目录
2、通过 ThreadPoolExecutor 创建的线程池
总体来说可分为 2 类
1. 通过 ThreadPoolExecutor 创建的线程池;
2. 通过 Executors 创建的线程池。
1、通过 Executors 创建的线程池
1. Executors.newFixedThreadPool:创建⼀个固定⼤⼩的线程池,可控制并发的线程数,超出的线程会在队列中等待;
2. Executors.newCachedThreadPool:创建⼀个可缓存的线程池,若线程数超过处理所需,缓存⼀段时间后会回收,若线程数不够,则新建线程;
3. Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor:创建单个线程数的线程池,它可以保证先进先出的执⾏顺序;
4. Executors.newScheduledThreadPool:创建⼀个可以执⾏延迟任务的线程池;
5. Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor:创建⼀个单线程的可以执⾏延迟任务的线程池;
6. Executors.newWorkStealingPool:创建⼀个抢占式执⾏的线程池(任务执⾏顺序不确定)【JDK1.8 添加】。
2、通过 ThreadPoolExecutor 创建的线程池
1、创建参数
/**
*@param corePoolSize 核心线程数
*@param maximumPoolSize 最大线程数
* @param keepAliveTime 当线程数大于核心时,这是多余空闲线程在终止前等待新任务的最大时间。
* @param unit 参数时间单位
* @param workQueue 用于在任务执行前保存任务的队列。
* @param threadFactory 执行器创建新线程时使用的工厂
* @param handler 当执行被阻塞时使用的处理程序
*/
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
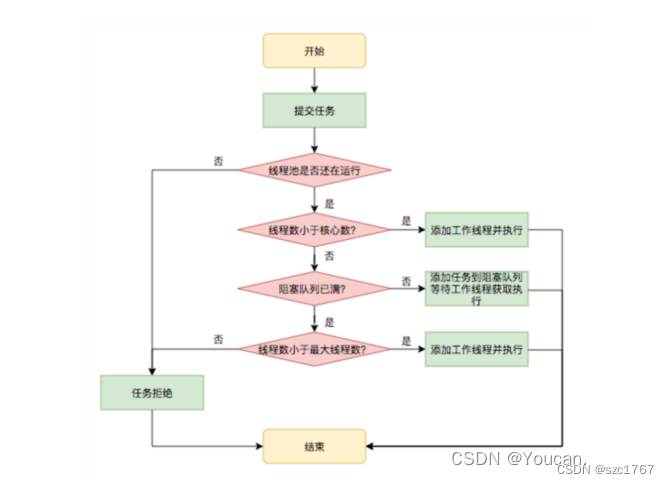
RejectedExecutionHandler handler);2、线程池执行流程
3、拒绝策略 handler
3.1 AbortPolicy
直接抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常,拒绝执行
3.2 CallerRunsPolicy
它直接在{@code execute}方法的调用线程中运行被拒绝的任务,除非执行器被关闭,在这种情况下任务被丢弃。
即转变为当前主线程将提交的任务同步完成
3.3 DiscardOldestPolicy
在执行器未被关闭的情况下,丢弃最老的未被执行任务
3.4 DiscardPolicy
忽略最新的任务
3.5 自定义拒绝策略
new RejectedExecutionHandler(){
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
// 自定义策略
}
}4、执行任务的方法
1. execute
// 执行任务
void execute(Runnable command);
2. submit
// 提交任务 task,用返回值 Future 获得任务执行结果
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
Future<String> future = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("running");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return "ok";
});
3. invokeAll
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException;
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,带超时时间
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
List<Future<String>> futures = pool.invokeAll(Arrays.asList(
() -> {
log.debug("begin");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return "1";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin");
Thread.sleep(500);
return "2";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin");
Thread.sleep(2000);
return "3";
}
));
4. invokeAny
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,哪个任务先成功执行完毕,返回此任务执行结果,其它任务取消
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,哪个任务先成功执行完毕,返回此任务执行结果,其它任务取消,带超时时间
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
String result = pool.invokeAny(Arrays.asList(
() -> {
log.debug("begin 1");
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("end 1");
return "1";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin 2");
Thread.sleep(500);
log.debug("end 2");
return "2";
},
() -> {
log.debug("begin 3");
Thread.sleep(2000);
log.debug("end 3");
return "3";
}
));
5、关闭线程池的方法
5.1 shutdown()
使当前未执行完的任务继续执行
而队列中未执行的任务会继续执行,不删除队列中的任务
不再允许添加新的任务
shutdown 方法不会阻塞主方法。
5.2 shutdownNow()
使当前未执行完的任务继续执行
队列中未执行的任务不再执行,删除队列中的任务
不再允许添加新的任务
shutdown 方法不会阻塞主方法。