深度学习之语义分割概念
文章目录
前言
常见的分割任务:
-
语义分割(semantic segmentation):对图像中的每一个像素进行分类属于哪个类别,语义分割的目标是将图像中的每个像素归类到相应的类别中,但它不能区分不同的物体实例。(FCN)
-
实例分割(Instance segmentation):不但对图像中的每一个像素进行分类还在具体分类的基础上区别开不同的实例,实例分割看成是目标检测(定位)+语义分割(分割)。(Mask R-CNN)
-
全景分割(Panoramic segmentation):为图像的每个像素分配一个语义标签和一个唯一的实例标识符,可以看成是语义分割和实例分割的综合方法。(Panoptic FPN)
三种方法的分割精细程度递增,难度也递增。
一、语义分割任务常见数据集格式
1.PASCAL VOC
根据索引在JPEGImages 文件夹中找到对应的图片。以2007_000323为例,可以找到2007_000323.jpg文件
标注的图片格式是PNG格式,是一通道的图片,但是采用调色板的格式进行存储,比如像素0对应的是(0,0,0)黑色,像素1对应的是(127,0,0)深红色,像素255对应的是(224,224,129),因此可以映射到彩色图像。
注意,在语义分割中对应的标注图像(.png)用PIL的Image.open()函数读取时,默认是P模式,即一个单通道的图像。在背景处的像素值为0,目标边缘处用的像素值为255(训练时一般会忽略像素值为255的区域),目标区域内根据目标的类别索引信息进行填充,例如人对应的目标索引是15,所以目标区域的像素值用15填充。
注意:边缘(难以确定属于哪个物体)和忽略的像素(难以分割的区域)都设置为255,在计算损失时忽略这些地方。
在Pascal VOC数据集中各目标类别名称与类别索引对应关系:
{
"background": 0,
"aeroplane": 1,
"bicycle": 2,
"bird": 3,
"boat": 4,
"bottle": 5,
"bus": 6,
"car": 7,
"cat": 8,
"chair": 9,
"cow": 10,
"diningtable": 11,
"dog": 12,
"horse": 13,
"motorbike": 14,
"person": 15,
"pottedplant": 16,
"sheep": 17,
"sofa": 18,
"train": 19,
"tvmonitor": 20
}
参考资料:PASCAL VOC2012数据集介绍
2.MS COCO
MS COCO数据集的标注格式是针对每一个目标都标注了多边形(polygons)坐标[x0,y0,x1,y1…],比如
但是语义分割的标签希望是PNG格式,那么我们便需要将polygons的坐标信息转换为Pascal VOC的PNG图片,可以示例程序进行转换,读取每张图像的segmentation信息:
官方有给出一个读取MS COCO数据集信息的API–pycocotools
- Linux系统安装pycocotools:
pip install pycocotools
- Windows系统安装pycocotools:
pip install pycocotools-windows
import os
import random
import numpy as np
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
from pycocotools import mask as coco_mask
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
random.seed(0)
json_path = "/data/coco2017/annotations/instances_val2017.json"
img_path = "/data/coco2017/val2017"
# random pallette
pallette = [0, 0, 0] + [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(255*3)]
# load coco data
coco = COCO(annotation_file=json_path)
# get all image index info
ids = list(sorted(coco.imgs.keys()))
print("number of images: {}".format(len(ids)))
# get all coco class labels
coco_classes = dict([(v["id"], v["name"]) for k, v in coco.cats.items()])
# 遍历前三张图像
for img_id in ids[:3]:
# 获取对应图像id的所有annotations idx信息
ann_ids = coco.getAnnIds(imgIds=img_id)
# 根据annotations idx信息获取所有标注信息
targets = coco.loadAnns(ann_ids)
# get image file name
path = coco.loadImgs(img_id)[0]['file_name']
# read image
img = Image.open(os.path.join(img_path, path)).convert('RGB')
img_w, img_h = img.size
masks = []
cats = []
for target in targets:
cats.append(target["category_id"]) # get object class id
polygons = target["segmentation"] # get object polygons
rles = coco_mask.frPyObjects(polygons, img_h, img_w)
mask = coco_mask.decode(rles)
if len(mask.shape) < 3:
mask = mask[..., None]
mask = mask.any(axis=2)
masks.append(mask)
cats = np.array(cats, dtype=np.int32)
if masks:
masks = np.stack(masks, axis=0)
else:
masks = np.zeros((0, height, width), dtype=np.uint8)
# merge all instance masks into a single segmentation map
# with its corresponding categories
target = (masks * cats[:, None, None]).max(axis=0)
# discard overlapping instances
target[masks.sum(0) > 1] = 255
target = Image.fromarray(target.astype(np.uint8))
target.putpalette(pallette)
plt.imshow(target)
plt.show()
通过pycocotools读取的图像segmentation信息,配合matplotlib库绘制标注图像如下:
参考资料:MS COCO数据集介绍以及pycocotools简单使用
二、语义分割结果的具体形式
左图为原图,右图为结果图,结果图是PNG,仍然是单通道,采用调色板模式,mask蒙版,每个像素的数值对应的是一个类别的索引,好处是方便可视化结果。
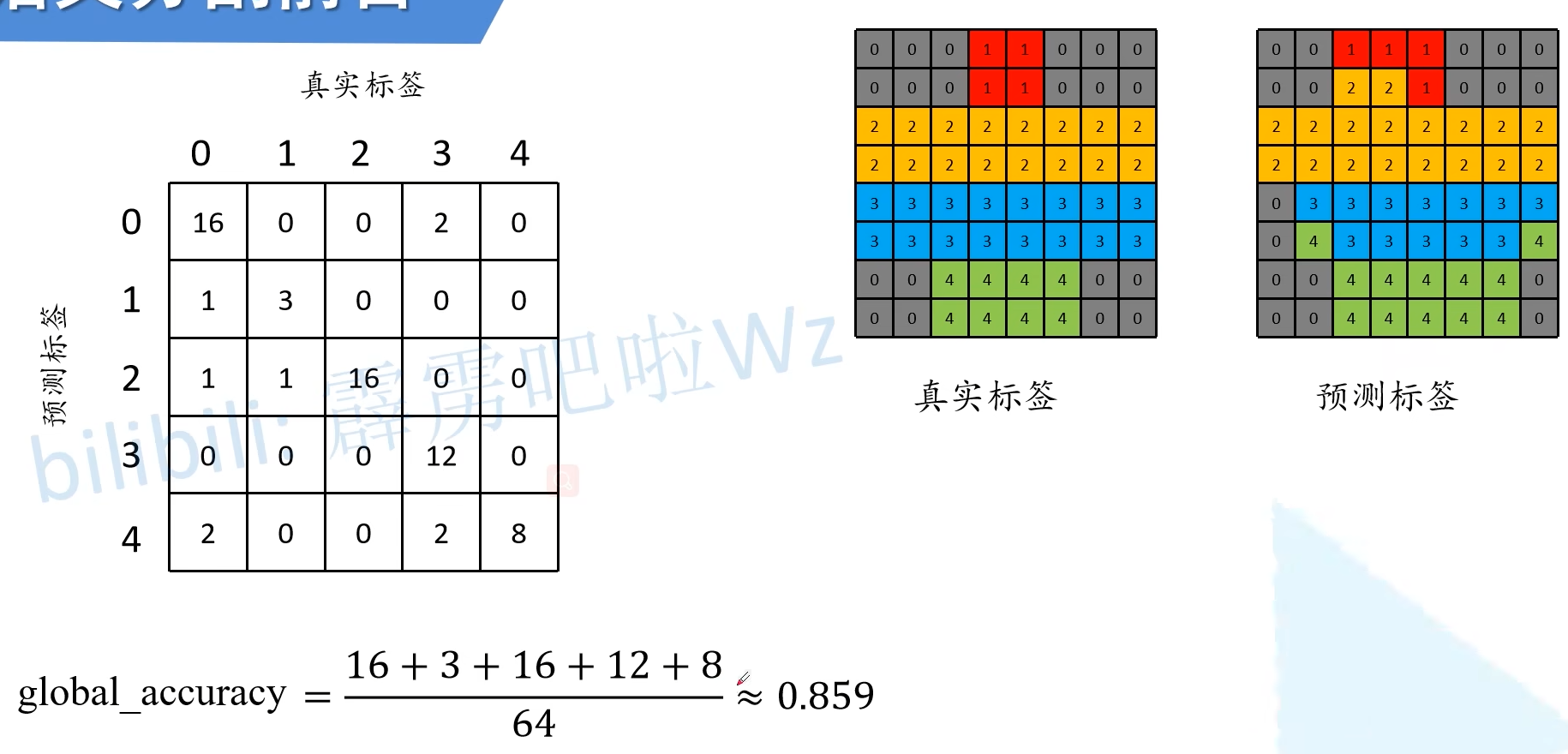
三、语义分割常见的评价指标
在论文中使用最多的评价指标是mean IoU。
通过构建混淆矩阵来计算评价指标:
预测正确用绿色表示,预测错误的采用红色表示。
像素准确率(PA):
平均像素准确率(PA):
平均mIou:
四、语义分割标注工具
1.Labelme
2.EISeg
3.X-Anylabeling
总结
本文主要介绍语义分割的基本概念,包括数据集格式和分割结果以及标注工具。