注意:大部分题目都是我自己主观的代码,很多没有参考题解,但是都是AC的,我喜欢自己做,不到万不得已别去看谢大题解,因为脑袋疼,因此别抱怨不按题解来写文章。
另外,写oj如果是WA那么先观察是不是cin和scanf混用,oj不能混用,如果是TLE而且时间复杂度已经很低了,那么检查一下是不是用了cin没有关闭同步,我建议是用stdio.h然后用sacnf和printf。
1.Candy-1187
样例输入
3 4 5 0
样例输出
1 2 4
题解思路:取模,得到S0,S1,S2,在每个序列中各取三个,然后三个序列每次都取一个,所以SUM=S0取三个+S1取三个+S2取三个+S0*S1*S2;
我的思路:找规律(每次增加的增加多少,建议还是用题解思路做,因为规律我说不清)
AC代码(个人认为难度:2,标准难度:2)
| Memory: 11044K | Time: 265MS |
#include <iostream>
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
long long res[1100000];
int main()
{
res[3]=1;
long long ans=0,temp=1;
long long a[3]={1,2,1};
for(long long i=4;i<=1100000;i++){
if(ans>=3){
for(long long j=0;j<3;j++){
a[j]++;
}
ans=0;
}
res[i]=(res[i-1]+temp)%(mod);
temp+=a[ans++];
}
long long n;
cin>>n;
while(n!=0){
cout<<res[n]<<endl;
cin>>n;
}
return 0;
}2.Permutation-1241
样例输入
3 3 1 2 3 3 2 1 3 3 2 3 1
样例输出
1 2 3
思路:弄清置换是什么就行,Pn=Pn-1*P1,然后找到每个数到终点位置要置换的次数(因为每个数都会有轮回的,比如第一个数3个轮回就找到了,第二个数4个轮回才找到,那么第12个轮回必然就都会找到),然后求他们最小公倍数;
AC代码(个人认为难度:3,标准难度:2)
| Memory: 2448K | Time: 125MS |
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll lmp(ll a,ll b)//求最大公因数,最大公倍数就等于两数相乘然后除以最大公因数
{
while(a%b!=0){
ll c=a;
a=b;
b=c%b;
}
return b;
}
int main()
{
ll t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
ll ans=1;
ll n;
cin>>n;
vector<ll>res;
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++){
ll nums;
cin>>nums;
res.push_back(nums);
}
for(ll i=0;i<res.size();i++){
ll temp=res[i],ant=1;
while(temp!=i+1){
ant++;
temp=res[temp-1];
}
ans=ans*ant/lmp(ans,ant);//求最大公倍数
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
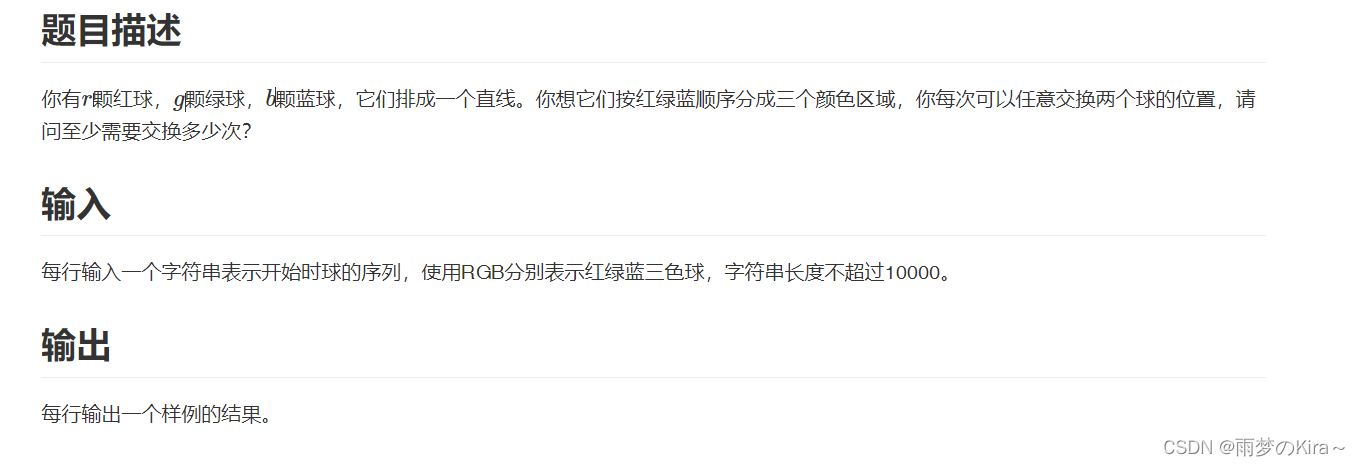
}3.RBG-1266
题解思路:
个人思路:贪心,我们先统计RGB有多少个,然后在R的地盘,如果出现G,那么就先跟G区域的R交换,如果G区域没有那么再去B区域交换;如果出现B那么就先去B区域交换,如果没有再返回去G区域交换,就是一句话:尽量换到属于自己的区域就行了。
AC代码(个人难度:2,标准难度:2)
| Memory: 2416K | Time: 296MS |
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char s[10001];
while(scanf("%s",s)!=EOF){
long long r=0,g=0,b=0,res=0;
int len=strlen(s);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){//统计个数
if(s[i]=='R'){
r++;
}
else if(s[i]=='G'){
g++;
}
else{
b++;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<r;i++){//如果是G,那么现在G区域交换,没有的话自然而然过度到B区域
if(s[i]=='G'){
for(int j=r;j<len;j++){
if(s[j]=='R'){
swap(s[i],s[j]);
res++;
break;
}
}
}
else if(s[i]=='B'){//如果是B区域
bool flag=false;//是否找到
for(int j=r+g;j<len;j++){
if(s[j]=='R'){//找到了就不需要去G区域找了
swap(s[i],s[j]);
flag=true;
res++;
break;
}
}
if(!flag){//如果没找到就要去G区域找
for(int j=r;j<r+g;j++){
if(s[j]=='R'){
swap(s[i],s[j]);
res++;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
for(int i=r;i<r+g;i++){//我们前面已经完全把R找好位置了,现在只要交换G和B,那么直接交换就行了
if(s[i]!='G'){
for(int j=r+g;j<len;j++){
if(s[j]=='G'){
swap(s[i],s[j]);
res++;
break;
}
}
}
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
return 0;
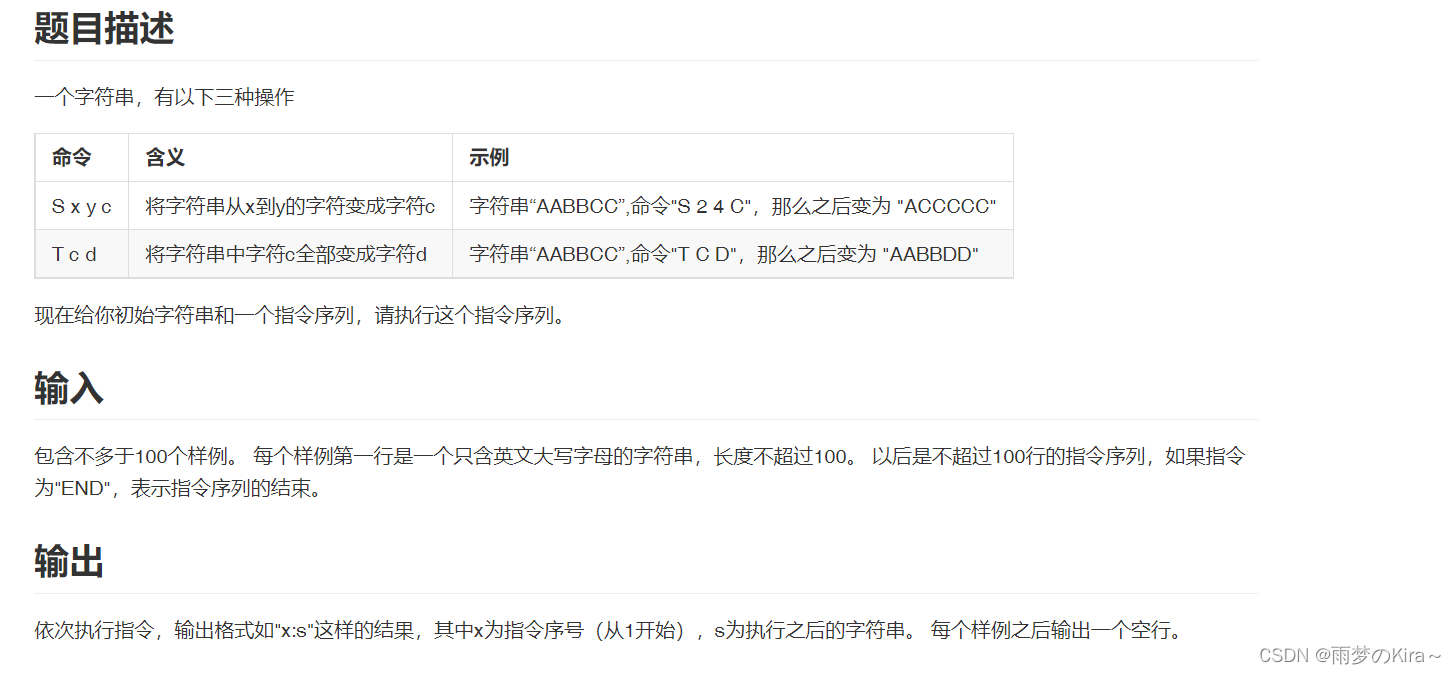
}4.String-1299
样例输入
AABBCC S 2 4 C T C D END AABBCC T C D S 2 4 C END
样例输出
1:ACCCCC 2:ADDDDD 1:AABBDD 2:ACCCDD
思路:暴力模拟,水题,注意输入输出就行了。
AC代码(个人难度:1,标准难度:1)
| Memory: 2492K | Time: 62MS |
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char s[200];
while(cin>>s){
string res;
int i=0;
while(!(s[0]=='E'&&s[1]=='N'&&s[2]=='D')){
if(res.empty()){
i=0;
res=s;
//cout<<res<<endl;
}
else if(s[0]=='S'){
i++;
int x,y;
char a;
cin>>x>>y>>a;
for(int i=x-1;i<y;i++){
if(i>=res.size()){
break;
}
res[i]=a;
}
cout<<i<<":";
cout<<res<<endl;
}
else{
i++;
char a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
for(int i=0;i<res.size();i++){
if(res[i]==a){
res[i]=b;
}
}
cout<<i<<":";
cout<<res<<endl;
}
cin>>s;
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
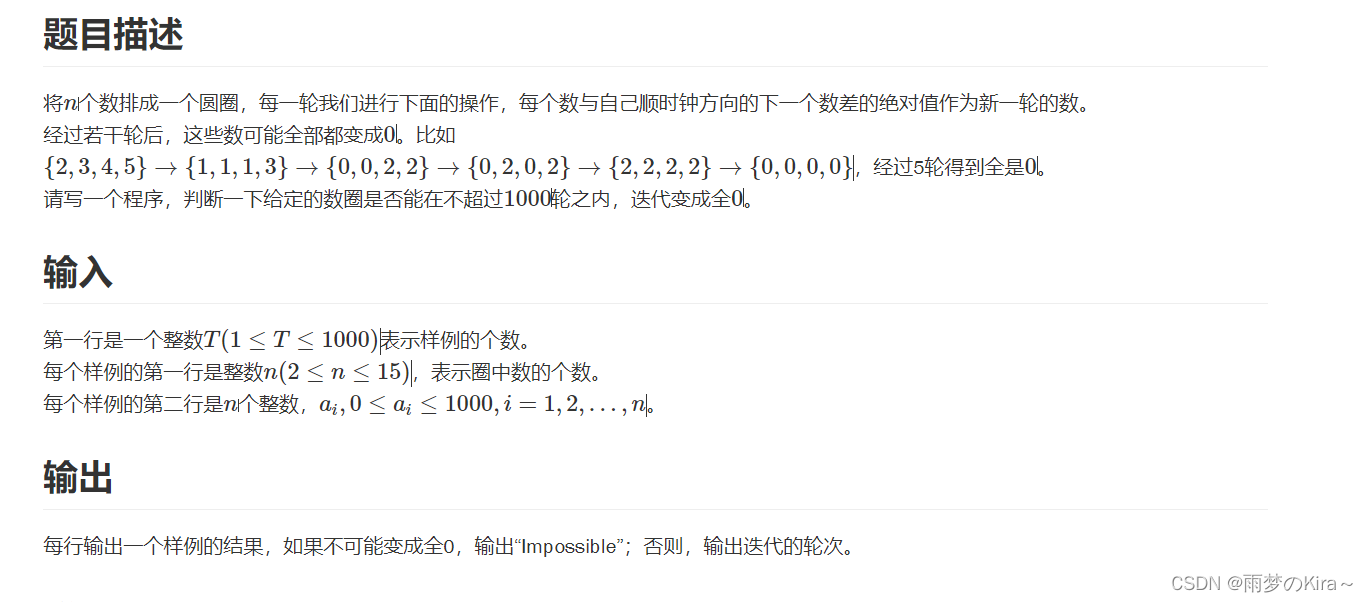
}5.Zeros-1301
样例输入
2 4 2 3 4 5 3 1 3 5
样例输出
5 Impossible
思路:模拟
AC代码(个人难度:1,标准难度:1)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
bool fun(vector<int>&res)
{
for(int i=0;i<res.size();i++){
if(res[i]!=0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<int>res;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int nums;
cin>>nums;
res.push_back(nums);
}
int counts=1;
while(counts++){
if(counts>=1000){
cout<<"Impossible"<<endl;
break;
}
else{
int temp=res[0];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(i==n-1){
res[i]=abs(temp-res[i]);
}
else{
res[i]=abs(res[i+1]-res[i]);
}
}
}
if(fun(res)){
cout<<counts-1<<endl;
break;
}
}
}
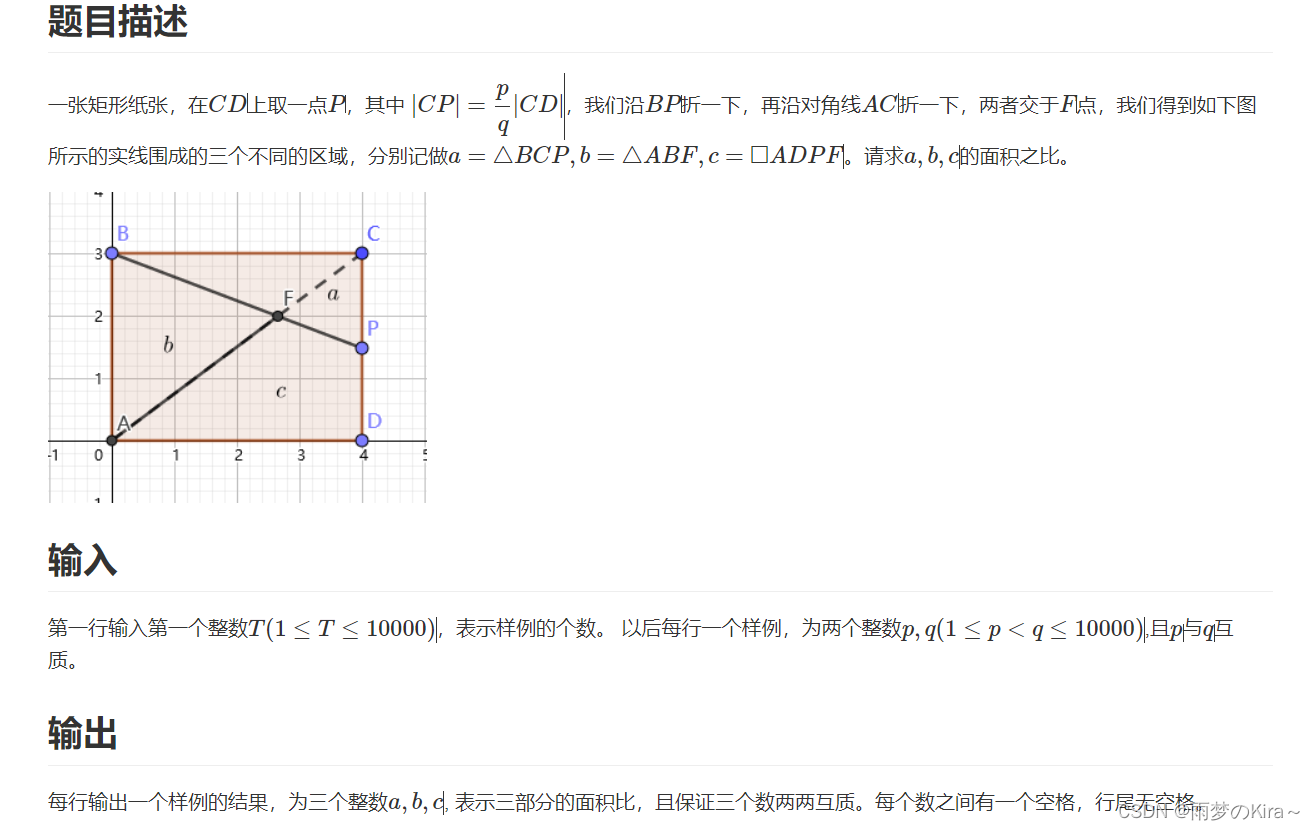
}6.折纸-贰-1379
样例输入
1 1 2
样例输出
3 4 5
思路:数学,也是水题,不多说。
AC代码(个人难度:1,标准难度:1)
| Memory: 2428K | Time: 125MS |
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int lmp(int a,int b)
{
while(a%b!=0){
int c=a;
a=b;
b=c%b;
}
return b;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
int p,q;
cin>>p>>q;
int a=p*q+p*p;
int b=q*q;
int c=p*q+q*q-p*p;
int temp=lmp(a,b);
int res=lmp(temp,c);
cout<<a/res<<" "<<b/res<<" "<<c/res<<endl;
}
return 0;
}7.大佬带带我-1384
样例输入
5 3 10 3 10 4 15 1 1 2 5 3 1 2 3 4 1 5
样例输出
1 0 2 1 0
样例解释
1号,按能力值可以带2和4号,但是他不喜欢2号,所以只能带4号1个人。 2号,能力值最低,不能带任何人,所以是0个。 3号,按能力值可以带2和4号,他没有不喜欢谁,2和4号也都没有不喜欢他,所以他可以带2个人。 4号,按能力值可以带2号,两者没有不喜欢关系,所以4号可以带1个。 5号,按能力可以带1,2,3,4号,但是他不喜欢1,2,3号,4号又不喜欢他,所以他不能带任何人。
思路:暴力模拟,用结构体保存人物的id和能力值it,然后排序;
然后保存相互讨厌的人,在遍历的时候过滤掉就行,
难点在于如何保存相互讨厌的人,我的办法是用二维容器,然后再遍历的时候作标记(题目真恶心)。
AC代码(个人难度:4,标准难度:4)
| Memory: 8368K | Time: 1685MS |
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
vector<int>ans[10001];//二维数组表示不喜欢的人
int ch[10001];//结果
struct node
{
int id;
int it;
}res[10001];
int cmp(node a,node b)
{
if(a.it!=b.it){
return a.it<b.it;
}
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&res[i].it);
res[i].id=i+1;
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
int nums,ids;
scanf("%d%d",&ids,&nums);
for(int j=0;j<nums;j++){
int value;
scanf("%d",&value);
ans[ids].push_back(value);
ans[value].push_back(ids);//记录相互不喜欢的人,注意一定得是相互啊
}
}
sort(res,res+n,cmp);//从小到大排序
memset(ch,0,sizeof(ch));
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int sum=0;
int a[10001];
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
for(int k=0;k<ans[res[i].id].size();k++){//标记一下,不喜欢就标位1,这样还可以去重
a[ans[res[i].id][k]]=1;
}
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
if(a[res[j].id]!=1&&res[j].it!=res[i].it){
sum++;
}
}
ch[res[i].id]=sum;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(i==n){
printf("%d",ch[i]);
}
else{
printf("%d ",ch[i]);
}
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
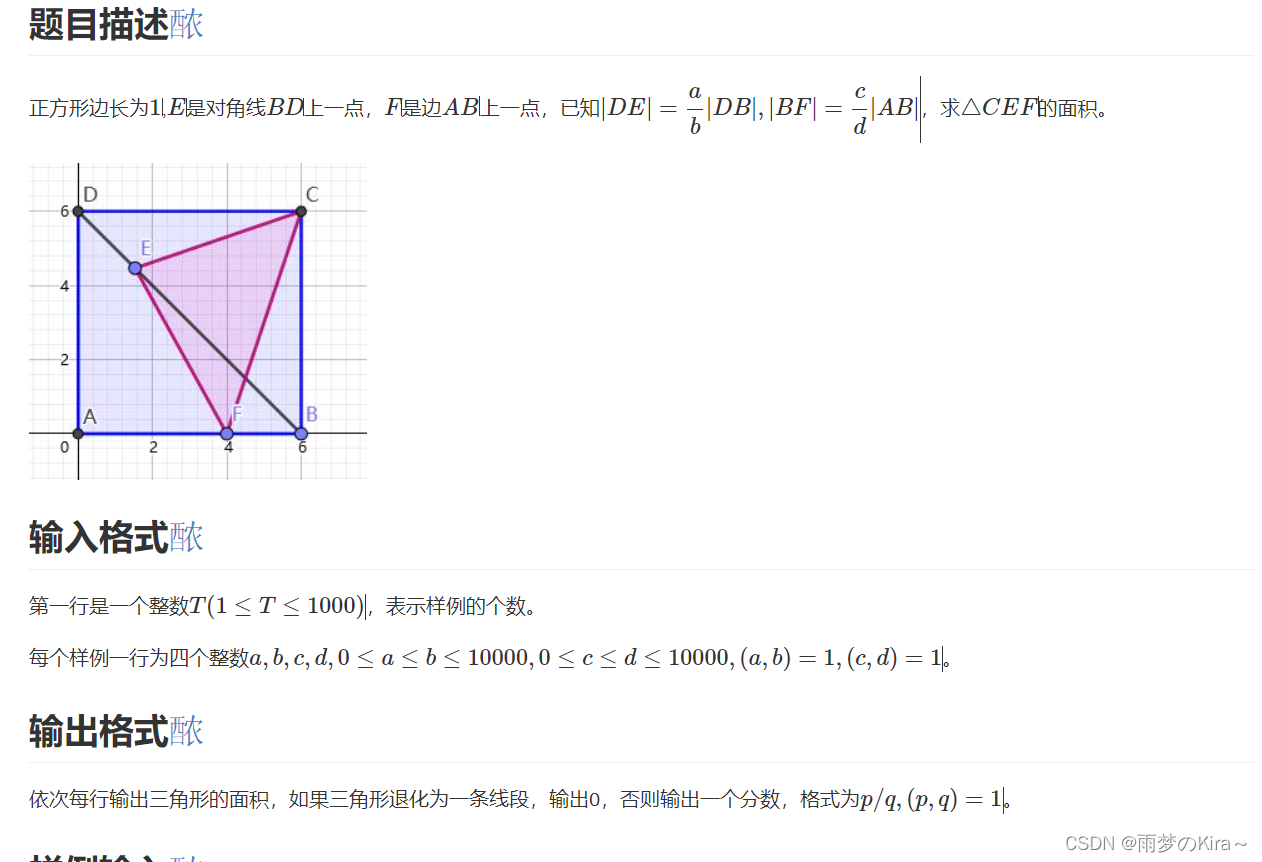
}8.面积-1385
样例输入
2 1 2 1 1 1 3 1 3
样例输出
0 5/18
思路:数学,然后再注意一下特殊情况就行了。
AC代码(个人难度:1,题解难度:1)
| Memory: 2424K | Time: 15MS |
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll lmp(ll a,ll b)
{
while(a%b!=0){
ll c=a;
a=b;
b=c%b;
}
return b;
}
int main()
{
ll t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
ll a,b,c,d;
cin>>a>>b>>c>>d;
ll n=a*d+c*b+d*b-c*b+a*c;
ll m=2*d*b;
ll temp=lmp(n,m);
n/=temp;
m/=temp;
if(m-n==0){
cout<<0<<endl;
}
else if(m-n<0){
cout<<n-m<<"/"<<m<<endl;;
}
else{
cout<<m-n<<"/"<<m<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}9.彩球-1386
样例输入
2 5 1 2 3 2 1 5 1 2 1 2 1
样例输出
4 0
思路:还是按谢大的来,要熟练地用哈希表或者map,我本以为这个题目两重循环已经够快了,是真的没想到只要在三种里面去掉一种和两种就行了。我是笨比。另外还有一种递推解法(肖大佬的解法),简单来说取三种可以由取两种得到,而取两种又能由取一种得到。很久没这样想了我也懒得写。就按原始的来吧,注意用c的一定要用stdio.h和scanf,不然必定超时。
AC代码(个人难度:4,题解难度:3)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main()
{
ll t;
scanf("%lld",&t);
while(t--){
unordered_map<ll,ll>a;
ll n;
scanf("%lld",&n);
ll res[10001];
memset(res,0,sizeof(res));
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%lld",&res[i]);
a[res[i]]++;
}
ll sum=n*(n-1)*(n-2)/6;
for(auto it=a.begin();it!=a.end();it++){
ll y=it->second;
if(y==2){
sum-=n-2;//减去两种相同的
}
else if(y>=3){
sum-=y*(y-1)*(y-2)/6;//减去三种相同的
sum-=y*(y-1)/2*(n-y);//减去三种里面两种相同的
}
}
printf("%lld\n",sum);
}
return 0;
}10.完全区间-1387
我以前的博客有,可以去翻我以前的题解。
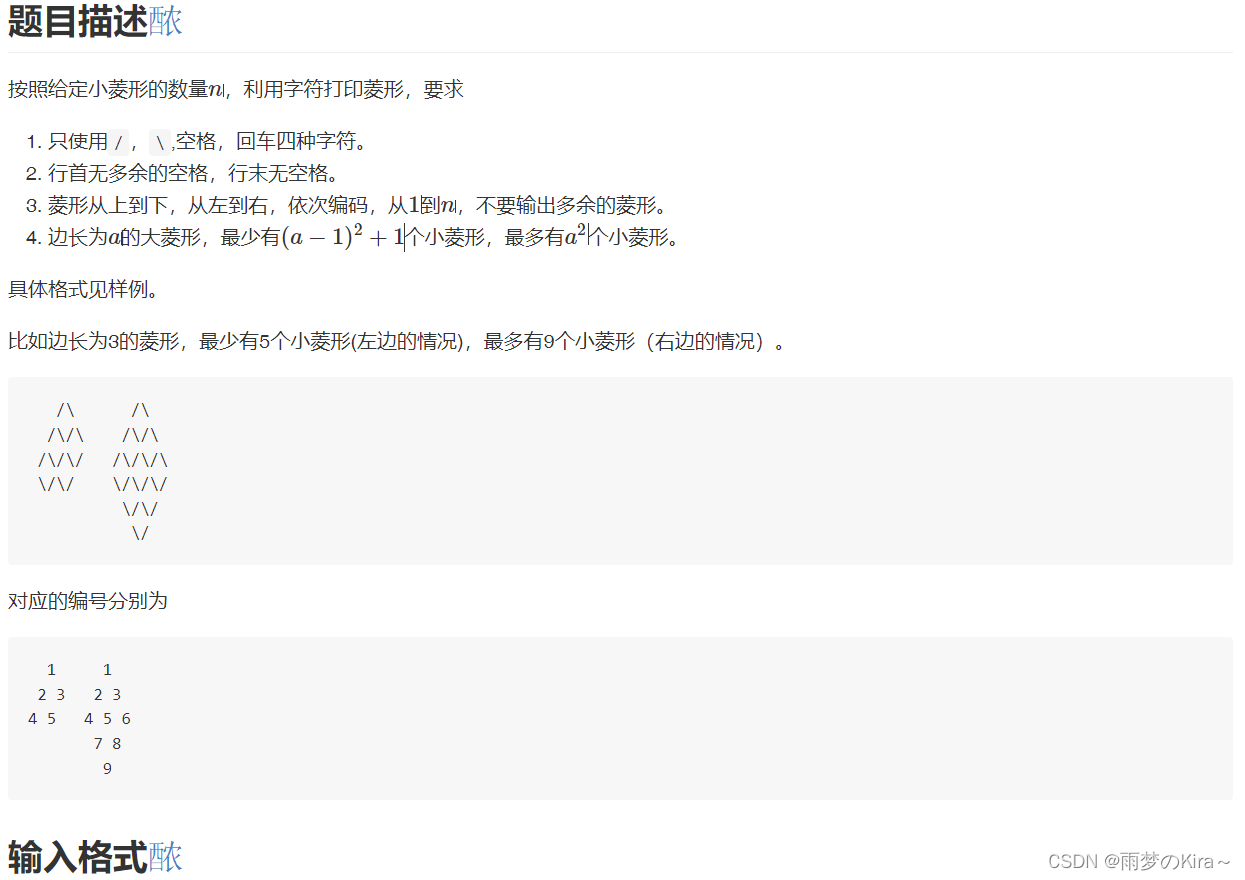
11.菱形-1403
样例输入
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0
样例输出
/\ \/ /\ /\/ \/ /\ /\/\ \/\/ /\ /\/\ \/\/ \/ /\ /\/\ /\/\/ \/\/ /\ /\/\ /\/\/\ \/\/\/ /\ /\/\ /\/\/\ \/\/\/ \/
思路:我觉得挺简单的,不知道为什么很多人拿二维数组算来算去。
我们先来考虑上部分,是由“/\”和“/”组成
下部分仅仅只有“\/”组成。
那么就很简单了,上一部分每一行应该打印的个数就是行数,比如第一行就一个菱形,第二行两个菱形......如果上一部分某行菱形个数不足行数,那么就多打印“/”就行,其他全都是“/\”;
下一部分就别管了,有多少就打印多少“\/”。
AC代码(个人难度:2,标准难度:3)
| Memory: 2388K | Time: 15MS |
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
int left[21],right[21];
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++){
left[i]=(i-1)*(i-1)+1;
right[i]=i*i;
}
cin>>n;
while(n!=0){//先由公式推出边长m
int m=0;
for(int i=1;i<=21;i++){
if(n>=left[i]&&n<=right[i]){
m=i;
break;
}
}
int nums=n;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m-i;j++){
cout<<" ";
}
if(nums>=i){//如果一行够这么多,就只打印“/\”
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
cout<<"/"<<"\\";
}
}
else{
for(int j=0;j<nums;j++){
cout<<"/"<<"\\";
}
cout<<"/";//不够就得多打印“/”咯
}
nums-=i;
cout<<endl;
}
nums=n-(m*(m-1))/2;//因为上一部分和下一部分在中间是重复的,注意一下下部分应该打印的个数即可,其他同理
for(int i=m;i>=1;i--){
if(nums<=0){
break;
}
for(int j=0;j<m-i;j++){
cout<<" ";
}
if(nums>=i){
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
cout<<"\\"<<"/";//只管打印“\/”
}
}
else{
for(int j=0;j<nums;j++){
cout<<"\\"<<"/";
}
}
nums-=i;
cout<<endl;
}
cin>>n;
}
return 0;
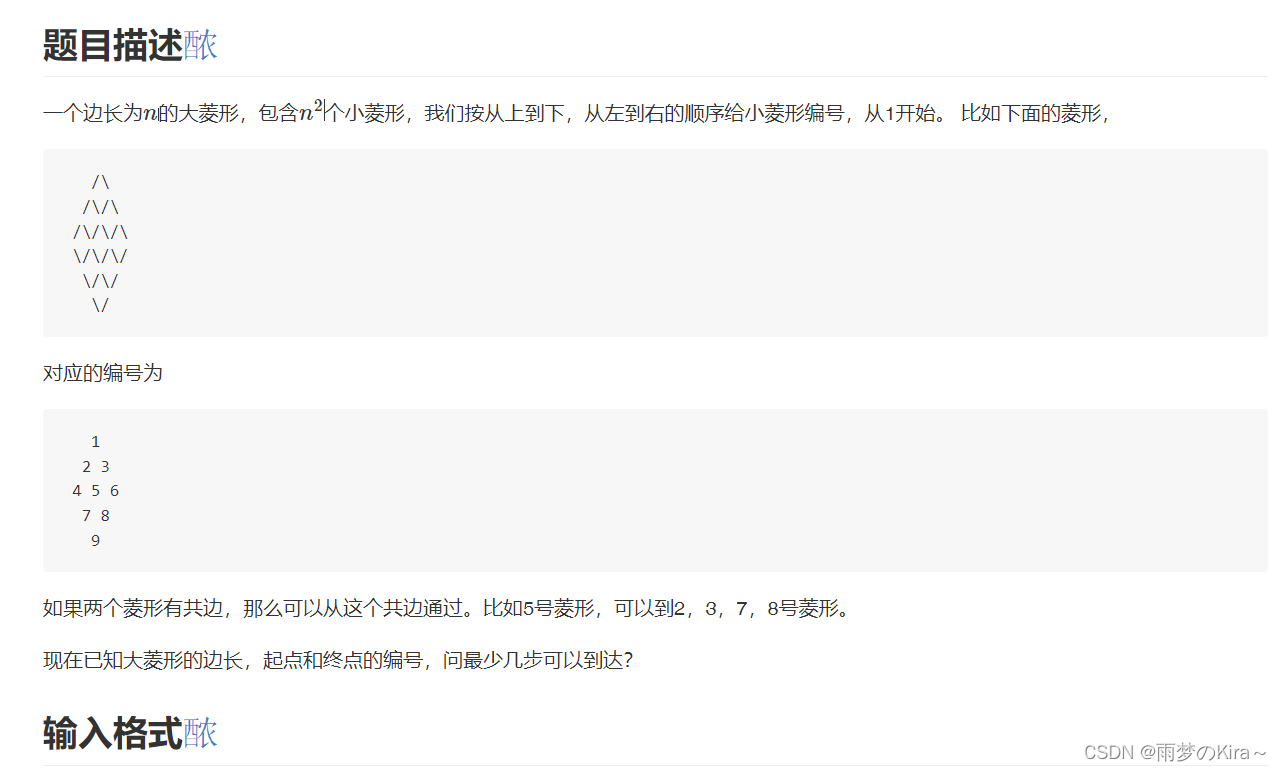
}12-菱形2-1404
样例输入
2 2 1 3 3 1 7
样例输出
1 3
题解思路:菱形转过45°是正方形,相当于求这个正方形两点最短距离,这个找到坐标即可,因此找到对应的坐标才是难点。
我的思路:直接当做菱形看,找到坐标,左边left距离为abs(y1-x1+x0-y0),右边right距离为abs(x1+y1-x0-y0),目标距离为(left+right)/2,证明我会在有空的时候给出。
AC代码(个人难度:4,标准难度:3)
| Memory: 1432K | Time: 906MS |
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main()
{
ll t;
scanf("%lld",&t);
while(t--){
ll n,s,e;
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&n,&s,&e);
if(s>e){//一定要是一上一下的排序
ll temp=s;
s=e;
e=temp;
}
ll x=0,y=1,b[4];//b的四个数组表示两个点的坐标。
int sign=0,flag=0;
for(ll i=0;i<2*n-1;i++){//直接看做菱形坐标,啥也不管
x+=y;
//printf("%lld ",x);
y--;
if(x>=s&&sign==0){
sign=1;
b[0]=y-(x-s)*2;
b[1]=i;
}
if(x>=e&&flag==0){
flag=1;
b[2]=y-(x-e)*2;
b[3]=i;
break;
}
y++;
if(i<n-1){
y++;
}
else{
y--;
}
}
//printf("%lld%lld %lld%lld",b[0],b[1],b[2],b[3]);
ll left=abs(b[3]-b[2]+b[0]-b[1]);//递推出的公式
ll right=abs(b[2]+b[3]-b[0]-b[1]);
//printf("%d%d\n",left,right);
printf("%lld\n",(left+right)/2);
}
return 0;
}13.世界杯-1405
样例输入
2 2 1.3 4.8 10.5 1.4 4.0 9.7 2 1.3 5.6 9.8 1.45 5.0 8.9
样例输出
No Yes
思路:想到了就很简单,本金/赔率=亏本息,因此只要本息>本金即可。所以我们三个状态都得买,只要存在某三个状态使得亏本息<本金那么一定能赚。
AC代码(个人难度:2,标准难度:2)
| Memory: 2444K | Time: 202MS |
#include <iostream>
#define maxn 1000
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
int n;
cin>>n;
double res[15][3];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>res[i][0];
cin>>res[i][1];
cin>>res[i][2];
}
double s=0,x=1;//x表示本金
int flag=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){//三重循环,因为三种情况都得买
s=0;
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
for(int k=0;k<n;k++){
s=x/res[i][0]+x/res[j][1]+x/res[k][2];
if(s<1){//如果亏本息小于本金1,就一定Yes
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag==1){
break;
}
}
if(flag==1){
break;
}
}
if(flag==0){
cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
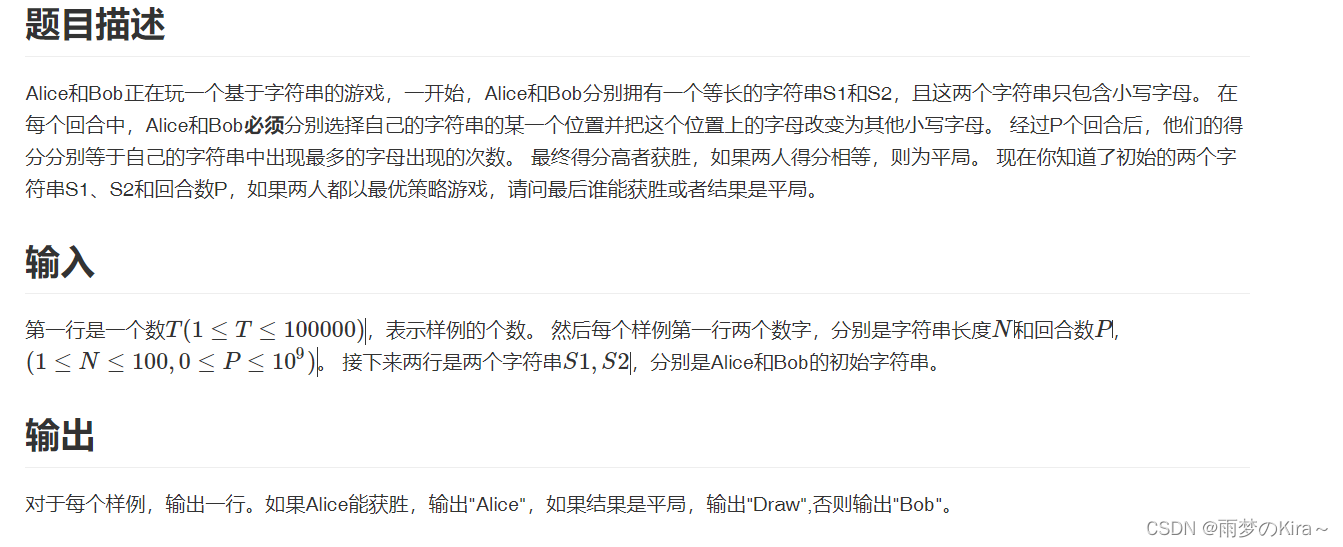
}14.String Game-1406
样例输入
4 6 2 xxxttu xxttuu 6 5 xxxttu xxttuu 6 3 xtuxtu xxttuu 4 0 alic ebob
样例输出
Alice Draw Draw Bob
思路:这是一个思维题,考虑特殊情况即可,另外,举个例子,xxxu,三回合,它也能变成xxxx。当xxxx,一回合,那么只能减少1;
AC代码(个人难度:3,标准难度:3)
| Memory: 2296K | Time: 265MS |
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
template<class t>inline void read( t &res){
char c;t flag=1;
while((c=getchar())<'0'||c>'9')if(c=='-')flag=-1;res=c-'0';
while((c=getchar())>='0'&&c<='9')res=res*10+c-'0';res*=flag;
}
int main()
{
ll t;
read(t);
while(t--){
ll n,m;
ll a[30],b[30];
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
memset(b,0,sizeof(b));
read(n);//快读,用scanf也行
read(m);
ll count0=0,count1=0;
char s[101],st[101];
gets(s);
gets(st);
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++){
a[s[i]-'a']++;
if( a[s[i]-'a']>count0){
count0=a[s[i]-'a'];
}
b[st[i]-'a']++;
if(b[st[i]-'a']>count1){
count1=b[st[i]-'a'];
}
}
ll res0=0,res1=0;
if(count0==n){
if(m==1){//特殊情况
res0=n-1;
}
else{
res0=n;
}
}
else if(m>=n-count0){//剩余长度大于回合数的
res0=n;
}
else{
res0=m+count0;//剩余长度小于回合数的
}
if(count1==n){
if(m==1){
res1=n-1;
}
else{
res1=n;
}
}
else if(m>=n-count1){
res1=n;
}
else{
res1=m+count1;
}
if(res0==res1){
printf("Draw\n");
}
else if(res0>res1){
printf("Alice\n");
}
else{
printf("Bob\n");
}
}
return 0;
}15.Min Base II-1411
样例输入
5 0 1 4 5 1000000000000000000
样例输出
2 2 3 3 44
思路:模拟,在此说明一下,如果数据不超过int,你可以用itoa或者bitsize函数来做。
AC代码(个人难度:2,标准难度:2)
| Memory: 2424K | Time: 30MS |
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main()
{
ll t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
ll n;
cin >> n;
if (n == 0 || n == 1) {
cout << 2 << endl;
}
for (int i = 2;i <= n;i++) {
ll m = n;
ll flag = 0;
ll s[101];
memset(s, 0, sizeof(s));
while (m != 0) {//进制转换
s[m%i]++;
m /= i;
}
ll nums = 0;
for (int j = 0;j <46;j++) {//找到不属于0的点,最高循环是44,防止溢出你可以多来几次循环,不影响
if (s[j] != 0) {
nums = s[j];
break;
}
}
for (int j = 0;j < 46;j++) {
if (s[j] != 0 && s[j] != nums) {
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if (flag == 0) {
cout << i << endl;
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
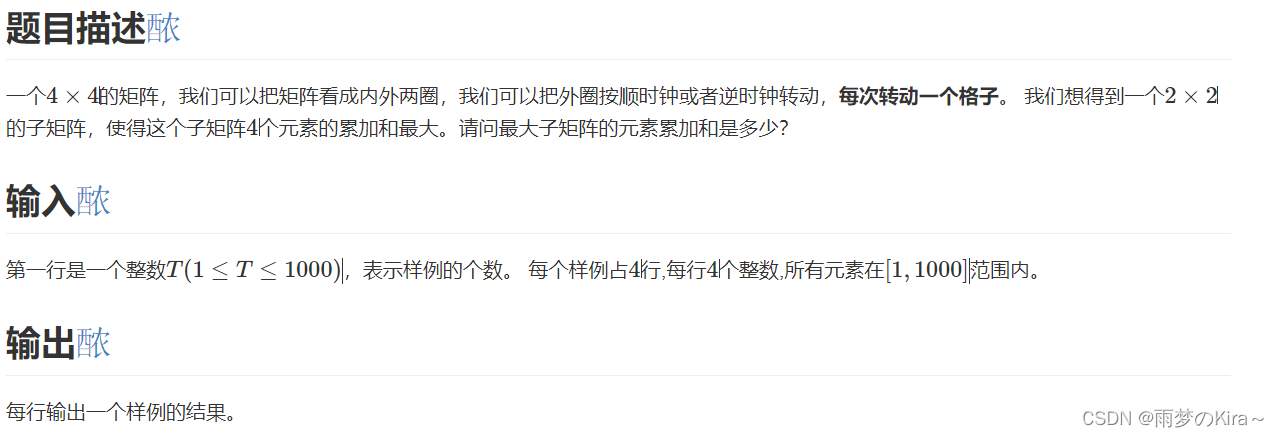
}16.Rotate Again-1412
样例输入
2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 2 2 1 1 4 4 3 3
样例输出
56 15
提示
第一个样例,逆时钟旋转1格,得到最大子矩阵为
11 16 14 15
第二个样例,逆时钟旋转5格,得到最大子矩阵为
3 4 4 4
思路:模拟,没啥说的。将矩阵外部用数组保存起来,然后一直轮换即可,注意循环条件
AC代码(个人难度:2,标准难度:2)
| Memory: 2412K | Time: 61MS |
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
int ch[4][4];
int a[12];
void nums(int *res)//求各个相加的值
{
res[0]=a[11]+a[0]+a[1]+ch[1][1];
res[1]=a[1]+a[2]+ch[1][1]+ch[1][2];
res[2]=a[2]+a[3]+a[4]+ch[1][2];
res[3]=a[4]+a[5]+ch[1][2]+ch[2][2];
res[4]=a[5]+a[6]+a[7]+ch[2][2];
res[5]=a[10]+a[11]+ch[2][1]+ch[2][2];
res[6]=a[8]+a[9]+a[10]+ch[2][1];
res[7]=a[7]+a[8]+ch[1][1]+ch[2][1];
res[8]=ch[1][1]+ch[1][2]+ch[2][1]+ch[2][2];
}
void change()//转
{
int temp=a[0];
for(int i=0;i<12;i++){
if(i!=11){
a[i]=a[i+1];
}
else{
a[i]=temp;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
for(int j=0;j<4;j++){
cin>>ch[i][j];
}
}
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));//-----外围数字-----//
a[0]=ch[0][0];
a[1]=ch[0][1];
a[2]=ch[0][2];
a[3]=ch[0][3];
a[4]=ch[1][3];
a[5]=ch[2][3];
a[6]=ch[3][3];
a[7]=ch[3][2];
a[8]=ch[3][1];
a[9]=ch[3][0];
a[10]=ch[2][0];
a[11]=ch[1][0]; //-----外围数字-----//
int res[9];
memset(res,0,sizeof(res));
nums(res);
int maxs=*max_element(res,res+9);//初始最大值,因为有9个子矩阵
for(int i=0;i<15;i++){
change();
nums(res);
int x=*max_element(res,res+9);
maxs=max(maxs,x);
}
cout<<maxs<<endl;
}
return 0;
}17.Sum of Sequence-1415
样例输入
2 4 10 2 5 7 1 6 10 11 2 20 6 8 7
样例输出
15 14
样例解释
第一个样例分成2,5和7,1,结果为 7+8 = 15。 第二个样例分成11,2,20,6和8,7,结果为9+5 = 14。
思路:一个典型的前缀和问题,S2=SUM-S1,我们在输入的时候顺便把数组更新为前缀和,然后再遍历一次求余数即可。
AC代码(个人难度:2,标准难度:2)
| Memory: 1832K | Time: 1093MS |
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll res[50001];
int main()
{
ll t;
scanf("%lld",&t);
while(t--){
ll n,p;
scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&p);
ll sum=0;//最后的总和
memset(res,0,sizeof(res));
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%lld",&res[i]);
sum+=res[i];//前缀和
if(i>0){
res[i]+=res[i-1];
}
}
ll maxs=0;
for(ll i=n-1;i>=0;i--){//前缀和
//printf("%lld ",(sum-res[i])%p+res[i]%p);
if(maxs<((sum-res[i])%p+res[i]%p)){
maxs=(sum-res[i])%p+res[i]%p;
}
}
printf("%lld\n",maxs);
}
return 0;
}但是不知道为什么不知道是数据问题还是题目问题,我第一次没有用前缀和也能过,希望有大佬能够指出,贴:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll res[50001];
int main()
{
ll t;
scanf("%lld",&t);
while(t--){
ll n,p;
scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&p);
ll sum=0;
memset(res,0,sizeof(res));
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%lld",&res[i]);//未用前缀和
sum+=res[i];
}
ll maxs=0;
for(ll i=n-1;i>=0;i--){
//printf("%lld ",(sum-res[i])%p+res[i]%p);//没用前缀和直接一个比
if(maxs<((sum-res[i])%p+res[i]%p)){
maxs=(sum-res[i])%p+res[i]%p;
}
}
printf("%lld\n",maxs);
}
return 0;
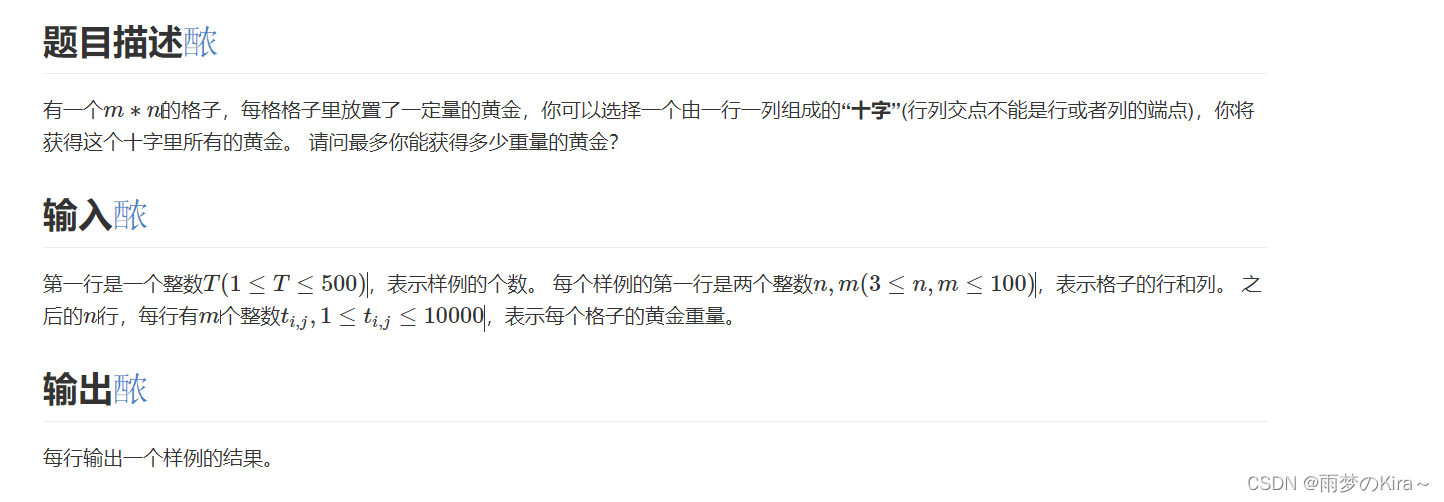
}18.黄金十字-1420
样例输入
2 3 3 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 4 4 1 1 1 1 1 2 3 4 4 3 2 1 1 1 1 1
样例输出
10 15
样例解释
第一个样例,只有一个中心点在(2,2)的十字可以选择,所以是10。
第二个样例,中心点在(2,2)或(3,3)的十字是答案,为15。
思路:模拟,算出每个行和列的总和,然后相加,再去掉中间重复的点
AC代码(个人难度:2,标准难度:2)
| Memory: 2340K | Time: 888MS |
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
int ch[100][100];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
scanf("%d",&ch[i][j]);
}
}
int row[100],cow[100];//行,列
memset(row,0,sizeof(row));
memset(cow,0,sizeof(cow));
int ans=0,ant=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n-2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
row[ans]+=ch[i][j];//求行总值
}
ans++;//行个数
}
for(int i=1;i<=m-2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
cow[ant]+=ch[j][i];//求列总值
}
ant++;//列个数
}
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<ans;i++){
for(int j=0;j<ant;j++){
sum=max(sum,row[i]+cow[j]-ch[i+1][j+1]);//去掉中间
}
}
printf("%d\n",sum);
}
return 0;
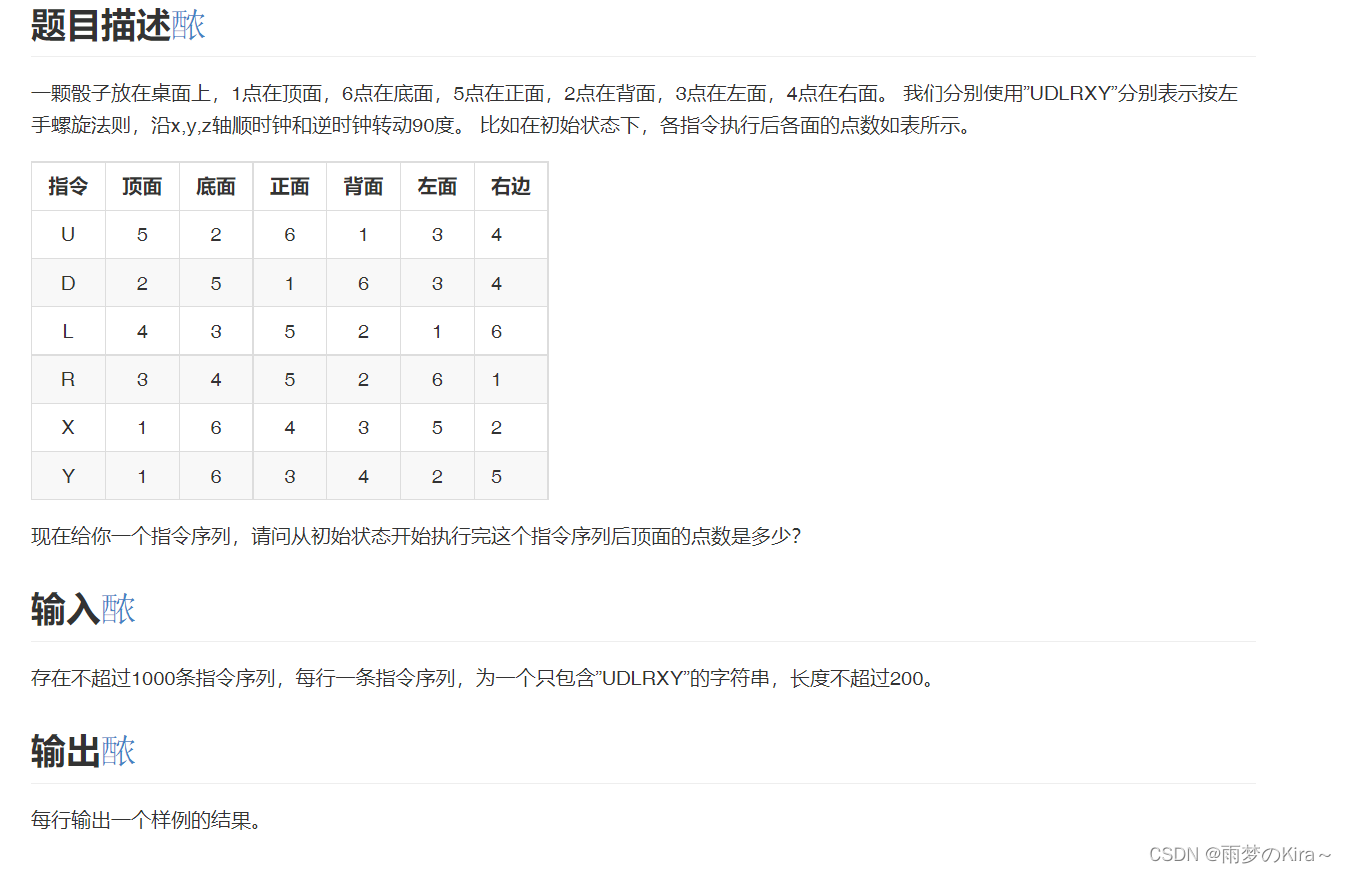
}19.Dice I-1420
样例输入
UDLRXY LUUDD UULDD
样例输出
1 4 3
思路:模拟,用一个6数组保存六个面,然后根据各个指令进行操作即可。
AC代码(个人难度:2,标准难度:2)
| Memory: 2336K | Time: 45MS |
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char s[201];
while(scanf("%s",s)!=EOF){
int a[6]={2,1,5,6,3,4};
//printf("%d",strlen(s));
for(int i=0;i<strlen(s);i++){
if(s[i]=='U'){//不同指令
int temp=a[0];
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
if(i==3){
a[i]=temp;
}
else{
a[i]=a[i+1];
}
}
}
else if(s[i]=='D'){
int temp=a[3];
for(int i=3;i>=0;i--){
if(i==0){
a[i]=temp;
}
else{
a[i]=a[i-1];
}
}
}
else if(s[i]=='L'){
int temp=a[1];
a[1]=a[5];
a[5]=a[3];
a[3]=a[4];
a[4]=temp;
}
else if(s[i]=='R'){
int temp=a[1];
a[1]=a[4];
a[4]=a[3];
a[3]=a[5];
a[5]=temp;
}
else if(s[i]=='X'){
int temp=a[0];
a[0]=a[4];
a[4]=a[2];
a[2]=a[5];
a[5]=temp;
}
else{
int temp=a[0];
a[0]=a[5];
a[5]=a[2];
a[2]=a[4];
a[4]=temp;
}
/*for(int i=0;i<6;i++){
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}*/
}
printf("%d\n",a[1]);
}
return 0;
}20.Dice-1426
样例输入
2 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 7 8 9 3 4 5 6 7 8
样例输出
720 810
思路:直接暴力set容器,注意一位数二位数三位数都是满足条件的,不会set的可以用三维数组做。
AC代码(个人难度:2,标准难度:2)
| Memory: 2244K | Time: 328MS |
#include <stdio.h>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
set<int>res;
int a[6],b[6],c[6];
for(int i=0;i<6;i++){
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
res.insert(a[i]);//一位数
}
for(int i=0;i<6;i++){
scanf("%d",&b[i]);
res.insert(b[i]);//一位数
}
for(int i=0;i<6;i++){
scanf("%d",&c[i]);
res.insert(c[i]);//一位数
}
for(int i=0;i<6;i++){
for(int j=0;j<6;j++){
for(int k=0;k<6;k++){//三位数
res.insert(a[i]*100+b[j]*10+c[k]);
res.insert(a[i]*100+c[j]*10+b[k]);
res.insert(b[i]*100+a[j]*10+c[k]);
res.insert(b[i]*100+c[j]*10+a[k]);
res.insert(c[i]*100+b[j]*10+a[k]);
res.insert(c[i]*100+a[j]*10+b[k]);
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<6;i++){
for(int j=0;j<6;j++){//二位数
res.insert(a[i]*10+b[j]);
res.insert(a[j]*10+b[i]);
res.insert(a[i]*10+c[j]);
res.insert(a[j]*10+c[i]);
res.insert(b[i]*10+a[j]);
res.insert(b[j]*10+c[i]);
res.insert(b[i]*10+c[j]);
res.insert(b[j]*10+a[i]);
res.insert(c[i]*10+a[j]);
res.insert(c[j]*10+b[i]);
res.insert(c[i]*10+b[j]);
res.insert(c[j]*10+b[i]);
}
}
printf("%d\n",res.size());
}
return 0;
}