前言
Fragment基础使用笔记
一、基础使用
Activity布局和文件
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:baselineAligned="false">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment1"
android:name="com.henry.FragmentTest.test1.Fragment1"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment2"
android:name="com.henry.FragmentTest.test1.Fragment2"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>
public class fragmentactivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_fragments);
}
}
两个Fragment布局文件
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#00ff00" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="This is fragment 1"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="25sp" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#ffff00" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="This is fragment 2"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="25sp" />
</LinearLayout>
Fragment文件
public class Fragment1 extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment1, container, false);
}
}
public class Fragment2 extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment2, container, false);
}
}
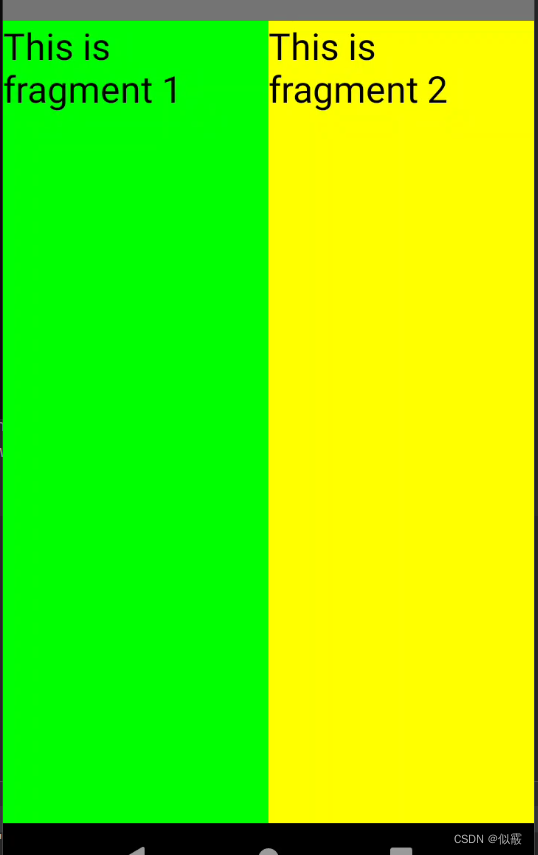
显示:一个Activity很融洽地包含了两个Fragment,这两个Fragment平分了整个屏幕,效果如下:
二、动态添加Fragment
activity修改布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/main_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.henry.PreferenceTest.FragmentActivity"
android:orientation="horizontal">
</LinearLayout>
activity动态获取fragment
public class fragmentactivity extends AppCompatActivity {
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_fragments);
Display display = getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay();
if (display.getWidth() > display.getHeight()) {
Fragment1 fragment1 = new Fragment1();
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction().replace(R.id.main_layout, fragment1).commit();
} else {
Fragment2 fragment2 = new Fragment2();
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction().replace(R.id.main_layout, fragment2).commit();
}
}
}
步骤如下:
获取到FragmentManager,在Activity中可以直接通过getFragmentManager得到。
开启一个事务,通过调用beginTransaction方法开启。
向容器内加入Fragment,一般使用replace方法实现,需要传入容器的id和Fragment的实例。
提交事务,调用commit方法提交。
三、Fragment的生命周期
Fragment 的生命周期包括以下方法:
onAttach(): 当 Fragment 与 Activity 关联时调用。
onCreate(): 当 Fragment 创建时调用。
onCreateView(): 创建 Fragment 的视图层次结构时调用。
onActivityCreated(): 当与 Fragment 相关联的 Activity 完成 onCreate() 方法后调用。
onStart(): 当 Fragment 可见时调用。
onResume(): 当 Fragment 可交互时调用。
onPause(): 当 Fragment 失去焦点但仍可见时调用。
onStop(): 当 Fragment 不再可见时调用。
onDestroyView(): 当 Fragment 的视图层次结构被销毁时调用。
onDestroy(): 当 Fragment 被销毁时调用。
onDetach(): 当 Fragment 与 Activity 解除关联时调用。
下面是 Fragment 生命周期方法的执行顺序:
当 Fragment 被添加到 Activity 时,依次执行 onAttach()、onCreate()、onCreateView()、onActivityCreated()、onStart()、onResume()。
当 Activity 进入后台或另一个 Fragment 覆盖当前 Fragment 时,依次执行 onPause()、onStop()。
当 Activity 回到前台或当前 Fragment 重新获得焦点时,依次执行 onStart()、onResume()。
当 Fragment 被移除或 Activity 被销毁时,依次执行 onPause()、onStop()、onDestroyView()、onDestroy()、onDetach()。
四、Fragment之间进行通信
activity回到示例一中,包含两个fragment。
修改fragment2.xml,添加一个按钮:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="#ffff00" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="This is fragment 2"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="25sp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Get fragment1 text"
/>
</LinearLayout>
fragment1.xml,为TextView添加一个id
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#00ff00" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/fragment1_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="This is fragment 1"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:textSize="25sp" />
</LinearLayout>
修改Fragment2.java,添加onActivityCreated方法,并处理按钮的点击事件:
public class Fragment2 extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment2, container, false);
}
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
Button button = (Button) getActivity().findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
TextView textView = (TextView) getActivity().findViewById(R.id.fragment1_text);
Toast.makeText(getActivity(), textView.getText(), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
}
}
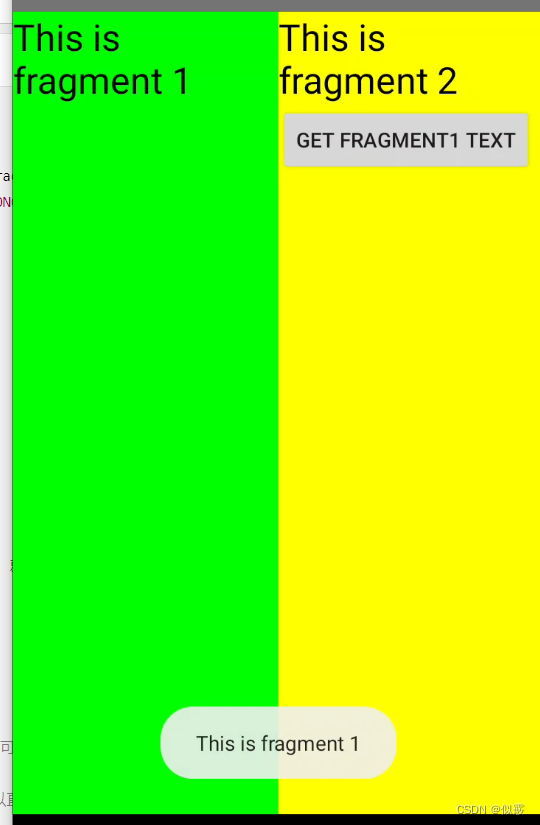
运行程序,点击一下fragment2上的按钮,效果如下
getActivity方法可以让Fragment获取到关联的Activity,然后再调用Activity的findViewById方法,就可以获取到和这个Activity关联的其它Fragment的视图了。
Fragment 之间还可以通过以下几种方式进行通信:
- 通过 Activity:Fragment 可以通过与 Activity 通信来实现 Fragment 之间的通信。Fragment 可以通过 getActivity() 方法获取关联的 Activity,并通过 Activity 的方法或接口来传递数据或事件。
- 直接调用其他 Fragment 的方法:如果一个 Fragment 持有对另一个 Fragment 的引用,可以直接调用另一个 Fragment 的公共方法来进行通信。这种方式适用于两个 Fragment 之间存在直接的关联关系的情况。
- 使用 Bundle:可以通过设置 Fragment 的参数(通过 setArguments() 方法)来传递数据,在另一个 Fragment 中通过 getArguments() 方法获取数据。这种方式适用于需要在 Fragment 创建时传递数据的情况。
- 使用接口回调:定义一个接口,在一个 Fragment 中实现该接口并在另一个 Fragment 中持有该接口的引用。通过接口回调的方式,一个 Fragment 可以调用另一个 Fragment 实现的接口方法来进行通信。
- 使用广播:通过发送广播来实现 Fragment 之间的通信。一个 Fragment 发送广播,另一个 Fragment 注册广播接收器来接收广播消息。这种方式适用于需要跨组件通信的情况。
- 使用共享 ViewModel:使用 Architecture Components 中的 ViewModel 来实现 Fragment 之间的通信。多个 Fragment 可以通过共享同一个 ViewModel 实例来共享数据和状态。
五、Fragment兼容手机和平板示例
核心在于实现两个activity_main布局文件,一个是res/layout,另一个在res/layout-land
Android系统又会根据当前的运行环境判断程序是否运行在大屏幕设备上,如果运行在大屏幕设备上,就加载layout-land目录下的activity_main.xml,否则就默认加载layout目录下的activity_main.xml。
res/layout/activity_main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/menu_fragment"
android:name="com.henry.FragmentTest.test1.MenuFragment"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
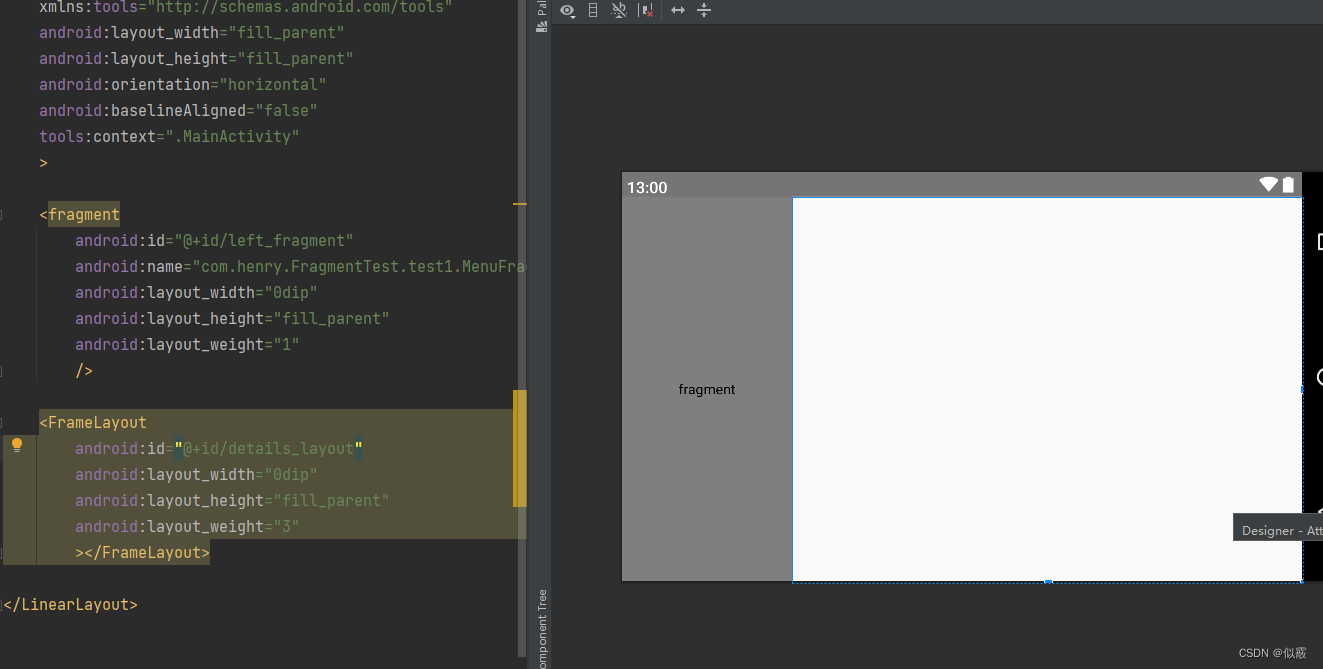
res/layout-land/activity_main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:baselineAligned="false"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
>
<fragment
android:id="@+id/left_fragment"
android:name="com.henry.FragmentTest.test1.MenuFragment"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/details_layout"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="3"
></FrameLayout>
</LinearLayout>
fragmentactivity.java
public class fragmentactivity extends AppCompatActivity {
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_fragments);
}
}
MenuFragment.java
public class MenuFragment extends Fragment implements AdapterView.OnItemClickListener {
/**
* 菜单界面中只包含了一个ListView。
*/
private ListView menuList;
/**
* ListView的适配器。
*/
private ArrayAdapter<String> adapter;
/**
* 用于填充ListView的数据,这里就简单只用了两条数据。
*/
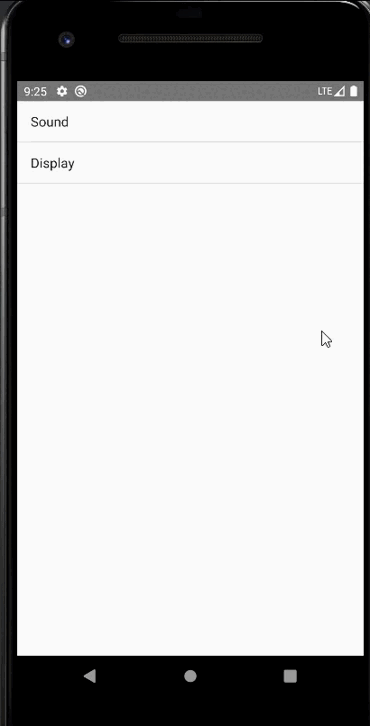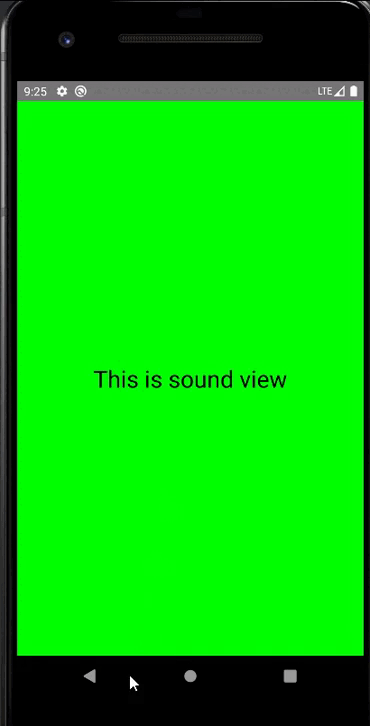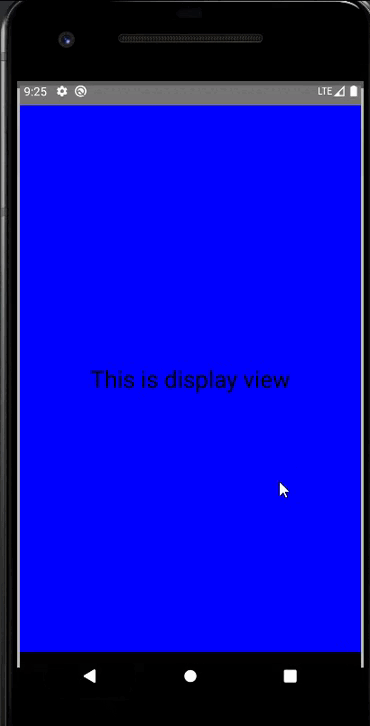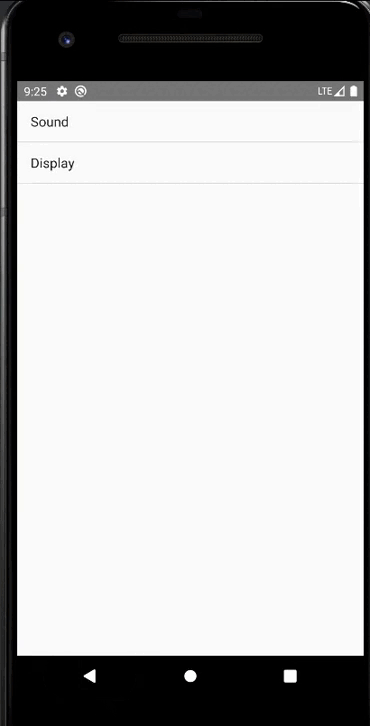
private String[] menuItems = {"Sound", "Display"};
/**
* 是否是双页模式。如果一个Activity中包含了两个Fragment,就是双页模式。
*/
private boolean isTwoPane;
/**
* 当Activity和Fragment建立关联时,初始化适配器中的数据。
*/
@Override
public void onAttach(Activity activity) {
super.onAttach(activity);
adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(activity, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, menuItems);
}
/**
* 加载menu_fragment布局文件,为ListView绑定了适配器,并设置了监听事件。
*/
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.menu_fragment, container, false);
menuList = (ListView) view.findViewById(R.id.menu_list);
menuList.setAdapter(adapter);
menuList.setOnItemClickListener(this);
return view;
}
/**
* 当Activity创建完毕后,尝试获取一下布局文件中是否有details_layout这个元素,如果有说明当前
* 是双页模式,如果没有说明当前是单页模式。
*/
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
if (getActivity().findViewById(R.id.details_layout) != null) {
isTwoPane = true;
} else {
isTwoPane = false;
}
}
/**
* 处理ListView的点击事件,会根据当前是否是双页模式进行判断。如果是双页模式,则会动态添加Fragment。
* 如果不是双页模式,则会打开新的Activity。
*/
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> arg0, View view, int index, long arg3) {
if (isTwoPane) {
Fragment fragment = null;
if (index == 0) {
fragment = new SoundFragment();
} else if (index == 1) {
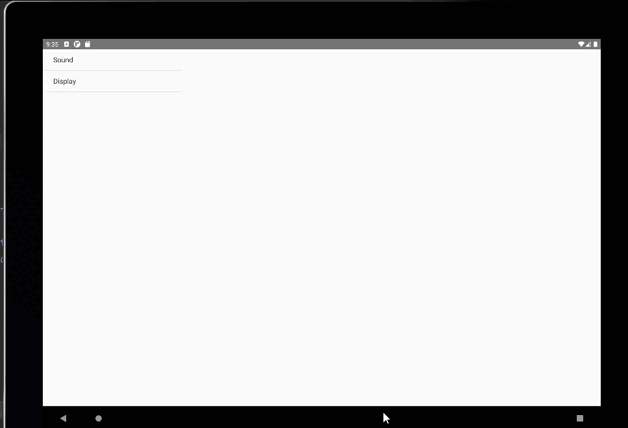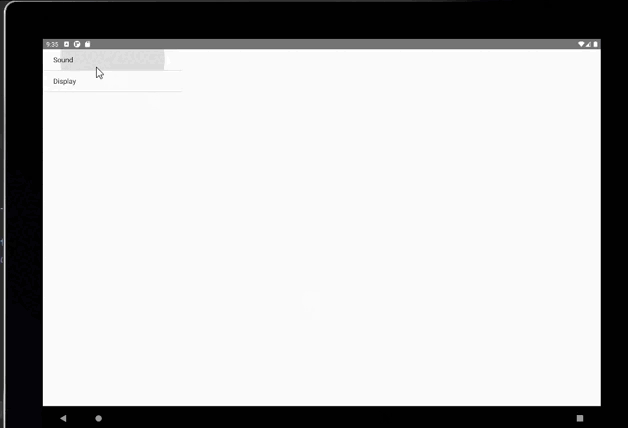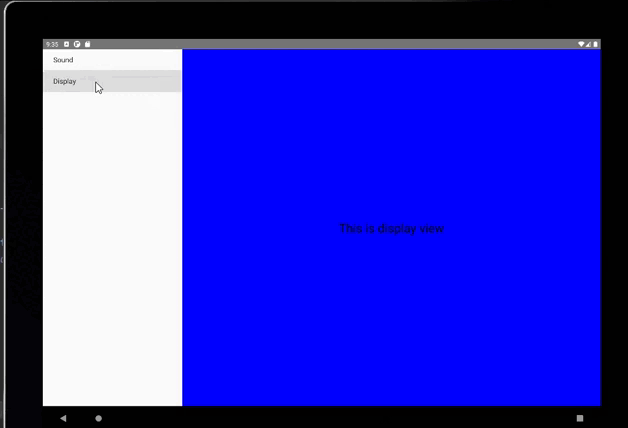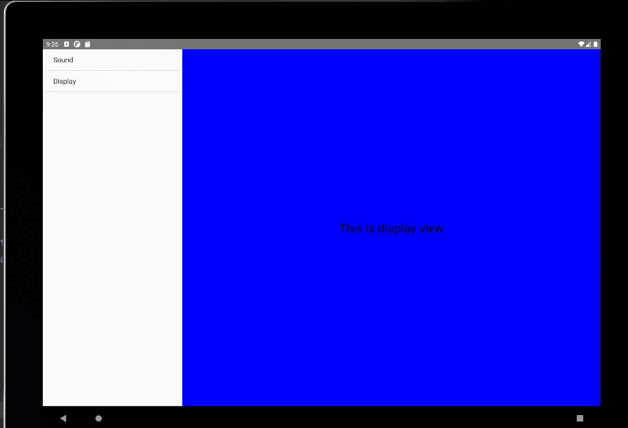
fragment = new DisplayFragment();
}
getFragmentManager().beginTransaction().replace(R.id.details_layout, fragment).commit();
} else {
Intent intent = null;
if (index == 0) {
intent = new Intent(getActivity(), SoundActivity.class);
} else if (index == 1) {
intent = new Intent(getActivity(), DisplayActivity.class);
}
startActivity(intent);
}
}
}
使用了ArrayAdapter初始化ListView
menu_fragment.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<ListView
android:id="@+id/menu_list"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
</ListView>
</LinearLayout>
SoundFragment.java
public class SoundFragment extends Fragment {
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.sound_fragment, container, false);
return view;
}
}
对应的布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#00ff00"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:textSize="28sp"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:text="This is sound view"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
DisplayFragment.java
public class DisplayFragment extends Fragment {
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.display_fragment, container, false);
return view;
}
}
对应的布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#0000ff"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:textSize="28sp"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:text="This is display view"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
SoundActivity.java
public class SoundActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.sound_activity);
}
}
对应的布局,SoundFragment
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<fragment xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/sound_fragment"
android:name="com.henry.FragmentTest.test1.SoundFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
</fragment>
DisplayFragment
public class DisplayFragment extends Fragment {
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.display_fragment, container, false);
return view;
}
}
对应的布局,DisplayFragment
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#0000ff"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:textSize="28sp"
android:textColor="#000000"
android:text="This is display view"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
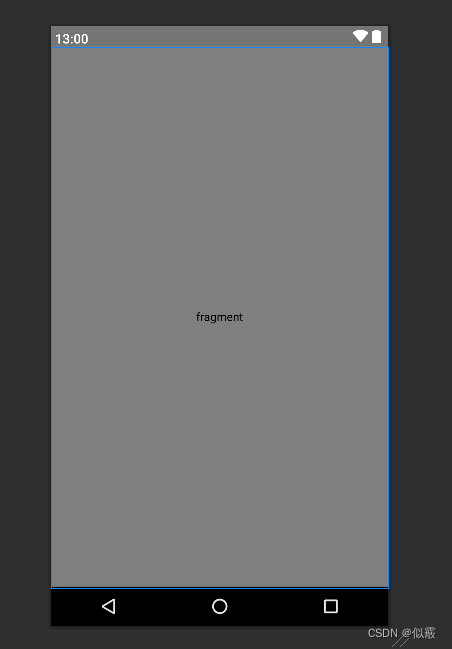
手机上显示:
平板上显示: