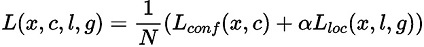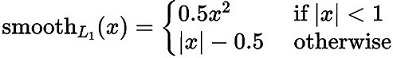今天是参加昇思25天学习打卡营的第18天,今天打卡的课程是“SSD目标检测”,这里做一个简单的分享。
1.简介
在第15天的学习内容中,我们接触到了用于图像语义分割的VGG-16模型,今天学习的内容也是在VGG-16的基础上实现目标检测。
目标检测任务的实现目标是识别图像中存在物体,标识其边界并进行分类识别。
SSD,全称Single Shot MultiBox Detector,是Wei Liu在ECCV 2016上提出的一种目标检测算法。使用Nvidia Titan X在VOC 2007测试集上,SSD对于输入尺寸300x300的网络,达到74.3%mAP(mean Average Precision)以及59FPS;对于512x512的网络,达到了76.9%mAP ,超越当时最强的Faster RCNN(73.2%mAP)。具体可参考论文[1]。 SSD目标检测主流算法分成可以两个类型:
two-stage方法:RCNN系列
通过算法产生候选框,然后再对这些候选框进行分类和回归。
one-stage方法:YOLO和SSD
直接通过主干网络给出类别位置信息,不需要区域生成。
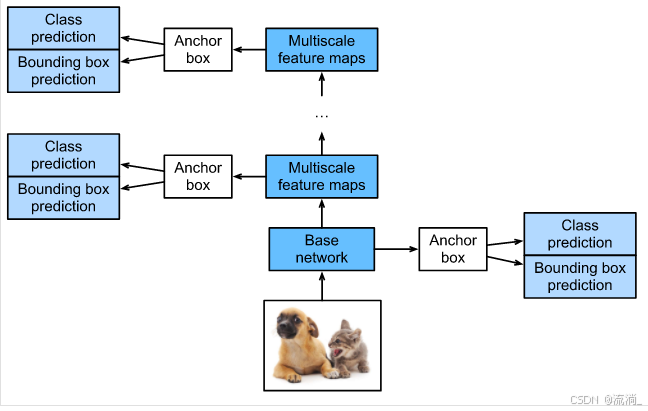
SSD是单阶段的目标检测算法,通过卷积神经网络进行特征提取,取不同的特征层进行检测输出,所以SSD是一种多尺度的检测方法。在需要检测的特征层,直接使用一个3 ×
3卷积,进行通道的变换。SSD采用了anchor的策略,预设不同长宽比例的anchor,每一个输出特征层基于anchor预测多个检测框(4或者6)。采用了多尺度检测方法,浅层用于检测小目标,深层用于检测大目标。SSD的框架如下图:
2.模型结构
2.1模型结构
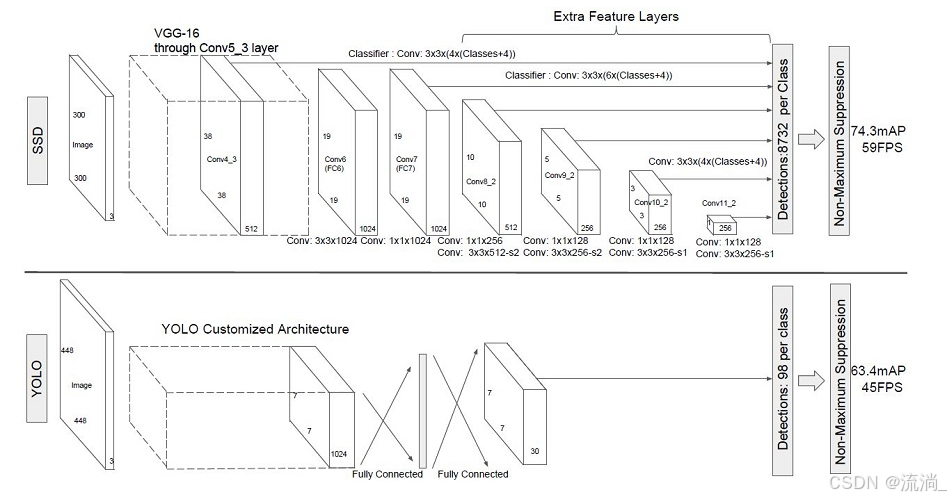
SSD采用VGG16作为基础模型,然后在VGG16的基础上新增了卷积层来获得更多的特征图以用于检测。SSD的网络结构如图所示。上面是SSD模型,下面是YOLO模型,可以明显看到SSD利用了多尺度的特征图做检测。
两种单阶段目标检测算法的比较:
SSD先通过卷积不断进行特征提取,在需要检测物体的网络,直接通过一个3 ×× 3卷积得到输出,卷积的通道数由anchor数量和类别数量决定,具体为(anchor数量*(类别数量+4))。
SSD对比了YOLO系列目标检测方法,不同的是SSD通过卷积得到最后的边界框,而YOLO对最后的输出采用全连接的形式得到一维向量,对向量进行拆解得到最终的检测框。
2.2 模型特点
-
多尺度检测
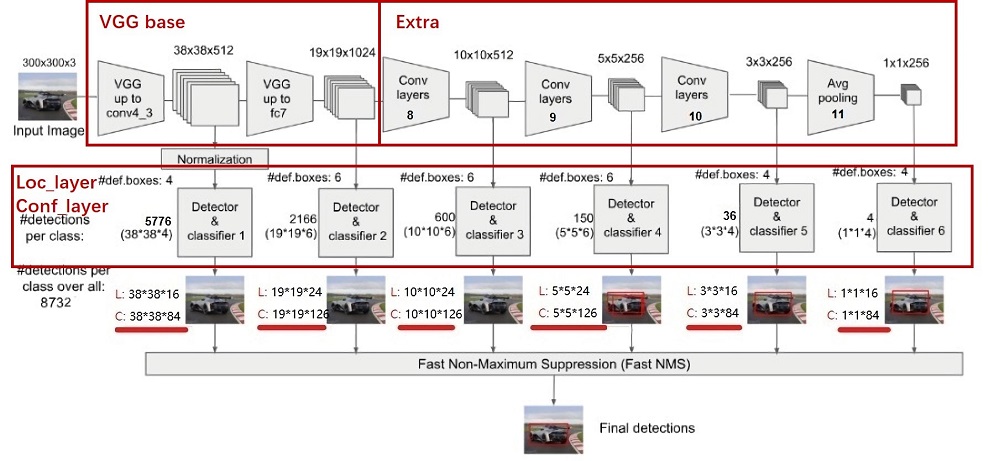
在SSD的网络结构图中我们可以看到,SSD使用了多个特征层,特征层的尺寸分别是38 ×× 38,19 ×× 19,10 ×× 10,5 ×× 5,3 ×× 3,1 ×× 1,一共6种不同的特征图尺寸。大尺度特征图(较靠前的特征图)可以用来检测小物体,而小尺度特征图(较靠后的特征图)用来检测大物体。多尺度检测的方式,可以使得检测更加充分(SSD属于密集检测),更能检测出小目标。
-
采用卷积进行检测
与YOLO最后采用全连接层不同,SSD直接采用卷积对不同的特征图来进行提取检测结果。对于形状为m ×× n ×× p的特征图,只需要采用3 ×× 3 ×× p这样比较小的卷积核得到检测值。
-
预设anchor
在YOLOv1中,直接由网络预测目标的尺寸,这种方式使得预测框的长宽比和尺寸没有限制,难以训练。在SSD中,采用预设边界框,我们习惯称它为anchor(在SSD论文中叫default bounding boxes),预测框的尺寸在anchor的指导下进行微调。
3.核心代码
3.1 模型定义
SSD的网络结构主要分为以下几个部分:
在mindspore环境下实现该模型的核心代码如下:
from mindspore import nn
def _make_layer(channels):
in_channels = channels[0]
layers = []
for out_channels in channels[1:]:
layers.append(nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=3))
layers.append(nn.ReLU())
in_channels = out_channels
return nn.SequentialCell(layers)
class Vgg16(nn.Cell):
"""VGG16 module."""
def __init__(self):
super(Vgg16, self).__init__()
self.b1 = _make_layer([3, 64, 64])
self.b2 = _make_layer([64, 128, 128])
self.b3 = _make_layer([128, 256, 256, 256])
self.b4 = _make_layer([256, 512, 512, 512])
self.b5 = _make_layer([512, 512, 512, 512])
self.m1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, pad_mode='SAME')
self.m2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, pad_mode='SAME')
self.m3 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, pad_mode='SAME')
self.m4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, pad_mode='SAME')
self.m5 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, pad_mode='SAME')
def construct(self, x):
# block1
x = self.b1(x)
x = self.m1(x)
# block2
x = self.b2(x)
x = self.m2(x)
# block3
x = self.b3(x)
x = self.m3(x)
# block4
x = self.b4(x)
block4 = x
x = self.m4(x)
# block5
x = self.b5(x)
x = self.m5(x)
return block4, x
import mindspore as ms
import mindspore.nn as nn
import mindspore.ops as ops
def _last_conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=1, pad_mod='same', pad=0):
in_channels = in_channel
out_channels = in_channel
depthwise_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, pad_mode='same',
padding=pad, group=in_channels)
conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, pad_mode='same', has_bias=True)
bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channel, eps=1e-3, momentum=0.97,
gamma_init=1, beta_init=0, moving_mean_init=0, moving_var_init=1)
return nn.SequentialCell([depthwise_conv, bn, nn.ReLU6(), conv])
class FlattenConcat(nn.Cell):
"""FlattenConcat module."""
def __init__(self):
super(FlattenConcat, self).__init__()
self.num_ssd_boxes = 8732
def construct(self, inputs):
output = ()
batch_size = ops.shape(inputs[0])[0]
for x in inputs:
x = ops.transpose(x, (0, 2, 3, 1))
output += (ops.reshape(x, (batch_size, -1)),)
res = ops.concat(output, axis=1)
return ops.reshape(res, (batch_size, self.num_ssd_boxes, -1))
class MultiBox(nn.Cell):
"""
Multibox conv layers. Each multibox layer contains class conf scores and localization predictions.
"""
def __init__(self):
super(MultiBox, self).__init__()
num_classes = 81
out_channels = [512, 1024, 512, 256, 256, 256]
num_default = [4, 6, 6, 6, 4, 4]
loc_layers = []
cls_layers = []
for k, out_channel in enumerate(out_channels):
loc_layers += [_last_conv2d(out_channel, 4 * num_default[k],
kernel_size=3, stride=1, pad_mod='same', pad=0)]
cls_layers += [_last_conv2d(out_channel, num_classes * num_default[k],
kernel_size=3, stride=1, pad_mod='same', pad=0)]
self.multi_loc_layers = nn.CellList(loc_layers)
self.multi_cls_layers = nn.CellList(cls_layers)
self.flatten_concat = FlattenConcat()
def construct(self, inputs):
loc_outputs = ()
cls_outputs = ()
for i in range(len(self.multi_loc_layers)):
loc_outputs += (self.multi_loc_layers[i](inputs[i]),)
cls_outputs += (self.multi_cls_layers[i](inputs[i]),)
return self.flatten_concat(loc_outputs), self.flatten_concat(cls_outputs)
class SSD300Vgg16(nn.Cell):
"""SSD300Vgg16 module."""
def __init__(self):
super(SSD300Vgg16, self).__init__()
# VGG16 backbone: block1~5
self.backbone = Vgg16()
# SSD blocks: block6~7
self.b6_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=3, padding=6, dilation=6, pad_mode='pad')
self.b6_2 = nn.Dropout(p=0.5)
self.b7_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=1024, kernel_size=1)
self.b7_2 = nn.Dropout(p=0.5)
# Extra Feature Layers: block8~11
self.b8_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1024, out_channels=256, kernel_size=1, padding=1, pad_mode='pad')
self.b8_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=512, kernel_size=3, stride=2, pad_mode='valid')
self.b9_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=128, kernel_size=1, padding=1, pad_mode='pad')
self.b9_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, stride=2, pad_mode='valid')
self.b10_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=128, kernel_size=1)
self.b10_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, pad_mode='valid')
self.b11_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=128, kernel_size=1)
self.b11_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, pad_mode='valid')
# boxes
self.multi_box = MultiBox()
def construct(self, x):
# VGG16 backbone: block1~5
block4, x = self.backbone(x)
# SSD blocks: block6~7
x = self.b6_1(x) # 1024
x = self.b6_2(x)
x = self.b7_1(x) # 1024
x = self.b7_2(x)
block7 = x
# Extra Feature Layers: block8~11
x = self.b8_1(x) # 256
x = self.b8_2(x) # 512
block8 = x
x = self.b9_1(x) # 128
x = self.b9_2(x) # 256
block9 = x
x = self.b10_1(x) # 128
x = self.b10_2(x) # 256
block10 = x
x = self.b11_1(x) # 128
x = self.b11_2(x) # 256
block11 = x
# boxes
multi_feature = (block4, block7, block8, block9, block10, block11)
pred_loc, pred_label = self.multi_box(multi_feature)
if not self.training:
pred_label = ops.sigmoid(pred_label)
pred_loc = pred_loc.astype(ms.float32)
pred_label = pred_label.astype(ms.float32)
return pred_loc, pred_label
3.2 损失函数
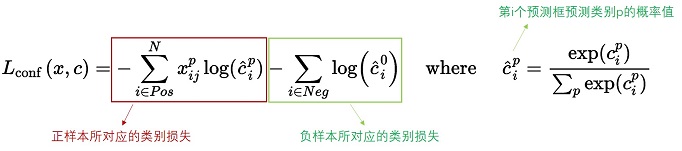
SSD算法的目标函数分为两部分:计算相应的预选框与目标类别的置信度误差(confidence loss, conf)以及相应的位置误差(locatization loss, loc):
其中:
N 是先验框的正样本数量;
c 为类别置信度预测值;
l 为先验框的所对应边界框的位置预测值;
g 为ground truth的位置参数
α 用以调整confidence loss和location loss之间的比例,默认为1。
- 对于位置损失函数
针对所有的正样本,采用 Smooth L1 Loss, 位置信息都是 encode 之后的位置信息。
- 对于置信度损失函数
置信度损失是多类置信度©上的softmax损失。
def class_loss(logits, label):
"""Calculate category losses."""
label = ops.one_hot(label, ops.shape(logits)[-1], Tensor(1.0, ms.float32), Tensor(0.0, ms.float32))
weight = ops.ones_like(logits)
pos_weight = ops.ones_like(logits)
sigmiod_cross_entropy = ops.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, label, weight.astype(ms.float32), pos_weight.astype(ms.float32))
sigmoid = ops.sigmoid(logits)
label = label.astype(ms.float32)
p_t = label * sigmoid + (1 - label) * (1 - sigmoid)
modulating_factor = ops.pow(1 - p_t, 2.0)
alpha_weight_factor = label * 0.75 + (1 - label) * (1 - 0.75)
focal_loss = modulating_factor * alpha_weight_factor * sigmiod_cross_entropy
return focal_loss
3.3 Metrics
在SSD中,训练过程是不需要用到非极大值抑制(NMS),但当进行检测时,例如输入一张图片要求输出框的时候,需要用到NMS过滤掉那些重叠度较大的预测框。
非极大值抑制的流程如下:
- 根据置信度得分进行排序
- 选择置信度最高的比边界框添加到最终输出列表中,将其从边界框列表中删除
- 计算所有边界框的面积
- 计算置信度最高的边界框与其它候选框的IoU
- 删除IoU大于阈值的边界框
- 重复上述过程,直至边界框列表为空
import json
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
from pycocotools.cocoeval import COCOeval
def apply_eval(eval_param_dict):
net = eval_param_dict["net"]
net.set_train(False)
ds = eval_param_dict["dataset"]
anno_json = eval_param_dict["anno_json"]
coco_metrics = COCOMetrics(anno_json=anno_json,
classes=train_cls,
num_classes=81,
max_boxes=100,
nms_threshold=0.6,
min_score=0.1)
for data in ds.create_dict_iterator(output_numpy=True, num_epochs=1):
img_id = data['img_id']
img_np = data['image']
image_shape = data['image_shape']
output = net(Tensor(img_np))
for batch_idx in range(img_np.shape[0]):
pred_batch = {
"boxes": output[0].asnumpy()[batch_idx],
"box_scores": output[1].asnumpy()[batch_idx],
"img_id": int(np.squeeze(img_id[batch_idx])),
"image_shape": image_shape[batch_idx]
}
coco_metrics.update(pred_batch)
eval_metrics = coco_metrics.get_metrics()
return eval_metrics
def apply_nms(all_boxes, all_scores, thres, max_boxes):
"""Apply NMS to bboxes."""
y1 = all_boxes[:, 0]
x1 = all_boxes[:, 1]
y2 = all_boxes[:, 2]
x2 = all_boxes[:, 3]
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
order = all_scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
if len(keep) >= max_boxes:
break
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= thres)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
return keep
class COCOMetrics:
"""Calculate mAP of predicted bboxes."""
def __init__(self, anno_json, classes, num_classes, min_score, nms_threshold, max_boxes):
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.classes = classes
self.min_score = min_score
self.nms_threshold = nms_threshold
self.max_boxes = max_boxes
self.val_cls_dict = {i: cls for i, cls in enumerate(classes)}
self.coco_gt = COCO(anno_json)
cat_ids = self.coco_gt.loadCats(self.coco_gt.getCatIds())
self.class_dict = {cat['name']: cat['id'] for cat in cat_ids}
self.predictions = []
self.img_ids = []
def update(self, batch):
pred_boxes = batch['boxes']
box_scores = batch['box_scores']
img_id = batch['img_id']
h, w = batch['image_shape']
final_boxes = []
final_label = []
final_score = []
self.img_ids.append(img_id)
for c in range(1, self.num_classes):
class_box_scores = box_scores[:, c]
score_mask = class_box_scores > self.min_score
class_box_scores = class_box_scores[score_mask]
class_boxes = pred_boxes[score_mask] * [h, w, h, w]
if score_mask.any():
nms_index = apply_nms(class_boxes, class_box_scores, self.nms_threshold, self.max_boxes)
class_boxes = class_boxes[nms_index]
class_box_scores = class_box_scores[nms_index]
final_boxes += class_boxes.tolist()
final_score += class_box_scores.tolist()
final_label += [self.class_dict[self.val_cls_dict[c]]] * len(class_box_scores)
for loc, label, score in zip(final_boxes, final_label, final_score):
res = {}
res['image_id'] = img_id
res['bbox'] = [loc[1], loc[0], loc[3] - loc[1], loc[2] - loc[0]]
res['score'] = score
res['category_id'] = label
self.predictions.append(res)
def get_metrics(self):
with open('predictions.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump(self.predictions, f)
coco_dt = self.coco_gt.loadRes('predictions.json')
E = COCOeval(self.coco_gt, coco_dt, iouType='bbox')
E.params.imgIds = self.img_ids
E.evaluate()
E.accumulate()
E.summarize()
return E.stats[0]
class SsdInferWithDecoder(nn.Cell):
"""
SSD Infer wrapper to decode the bbox locations."""
def __init__(self, network, default_boxes, ckpt_path):
super(SsdInferWithDecoder, self).__init__()
param_dict = ms.load_checkpoint(ckpt_path)
ms.load_param_into_net(network, param_dict)
self.network = network
self.default_boxes = default_boxes
self.prior_scaling_xy = 0.1
self.prior_scaling_wh = 0.2
def construct(self, x):
pred_loc, pred_label = self.network(x)
default_bbox_xy = self.default_boxes[..., :2]
default_bbox_wh = self.default_boxes[..., 2:]
pred_xy = pred_loc[..., :2] * self.prior_scaling_xy * default_bbox_wh + default_bbox_xy
pred_wh = ops.exp(pred_loc[..., 2:] * self.prior_scaling_wh) * default_bbox_wh
pred_xy_0 = pred_xy - pred_wh / 2.0
pred_xy_1 = pred_xy + pred_wh / 2.0
pred_xy = ops.concat((pred_xy_0, pred_xy_1), -1)
pred_xy = ops.maximum(pred_xy, 0)
pred_xy = ops.minimum(pred_xy, 1)
return pred_xy, pred_label
4.小结
SSD目标检测是FCN图像语义分割的进阶任务,今天学习内容主要也是了解SSD目标检测实现的原理、采用的模型结构、损失函数的设计、评估函数的设计以及基于mindspore实现SSD目标检测的主要代码。经过今天的学习,可以大致了解和掌握实现目标检测的基本流程,为后续深入学习目标检测有一个初步的基础。今天的学习的内容主要来自Wei Liu在ECCV 2016上提出的一种目标检测算法论文,想要深入学习的话可以学习一下此论文。
5.引用文献
[1] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector[C]//European conference on computer vision. Springer, Cham, 2016: 21-37.
以上是第18天的学习内容,附上今日打卡记录: