_user(IDB)
C = sm9_A.encrypt(IDB, message, 0xAAC0541779C8FC45E3E2CB25C12B5D2576B2129AE8BB5EE2CBE5EC9E785C)
assert C.hex().swapcase().endswith('378CDD5DA9513B1C')
res, content = sm9_B.decrypt(C)
if not res:
print('解密错误:', content)
return
assert message == content.decode()
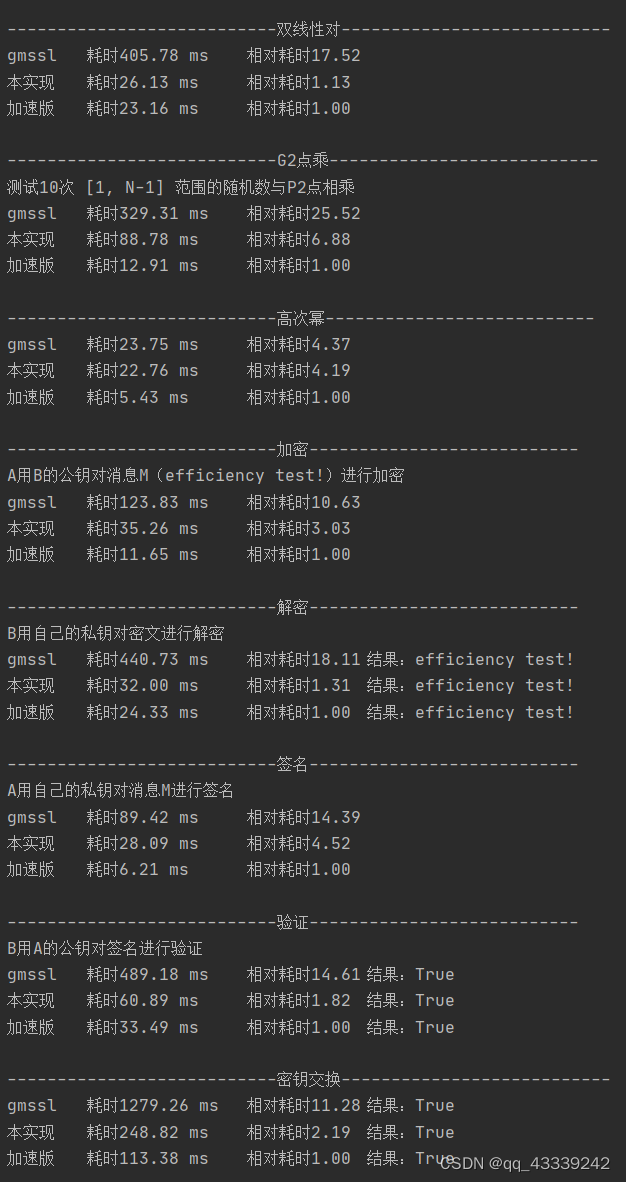
print("success")运行结果如下,可见实际算法比上版有20%~4倍提升不等:
hggm国密算法Python库自2022年3月开始开发,2022年4月首次公开,目前已经包含SM2、SM3、SM4、SM9、ZUC的慢速版和快速版,基本完善了。出于个人研究学习的兴趣,纰漏在所难免,可继续改进提升的地方还很多,望各位不吝赐教,我会持续更新优化。从一开始就坚持完全开源,希望能帮到大家,也希望能以个人之所学为网安事业尽绵薄之力。
但愿这不止是完结,而是全新的开始。